Abstract
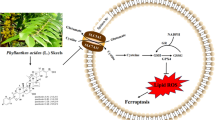
Mitochondrial bioenergy plays a vital role in the occurrence and development of cancer. Although strategies to impede mitochondrial energy supply have been rapidly developed, the anticancer efficacy is still far from satisfactory, mainly attributed to the hybrid metabolic pathways of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) and glycolysis. Herein, we construct a cancer cell membrane camouflaged nano-inhibitor, mTPPa-Sy nanoparticle (NP), which co-encapsulates OXPHOS inhibitor (mitochondrial-targeting photosensitizers: TPPa) and glycolysis inhibitor (syrosingopine (Sy)) for synergistically blocking the two different energy pathways. The mTPPa-Sy NPs exhibit precision tumor-targeting due to the high affinity between the biomimic membrane and the homotypic cancer cells. Under laser irradiation, the mitochondrial-targeting TPPa, which is synthesized by conjugating pyropheophorbide a (PPa) with triphenylphosphin, produces excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) and further disrupts the OXPHOS. Interestingly, OXPHOS inhibition reduces O2 consumption and improves ROS production, further constructing a closed-loop OXPHOS inhibition system. Moreover, TPPa-initiated OXPHOS inhibition in combination with the Sy-triggered glycolysis inhibition results in lethal energy depletion, significantly suppressing tumor growth even after a single treatment. Our findings highlight the necessity and effectiveness of synergetic lethal energy depletion, providing a prospective strategy for efficient cancer therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heiden, M. G. V. Targeting cancer metabolism: A therapeutic window opens. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 671–684.
Rodríguez-Enríquez, S.; Marín-Hernández, A.; Gallardo-Pérez, J. C.; Carreño-Fuentes, L.; Moreno-Sánchez, R. Targeting of cancer energy metabolism. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 29–48.
Weinberg, S. E.; Chandel, N. S. Targeting mitochondria metabolism for cancer therapy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 9–15.
Park, J. H.; Vithayathil, S.; Kumar, S.; Sung, P. L.; Dobrolecki, L. E.; Putluri, V.; Bhat, V. B.; Bhowmik, S. K.; Gupta, V.; Arora, K. et al. Fatty acid oxidation-driven src links mitochondrial energy reprogramming and oncogenic properties in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 2154–2165.
Wan, S. S.; Liu, M. D.; Cheng, Q.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, X. Z. A mitochondria-driven metabolic sensing nanosystem for oxygen availability and energy blockade of cancer. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 2000019.
Zhu, Y. X.; Jia, H. R.; Gao, G.; Pan, G. Y.; Jiang, Y. W.; Li, P. L.; Zhou, N. X.; Li, C. C.; She, C.; Ulrich, N. W. et al. Mitochondria-acting nanomicelles for destruction of cancer cells via excessive mitophagy/autophagy-driven lethal energy depletion and phototherapy. Biomaterials. 2020, 232, 119668.
Luo, X. J.; Gong, X. Q.; Su, L. Y.; Lin, H. Y.; Yang, Z. X.; Yan, X. M.; Gao, J. H. Activatable mitochondria-targeting organoarsenic prodrugs for bioenergetic cancer therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 1403–1410.
Jia, D. Y.; Park, J. H.; Jung, K. H.; Levine, H.; Kaipparettu, B. A. Elucidating the metabolic plasticity of cancer: Mitochondrial reprogramming and hybrid metabolic states. Cells 2018, 7, 21.
Zacksenhaus, E.; Shrestha, M.; Liu, J. C.; Vorobieva, I.; Chung, P. E. D.; Ju, Y.; Nir, U.; Jiang, Z. Mitochondrial OXPHOS induced by RB1 deficiency in breast cancer: Implications for anabolic metabolism, stemness, and metastasis. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 768–779.
Ashworth, A.; Lord, C. J. Synthetic lethal therapies for cancer: What’s next after PARP inhibitors? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 564–576.
