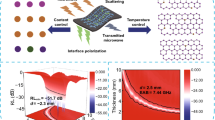
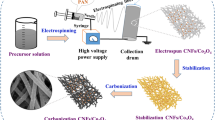
Abstract
Two-dimensional metal carbide or nitride materials (MXenes) are widely used in electromagnetic wave absorption because of their unique structure. Herein, a novel composite preparation strategy has been proposed to design dendritic nanofibers based on the electrostatic spinning methods. The multifunctional MXene nanosheets are used as the dendritic matrix, and magnetic nanoparticles are embedded in the nanosheets as magnetic loss units. Multidimensional nanocomposites have interlaced carbon fiber networks, large-scale magnetically coupled networks, and a lot of multi-heterojunction interface structures, which endow the composites with extraordinary conduction loss, magnetic loss, and polarization loss capabilities, respectively. The impedance matching and loss mechanisms of the composites are improved by optimizing the synergistic relationship between the components and building a suitable structure. The optimum reflection loss (RL) of −54.1 dB is achieved at 2.7 mm and a wide effective absorption bandwidth (EAB, RL below −10 dB) of 7.76 GHz is obtained at a small thickness of 2.1 mm for the nanocomposites. The distinctive microstructures of the nanofibrous membranes give rise to their flexibility, waterproof, and electromagnetic wave absorption performance and endow the nanofibrous membranes potential to be utilized as lightweight, efficient electromagnetic wave protective fabric in harsh environment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, J. Q.; Liu, L.; Jiao, S. L.; Ma, K. J.; Lv, J.; Yang, J. J. Hierarchical carbon fiber@MXene@MoS2 core—sheath synergistic microstructure for tunable and efficient microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002595.
Lv, H. L.; Yang, Z. H.; Wang, P. L.; Ji, G. B.; Song, J. Z.; Zheng, L. R.; Zeng, H. B.; Xu, Z. C. A voltage-boosting strategy enabling a low-frequency, flexible electromagnetic wave absorption device. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706343.
Zhao, Z. H.; Zhou, X. J.; Kou, K. C.; Wu, H. J. PVP-assisted transformation of ZIF-67 into cobalt layered double hydroxide/carbon fiber as electromagnetic wave absorber. Carbon 2021, 173, 80–90.
Stam, R.; Yamaguchi-Sekino, S. Occupational exposure to electromagnetic fields from medical sources. Ind. Health 2018, 56, 96–105.
Carpenter, D. O. Human disease resulting from exposure to electromagnetic fields. Rev. Environ. Health 2013, 28, 159–172.
Liu, L. X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H. B.; Wang, Q. W.; Guan, F. L.; Yu, Z. Z. Flexible and multifunctional silk textiles with biomimetic leaflike MXene/silver nanowire nanostructures for electromagnetic interference shielding, humidity monitoring, and self-derived hydrophobicity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1905197.
Wang, Z. X.; Jiao, B.; Qing, Y. C.; Nan, H. Y.; Huang, L. Q.; Wei, W.; Peng, Y.; Yuan, F.; Dong, H.; Hou, X. et al. Flexible and transparent ferroferric oxide-modified silver nanowire film for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 2826–2834.
Wang, W.; Li, W. Y.; Gao, C. C.; Tian, W. C.; Sun, B.; Yu, D. A novel preparation of silver-plated polyacrylonitrile fibers functionalized with antibacterial and electromagnetic shielding properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 342, 120–126.
Chen, H. C.; Lee, K. C.; Jin, J. H. Electromagnetic and electrostatic shielding properties of co-weaving-knitting fabrics reinforced composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 1249–1256.
Ma, M. L.; Liao, Z. J.; Su, X. W.; Zheng, Q. X.; Liu, Y. Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wan, F. Magnetic CoNi alloy particles embedded N-doped carbon fibers with polypyrrole for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 2203–2212.
Qian, J. J.; Du, B.; He, C.; Cai, M.; Zhong, X. R.; Xiong, H.; Zeng, S. H.; Shui, A. Z. Multiscale SiCnw and carbon fiber reinforced SiOC ceramic with enhanced mechanical and microwave absorption properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 105, 3456–3468.
Li, S. Z.; Ma, L.; Lei, Z. X.; Hua, A.; Zhang, A. Q.; Song, Y. H.; Liu, F. C.; Geng, D. Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, S. et al. Bifunctional two-dimensional nanocomposite for electromagnetic wave absorption and comprehensive anti-corrosion. Carbon 2022, 186, 520–529.
