Abstract
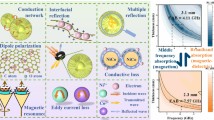
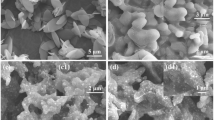
To achieve excellent electromagnetic wave (EMW) absorption properties, the microstructure design of the absorber is critical. In this work, six kinds of N-Ni/C nanostructures with different morphologies were prepared by one-step hydrothermal method and high temperature carbonization by adjusting the types of nickel salts and reaction solvents. The EMW absorption performance of six different morphologies of N-Ni/C nanostructures was compared and analyzed. Among them, it is found that the nanoflower-like N-Ni/C composite has excellent dielectric loss and magnetic loss synergistic effect due to its polycrystalline structure, and can obtain excellent EMW absorption performance. The minimum reflection loss value at a thickness of 1.9 mm is −59.56 dB at 16.88 GHz, and the effective absorption bandwidth value reaches 6.0 GHz at a thickness of 2.2 mm. Our research shows that different morphologies and multiple lattice structures of nanostructures with the same composition have a significant influence on EMW absorption performance, which provides new research ideas for developing high-performance EMW absorbing materials.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, S.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G. L. Electrospun Fe0.64Ni0.36/MXene/CNFs nanofibrous membranes with multicomponent heterostructures as flexible electromagnetic wave absorbers. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 3395–3407.
Fu, X. Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, L.; Cao, M. S. Vertically implanting MoSe2 nanosheets on the RGO sheets towards excellent multi-band microwave absorption. Carbon 2022, 197, 324–333.
Yang, Y. N.; Xia, L.; Zhang, T.; Shi, B.; Huang, L. N.; Zhong, B.; Zhang, X. Y.; Wang, H. T.; Zhang, J.; Wen, G. W. Fe3O4@LAS/RGO composites with a multiple transmissionabsorption mechanism and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 510–518.
Chen, X. L.; Shi, T.; Wu, G. L.; Lu, Y. Design of molybdenum disulfide@polypyrrole compsite decorated with Fe3O4 and superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 572, 227–235.
Wang, C. X.; Liu, Y.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhao, W. R.; Wu, G. T. Multicomponent nanoparticles synergistic one-dimensional nanofibers as heterostructure absorbers for tunable and efficient microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 13.
Liu, Y.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhou, J. X.; Wu, G. L. Multi-hierarchy heterostructure assembling on MnO2 nanowires for optimized electromagnetic response. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 28, 100845.
Li, W. C.; Zhang, B. H.; Ying, Y.; Yu, J.; Zheng, J. W.; Qiao, L.; Li, J.; Che, S. L. An optically transparent unequal proportional coding metasurface with absorption and diffusion integrated mechanism for ultra-broadband RCS reduction. Opt. Mater. 2022, 133, 112801.
Gao, Z. G.; Xu, B. H.; Ma, M. L.; Feng, A. L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. H.; Jia, Z. R.; Wu, G. L. Electrostatic self-assembly synthesis of ZnFe2O4 quantum dots (ZnFe2O4@C) and electromagnetic microwave absorption. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2019, 179, 107417.
Zhou, J. X.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G. L. Construction of 3D conductive network by flower-like V2O3 synergy with magnetic NiCo for superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 29, 100902.
Pan, F.; Rao, Y. P.; Batalu, D.; Cai, L.; Dong, Y. Y.; Zhu, X. J.; Shi, Y. Y.; Shi, Z.; Liu, Y. W.; Lu, W. Macroscopic electromagnetic cooperative network-enhanced MXene/Ni chains aerogel-based microwave absorber with ultra-low matching thickness. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 140.
Chang, M.; Li, Q. Y.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhao, W. R.; Wu, G. L. Tuning microwave absorption properties of Ti3C2Tx MXene-based materials: Component optimization and structure modulation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 148, 150–170.
Zhang, X.; Qiao, J.; Jiang, Y. Y.; Wang, F. L.; Tian, X. L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L. L.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. R. Carbon-based MOF derivatives: Emerging efficient electromagnetic wave absorption agents. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 135.
