Abstract
Numerous scientific evidences have revealed that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in the progression of human complex diseases and biological life activities. Therefore, identifying novel and potential disease-related lncRNAs is helpful to diagnosis, prognosis and therapy of many human complex diseases. Since traditional laboratory experiments are cost and time-consuming, a great quantity of computer algorithms have been proposed for predicting the relationships between lncRNAs and diseases. However, there are still much room for the improvement. In this paper, we introduce an accurate framework named LDAEXC to infer LncRNA–Disease Associations with deep autoencoder and XGBoost Classifier. LDAEXC utilizes different similarity views of lncRNAs and human diseases to construct features for each data sources. Then, the reduced features are obtained by feeding the constructed feature vectors into a deep autoencoder, and at last an XGBoost classifier is leveraged to calculate the latent lncRNA–disease-associated scores using reduced features. The fivefold cross-validation experiments on four datasets showed that LDAEXC reached AUC scores of 0.9676 ± 0.0043, 0.9449 ± 0.022, 0.9375 ± 0.0331 and 0.9556 ± 0.0134, respectively, significantly higher than other advanced similar computer methods. Extensive experiment results and case studies of two complex diseases (colon and breast cancers) further indicated the practicability and excellent prediction performance of LDAEXC in inferring unknown lncRNA–disease associations.
Graphical Abstract
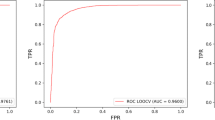
TLDAEXC utilizes disease semantic similarity, lncRNA expression similarity, and Gaussian interaction profile kernel similarity of lncRNAs and diseases for feature construction. The constructed features are fed to a deep autoencoder to extract reduced features, and an XGBoost classifier is used to predict the lncRNA–disease associations based on the reduced features. The fivefold and tenfold cross-validation experiments on a benchmark dataset showed that LDAEXC could achieve AUC scores of 0.9676 and 0.9682, respectively, significantly higher than other state-of-the-art similar methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets used in our experiments are downloaded from public available sources, which has been described in Sect. 2.1
References
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W (2009) Evolution and functions of long noncoding rnas. Cell 136(4):629–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.006
Xiao B, Zhang X, Li Y, Tang Z, Yang S, Mu Y, Cui W, Ao H, Li K (2009) Identification, bioinformatic analysis and expression profiling of candidate mrna-like non-coding rnas in sus scrofa. J Genet Genom 36(12):695–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60162-9
Chen X, Sun YZ, Guan N, Qu J, Li JQ (2019) Computational models for lncrna function prediction and functional similarity calculation. Brief Funct Genom 18(1):58–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/ely031
Lukiw WJ, Handley P, Wong L, Mclachlan DRC (1992) Bc200 rna in normal human neocortex, non-alzheimer dementia (nad), and senile dementia of the alzheimer type (ad). Neurochem Res 17(6):591–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00968788
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings HM (2010) Long non-coding rna hotair reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 464(7291):1071–1076. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08975
Sun M, Xia R, Jin F, Xu T, Liu Z, De W, Liu X (2014) Downregulated long noncoding rna meg3 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer. Tumor Biol 35:1065–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1142-z
Chen X, Yan CC, Zhang X, You Z-H (2016) Long non-coding rnas and complex diseases: from experimental results to computational models. Brief Bioinform 18(4):558–576. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbw060
Jia F, Jiang S, Wu Z, Liang Y (2022) Research on lncrna and disease associations prediction base on data mining. J Phys Conf Ser 2219(1):012029. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2219/1/012029
Lu C, Yang M, Luo F, Wu F-X, Li M, Pan Y, Li Y, Wang J (2018) Prediction of lncrna-disease associations based on inductive matrix completion. Bioinformatics 34(19):3357–3364. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty327
Fu G, Wang J, Domeniconi C, Yu G (2018) Matrix factorization-based data fusion for the prediction of lncrna-disease associations. Bioinformatics 34(9):1529–1537. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx794
Wang Y, Yu G, Wang J, Fu G, Guo M, Domeniconi C (2020) Weighted matrix factorization on multi-relational data for lncrna-disease association prediction. Methods 173:32–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.06.015
Zeng M, Lu C, Fei Z, Wu F-X, Li Y, Wang J, Li M (2021) Dmflda: a deep learning framework for predicting lncrna-disease associations. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinf 18(6):2353–2363. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2020.2983958
Sun J, Shi H, Wang Z, Zhang C, Liu L, Wang L, He W, Hao D, Liu S, Zhou M (2014) Inferring novel lncrna-disease associations based on a random walk model of a lncrna functional similarity network. Mol BioSyst 10(8):2074–2081. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3mb70608g
Yu G, Fu G, Lu C, Ren Y, Wang J (2017) Brwlda: bi-random walks for predicting lncrna-disease associations. Oncotarget 8(36):60429. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19588
Xie G, Huang B, Sun Y, Wu C, Han Y (2021) Rwsf-blp: a novel lncrna-disease association prediction model using random walk-based multi-similarity fusion and bidirectional label propagation. Mol Genet Genom 296:473–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-021-01764-3