Ma, L.; Hamidinejad, M.; Zhao, B.; Liang, C. Y.; Park, C. B. Layered foam/film polymer nanocomposites with highly efficient EMI shielding properties and ultralow reflection. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 19.
Zhao, H. Q.; Jin, C. Q.; Lu, P.; Xiao, Z. M.; Cheng, Y. Anchoring well-dispersed magnetic nanoparticles on biomass-derived 2D porous carbon nanosheets for lightweight and efficient microwave absorption. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 154, 106773.
Huang, B.; Hu, H. L.; Lim, S.; Tang, X. Z.; Huang, X. Z.; Liu, Y.; Yue, J. L. Gradient FeNi-SiO2 films on SiC fiber for enhanced microwave absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 897, 163204.
Duan, N. M.; Shi, Z. Y.; Wang, Z. H.; Zou, B.; Zhang, C. P.; Wang, J. L.; Xi, J. R.; Zhang, X. S.; Zhang, X. Z.; Wang, G. L. Mechanically robust Ti3C2Tx MXene/carbon fiber fabric/thermoplastic polyurethane composite for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding applications. Mater. Des. 2022, 214, 110382.
Liu, L. X.; Guo, R.; Gao, J.; Ding, Q.; Fan, Y. C.; Yu, J. Y. Mechanically and environmentally robust composite nanofibers with embedded MXene for wearable shielding of electromagnetic wave. Compos. Commun. 2022, 30, 101094.
Wu, F.; Liu, Z. H.; Wang, J. Q.; Shah, T.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Zhang, B. L. Template-free self-assembly of MXene and CoNi-bimetal MOF into intertwined one-dimensional heterostructure and its microwave absorbing properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130591.
Zhao, H. Q.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, L. J.; Zhang, B. S.; Wang, L. P.; Ji, G. B.; Xu, Z. J. Biomass-derived porous carbon-based nanostructures for microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 24.
Wu, R. B.; Yang, Z. H.; Fu, M. S.; Zhou, K. In-situ growth of SiC nanowire arrays on carbon fibers and their microwave absorption properties. J. Alloys Compd 2016, 687, 833–838.
Zhang, K. L.; Zhang, J. Y.; Hou, Z. L.; Bi, S.; Zhao, Q. L. Multifunctional broadband microwave absorption of flexible graphene composites. Carbon 2019, 141, 608–617.
Xu, C.; Wu, F.; Duan, L. Q.; Xiong, Z. M.; Xia, Y. L.; Yang, Z. Q.; Sun, M. X.; Xie, A. M. Dual-interfacial polarization enhancement to design tunable microwave absorption nanofibers of SiC@C@PPy. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 1505–1513.
Zhao, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. G. 3D flower-like hollow CuS@PANI microspheres with superb X-band electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 126, 141–151.
Li, X.; Yu, L. M.; Zhao, W. K.; Shi, Y. Y.; Yu, L. J.; Dong, Y. B.; Zhu, Y. F.; Fu, Y. Q.; Liu, X. D.; Fu, F. Y. Prism-shaped hollow carbon decorated with polyaniline for microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122393.
Feng, J.; Zong, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Long, G. K.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. H.; Zheng, X. L. Optimization of porous FeNi3/N-GN composites with superior microwave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 441–451.
Luo, J. L.; Guo, H.; Zhou, J.; Guo, F.; Liu, G. G.; Hao, G. Z.; Jiang, W. Rational construction of heterogeneous interfaces for bimetallic MOFs-derived/rGO composites towards optimizing the electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132238.
Li, L.; Li, G. L.; Ouyang, W. J.; Zhang, Y. P.; Zeng, F. Z.; Liu, C. Y.; Lin, Z. Bimetallic MOFs derived FeM(II)-alloy@C composites with high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127609.
Xiong, Y.; Xu, L. L.; Yang, C. X.; Sun, Q. F.; Xu, X. J. Implanting FeCo/C nanocages with tunable electromagnetic parameters in anisotropic wood carbon aerogels for efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 18863–18871.
Jian, X.; Wu, B.; Wei, Y. F.; Dou, S. X.; Wang, X. L.; He, W. D.; Mahmood, N. Facile synthesis of Fe3O4/GCs composites and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6101–6109.