Quan, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M. J.; Liu, J.; Jia, Q.; Lu, X. C.; Chen, J.; Huang, X. G. A rational design of multiple-layer films with continuous impedance gradient variation for enhanced microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 3625–3631.
Wu, G. L.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhou, X. F.; Nie, G. Z.; Lv, H. L. Interlayer controllable of hierarchical MWCNTs@C@FexOy cross-linked composite with wideband electromagnetic absorption performance. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 128, 105687.
Jia, Z. R.; Zhang, X. Y.; Gu, Z.; Wu, G. L. MOF-derived Ni-Co bimetal/porous carbon composites as electromagnetic wave absorber. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 28.
Sun, C. H.; Li, Q. Y.; Jia, Z. R.; Wu, G. L.; Yin, P. F. Hierarchically flower-like structure assembled with porous nanosheet-supported MXene for ultrathin electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140277.
Han, Y. X.; He, M. K.; Hu, J. W.; Liu, P. B.; Liu, Z. W.; Ma, Z. L.; Ju, W. B.; Gu, J. W. Hierarchical design of FeCo-based microchains for enhanced microwave absorption in C band. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 1773–1778.
Pang, H. F.; Duan, Y. P.; Dai, X. H.; Huang, L. X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X. J. The electromagnetic response of composition-regulated honeycomb structural materials used for broadband microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 88, 203–214.
Liu, Y.; Zhou, X. F.; Jia, Z. R.; Wu, H. J.; Wu, G. L. Oxygen vacancy-induced dielectric polarization prevails in the electromagnetic wave-absorbing mechanism for Mn-based MOFs-derived composites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204499.
Zhao, T. B.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G. L. Multiphase molybdenum carbide doped carbon hollow sphere engineering: The superiority of unique double-shell structure in microwave absorption. Small 2023, 19, 2206323.
Wu, G. L.; Zhang, H. X.; Luo, X. X.; Yang, L. J.; Lv, H. L. Investigation and optimization of Fe/ZnFe2O4 as a wide-band electromagnetic absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 536, 548–555.
Zhou, X. F.; Jia, Z. R.; Feng, A. L.; Kou, J. H.; Cao, H. J.; Liu, X. H.; Wu, G. L. Construction of multiple electromagnetic loss mechanism for enhanced electromagnetic absorption performance of fish scale-derived biomass absorber. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2020, 192, 107980.
Yang, B. T.; Fang, J. F.; Xu, C. Y.; Cao, H.; Zhang, R. X.; Zhao, B.; Huang, M. Q.; Wang, X. Y.; Lv, H. L.; Che, R. C. One-dimensional magnetic FeCoNi alloy toward low-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 170.
Wang, L. X.; Guan, Y. K.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, H. L.; Pan, S. B.; Yu, M. X.; Zhang, Q. T. Efficient ferrite/Co/porous carbon microwave absorbing material based on ferrite@metal-organic framework. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 945–955.
Ren, L. G.; Wang, Y. Q.; Zhang, X.; He, Q. C.; Wu, G. L. Efficient microwave absorption achieved through in situ construction of core-shell CoFe2O4@mesoporous carbon hollow spheres. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 504–514.
Hu, S. C.; Zhou, Y. M.; He, M.; Liao, Q.; Yang, H. Y.; Li, H. F.; Xu, R.; Ding, Q. H. Hollow Ni-Co layered double hydroxides-derived NiCo-alloy@g-C3N4 microtubule with high-performance microwave absorption. Mater. Lett. 2018, 231, 171–174.
Wang, Y. Q.; Zhao, H. B.; Cheng, J. B.; Liu, B. W.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Y. Z. Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx@ZnO hollow spheres with excellent microwave absorption inspired by the visual phenomenon of eyeless urchins. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 76.
Zhang, Y. L.; Ruan, K. P.; Gu, J. W. Flexible sandwich-structured electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposite films with excellent thermal conductivities. Small 2021, 17, 2101951.
Wang, Y.; Di, X. C.; Chen, J.; She, L. N.; Pan, H. G.; Zhao, B.; Che, R. C. Multi-dimensional C@NiCo-LDHs@Ni aerogel: Structural and componential engineering towards efficient microwave absorption, anti-corrosion, and thermal-insulation. Carbon 2022, 191, 625–635.
