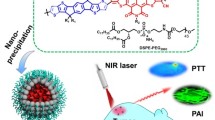
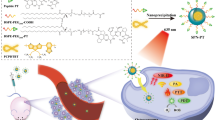
Abstract
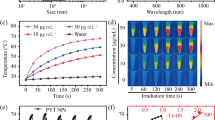
Semiconducting polymer nanoparticles (SPNs) have shown great promise in second near-infrared window (NIR-II) phototheranostics. However, the issue of long metabolic time significantly restricts the clinical application of SPNs. In this study, we rationally designed a biodegradable SPN (BSPN50) for NIR-II fluorescence imaging-guided photodynamic therapy (PDT). BSPN50 is prepared by encapsulating a biodegradable SP (BSP50) with an amphiphilic copolymer F-127. BSP50 is composed of NIR-II fluorescent diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP) segment and degradable poly(phenylenevinylene) (PPV) segment with the ratio of 50/50. BSPN50 has both satisfactory degradability under myeloperoxidase (MPO)/hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and NIR-II fluorescence emission upon 808 nm laser excitation. Furthermore, BSPN50 shows good photodynamic efficacy under 808 nm laser irradiation. BSPN50 shows a faster degradation rate than BSPN100 which has no PPV segment both in vitro and in vivo. In addition, BSPN50 can effectively diagnose tumor via NIR-II fluorescence imaging and inhibit the tumor growth by PDT. Thus, our study provides a rational approach to construct biodegradable nanoplatforms for efficient tumor NIR-II phototheranostics.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng, G. X.; Zhang, G. Q.; Ding, D. Design of superior phototheranostic agents guided by Jablonski diagrams. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8179–8234.
Chen, C.; Ou, H. L.; Liu, R. H.; Ding, D. Regulating the photophysical property of organic/polymer optical agents for promoted cancer phototheranostics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1806331.
Yin, X. R.; Cheng, Y. F.; Feng, Y.; Stiles, W. R.; Park, S. H.; Kang, H.; Choi, H. S. Phototheranostics for multifunctional treatment of cancer with fluorescence imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 189, 114483.
He, S. S.; Cheng, P. H.; Pu, K. Y. Activatable near-infrared probes for the detection of specific populations of tumour-infiltrating leukocytes in vivo and in urine. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 7, 281–297.
Zhou, H.; Yi, W. R.; Li, A. G.; Wang, B.; Ding, Q. H.; Xue, L. R.; Zeng, X. D.; Feng, Y. Z.; Li, Q. Q.; Wang, T. et al. Specific Small-Molecule NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging of Osteosarcoma and Lung Metastasis. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 1901224.
Lei, Z. H.; Zhang, F. Molecular engineering of NIR-II fluorophores for improved biomedical detection. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16294–16308.
Shou, K. Q.; Qu, C. R.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H. B.; Hong, X. C.; Yu, A. X.; Cheng, Z. Multifunctional biomedical imaging in physiological and pathological conditions using a NIR-II probe. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700995.
Zhao, J. Y.; Zhong, D.; Zhou, S. B. NIR-I-to-NIR- II fluorescent nanomaterials for biomedical imaging and cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 349–365.
Chen, Y.; Pei, P.; Lei, Z. H.; Zhang, X.; Yin, D. R.; Zhang, F. A promising NIR-II fluorescent sensor for peptide-mediated long-term monitoring of kidney dysfunction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 15809–15815.
Zeng, X. D.; Xie, L. R.; Chen, D. L.; Li, S. S.; Nong, J. X.; Wang, B.; Tang, L.; Li, Q. Q.; Li, Y.; Deng, Z. X. et al. A bright NIR-II fluorescent probe for breast carcinoma imaging and image-guided surgery. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 14287–14290.
Lan, Q. C.; Yu, P.; Yan, K.; Li, X. M.; Zhang, F.; Lei, Z. H. Polymethine molecular platform for ratiometric fluorescent probes in the second near-infrared window. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 21010–21015.
Yang, N.; Song, S.; Liu, C.; Ren, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, S. J.; Yu, C. An aza-BODIPY-based NIR-II luminogen enables efficient phototheranostics. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 4815–4821.
Sun, P. F.; Jiang, X. Y.; Sun, B.; Wang, H.; Li, J. W.; Fan, Q. L.; Huang, W. Elecfron-acceptor density adjustments for preparation conjugated polymers with NIR-II absorption and brighter NIR-II fluorescence and 1064 nm active photothermal/gas therapy. Biomaterials 2022, 280, 121319.
Jiang, Y. Y.; Pu, K. Y. Multimodal biophotonics of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1840–1849.
Wang, X.; Wu, M.; Li, H. Z.; Jiang, J. L.; Zhou, S. S.; Chen, W. Z.; Xie, C.; Zhen, X.; Jiang, X. Q. Enhancing penetration ability of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for sonodynamic therapy of large solid tumor. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2022, 9, e2104125.
Li, J. C.; Zhen, X.; Lyu, Y.; Jiang, Y. Y.; Huang, J. G.; Pu, K. Y. Cell membrane coated semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for enhanced multimodal cancer phototheranostics. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 8520–8530.
Lin, H. R.; Bai, H. T.; Yang, Z. W.; Shen, Q.; Li, M. Y.; Huang, Y. M.; Lv, F. T.; Wang, S. Conjugated polymers for biomedical applications. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 7232–7244.
Wang, W. Q.; Zhang, X.; Ni, X. Y.; Zhou, W.; Xie, C.; Huang, W.; Fan, Q. L. Semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for NIR-II fluorescence imaging-guided photothermal/thermodynamic combination therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 846–853.
