Abstract
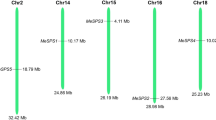
In higher plants, sucrose synthase (Susy, EC 2.4.1.13) as an enzyme with a core function, involved in the synthesis and breakdown of sugars, and plays an important role in growth and metabolism. Although, the different genes encoding Susy isozyme proteins have been cloned and functionally verified in several plant species, to date detailed information about the Susy genes is lacking in Sorghum. Here, we demonstrated the identification of five novel Susy genes from the sorghum genome database. Sequence, structure and phylogenetic analyses of these five SbSusy genes revealed evolutionary conservation through Susy gene family members across Sorghum and other crop plants. The expression of sorghum Susy genes was investigated via transcriptome database in various developmental stages and different tissues. Further qRT-PCR was performed to reveal the induction of SbSusy genes under salt, drought and sugar induction. The results indicated that all Susy genes were differentially expressed in various tissues and highly associated with sucrose metabolism. This study shows a theoretical reference of Susy genes in Sorghum, which provides new insights for the knowledge of the evolution relationships, and basic information to help clarify the molecular mechanism of Susy synthase genes in Sorghum.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah M, Cao YP, Cheng X, Meng DD, Chen Y, Shakoor A, Gao JS, Cai YP (2018) The sucrose synthase gene family in chinese pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.): structure, expression, and evolution. Molecules 23(5):1144–1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051144
Angeles-Nunez JG, Tiessen A (2010) Arabidopsis sucrose synthase 2 and 3 modulate metabolic homeostasis and direct carbon towards starch synthesis in developing seeds. Planta 232(3):701–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1207-9
Astrid W (2018) Transitioning to the next phase: the role of sugar signaling throughout the plant life cycle. Plant Physiol 176(2):1075–1084. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01229
Barratt DH, Barber L, Kruger NJ, Smith AM, Wang TL, Martin C (2001) Multiple, distinct isoforms of sucrose synthase in pea. Plant Physiol 127(2):655–664. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.010297
Baud S, Vaultier MN, Rochat C (2004) Structure and expression profile of the sucrose synthase multigene family in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 55(396):397–409. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh047
Bezrutczyk M, Yang J, Eom JS, Prior M, Sosso D, Hartwig T, Szurek B, Oliva R, Vera-Cruz C, White FF, Yang B, Frommer W (2018) Sugar flux and signaling in plant-microbe interactions. Plant Jounal 93(4):675–685. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13775
Calvino M, Bruggmann R, Messing J (2011) Characterization of the small RNA component of the transcriptome from grain and sweet sorghum stems. BMC Genomics 12(1):356–368. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-356
Chen A, He S, Li F, Li Z, Ding M, Liu Q, Rong J (2012) Analyses of the sucrose synthase gene family in cotton: structure, phylogeny and expression patterns. BMC Plant Biol 12(1):85–102. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-85
Duncan KA, Hardin SC, Huber SC (2006) The three maize sucrose synthase isoforms differ in distribution, localization, and phosphorylation. Plant Cell Physiol 47(7):959–971. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcj068
Durand M, Mainson D, Porcheron B, Maurousset L, Lemoine R, Pourtau N (2018) Carbon source-sink relationship in Arabidopsis thaliana: the role of sucrose transporters. Planta 247(3):587–611
El-Gebali S, Mistry J, Bateman A, Eddy SR, Luciani A, Potter SC, Qureshi M, Richardson LJ, Salazar GA, Smart A, Sonnhammer ELL, Hirsh L, Paladin L, Piovesan D, Tosatto SCE, Finn RD (2019) The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D427–D432. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky995
Fan CF, Wang GY, Wang YM, Zhang R, Wang YT, Feng SQ, Luo KM, Peng LC (2019a) Sucrose synthase enhances hull size and grain weight by regulating cell division and starch accumulation in transgenic rice. Int J Mol Sci 20(20):4971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20204971