Zhang, H. X.; Wang, B. B.; Feng, A. L.; Zhang, N.; Jia, Z. R.; Huang, Z. Y.; Liu, X. H.; Wu, G. L. Mesoporous carbon hollow microspheres with tunable pore size and shell thickness as efficient electromagnetic wave absorbers. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2019, 167, 690–699.
Liang, J.; Ye, F.; Cao, Y. C.; Mo, R.; Cheng, L. F.; Song, Q. Defect-engineered graphene/Si3N4 multilayer alternating core-shell nanowire membrane: A plainified hybrid for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200141.
Liu, H. H.; Li, Y. J.; Yuan, M. W.; Sun, G. B.; Li, H. F.; Ma, S. L.; Liao, Q. L.; Zhang, Y. In situ preparation of cobalt nanoparticles decorated in N-doped carbon nanofibers as excellent electromagnetic wave absorbers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22591–22601.
Qiu, S.; Lyu, H.; Liu, J. R.; Liu, Y. Z.; Wu, N. N.; Liu, W. Facile synthesis of porous nickel/carbon composite microspheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption by magnetic and dielectric losses. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20258–20266.
Wei, Y.; Wang, X. X.; Zhang, J. W.; Liu, H. J.; Lv, X. Y.; Zhang, M. M.; Liu, S. C.; Gong, C. H. Facile approach of Ni/C composites from Ni/cellulose composites as broadband microwave absorbing materials. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 31129–31132.
Lv, X. Y.; Guo, J. H.; Zhao, C.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J. W.; Wu, Z. S.; Gong, C. H. Investigation on the enhanced electromagnetism of Ni/RGO nanocomposites synthesized by an in situ process. Matter. Lett. 2017, 201, 43–45.
Huang, X. M.; Liu, X. H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J. X.; Wu, G. L.; Jia, Z. R. Construction of NiCeOx nanosheets-skeleton cross-linked by carbon nanotubes networks for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 147, 16–25.
Gao, T.; Zhao, R. Z.; Li, Y. X.; Zhu, Z. Y.; Hu, C. L.; Ji, L. Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X. F. Sub-nanometer Fe clusters confined in carbon nanocages for boosting dielectric polarization and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204370.
Xiao, J. X.; Qi, X. S.; Gong, X.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Y. L.; Xie, R.; Zhong, W. Defect and interface engineering in core@shell structure hollow carbon@MoS2 nanocomposites for boosted microwave absorption performance. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 7778–7787.
Qin, M.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. Dielectric loss mechanism in electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2022, 9, 2105553.
Zhang, X.; Tian, X. L.; Liu, C.; Qiao, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. R.; Zeng, Z. H. MnCo-MOF-74 derived porous MnO/Co/C heterogeneous nanocomposites for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2022, 194, 257–266.
Hou, T. Q.; Wang, B. B.; Jia, Z. R.; Wu, H. J.; Lan, D.; Huang, Z. Y.; Feng, A. L.; Ma, M. L.; Wu, G. L. A review of metal oxide-related microwave absorbing materials from the dimension and morphology perspective. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 10961–10984.
Yao, L. H.; Cao, W. Q.; Zhao, J. G.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Y. C.; Jiang, S.; Pan, Q. L.; Song, J.; Zhu, Y. Q.; Cao, M. S. Regulating bifunctional flower-like NiFe2O4/graphene for green EMI shielding and lithium ion storage. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 127, 48–60.
Li, W. J.; Li, W. C.; Ying, Y.; Yu, J.; Zheng, J. W.; Qiao, L.; Li, J.; Che, S. L. Multifunctional flower-like core-shell Fe/Fe4N@SiO2 composites for broadband and high-efficiency ultrathin electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 132, 90–99.
Quan, B.; Liang, X. H.; Ji, G. B.; Zhang, Y. N.; Xu, G. Y.; Du, Y. W. Cross-linking-derived synthesis of porous CoxNiy/C nanocomposites for excellent electromagnetic behaviors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 38814–38823.