Liu, S. J.; Ou, H. L.; Li, Y. Y.; Zhang, H. K.; Liu, J. K.; Lu, X. F.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Ding, D.; Tang, B. Z. Planar and twisted molecular structure leads to the high brightness of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for NIR-IIa fluorescence imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15146–15156.
Tang, Y. F.; Li, Y. Y.; Lu, X. M.; Hu, X. M.; Zhao, H.; Hu, W. B.; Lu, F.; Fan, Q. L.; Huang, W. Bio- erasable intermolecular donor-acceptor interaction of organic semiconducting nanoprobes for activatable NIR-II fluorescence imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807376.
Tang, Y. F.; Li, Y. Y.; Wang, Z.; Pei, F.; Hu, X. M.; Ji, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Hu, W. B.; Lu, X. M. et al. Organic semiconducting nanoprobe with redox-activatable NIR-II fluorescence for in vivo real-time monitoring of drug toxicity. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 27–30.
Chen, Y.; Yu, H. L.; Wang, Y. S.; Sun, P. F.; Fan, Q. L.; Ji, M. Thiadiazoloquinoxaline derivative-based NIR-II organic molecules for NIR-II fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy. Biomater. Sei. 2022, 10, 2772–2788.
Xie, C.; Zhou, W.; Zeng, Z. L.; Fan, Q. L.; Pu, K. Y. Gaffted semiconducting polymer amphiphiles for multimodal optical imaging and combination phototherapy. Chem. Sci. 2020, 17, 10553–10570.
Zhen, X.; Pu, K. Y.; Jiang, X. Q. Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal therapy of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles: Signal amplification and second near-infrared construction. Small 2021, 17, 2004723.
Jiang, Y. Y.; Upputuri, P. K.; Xie, C.; Zeng, Z. L.; Sharma, A.; Zhen, X.; Li, J. C.; Huang, J. G.; Pramanik, M.; Pu, K. Y. Metabolizable semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for second near-infrared photoacoustic imaging. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808166.
Yang, G. B.; Phua, S. Z. F.; Bindra, A. K.; Zhao, Y. L. Degradability and clearance of inorganic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805730.
Wu, C. F.; Chiu, D. T. Highly fluorescent semiconducting polymer dots for biology and medicine. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3086–3109.
Jiang, Y. Y.; Li, J. C.; Zeng, Z. L.; Xie, C.; Lyu, Y.; Pu, K. Y. Organic photodynamic nanoinhibitor for synergistic cancer therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8161–8165.
Feng, L. H.; Zhu, C. L.; Yuan, H. X.; Liu, L. B.; Lv, F. T.; Wang, S. Conjugated polymer nanoparticles: Preparation, properties, functionalization and biological applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6620–6633.
Li, J. C.; Rao, J. H.; Pu, K. Y. Recent progress on semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for molecular imaging and cancer phototherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 155, 217–235.
Xie, C.; Zhen, X.; Miao, Q. Q.; Lyu, Y.; Pu, K. Y. Self-assembled semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for ultrasensitive near-infrared afterglow imaging of metastatic tumors. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801331.
Lyu, Y.; Zeng, J. F.; Jiang, Y. Y.; Zhen, X.; Wang, T.; Qiu, S. S.; Lou, X.; Gao, M. Y.; Pu, K. Y. Enhancing both biodegradability and efficacy of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1801–1810.
Miao, Q. Q.; Xie, C.; Zhen, X.; Lyu, Y.; Duan, H. W.; Liu, X. G.; Jokerst, J. V.; Pu, K. Y. Molecular afterglow imaging with bright, biodegradable polymer nanoparticles. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1102–1110.
Huang, H. Y.; Xie, W. S.; Wan, Q.; Mao, L. C.; Hu, D. N.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X. Y.; Wei, Y. A self-degradable conjugated polymer for photodynamic therapy with reliable postoperative safety. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2022, 9, 2104101.
Guo, C. R.; Sileikaite, I.; Davies, M. J.; Hawkins, C. L. Myeloperoxidase modulates hydrogen peroxide mediated cellular damage in murine macrophages. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9, 1255.
Cui, D.; Xie, C.; Li, J. C.; Lyu, Y.; Pu, K. Y. Semiconducting photosensitizer-incorporated copolymers as near-infrared afterglow nanoagents for tumor imaging. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2018, 7, 1800329.
Emrullahoǧlu, M.; Üçüncü, M.; Karakus, E. A BODIPY aldoxime-based chemodosimeter for highly selective and rapid detection of hypochlorous acid. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7836–7838.
Yin, C.; Zhen, X.; Fan, Q. L.; Huang, W.; Pu, K. Y. Degradable semiconducting oligomer amphiphile for ratiometric photoacoustic imaging of hypochlorite. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4174–4182.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22174070 and 22205115), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20230060), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu University (No. 21KJB150022), the Research startup fund of NJUPT (no. NY220149), Natural Science Foundation of NJUPT (no. NY221088), the Project of State Key Laboratory of Organic Electronics and Information Displays, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Nos. GZR2022010012 and GZR2023010022), and the Synergetic Innovation Center for Organic Electronics and Information Displays for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2024_6434_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Rational design of biodegradable semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for NIR-II fluorescence imaging-guided photodynamic therapy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, X., Shen, J., Xu, Z. et al. Rational design of biodegradable semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for NIR-II fluorescence imaging-guided photodynamic therapy. Nano Res. 17, 5399–5408 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6434-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6434-7