Abstract
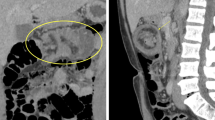
Small bowel intussusception in adults is rare. Unlike children, adults with intussusception generally have a causative lead point, of which a majority is benign. We report the case of a 55-year-old woman with systemic lupus erythematosus on steroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs who presented with intermittent melena. Contrast computed tomography revealed intussusception of the terminal ileum, with a low density mass which had advanced into the cecum as the lead point. The patient was diagnosed with ileocolic intussusception. The mass was observed in the terminal ileum on colonoscopy, indicating spontaneous reduction. As endoscopic treatment did not appear feasible, laparoscopic small bowel resection was performed with no complications. The resected specimen revealed a pedunculated mass over a healed ulcer. Pathology showed a deep ulcer reaching the subserosa with fibro-granulation, with no evidence of mesenteric vasculitis, thrombus, bacteria, fungi, granulomas, lipoma, or other tumors. The patient was diagnosed with ileocolic intussusception due to a fibro-granulation mass formed on a healed ulcer. Based on the patient’s systemic lupus erythematosus being well controlled, the absence of other causative factors, and the discovery of several small bowel erosions on subsequent capsule endoscopy, the ulcer was strongly suspected to be drug induced. Both steroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were reduced and proton pump inhibitors were discontinued by her rheumatologist after surgery. No recurrence has been observed during 4 months of follow-up.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hong KD, Kim J, Ji W, et al. Adult intussusception: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tech Coloproctol. 2019;23:315–24.
Namikawa T, Hokimoto N, Okabayashi T, et al. Adult ileoileal intussusception induced by an ileal lipoma diagnosed preoperatively: report of a case and review of the literature. Surg Today. 2012;42:686–92.
Janssens P, Arnaud L, Galicier L, et al. Lupus enteritis: from clinical findings to therapeutic management. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:67.
Ju JH, Min JK, Jung CK, et al. Lupus mesenteric vasculitis can cause acute abdominal pain in patients with SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5:273–81.
Hermann G. Intussusception secondary to mesenteric arteries complication of systemic lupus erythematosus in a 5-year-old child. J Am Med Assoc. 1967;200(1):74–5.
Wei CC, Chen JH, Cheng HH. Systemic lupus erythematosus with intussusception: a case report. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 1996;58:58–61.
Chang DK, Yoo DH, Kim TH, et al. Burkitt’s lymphoma presenting as ileocaecal intussusception in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 1999;18:253–6.
Lin YJ, Chen PC, Chen HA. Mesenteric vasculitis causing ileocecal intussusception as the initial presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report. Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32(Suppl 1):S37-40.
Zhang J, Fang M, Wang Y, et al. Intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2011;20:1324–8.
Glijn N, Korswagen LA, Lam Tse WK. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) an unusual cause of ileocolic intussusception. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017:2bcr2017220185.
Zhou JF, Liu SY, Zheng Y. Intussusception merged with systemic lupus erythematosus: one case report and retrospective analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37:285–8.
Lingala S, Moore A, Kadire S, et al. Unusual presentation of duodenal ulcer presenting with duodenal intussusception. ACG Case Rep J. 2018;5:e25.
Katsanos KH, Voulgari PV, Tsianos EV. Inflammatory bowel disease and lupus: a systematic review of the literature. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6:735–42.
Marginean EC. The ever-changing landscape of drug-induced injury of the lower gastrointestinal tract. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:748–58.
Takeuchi K, Satoh H. NSAID-induced small intestinal damage–roles of various pathogenic factors. Digestion. 2015;91:218–32.
Tai FWD, McAlindon ME. NSAIDs and the small bowel. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2018;34:175–82.
Lee B-I, Choi H, Choi K-Y, et al. Clinical characteristics of small bowel tumors diagnosed by double-balloon endoscopy: KASID multi-center study. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56:2920–7.
Yoshimura H, Murata K, Takase K, et al. A case of lipoma of the terminal ileum treated by endoscopic removal. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997;46:461–3.
Matsumoto T, Iida M, Matsui T, et al. Submucosal tumors of the terminal ileum managed by endoscopic polypectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1990;36:505–9.
Noda H, Ogasawara N, Tamura Y, et al. Successful endoscopic submucosal dissection of a large terminal ileal lipoma. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2016;10:506–11.
Morimoto T, Fu K-I, Konuma H, et al. Peeling a giant ileal lipoma with endoscopic unroofing and submucosal dissection. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1676–9.
Rahmi G, Samaha E, Lorenceau-Savale C, et al. Small bowel polypectomy by double balloon enteroscopy: correlation with prior capsule endoscopy. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;5:219–25.
de Latour RA, Kilaru SM, Gross SA. Management of small bowel polyps: a literature review. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2017;31:401–8.
Ohmiya N, Nakamura M, Tahara T, et al. Management of small-bowel polyps at double-balloon enteroscopy. Ann Transl Med. 2014;2:30.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
The authors have received no funding for the publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Takeshi Okamoto wrote the manuscript and performed the colonoscopy. Both authors critically reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Takeshi Okamoto and Katsuyuki Fukuda declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human or animal rights
This case report does not include any data about human subjects.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case report.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okamoto, T., Fukuda, K. Ileocolic intussusception caused by mass-forming fibro-granulation from healed ulcer masquerading as small bowel lipoma. Clin J Gastroenterol 14, 522–530 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-020-01329-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-020-01329-8