Zhou, X.; Zhao, B.; Lv, H. L. Low-dimensional cobalt doped carbon composite towards wideband electromagnetic dissipation. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 70–79.
Cao, X. L.; Liu, X. H.; Zhu, J. H.; Jia, Z. R.; Liu, J. K.; Wu, G. L. Optimal particle distribution induced interfacial polarization in hollow double-shell composites for electromagnetic waves absorption performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 634, 268–278.
Cheng, J. Y.; Zhang, H. B.; Ning, M. Q.; Raza, H.; Zhang, D. Q.; Zheng, G. P.; Zheng, Q. B.; Che, R. C. Emerging materials and designs for low- and multi-band electromagnetic wave absorbers: The search for dielectric and magnetic synergy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200123.
Gao, F.; Yang, Y. Z.; Qiu, W. W.; Song, Z. P.; Wang, Q. X.; Niu, L. Ni3C/Ni nanochains for electrochemical sensing of glucose. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 8520–8529.
Wang, S. Y.; Wang, Y. R.; Sun, C. H.; Qi, S. Q.; Wang, B. B.; Li, D. H.; Wu, G. L. Multifunctional carbon nanofibers coated Co-Zn alloy nanoparticles composite for efficient enenrgy conversion and microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 932, 167458.
Zhang, S. J.; Li, J. Y.; Jin, X. T.; Wu, G. L. Current advances of transition metal dichalcogenides in electromagnetic wave absorption: A brief review. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 428–445.
Hu, F. Y.; Wang, X. H.; Bao, S.; Song, L. M.; Zhang, S.; Niu, H. H.; Fan, B. B.; Zhang, R.; Li, H. X. Tailoring electromagnetic responses of delaminated Mo2TiC2T. MXene through the decoration of Ni particles of different morphologies. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 440, 135855.
Zhang, H. B.; Cheng, J. Y.; Wang, H. H.; Huang, Z. H.; Zheng, Q. B.; Zheng, G. P.; Zhang, D. Q.; Che, R. C.; Cao, M. S. Initiating VB-group laminated NbS2 electromagnetic wave absorber toward superior absorption bandwidth as large as 6.48 GHz through phase engineering modulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2108194.
Yang, W. T.; Sun, J. W.; Liu, D. Y.; Fu, W. W.; Dong, Y. B.; Fu, Y. Q.; Zhu, Y. F. Rational design of hierarchical structure of carbon@polyaniline composite with enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 2022, 194, 114–126.
Ren, X. Y.; Song, Y. H.; Gao, Z. G.; Wu, Y. L.; Jia, Z. R.; Wu, G. L. Rational manipulation of composition and construction toward Zn/Co bimetal hybrids for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 254–261.
Yang, J. J.; Wang, J. Q.; Li, H. Q.; Wu, Z.; Xing, Y. Q.; Chen, Y. F.; Liu, L. MoS2/MXene aerogel with conformal heterogeneous interfaces tailored by atomic layer deposition for tunable microwave absorption. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2022, 9, 2101988.
Wu, D.; Wang, Y. Q.; Deng, S. L.; Lan, D.; Xiang, Z. N.; He, Q. C. Heterostructured CoFe@N-doped carbon porous polyhedron for efficient microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 1859–1868.
Feng, X.; Yin, P. F.; Zhang, L. M.; Sun, X. Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Lu, C. F.; Gao, Z. H.; Zhan, Y. X. Innovative preparation of Co@CuFe2O4 composite via ball-milling assisted chemical precipitation and annealing for glorious electromagnetic wave absorption. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 559–569.
Song, L. M.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y. Q.; Guan, L.; Zhu, Y. Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, H. L.; Putra, B. R.; Zhang, R.; Fan, B. B. Multifunctional SiC@SiO2 nanofiber aerogel with ultrabroadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 152.
Xu, C. Y.; Liu, P. B.; Wu, Z. C.; Zhang, H. B.; Zhang, R. X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Y.; Yang, B. T.; Yang, Z. Q. et al. Customizing heterointerfaces in multilevel hollow architecture constructed by magnetic spindle arrays using the polymerizing-etching strategy for boosting microwave absorption. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2022, 9, 2200804.