Huo, D.; Zhu, J. F.; Chen, G. J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, C.; Luo, X. Y.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X. Q.; Gu, Z.; Hu, Y. Eradication of unresectable liver metastasis through induction of tumour specific energy depletion. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3051.
Allison, R. R.; Moghissi, K. Photodynamic therapy (PDT): PDT mechanisms. Clin. Endosc. 2013, 46, 24–29.
Zhao, D. Y.; Tao, W. H.; Li, S. H.; Li, L. X.; Sun, Y. X.; Li, G. T.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Lin, B.; Luo, C. et al. Light-triggered dualmodality drug release of self-assembled prodrug-nanoparticles for synergistic photodynamic and hypoxia-activated therapy. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 886–894.
Wang, M. L.; Zhai, Y. L.; Ye, H.; Lv, Q. Z.; Sun, B. J.; Luo, C.; Jiang, Q. K.; Zhang, H. T.; Xu, Y. J.; Jing, Y. K. et al. High co-loading capacity and stimuli-responsive release based on cascade reaction of self-destructive polymer for improved chemophotodynamic therapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 7010–7023.
Luo, C.; Sun, B. J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhao, H. Q.; Sun, M. C.; Li, Z. B. et al. Self-facilitated ROS-responsive nanoassembly of heterotypic dimer for synergistic chemophotodynamic therapy. J. Control Release 2019, 302, 79–89.
Cheng, H.; Fan, J. H.; Zhao, L. P.; Fan, G. L.; Zheng, R. R.; Qiu, X. Z.; Yu, X. Y.; Li, S. Y.; Zhang, X. Z. Chimeric peptide engineered exosomes for dual-stage light guided plasma membrane and nucleus targeted photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 2019, 211, 14–24.
Huang, H. Y.; Yu, B. L.; Zhang, P. Y.; Huang, J. J.; Chen, Y.; Gasser, G.; Ji, L. N.; Chao, H. Highly charged ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes as lysosome-localized photosensitizers for two-photon photodynamic therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14049–14052.
Lv, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K. Y.; Yang, H. R.; Liu, S. J.; Xu, A. Q.; Guo, S.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, W. A mitochondria-targeted photosensitizer showing improved photodynamic therapy effects under hypoxia. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9947–9951.
Klosowski, E. M.; de Souza, B. T. L.; Mito, M. S.; Constantin, R. P.; Mantovanelli, G. C.; Mewes, J. M.; Bizerra, P. F. V.; da Costa Menezes, P. V. M.; Gilglioni, E. H.; Utsunomiya, K. S. et al. The photodynamic and direct actions of methylene blue on mitochondrial energy metabolism: A balance of the useful and harmful effects of this photosensitizer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 153, 34–53.
Benjamin, D.; Colombi, M.; Hindupur, S. K.; Betz, C.; Lane, H. A.; El-Shemerly, M. Y. M.; Lu, M.; Quagliata, L.; Terracciano, L.; Moes, S. et al. Syrosingopine sensitizes cancer cells to killing by metformin. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601756.
Xu, Y. Y.; Guo, Y. D; Chen, L.; Ni, D. L.; Hu, P.; Shi, J. L. Tumor chemical suffocation therapy by dual respiratory inhibitions. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 7763–7769.
Ashton, T. M.; McKenna, W. G.; Kunz-Schughart, L. A.; Higgins, G. S. Oxidative phosphorylation as an emerging target in cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2482–2490.
Benjamin, D.; Robay, D.; Hindupur, S. K.; Pohlmann, J.; Colombi, M.; El-Shemerly, M. Y.; Maira, S. M.; Moroni, C.; Lane, H. A.; Hall, M. N. Dual inhibition of the lactate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 is synthetic lethal with metformin due to NAD+ depletion in cancer cells. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 3047–3058.e4.