Jian, X.; Xiao, X. Y.; Deng, L. J.; Tian, W.; Wang, X.; Mahmood, N.; Dou, S. X. Heterostructured nanorings of Fe-Fe3O4@C hybrid with enhanced microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9369–9378.
Xue, W.; Yang, G.; Bi, S.; Zhang, J. Y.; Hou, Z. L. Construction of caterpillar-like hierarchically structured Co/MnO/CNTs derived from MnO2/ZIF-8@ZIF-67 for electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2021, 173, 521–527.
Hou, Z. L.; Du, K. R.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Bi, S.; Zhang, J. Y. Nanoarchitectonics of MnO2 nanotubes as sea urchin-like aggregates for dielectric response and microwave absorption with a wide concentration domain. Nano Res. 2022, in press, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5099-3.
Tang, M.; Zhang, J. Y.; Bi, S.; Hou, Z. L.; Shao, X. H.; Zhan, K. T.; Cao, M. S. Ultrathin topological insulator absorber: Unique dielectric behavior of Bi2Te3 nanosheets based on conducting surface states. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 33285–33291.
Wei, H. J.; Yin, X. W.; Hou, Z. X.; Jiang, F. R.; Xu, H. L.; Li, M. H.; Zhang, L. T.; Cheng, L. F. A novel SiC-based microwave absorption ceramic with Sc2Si2O7 as transparent matrix. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 4189–4197.
Wei, H. J.; Yin, X. W.; Jiang, F. R.; Hou, Z. X.; Cheng, L. F.; Zhang, L. T. Optimized design of high-temperature microwave absorption properties of CNTs/Sc2Si2O7 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 823, 153864.
Guo, Y.; Jian, X.; Zhang, L.; Mu, C. H.; Yin, L. J.; Xie, J. L.; Mahmood, N.; Dou, S. X.; Che, R. C.; Deng, L. J. Plasma-induced FeSiAl@Al2O3@SiO2 core—shell structure for exceptional microwave absorption and anti-oxidation at high temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123371.
Zhang, H. Y.; Cao, F.; Xu, H.; Tian, W.; Pan, Y.; Mahmood, N.; Jian, X. Plasma-enhanced interfacial engineering of FeSiAl@PUA@SiO2 hybrid for efficient microwave absorption and anti-corrosion. Nano Res. 2022, in press, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5100-1.
Tian, W.; Li, J. Y.; Liu, Y. F.; Ali, R.; Guo, Y.; Deng, L. J.; Mahmood, N., Jian, X. Atomic-scale layer-by-layer deposition of FeSiAl@ZnO@Al2O3 hybrid with threshold anti-corrosion and ultrahigh microwave absorption properties in low-frequency bands. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 161.
Yu, L. H.; Fan, Z. D.; Shao, Y. L.; Tian, Z. N.; Sun, J. Y.; Liu, Z. F. Versatile N-doped MXene ink for printed electrochemical energy storage application. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901839.
Zhang, Y. L.; Ruan, K. P.; Shi, X. T.; Qiu, H.; Pan, Y.; Yan, Y.; Gu, J. W. Ti3C2Tx/rGO porous composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding performances. Carbon 2021, 175, 271–280.
Naqvi, S. R.; Shukla, V.; Jena, N. K.; Luo, W.; Ahuja, R. Exploring two-dimensional M2NS2 (M = Ti, V) MXenes based gas sensors for air pollutants. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 19, 100574.
Brady, A.; Liang, K.; Vuong, V. Q.; Sacci, R.; Prenger, K.; Thompson, M.; Matsumoto, R.; Cummings, P.; Irle, S.; Wang, H. W. et al. Pre-sodiated Ti3C2Tx MXene structure and behavior as electrode for sodium-ion capacitors. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2994–3003.
Wu, Z. Y.; Li, C. R.; Li, Z.; Feng, K.; Cai, M. J.; Zhang, D. K.; Wang, S. H.; Chu, M. Y.; Zhang, C. C.; Shen, J. H. et al. Niobium and titanium carbides (MXenes) as superior photothermal supports for CO2 photocatalysis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5696–5705.
Yuan, W. Y.; Cheng, L. F.; An, Y. R.; Lv, S. L.; Wu, H.; Fan, X. L.; Zhang, Y. N.; Guo, X. H.; Tang, J. W. Laminated hybrid junction of sulfur-doped TiO2 and a carbon substrate derived from Ti3C2 MXenes: Toward highly visible light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700870.