Lu, Z. X.; Ren, F.; Guo, Z. Z.; Dai, Z.; Fu, B. Q.; Zong, Z.; Zhang, F. D.; Jin, Y. L.; Chen, Z. Y.; Ren, P. G. Facile construction of core-shell carbon@CoNiO2 derived from yeast for broadband and high-efficiency microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 625, 415–424.
Song, L. M.; Fan, B. B.; Chen, Y. Q.; Gao, Q. C.; Li, Z.; Wang, H. L.; Zhang, X. Y.; Guan, L.; Li, H. X.; Zhang, R. Ultralight and hyperelastic SiC nanofiber aerogel spring for personal thermal energy regulation. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 1235–1248.
Sun, M. X.; Wang, D. R.; Xiong, Z. M.; Zhang, Z. W.; Qin, L.; Chen, C. C.; Wu, F.; Liu, P. B. Multi-dimensional Ni@C-CoNi composites with strong magnetic interaction toward superior microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 130, 176–183.
Wu, L. H.; Liu, X.; Wan, G. P.; Peng, X. G.; He, Z. Y.; Shi, S. H.; Wang, G. Z. Ni/CNTs and carbon coating engineering to synergistically optimize the interfacial behaviors of TiO2 for thermal conductive microwave absorbers. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 448, 137600.
Lei, L.; Yao, Z. J.; Zhou, J. T.; Zheng, W. J.; Wei, B.; Zu, J. Q.; Yan, K. Y. Hydrangea-like Ni/NiO/C composites derived from metal-organic frameworks with superior microwave absorption. Carbon 2021, 173, 69–79.
Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y. X.; Zhang, C. L.; Wang, J.; Ji, J. L.; Li, K. X. Intense nonlinear dielectric and magnetic resonances of core–shell Ni@graphene composites and their improved microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 4910–4920.
Liu, D. W.; Yang, L.; Wang, F. Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Lv, T.; Zhao, H. J.; Du, Y. C. Hierarchical carbon nanotubes@Ni/C foams for high-performance microwave absorption. Carbon 2022, 196, 867–876.
Qiu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, H. B.; Wang, L.; Wang, M. Q.; Wen, B. Hollow Ni/C microspheres derived from Ni-metal organic framework for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123207.
Di, X. C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Cheng, R. R.; Yang, L. Q.; Wu, X. M. Heterostructure design of Ni/C/porous carbon nanosheet composite for enhancing the electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2021, 179, 566–678.
Gao, Z. G.; Ma, Z. H.; Lan, D.; Zhao, Z. H.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J.; Hou, Y. L. Synergistic polarization loss of MoS2-based multiphase solid solution for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112294.
Chen, X. L.; Shi, T.; Zhong, K. L.; Wu, G. L.; Lu, Y. Capacitive behavior of MoS2 decorated with FeS2@carbon nanospheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122240.
Zhang, Y. L.; Ruan, K. P.; Zhou, K.; Gu, J. W. Controlled distributed Ti3C2Tx hollow microspheres on thermally conductive polyimide composite films for excellent electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater., in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202211642.
Liu, D. W.; Du, Y. C.; Xu, P.; Liu, N.; Wang, Y. H.; Zhao, H. H.; Cui, L. R.; Han, X. J. Waxberry-like hierarchical Ni@C microspheres with high-performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 5037–5046.
Pan, C.; Zhang, J. Q.; Kou, K. C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G. L. Investigation of the through-plane thermal conductivity of polymer composites with in-plane oriented hexagonal boron nitride. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 120, 1–8.
Liu, J. L.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. Anion-doping-induced vacancy engineering of cobalt sulfoselenide for boosting electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200544.
Wang, C. H.; Zong, L. S.; Pan, Y. X.; Li, N.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J. Y.; Jian, X. G. Preparation and characterization of branch-like heteroatoms-doped Ni@C nanofibers for high-performance microwave absorption with thin thickness. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2021, 223, 109114.
Wu, H. J.; Wu, G. L.; Wang, L. D. Peculiar porous α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3, and Fe3O4 nanospheres: Facile synthesis and electromagnetic properties. Powder Technol. 2015, 269, 443–451.
