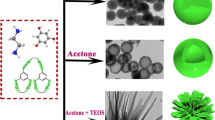
Abstract
Confined nanospace pyrolysis (CNP) has attracted increasing attention as a general strategy to prepare task-specific hollow structured porous carbons (HSPCs) in the past decade. The unique advantages of the CNP strategy include its outstanding ability in control of the monodispersity, porosity and internal cavity of HSPCs. As a consequence, the obtained HSPCs perform exceptionally well in applications where a high dispersibility and tailored cavity are particularly required, such as drug delivery, energy storage, catalysis and so on. In this review, the fundamentals of the CNP strategy and its advances in structural alternation is first summarized, then typical applications are discussed by exemplifying specific synthesis examples. In addition, this review offers insights into future developments for advanced task-specific hollow structured porous materials prepared by the CNP strategy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bin, D. S.; Li, Y. M.; Sun, Y. G.; Duan, S. Y.; Lu, Y. X.; Ma, J. M.; Cao, A. M.; Hu, Y. S.; Wan, L. J. Structural engineering of multishelled hollow carbon nanostructures for high-performance Na-ion battery anode. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800855.
Liu, J.; Kopold, P.; Wu, C.; Van Aken, P. A.; Maier, J.; Yu, Y. Uniform yolk-shell Sn4P3@C nanospheres as high-capacity and cycle-stable anode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3531–3538.
Pei, F.; Lin, L. L.; Fu, A.; Mo, S. G.; Ou, D. H.; Fang, X. L.; Zheng, N. F. A two-dimensional porous carbon-modified separator for high-energy-density Li-S batteries. Joule 2018, 2, 323–336.
Chen, C. H.; Wang, H. Y.; Han, C. L; Deng, J.; Wang, J.; Li, M. M.; Tang, M. H.; Jin, H. Y.; Wang, Y. Asymmetric flasklike hollow carbonaceous nanoparticles fabricated by the synergistic interaction between soft template and biomass. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2657–2663.
Zhang, H. B.; Liu, Y. Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, J. T.; Zhang, J.; Lou, X. W. D. Unveiling the activity origin of electrocatalytic oxygen evolution over isolated Ni atoms supported on a N-doped carbon matrix. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904548.
Kim, S. Y.; Jeong, H. M.; Kwon, J. H.; Ock, I. W.; Suh, W. H.; Stucky, G. D.; Kang, J. K. Nickel oxide encapsulated nitrogen-rich carbon hollow spheres with multiporosity for high-performance pseudocapacitors having extremely robust cycle life. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 188–194.
Chen, W. H.; Qiao, R.; Song, C. S.; Zhao, L. H.; Jiang, Z. J.; Maiyalagan, T.; Jiang, Z. Q. Tailoring the thickness of MoSe2 layer of the hierarchical double-shelled N-doped carbon@MoSe2 hollow nanoboxes for efficient and stable hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Catal. 2020, 381, 363–373.
Zhao, R. H.; Wang, H.; Gao, N.; Liu, R.; Guo, T. Y.; Wu, J. T.; Zhang, T.; Li, J. P.; Du, J. P.; Asefa, T. Hollow hemispherical carbon microspheres with Mo2C nanoparticles synthesized by precursor design: Effective noble metal-free catalysts for dehydrogenation. Small Methods 2020, 4, 1900597.
Yang, H.; Bradley, S. J.; Chan, A.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Nann, T.; Kruger, P. E.; Telfer, S. G. Catalytically active bimetallic nanoparticles supported on porous carbon capsules derived from metal-organic framework composites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11872–11881.
Liu, D. H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L. H.; Li, W. C.; Sun, T.; Lu, A. H. Switchable transport strategy to deposit active Fe/Fe3C cores into hollow microporous carbons for efficient chromium removal. Small 2013, 9, 3852–3857.
Chen, Y.; Xu, P. F.; Wu, M. Y.; Meng, Q. S.; Chen, H. R.; Shu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. X.; Li, Y. P.; Shi, J. L. Colloidal RBC-shaped, hydrophilic, and hollow mesoporous carbon nanocapsules for highly efficient biomedical engineering. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4294–4301.
Zhang, J. F.; Zhang, J.; Li, W. Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z. Y.; Zhang, W. J.; Tang, Y. B.; Chen, X. Y.; Liu, G.; Lee, C. S. Degradable hollow mesoporous silicon/carbon nanoparticles for photoacoustic imagingguided highly effective chemo-thermal tumor therapy in vitro and in vivo. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3007–3020.
Hofer, C. J.; Grass, R. N.; Zeltner, M.; Mora, C. A.; Krumeich, F.; Stark, W. J. Hollow carbon nanobubbles: Synthesis, chemical functionalization, and container-type behavior in water. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8761–8765.