Hou, T. Q.; Jia, Z. R.; Wang, B. B.; Li, H. B.; Liu, X. H.; Bi, L.; Wu, G. L. MXene-based accordion 2D hybrid structure with Co9S8/C/Ti3C2Tx as efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128875.
Deng, R. X.; Chen, B. B.; Li, H. G.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y.; Song, L. X. MXene/Co3O4 composite material: Stable synthesis and its enhanced broadband microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 488, 921–930.
Zhang, X.; Wang, H. H.; Hu, R.; Huang, C. Y.; Zhong, W. J.; Pan, L. M.; Feng, Y. B.; Qiu, T.; Zhang, C. F.; Yang, J. Novel solvothermal preparation and enhanced microwave absorption properties of Ti3C2Tx MXene modified by in situ coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 484, 383–391.
Wei, H. W.; Dong, J. D.; Fang, X. J.; Zheng, W. H.; Sun, Y. T.; Qian, Y.; Jiang, Z. X.; Huang, Y. D. Ti3C2Tx MXene/polyaniline (PANI) sandwich intercalation structure composites constructed for microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 169, 52–59.
Xu, G. F.; Wang, X. X.; Gong, S. D.; Wei, S.; Liu, J. Q.; Xu, Y. H. Solvent-regulated preparation of well-intercalated Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets and application for highly effective electromagnetic wave absorption. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 355201.
Wang, S. J.; Li, D. S.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L. Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx MXene/Ni chain/ZnO array hybrid nanostructures on cotton fabric for durable self-cleaning and enhanced microwave absorption. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8634–8645.
Zhou, C. L.; Wang, X. X.; Luo, H.; Deng, L. W.; Wei, S.; Zheng, Y. W.; Jia, Q.; Liu, J. Q. Rapid and direct growth of bipyramid TiO2 from Ti3C2Tx MXene to prepare Ni/TiO2/C heterogeneous composites for high-performance microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123095.
Li, Y.; Meng, F. B.; Mei, Y.; Wang, H. G.; Guo, Y. F.; Wang, Y.; Peng, F. X.; Huang, F.; Zhou, Z. W. Electrospun generation of Ti3C2Tx MXene@graphene oxide hybrid aerogel microspheres for tunable high-performance microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123512.
Wang, F. Y.; Sun, Y. Q.; Li, D. R.; Zhong, B.; Wu, Z. G.; Zuo, S. Y.; Yan, D.; Zhuo, R. F.; Feng, J. J.; Yan, P. X. Microwave absorption properties of 3D cross-linked Fe/C porous nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Carbon 2018, 134, 264–273.
Jiang, Y. L.; Fu, X. Y.; Zhang, Z. D.; Du, W.; Xie, P. T.; Cheng, C. B.; Fan, R. H. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of Fe3C/C nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 804, 305–313.
Hou, C. L.; Jiao, T. F.; Xing, R. R.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J. X.; Zhang, L. X. Preparation of TiO2 nanoparticles modified electrospun nanocomposite membranes toward efficient dye degradation for wastewater treatment. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 118–126.
Jin, C.; Wu, Z. C.; Yang, C. D.; Wang, L. Y.; Zhang, R. X.; Xu, H. L.; Che, R. C. Impedance amelioration of coaxial-electrospun TiO2@Fe/C@TiO2 vesicular carbon microtubes with dielectric-magnetic synergy toward highly efficient microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133640.
Zhi, D. D.; Li, T.; Qi, Z. H.; Li, J. Z.; Tian, Y. R.; Deng, W. T.; Meng, F. B. Core—shell heterogeneous graphene-based aerogel microspheres for high-performance broadband microwave absorption via resonance loss and sequential attenuation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 134496.
Xie, P. T.; Li, Y. F.; Hou, Q.; Sui, K. Y.; Liu, C. Z.; Fu, X. Y.; Zhang, J. X.; Murugadoss, V.; Fan, J. C.; Wang, Y. P. et al. Tunneling-induced negative permittivity in Ni/MnO nanocomposites by a bio-gel derived strategy. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 3029–3039.
Zhou, C. L.; Wang, X. X.; Luo, H.; Deng, L. W.; Wang, S. L.; Wei, S.; Zheng, Y. W.; Jia, Q.; Liu, J. Q. Interfacial design of sandwichlike CoFe@Ti3C2Tx composites as high efficient microwave absorption materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 494, 540–550.