Zhang, J.; Shen, L. M.; Li, X.; Song, W. T.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L. Nanoformulated codelivery of quercetin and alantolactone promotes an antitumor response through synergistic immunogenic cell death for microsatellite-stable colorectal cancer. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 12511–12524.
Ye, H.; Wang, K. Y.; Wang, M. L.; Liu, R. Z.; Song, H.; Li, N.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, W. J.; Du, Y. Q.; Yang, W. Q. et al. Bioinspired nanoplatelets for chemo-photothermal therapy of breast cancer metastasis inhibition. Biomaterials 2019, 206, 1–12.
Li, S. Y.; Cheng, H.; Xie, B. R.; Qiu, W. X.; Zeng, J. Y.; Li, C. X.; Wan, S. S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W. L.; Zhang, X. Z. Cancer cell membrane camouflaged cascade bioreactor for cancer targeted starvation and photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7006–7018.
Gao, F.; Tang, Y.; Liu, W. L.; Zou, M. Z.; Huang, C.; Liu, C. J.; Zhang, X. Z. Intra/extracellular lactic acid exhaustion for synergistic metabolic therapy and immunotherapy of tumors. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904639.
Thakur, A.; Qiu, G.; Xu, C.; Han, X.; Yang, T.; Ng, S. P.; Chan, K. W. Y.; Wu, C. M. L.; Lee, Y. Label-free sensing of exosomal MCT1 and CD147 for tracking metabolic reprogramming and malignant progression in glioma. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz6119.
Miranda-Gonçalves, V.; Granja, S.; Martinho, O.; Honavar, M.; Pojo, M.; Costa, B. M.; Pires, M. M.; Pinheiro, C.; Cordeiro, M.; Bebiano, G. et al. Hypoxia-mediated upregulation of MCT1 expression supports the glycolytic phenotype of glioblastomas. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46335–46353.
Morais-Santos, F.; Granja, S.; Miranda-Gonçalves, V.; Moreira, A. H. J.; Queirós, S.; Vilaça, J. L.; Schmitt, F. C.; Longatto-Filho, A.; Paredes, J.; Baltazar, F. et al. Targeting lactate transport suppresses in vivo breast tumour growth. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 19177–19189.
Yu, Z.; Guo, J. F.; Hu, M. Y.; Gao, Y. Q.; Huang, L. Icaritin exacerbates mitophagy and synergizes with doxorubicin to induce immunogenic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 4816–4828.
Huang, B. X.; Tian, J.; Jiang, D. W.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W. A. Niractivated “off/on” photodynamic therapy by a hybrid nanoplatform with upper critical solution temperature block copolymers and gold nanorods. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 3873–3883.
Zuo, S. Y.; Sun, B. J.; Yang, Y. X.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, M. R.; Sun, M. C.; Luo, C.; He, Z. G.; Sun, J. Probing the superiority of diselenium bond on docetaxel dimeric prodrug nanoassemblies: Small roles taking big responsibilities. Small 2020, 16, 2005039.
Yang, Y. X.; Sun, B. J.; Zuo, S. Y.; Li, X. M.; Zhou, S.; Li, L. X.; Luo, C.; Liu, H. Z.; Cheng, M. S.; Wang, Y. J. et al. Trisulfide bondmediated doxorubicin dimeric prodrug nanoassemblies with high drug loading, high self-assembly stability, and high tumor selectivity. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc1725.
Sun, Q. H.; Zhou, Z. X.; Qiu, N. S.; Shen, Y. Q. Rational design of cancer nanomedicine: Nanoproperty integration and synchronization. Adv. Mater. 2011, 29, 1606628.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81773656), Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (No. XLYC1808017), Shenyang Youth Science and Technology Innovation Talents Program (No. RC190454), and National Postdoctoral Foundation of China (No. 2021M693868).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, F., Jiang, Q., Li, L. et al. Synergetic lethal energy depletion initiated by cancer cell membrane camouflaged nano-inhibitor for cancer therapy. Nano Res. 15, 3422–3433 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3948-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3948-0