Chen, Y.; Chen, H. R.; Zeng, D. P.; Tian, Y. B.; Chen, F.; Feng, J. W.; Shi, J. L. Core/shell structured hollow mesoporous nanocapsules: A potential platform for simultaneous cell imaging and anticancer drug delivery. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6001–6013.
Zhang, S. J.; Qian, X. Q.; Zhang, L. L.; Peng, W. J.; Chen, Y. Composition-property relationships in multifunctional hollow mesoporous carbon nanosystems for pH-responsive magnetic resonance imaging and on-demand drug release. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7632–7643.
Lu, A. H.; Sun, T.; Li, W. C.; Sun, Q.; Han, F.; Liu, D. H.; Guo, Y. Synthesis of discrete and dispersible hollow carbon nanospheres with high uniformity by using confined nanospace pyrolysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11765–11768.
Liu, J.; Qiao, S. Z.; Chen, J. S.; Lou, X. W. D.; Xing, X. R.; Lu, G. Q. Yolk/shell nanoparticles: New platforms for nanoreactors, drug delivery and lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12578–12591.
Liu, T.; Zhang, L. Y.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J. G. Hollow carbon spheres and their hybrid nanomaterials in electrochemical energy storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803900.
Tian, H.; Liang, J.; Liu, J. Nanoengineering carbon spheres as nanoreactors for sustainable energy applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1903886.
Fu, A.; Wang, C. Z.; Pei, F.; Cui, J. Q.; Fang, X. L; Zheng, N. F. Recent advances in hollow porous carbon materials for Lithium-Sulfur batteries. Small 2019, 15, 1804786.
Prieto, G.; Tüysüz, H.; Duyckaerts, N.; Knossalla, J.; Wang, G. H.; Schüth, F. Hollow nano-and microstructures as catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14056–14119.
Qiao, Z. A.; Guo, B. K.; Binder, A. J.; Chen, J. H.; Veith, G. M.; Dai, S. Controlled synthesis of mesoporous carbon nanostructures via a “silica-assisted” strategy. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 207–212.
Fuertes, A. B.; Valle-Vigón, P.; Sevilla, M. One-step synthesis of silica@resorcinol-formaldehyde spheres and their application for the fabrication of polymer and carbon capsules. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 6124–6126.
Fang, X. L.; Zang, J.; Wang, X. L.; Zheng, M. S.; Zheng, N. F. A multiple coating route to hollow carbon spheres with foam-like shells and their applications in supercapacitor and confined catalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 6191–6197.
Lu, A. H.; Zhang, X. Q.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Q. W.; Schüth, F.; Chen, C. Y.; Cheng, F. Precise synthesis of discrete and dispersible carbon-protected magnetic nanoparticles for efficient magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1460–1469.
Wang, Q. G.; He, L.; Zhao, L. Y.; Liu, R. S.; Zhang, W. P.; Lu, A. H. Surface charge-driven nanoengineering of monodisperse carbon nanospheres with tunable surface roughness. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1906117.
Sun, Q.; Li, W. C.; Lu, A. H. Insight into structure-dependent self-activation mechanism in a confined nanospace of core-shell nanocomposites. Small 2013, 9, 2086–2090.
Yang, T. Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, R. F.; Chen, Z. G.; Xu, H. Y.; Qiao, S. Z. Monteiro, M. J. N-doped mesoporous carbon spheres as the oxygen reduction reaction catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18139–18146.
Du, J.; Yu, Y. F.; Liu, L.; Lv, H. J.; Chen, A. B.; Hou, S. L. Confined-space pyrolysis of polystyrene/polyacrylonitrile for Nitrogen-Doped hollow mesoporous carbon spheres with high supercapacitor performance. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 4402–4410.
Du, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y. F.; Hu, Z. P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B. B.; Chen, A. B. Tuning confined nanospace for preparation of N-doped hollow carbon spheres for high performance supercapacitors. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 303–309.
Du, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, B. B.; Yu, Y. F.; Lv, H. J.; Chen, A. B. Encapsulation pyrolysis synchronous deposition for hollow carbon sphere with tunable textural properties. Carbon 2019, 143, 467–474.
Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L. L.; Li, K. Q.; Yi, Y. K.; Song, S. Y.; Li, M. T.; Qiao, Z. A.; Dai, S. Space-confined polymerization: Controlled fabrication of nitrogen-doped polymer and carbon microspheres with refined hierarchical architectures. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807876.
Zhang, L. H.; He, B.; Li, W. C.; Lu, A. H. Surface free energy-induced assembly to the synthesis of grid-like multicavity carbon spheres with high level in-cavity encapsulation for lithium-sulfur cathode. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1701518.