Li, X.; You, W. B.; Xu, C. Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, L. T.; Li, Y. S.; Che, R. C. 3D seed-germination-like MXene with in situ growing CNTs/Ni heterojunction for enhanced microwave absorption via polarization and magnetization. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 157.
Wang, H. C.; Xiang, L.; Wei, W.; An, J.; He, J.; Gong, C. H.; Hou, Y. L. Efficient and lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber derived from metal organic framework-encapsulated cobalt nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 42102–42110.
Wang, Z. Y.; Sun, K.; Xie, P. T.; Hou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Q. L.; Fan, R. H. Design and analysis of negative permittivity behaviors in barium titanate/nickel metacomposites. Acta Mater. 2020, 185, 412–419.
Wang, Z. Y.; Sun, K.; Xie, P. T.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Q. L.; Fan, R. H. Permittivity transition from positive to negative in acrylic polyurethane-aluminum composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 188, 107969.
Dai, X. Y.; Du, Y. Z.; Yang, J. Y.; Wang, D.; Gu, J. W.; Li, Y. F.; Wang, S.; Xu, B. B.; Kong, J. Recoverable and self-healing electromagnetic wave absorbing nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 174, 27–32.
Zhong, B.; Wang, C. J.; Yu, Y. L.; Xia, L.; Wen, G. W. Facile fabrication of carbon microspheres decorated with B(OH)3 and α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: Superior microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 402–409.
Feng, J.; Pu, F. Z.; Li, Z. X.; Li, X. H.; Hu, X. Y.; Bai, J. T. Interfacial interactions and synergistic effect of CoNi nanocrystals and nitrogen-doped graphene in a composite microwave absorber. Carbon 2016, 104, 214–225.
Zhang, H. X.; Jia, Z. R.; Wang, B. B.; Wu, X. M.; Sun, T.; Liu, X. H.; Bi, L.; Wu, G. L. Construction of remarkable electromagnetic wave absorber from heterogeneous structure of Co-CoFe2O4@mesoporous hollow carbon spheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129960.
Cheng, Y.; Zhao, H. Q.; Lv, H. L.; Shi, T. F.; Ji, G. B.; Hou, Y. L. Lightweight and flexible cotton aerogel composites for electromagnetic absorption and shielding applications. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 1900796.
Ding, J. J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y. H.; Xing, L. S.; Yu, X. F.; Chen, G. Y.; Zhang, J.; Che, R. C. Boosted interfacial polarization from multishell TiO2@Fe3O4@PPy heterojunction for enhanced microwave absorption. Small 2019, 15, 1902885.
Xiang, Z.; Shi, Y. Y.; Zhu, X. J.; Cai, L.; Lu, W. Flexible and waterproof 2D/1D/0D construction of MXene-based nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave absorption, EMI shielding, and photothermal conversion. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 150.
Cao, M. S.; Han, C.; Wang, X. X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y. L.; Shu, J. C.; Yang, H. J.; Fang, X. Y.; Yuan, J. Graphene nanohybrids: Excellent electromagnetic properties for the absorbing and shielding of electromagnetic waves. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4586–4602.
He, P.; Cao, M. S.; Cao, W. Q.; Yuan, J. Developing MXenes from wireless communication to electromagnetic attenuation. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 115.
Zhao, Y. P.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Huang, H.; Zhao, G. L.; Cong, T. Z.; Zuo, X. Q.; Fan, Z.; Yang, S. T.; Pan, L. J. In situ construction of hierarchical core—shell Fe3O4@C nanoparticles—helical carbon nanocoil hybrid composites for highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2021, 171, 395–408.
Song, Q.; Ye, F.; Kong, L.; Shen, Q. L.; Han, L. Y.; Feng, L.; Yu, G. J.; Pan, Y. A. N.; Li, H. J. Graphene and MXene nanomaterials: Toward high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption in gigahertz band range. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000475.
Wang, G. Z.; Gao, Z.; Wan, G. P.; Lin, S. W.; Yang, P.; Qin, Y. High densities of magnetic nanoparticles supported on graphene fabricated by atomic layer deposition and their use as efficient synergistic microwave absorbers. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 704–716.
Yan, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, C. Y.; Zhu, C. L.; Zhang, X. T.; Chen, Y. J. Growth of CoFe2O4 hollow nanoparticles on graphene sheets for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 12781–12787.