Fan JW, Wang HY, Li X, Sui XL, Zhang ZX (2019b) Down-regulating cucumber sucrose synthase 4 (CsSUS4) suppresses the growth and development offlowers and fruits. Plant Cell Physiol 60(4):752–764. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcz040
Fernandes FM, Arrabaça MC, Carvalho LMM (2004) Sucrose metabolism in Lupinus albus L. under salt stress. Biol Plant 48(2):317. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOP.0000033465.59361.d2
Fernandez EB, Munoz FJ, Montero M, Etxeberria E, Sesma MT, Ovecka M, Bahaji A, Ezquer I, Li J, Prat S, Pozueta-Romero J (2009) Enhancing sucrose synthase activity in transgenic potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers results in increased levels of starch, ADPglucose and UDPglucose and total yield. Plant Cell Physiol 50(9):1651–1662. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcp108
Huang YC, Hsiang EC, Yang CC, Wang AY (2016) New insight into the catalytic properties of rice sucrose synthase. Plant Mol Biol 90(1–2):127–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0401-3
Huang Y, Liao Q, Hu SL, Cao Y, Xu G, Long ZJ, Lu XQ (2018) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of seven sucrose synthase genes in bamboo (Bambusa emeiensis): investigation of possible roles in the regulation of cellulose biosynthesis and response to hormones. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 32(2):316–323. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2017.1412271
Huang TW, Luo XL, Fan ZP, Yang YN, Wan W (2021) Genome-wide identification and analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Gene 769(1):145191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.145191
Jia H, Jiu S, Zhang C, Wang C, Tariq P, Liu Z, Wang B, Cui L, Fang J (2016) Abscisic acid and sucrose regulate tomato and strawberry fruit ripening through the abscisic acid-stress-ripening transcription factor. Plant Biotechnol J 14(10):2045–2065. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12563
Julius BT, Leach KA, Tran TM, Mertz RA, Braun DM (2017) Sugar Transporters in Plants: New Insights and Discoveries. Plant Cell Physiol 58(9):1442–1460. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcx090
Koch KE, Nolte KD, Duke ER, McCarty DR, Avigne WT (1992) Sugar levels modulate differential expression of maize sucrose synthase genes. Plant Cell 4(1):59–69. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.4.1.59
Lastdrager J, Hanson J, Smeekens S (2014) Sugar signals and the control of plant growth and development. J Exp Bot 65(3):799–807. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert474
Li F, Hao C, Yan L, Wu B, Qin X, Lai J, Song Y (2015) Gene structure, phylogeny and expression profile of the sucrose synthase gene family in cacao (Theobroma cacao L.). J Genet 94(3):461–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-015-0558-1
McKinley B, Rooney W, Wilkerson C, Mullet J (2016) Dynamics of biomass partitioning, stem gene expression, cell wall biosynthesis, and sucrose accumulation during development of Sorghum bicolor. Plant Jounal 88(4):662–680. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13269
Ruan YL (2014) Sucrose metabolism: gateway to diverse carbon use and sugar signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65(1):33–67. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-040251
Santaniello A, Loreti E, Gonzali S, Novi G, Perata P (2014) A reassessment of the role of sucrose synthase in the hypoxic sucrose-ethanol transition in Arabidopsis. Plant, Cell Environ 37(10):2294–2302. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12363
Slewinski TL (2012) Non-structural carbohydrate partitioning in grass stems: a target to increase yield stability, stress tolerance, and biofuel production. J Exp Bot 63(13):4647–4670. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers124
Stein O, Granot D (2019) An overview of sucrose synthases in plants. Front Plant Sci 10(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00095
Takehara K, Murata K, Yamaguchi T, Yamaguchi K, Chaya G, Kido S, Iwasaki Y, Ogiwara H, Ebitani T, Miura K (2018) Thermo-responsive allele of sucrose synthase 3 (Sus3) provides high-temperature tolerance during the ripening stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed Sci 68(3):336–342. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.18007