Yu, X. F.; Li, W. C.; Hu, Y. R.; Ye, C. Y.; Lu, A. H. Sculpturing solid polymer spheres into internal gridded hollow carbon spheres under controlled pyrolysis micro-environment. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 1565–1573.
Yang, T. Y.; Zhou, R. F.; Wang, D. W.; Jiang, S. P.; Yamauchi, Y.; Qiao, S. Z.; Monteiro, M. J.; Liu, J. Hierarchical mesoporous yolk-shell structured carbonaceous nanospheres for high performance electrochemical capacitive energy storage. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2518–2521.
Yang, T. Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Monteiro, M. J.; Qiao, S. Z. Facile Fabrication of core-shell-structured Ag@carbon and mesoporous yolk-shell-structured Ag@carbon@silica by an extended stöber method. Chem. -Eur. J. 2013, 19, 6942–6945.
Sun, Q.; He, B.; Zhang, X. Q.; Lu, A. H. Engineering of hollow core-shell interlinked carbon spheres for highly stable lithium-sulfur batteries. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 8504–8513.
Du, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y. F.; Lv, H. J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, A. B. Confined pyrolysis for direct conversion of solid resin spheres into yolk-shell carbon spheres for supercapacitor. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 1038–1044.
Du, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y. F.; Qin, Y. M.; Wu, H. X.; Chen, A. B. A confined space pyrolysis strategy for controlling the structure of hollow mesoporous carbon spheres with high supercapacitor performance. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4453–4462.
Zhang, X. H.; Li, Y. A.; Cao, C. B. Facile one-pot synthesis of mesoporous hierarchically structured silica/carbon nanomaterials. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13918–13921.
Zhang, H. H.; He, H. N.; Luan, J. Y.; Huang, X. B.; Tang, Y. G.; Wang, H. Y. Adjusting the yolk-shell structure of carbon spheres to boost the capacitive K+ storage ability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 23318–23325.
Yu, X. Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y. W.; Chen, H. Y.; Lou, X. W. Ultrathin MoS2 nanosheets supported on N-doped carbon nanoboxes with enhanced lithium storage and electrocatalytic properties. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7395–7398.
He, J. R.; Luo, L.; Chen, Y. F.; Manthiram, A. Yolk-shelled C@Fe3O4 nanoboxes as efficient sulfur hosts for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702707.
Yang, F. H.; Gao, H.; Hao, J. N.; Zhang, S. L.; Li, P.; Liu, Y. Q.; Chen, J.; Guo, Z. P. Yolk-shell structured FeP@C nanoboxes as advanced anode materials for rechargeable lithium-/potassium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808291.
Liu, Y.; Kou, W.; Li, X. C.; Huang, C. Q.; Shui, R. B.; He, G. H. Constructing patch-Ni-shelled Pt@Ni nanoparticles within confined nanoreactors for catalytic oxidation of insoluble polysulfides in Li-S batteries. Small 2019, 15, 1902431.
Zhang, H. W.; Noonan, O.; Huang, X. D.; Yang, Y. N.; Xu, C.; Zhou, L.; Yu, C. Z. Surfactant-free assembly of mesoporous carbon hollow spheres with large tunable pore sizes. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4579–4586.
Zang, J.; An, T. H.; Dong, Y. J.; Fang, X. L.; Zheng, M. S.; Dong, Q. F.; Zheng, N. F. Hollow-in-hollow carbon spheres with hollow foam-like cores for lithium-sulfur batteries. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 2663–2675.
Ye, J. C.; Zang, J.; Tian, Z. W.; Zheng, M. S.; Dong, Q. F. Sulfur and nitrogen co-doped hollow carbon spheres for sodium-ion batteries with superior cyclic and rate performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13223–13227.
Du, J.; Liu, L.; Hu, Z. P.; Yu, Y. F.; Qin, Y. M.; Chen, A. B. Order Mesoporous carbon spheres with precise tunable large pore size by encapsulated self-activation strategy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802332.
Zhang, X. Q.; Lu, A. H.; Sun, Q.; Yu, X. F.; Chen, J. Y.; Li, W. C. Unconventional synthesis of large pore ordered mesoporous carbon nanospheres for ionic liquid-based supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 5999–6005.
Zhang, X. Q.; Sun, Q.; Dong, W.; Li, D.; Lu, A. H.; Mu, J. Q.; Li, W. C. Synthesis of superior carbon nanofibers with large aspect ratio and tunable porosity for electrochemical energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 9449–9455.
Zhang, X. Q.; He, B.; Li, W. C.; Lu, A. H. Hollow carbon nanofibers with dynamic adjustable pore sizes and closed ends as hosts for high-rate lithium-sulfur battery cathodes. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1238–1246.