Tao, J. Q.; Zhou, J. T.; Yao, Z. J.; Jiao, Z. B.; Wei, B.; Tan, R. Y.; Li, Z. Multi-shell hollow porous carbon nanoparticles with excellent microwave absorption properties. Carbon 2021, 172, 542–555.
Lv, H. L.; Yang, Z. H.; Pan, H. G.; Wu, R. B. Electromagnetic absorption materials: Current progress and new frontiers. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 127, 100946.
Qiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D. M.; Kong, L. X.; Lv, L. F.; Yang, F.; Wang, F. L.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. R. Design and synthesis of TiO2/Co/carbon nanofibers with tunable and efficient electromagnetic absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122591.
Liu, L. L.; Zhang, S.; Yan, F.; Li, C. Y.; Zhu, C. L.; Zhang, X. T.; Chen, Y. J. Three-dimensional hierarchical MoS2 nanosheets/ultralong N-doped carbon nanotubes as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14108–14115.
Wang, J. W.; Wang, B. B.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Gao, C. H.; Xu, B. H.; Jia, Z. R.; Wu, G. L. Synthesis of 3D flower-like ZnO/ZnCo2O4 composites with the heterogeneous interface for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 586, 479–490.
Zhang, D. Q.; Zhang, H. B.; Cheng, J. Y.; Raza, H.; Liu, T. T.; Liu, B.; Ba, X. W.; Zheng, G. P.; Chen, G. H.; Cao, M. S. Customizing coaxial stacking VS2 nanosheets for dual-band microwave absorption with superior performance in the C- and Ku-bands. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 8, 5923–5933.
Gao, Z. G.; Jia, Z. R.; Wang, K. K.; Liu, X. H.; Bi, L.; Wu, G. L. Simultaneous enhancement of recoverable energy density and efficiency of lead-free relaxor-ferroelectric BNT-based ceramics. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 125951.
Li, Q. Q.; Zhao, Y. H.; Li, X. H.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Che, R. C. MOF induces 2D GO to assemble into 3D accordion-like composites for tunable and optimized microwave absorption performance. Small 2020, 16, 2003905.
Hou, T. Q.; Jia, Z. R.; Wang, B. B.; Li, H. B.; Liu, X. H.; Chi, Q. G.; Wu, G. L. Metal-organic framework-derived NiSe2-CoSe2@C/Ti3C2Txcomposites as electromagnetic wave absorbers. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130079.
Yue, Y.; Wang, Y. X.; Xu, X. D.; Cui, B. W.; Yao, Z. Q.; Wang, Y. X.; Wang, C. J.; Wang, Y. P.; Wang, Y. B. Continuous growth of carbon nanotubes on the surface of carbon fibers for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 1869–1878.
Wang, J.; Lin, X. Y.; Zhang, R. X.; Chu, Z. Y.; Huang, Z. Y. Transition metal dichalcogenides MX2 (M = Mo, W; X = S, Se, Te) and MX2-CIP composites: Promising materials with high microwave absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 743, 26–35.
Zhao, B.; Deng, J. S.; Liang, L. Y.; Zuo, C. Y. X.; Bai, Z. Y.; Guo, X. Q.; Zhang, R. Lightweight porous Co3O4 and Co/CoO nanofibers with tunable impedance match and configuration-dependent microwave absorption properties. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 6095–6106.
Zhang, X. C.; Liu, M. J.; Xu, J.; Ouyang, Q. Y.; Zhu, C. L.; Zhang, X. L.; Zhang, X. T.; Chen, Y. J. Flexible and waterproof nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays on cotton-derived carbon fiber for electromagnetic wave absorption and electric-thermal conversion. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133794.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2019YQ24), Taishan Scholars and Young Experts Program of Shandong Province (No. tsqn202103057), and the Qingchuang Talents Induction Program of Shandong Higher Education Institution (Research and Innovation Team of Structural-Functional Polymer Composites).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2022_5368_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Electrospun Fe0.64Ni0.36/MXene/CNFs nanofibrous membranes with multicomponent heterostructures as flexible electromagnetic wave absorbers
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Jia, Z., Zhang, Y. et al. Electrospun Fe0.64Ni0.36/MXene/CNFs nanofibrous membranes with multicomponent heterostructures as flexible electromagnetic wave absorbers. Nano Res. 16, 3395–3407 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5368-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5368-1