Thirugnanasambandam PP, Mason PJ, Hoang NV, Furtado A, Botha FC, Henry RJ (2019) Analysis of the diversity and tissue specificity of sucrose synthase genes in the long read transcriptome of sugarcane. BMC Plant Biol 19(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1733-y
Tong XL, Wang ZY, Ma BQ, Zhang CX, Zhu LC, Ma FW, Li MJ (2018) tructure and expression analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in apple. J Integr Agric 17(4):847–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61755-6
Wang F, Sanz A, Brenner ML, Smith A (1993) Sucrose synthase, starch accumulation, and tomato fruit sink strength. Plant Physiol 101(1):321–327. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.101.1.321
Wang Z, Wei P, Wu MZ, Xu YL, Li F, Luo ZP, Zhang JF, Chen A, Xie XD, Cao PJ, Lin FC, Yang J (2015) Analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in tobacco: structure, phylogeny, and expression patterns. Planta 242(1):153–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2297-1
Werr W, Frommer WB, Maas C, Starlinger P (1985) Structure of the sucrose synthase gene on chromosome 9 of Zea mays L. EMBO J 4(6):1373–1380. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03789.x
Xiaoyang X, Yongheng Y, Chunxiao L, Yuming S, Ting Z, Menglan H, Suzhen H, Haiyan Y (2019) The evolutionary history of the sucrose synthase gene family in higher plants. BMC Plant Biol 19(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-2181-4
Yang A, Dai XY, Zhang WH (2012) A R2R3-type MYB gene, OsMYB2, is involved in salt, cold, and dehydration tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 63(7):2541–2556. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err431
Zhang CH, Yu ML, Ma RJ, Shen ZJ, Zhang BB, Korir NK (2015) Structure, expression profile, and evolution of the sucrose synthase gene family in peach (Prunus persica). Acta Physiol Plant 37(4):81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1829-4
Zhao Y, Cheng XY, Liu XD, Wu HF, Bi HH, Xu HX (2018) The wheat MYB transcription factor TaMYB31 is involved in drought stress responses in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 9:1426. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01426
Zheng Y, Anderson S, Zhang Y, Garavito RM (2011) The structure of sucrose synthase-1 from Arabidopsis thaliana and its functional implications. J Biol Chem 286(41):36108–36118. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.275974
Zhu X, Wang M, Li X, Jiu S, Wang C, Fang J (2017) Genome-wide analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in grape (Vitis vinifera): structure, evolution, and expression profiles. Genes 8(4):1–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8040111
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Dr. Jiwei Zhang from Sichuan Agricultural University for providing Btx623 seeds for abiotic stress treatment.
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Initiation Fund for High-level Talents of China Three Gorges University (2016GCRC02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shaopeng Han: Investigation, Methodology, Writing-original draft. Yelei Lu: Writing, Resources, Data Curation. Chao Zhou: Conceptualization, Supervision. Yunwei Cheng: Resources, Data Curation. Yang Lv: Resources, Data Curation. Gongjian Zeng: Resources. Dechun Zhang: Writing-review & editing. Xinqiang Gao: Writing-review & editing. Xiangling Shen: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing-review & editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12298_2022_1166_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplement Figure 1. Identity matrix for SbSusy amino acid sequences. Colors from red to blue indicate high to low expressions. (TIF 1247 kb)
12298_2022_1166_MOESM2_ESM.tif
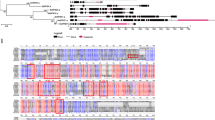
Supplementary Figure 2. Distribution of conserved motifs for SbSusy genes. Conserved motifs are marked by different colors on the right. (TIF 1639 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Han, S., Zhou, C. et al. Molecular identification and expression analysis of five sucrose synthase genes in Sorghum Bicolor. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 28, 697–707 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-022-01166-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-022-01166-8