Li, J. J.; Zhang, F.; Lu, H. B.; Guo, W. B.; He, X. D.; Yuan, Y. Heterogeneous rod-like Ni@C composites toward strong and stable microwave absorption performance. Carbon 2021, 181, 358–369.
Zhai, N. X.; Luo, J. H.; Xiao, M. W.; Zhang, Y. C.; Yan, W. X.; Xu, Y. In situ construction of Co@nitrogen-doped carbon/Ni nanocomposite for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2023, 203, 416–425.
Zhou, Y.; Zhou, W. J.; Ni, C. H.; Yan, S. G.; Yu, L. M.; Li, X. “Tree blossom” Ni/NC/C composites as high-efficiency microwave absorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132621.
Yue, L. Q.; Zhong, B.; Xia, L.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y. L.; Huang, X. X. Three-dimensional network-like structure formed by silicon coated carbon nanotubes for enhanced microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 177–186.
Xiang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y. Y.; Cai, L.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, H. J.; Zhu, X. J.; Dong, Y. Y.; Lu, W. Efficient microwave absorption of MOFs derived laminated porous Ni@C nanocomposites with waterproof and infrared shielding versatility. Carbon 2021, 185, 477–490.
Yi, P. S.; Yao, Z. J.; Zhou, J. T.; Wei, B.; Lei, L.; Tan, R. Y.; Fan, H. Y. Facile synthesis of 3D Ni@C nanocomposites derived from two kinds of petal-like Ni-based MOFs towards lightweight and efficient microwave absorbers. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 3119–3135.
Qiu, Y.; Yang, H. B.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, X. Y.; Wen, B.; Lin, Y. Constructing a nitrogen-doped carbon and nickel composite derived from a mixed ligand nickel-based a metal-organic framework toward adjustable microwave absorption. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 9204–9216.
Luo, J. H.; Li, X. P.; Yan, W. X.; Shu, P. C.; Mei, J. RGO supported bimetallic MOFs-derived Co/MnO/porous carbon composite toward broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2023, 205, 552–561.
Wu, M.; Darboe, A. K.; Qi, X. S.; Xie, R.; Qin, S. J.; Deng, C. Y.; Wu, G. L.; Zhong, W. Optimization, selective, and efficient production of CNTs/CoxFe3−xO4 core/shell nanocomposites as outstanding microwave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 11936–11949.
Qiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Lyu, L.; Yang, Y. F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L. L.; Liu, W.; Wang, F. L.; Liu, J. R. Non-magnetic bimetallic MOF-derived porous carbon-wrapped TiO2/ZrTiO4 composites for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 75.
Zhang, F.; Jia, Z. R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C. H.; Wang, B. B.; Xu, B. H.; Liu, X. H.; Wu, G. L. Tailoring nanoparticles composites derived from metal-organic framework as electromagnetic wave absorber. Mater. Today Phys. 2021, 20, 100475.
Huang, X. M.; Liu, X. H.; Jia, Z. R.; Wang, B. B.; Wu, X. M.; Wu, G. L. Synthesis of 3D cerium oxide/porous carbon for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 2021, 4, 1398–1412.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51407134 and 52002196), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Nos. ZR2019YQ24 and ZR2020QF084), the Taishan Scholars and Young Experts Program of Shandong Province (No. tsqn202103057), the Qingchuang Talents Induction Program of Shandong Higher Education Institution (Research and Innovation Team of Structural-Functional Polymer Composites), and the Special Financial of Shandong Province (Structural Design of High-efficiency Electromagnetic Wave-absorbing Composite Materials and Construction of Shandong Provincial Talent Teams (No. 37000022P990304116449)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2023_5687_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Macroscopic electromagnetic synergy network-enhanced N-doped Ni/C gigahertz microwave absorber with regulable microtopography
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Y., Zhu, Q., Zhu, J. et al. Macroscopic electromagnetic synergy network-enhanced N-doped Ni/C gigahertz microwave absorber with regulable microtopography. Nano Res. 16, 10666–10677 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5687-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5687-x