Wang L, Shang M, Dai Q, He P-A (2022) Prediction of lncrna-disease association based on a laplace normalized random walk with restart algorithm on heterogeneous networks. BMC Bioinform 23(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-021-04538-1
Wang L, Xuan Z, Zhou S, Kuang L, Pei T (2019) A novel model for predicting lncrna-disease associations based on the lncrna-mirna-disease interactive network. Curr Bioinform 14(3):269–278. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574893613666180703105258
Li J, Zhang S, Liu T, Ning C, Zhang Z, Zhou W (2020) Neural inductive matrix completion with graph convolutional networks for mirna-disease association prediction. Bioinformatics 36(8):2538–2546. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz965
Wang L, You Z-H, Huang Y-A, Huang D-S, Chan KC (2020) An efficient approach based on multi-sources information to predict circrna-disease associations using deep convolutional neural network. Bioinformatics 36(13):4038–4046. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz825
Chen X, Li T-H, Zhao Y, Wang C-C, Zhu C-C (2020) Deep-belief network for predicting potential mirna-disease associations. Brief Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa186
Lan W, Wu X, Chen Q, Peng W, Wang J, Chen YP (2022) Ganlda: graph attention network for lncrna-disease associations prediction. Neurocomputing 469:384–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.09.094
Xuan P, Pan S, Zhang T, Liu Y, Sun H (2019) Graph convolutional network and convolutional neural network based method for predicting lncrna-disease associations. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091012
Yang Q, Li X (2021) Bigan: Lncrna-disease association prediction based on bidirectional generative adversarial network. BMC Bioinform 22:357. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-021-04273-7
Wu Q-W, Xia J-F, Ni J-C, Zheng C-H (2021) Gaerf: predicting lncrna-disease associations by graph auto-encoder and random forest. Brief Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa391
Shi Z, Zhang H, Jin C, Quan X, Yin Y (2021) A representation learning model based on variational inference and graph autoencoder for predicting lncrna-disease associations. BMC Bioinform 22:136. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-021-04073-z
Wang L, Zhong C (2022) ggatlda: lncrna-disease association prediction based on graph-level graph attention network. BMC Bioinform 23:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-021-04548-z
Chen G, Wang Z, Wang D, Qiu C, Liu M, Chen X, Zhang Q, Yan G, Cui Q (2012) Lncrnadisease: a database for long-non-coding rna-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res 41:983–986. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1099
Parkinson H, Sansone S-A, Sarkans U, Rocca-Serra P, Brazma A (2006) Chapter 13—arrayexpress: a public repository for microarray data, pp 95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012164730-8/50198-2
Chen X, Yan G-Y (2013) Novel human lncrna-disease association inference based on lncrna expression profiles. Bioinformatics 29(20):2617–2624. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt426
Huang Y-A, Chen X, You Z-H, Huang D-S, Chan KC (2016) Ilncsim: improved lncrna functional similarity calculation model. Oncotarget 7(18):25902–25914. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8296
Ding L, Wang M, Sun D, Li A (2018) Tpglda: novel prediction of associations between lncrnas and diseases via lncrna-disease-gene tripartite graph. Sci Rep 8(1):1065. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19357-3
Wang D, Wang J, Lu M, Song F, Cui Q (2010) Inferring the human microrna functional similarity and functional network based on microrna-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 26(13):1644–1650. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq241
Chen X, Yang J-R, Guan N-N, Li J-Q (2018) Grmda: graph regression for mirna-disease association prediction. Front Physiol 9:92. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00092
van Laarhoven T, Nabuurs SB, Marchiori E (2011) Gaussian interaction profile kernels for predicting drug-target interaction. Bioinformatics 27(21):3036–3043. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr500
Altan G, Kutlu Y (2020) Generalization performance of deep autoencoder kernels for identification of abnormalities on electrocardiograms. In: Deep learning for data analytics, pp 37–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819764-6.00004-1
Altan G, Kutlu Y (2018) Hessenberg elm autoencoder kernel for deep learning. J Eng Technol Appl Sci 3(2):141–151. https://doi.org/10.30931/jetas.450252
Van Trees HL, Bell KL (2007) Improved bounds on the local mean square error and the bias of parameter estimators, pp 202–203
Chen T, Guestrin C (2016) Xgboost: a scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 785–794. https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
Altan G, Kutlu Y, Allahverdi N (2020) Deep learning on computerized analysis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 24(5):1344–1350. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2019.2931395
Altan G (2022) Deepoct: an explainable deep learning architecture to analyze macular edema on oct images. Eng Sci Technol 34:101091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2021.101091
Asmis TR, Saltz L (2008) Systemic therapy for colon cancer. Gastroenterol Clin N Am 37(1):287–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2007.12.005
Akram M, Iqbal M, Daniyal M, Khan AU (2017) Awareness and current knowledge of breast cancer. Biol Res 50(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-017-0140-9
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62172028 and Grant 61772197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, C., Xie, M. LDAEXC: LncRNA–Disease Associations Prediction with Deep Autoencoder and XGBoost Classifier. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 15, 439–451 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-023-00573-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-023-00573-z