Abstract
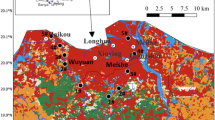
The principal environmental factors influencing the monthly dynamics of phytoplankton were examined from April to October in 2016 in 12 stations of Lake Wuliangsuhai (northwest China). Interestingly, in this lake, nutrient did not exhibit to be limiting for the phytoplankton growth. From April to October, the volume of total nitrogen (TN) range 0.66~22.22 mg/L, maximum volume was in W1 station in October; total phosphorus (TP) range 0.008~0.339 mg/L, maximum volume was in W2 station in April; NH4–N range 0.11~1.74mg/L, maximum volume was in W12 station in October. The most critical forcing factors were water quality physicochemical parameter variables, mainly water temperature (WT), salinity (Sal), conductivity (CON), total dissolved solids (TDS), pondus hydrogenii (pH), and water transparency (SD). The highest phytoplankton density (2.99 × 108 cells/L) was recorded in station W12 in June, and the lowest phytoplankton density (4.84 × 105 cells/L) in station W8 in May, in conditions of increasing water temperature in summer and lower water temperature in spring. Conversely, the highest species number (61 species) exhibited in station W5 in September, and the lowest species number (6 species) exhibited in station W1 in May. The physicochemical parameter variables, mainly WT, Sal, CON, TDS, pH, and SD, had a significant and measurable effect not only on the development of phytoplankton density but also on the monthly dynamics of the phytoplankton community. Our results revealed that the species number and density of the phytoplankton could serve as biological water quality indicators, which would give overall descriptions of water quality in Wuliangsuhai Lake.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belkinova D, Padisak J, Gecheva G, Cheshmedjiev S (2014) Phytoplankton based assessment of ecological status of Bulgarian lakes and comparison of metrics within the water framework directive. Appl Ecol Environ Res 12(1):83–103
Birk S, Bonne W, Borja A (2012) Three hundred ways to assess Europe’s surface waters: an almost complete overview of biological methods to implement the Water Framework Directive. Ecol Indic 18(2008):31–41
Čalic M, Krsinic F, Jasprica N, Pecarevic M (2013) Controlling factors of phytoplankton seasonal succession in oligotrophic Mali Ston Bay (south-eastern Adriatic). Environ Monit Assess 185(9):7543–7563
Chen XJ, Yang J, Du GS, Liu B (2015) The seasonal succession of phytoplankton functional groups and their driving factors in Haizi reservoir. Water Resources Protection 31(6):122–127
Guo J, Wei W, Yu YL, Song X, Zhang M (2015) Research progress on the eutrophication of Wuliangsuhai wetland. Chinese journal of ecology 34(11):3244–3252
Hao Y, Sun G, Zhang L, Gong X, Xu SS (2014) Relationship between community characteristics of the phytoplankton and environmental factors in Heihe River basin. Journal of Lake Sciences 26(1):121–130
Hu HJ, Wei YX (2006) The freshwater algae of China: systematics, taxonomy and ecology. Science press, Beijing
Jaworska B, Dunalska J, Gorniak D, Bowszys M (2014) Phytoplankton dominance structure and abundance as indicators of the trophic state and ecological status of Lake Kortowskie (northeast Poland) restored with selective hypolimnetic withdrawal. Archives of Polish Fisheries 22(1):7–15
Khenari AG, Maznah WOW, Yahya K (2010) Seasonal succession of phytoplankton community structure in the southern part of Caspian Sea. American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural and Environment Science 2010(2):146–155
Li X (2009) Modelling of eutrophic contaminants distribution and degradation processes in Lake Wuliangsuhai. Agricultural Water and Soil Engineering, Hohhot
Li CY, Liu TX, Gao RZ (2005) Study on the eutrophication synthetical evaluation and the season year change in Wuliangsuhai Lake. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering 16(2):11–15
Li X, Zhang S, Li CY, Li WP (2012) Ecological characteristics of phytoplankton community of Wuliangsuhai Lake in Inner Mongolia. Ecology & Environmental Sciences 21(11):1865–1869
Ma Y, Li G, Li J, Zhou H, Jiang B (2014) Seasonal succession of phytoplankton community and its relationship with environmental factors of North Temperate Zone water of the Zhalong Wetland, in China. Ecotoxicology 23(4):618–625
Puigserver M, Monerris N, Pablo J (2010) Abundance patterns of the toxic phytoplankton in coastal waters of the Balearic Archipelago (NW Mediterranean Sea): a multivariate approach. Hydrobiologia 644(1):145–157
Reynolds CS, Glaister MS (1993) Spatial and temporal changes in phytoplankton abundance in the upper and middle reaches of the River Severn. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 129(1):1–22
Saraswathy R, Muralidhar M, Ravichandran P (2012) Effect of nutrient level on phytoplankton population in zero water exchange shrimp culture farms. Indian Journal of Fisheries 59(2):115–120
The Hydrology Bureau of the Ministry of Water Resources, and the Yangtze River Basin Water Environment Monitoring Center (2012) Atlas of common algae in inland waters of China. The Yangtze River press, Wuhan
Weeks A, Conte MH, Harris RP (2012) The physical and chemical environment and changes in community structure associated with bloom evolution: the Joint Global Flux Study North Atlantic Bloom Experiment. Deep-Sea Res II Top Stud Oceanogr 40(93):347–368
Wu P, Deng JM, Qin BQ, Ma JR, Zhang YL (2013) Effects of enhanced water temperature and nutrient concentration on algal growth in winter and spring season in Lake Taihu, China. Res Environ Sci 26(10):1064–1071
Xu FL, Jorgensen SE, Tao S (1999) Ecological indicators for assessing freshwater ecosystem health. Ecol Model 116(1):77–106
Xu FL, Tao S, Dawson RW (2001) Lake ecosystem health assessment: indicators and methods. Water Res 35(13):3157–3167
Xu F, Yang ZF, Chen B (2012) Ecosystem health assessment of Baiyangdian Lake based on thermodynamic indicators. Procedia Environ Sci 13(1):2402–2413
Zhou FX, Chen JH (2011) Atlas of freshwater micro-organisms and benthic animals. Chemical industry press, Beijing
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation (51469026); Excellence in Youth Science and Technology Support Program Foundation (NJYT-15-B09); Innovation Guide award funds projects foundation (20121601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xing Li and Xiaojiang Chen wrote the draft of the manuscript, carried out the survey of previous studies, and performed the experiments. Jie Yang conceived the original idea of the proposed method. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Amjad Kallel
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(XLSX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Li, X. & Yang, J. The spatial and temporal dynamics of phytoplankton community and their correlation with environmental factors in Wuliangsuhai Lake, China. Arab J Geosci 14, 713 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07071-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07071-w