Liu, C.; Huang, X. D.; Wang, J.; Song, H.; Yang, Y. N.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. S.; Wang, L. J.; Yu, C. Z. Hollow mesoporous carbon nanocubes: Rigid-interface-induced outward contraction of metal-organic frameworks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705253.
Shang, L.; Yu, H. J.; Huang, X.; Bian, T.; Shi, R.; Zhao, Y. F.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Wu, L. Z.; Tung, C H.; Zhang, T. R. Well-dispersed ZIF-derived Co, N-co-doped carbon nanoframes through mesoporous-silica-protected calcination as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1668–1674.
Lei, C.; Han, F.; Sun, Q.; Li, W. C.; Lu, A. H. Confined nanospace pyrolysis for the fabrication of coaxial Fe3O4@C hollow particles with a penetrated mesochannel as a superior anode for Li-ion batteries. Chem.-Eur. J. 2014, 20, 139–145.
Han, F.; Li, W. C.; Lei, C.; He, B.; Oshida, K.; Lu, A. H. Selective formation of carbon-coated, metastable amorphous ZnSnO3 nanocubes containing mesopores for use as high-capacity lithium-ion battery. Small 2014, 10, 2637–2644.
Han, F.; Ma, L. J.; Sun, Q.; Lei, C.; Lu, A. H. Rationally designed carbon-coated Fe3O4 coaxial nanotubes with hierarchical porosity as high-rate anodes for lithium ion batteries. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1706–1717.
Cheng, F.; Li, W. C.; Lu, A. H. Using confined carbonate crystals for the fabrication of nanosized metal oxide@carbon with superior lithium storage capacity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15030–15035.
Wang, L. M.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X.; Wen, T.; Yin, J. J.; Wang, P. Y.; Bai, R.; Zhang, X. Q.; Zhang, L. H.; Lu, A. H. et al. Using hollow carbon nanospheres as a light-induced free radical generator to overcome chemotherapy resistance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1947–1955.
Gu, J. L.; Su, S. S.; Li, Y. S.; He, Q. J.; Shi, J. L. Hydrophilic mesoporous carbon nanoparticles as carriers for sustained release of hydrophobic anti-cancer drugs. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2101–2103.
Huang, X.; Wu, S. S.; Du, X. Z. Gated mesoporous carbon nanoparticles as drug delivery system for stimuli-responsive controlled release. Carbon 2016, 101, 135–142.
Xue, Z. H.; Zhang, F.; Qin, D. D.; Wang, Y. L.; Zhang, J. X.; Liu, J.; Feng, Y. J.; Lu, X. Q. One-pot synthesis of silver nanoparticle catalysts supported on N-doped ordered mesoporous carbon and application in the detection of nitrobenzene. Carbon 2014, 69, 481–489.
Tanaka, S.; Fujimoto, H.; Denayer, J. F. M.; Miyamoto, M.; Oumi, Y.; Miyake, Y. Surface modification of soft-templated ordered mesoporous carbon for electrochemical supercapacitors. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2015, 217, 141–149.
Jayaprakash, N.; Shen, J.; Moganty, S. S.; Corona, A.; Archer, L. A. Porous hollow carbon@sulfur composites for high-power lithium-sulfur batteries. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5904–5908.
Zhang, B.; Qin, X.; Li, G. R.; Gao, X. P. Enhancement of long stability of sulfur cathode by encapsulating sulfur into micropores of carbon spheres. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 1531–1537.
Zhou, W. D.; Wang, C. M.; Zhang, Q. L.; Abruña, H. D.; He, Y.; Wang, J. W.; Mao, S. X.; Xiao, X. C. Tailoring pore size of nitrogen-doped hollow carbon nanospheres for confining sulfur in lithium-sulfur batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1401752.
Zhou, G. M.; Zhao, Y. B.; Manthiram, A. Dual-confined flexible sulfur cathodes encapsulated in nitrogen-doped double-shelled hollow carbon spheres and wrapped with graphene for Li-S batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1402263.
Zhou, W. D.; Xiao, X. C.; Cai, M.; Yang, L. Polydopamine-coated, nitrogen-doped, hollow carbon-sulfur double-layered core-shell structure for improving lithium-sulfur batteries. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 5250–5256.
Yin, L. C.; Liang, J.; Zhou, G. M.; Li, F.; Saito, R.; Cheng, H. M. Understanding the interactions between lithium polysulfides and N-doped graphene using density functional theory calculations. Nano Energy 2016, 25, 203–210.
Yang, T. Y.; Liang, J.; Sultana, I.; Rahman, M. M.; Monteiro, M. J.; Chen, Y.; Shao, Z. P.; Silva, S. R. P.; Liu, J. Formation of hollow MoS2/carbon microspheres for high capacity and high rate reversible alkali-ion storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 8280–8288.
An, W. L.; Fu, J. J.; Su, J. J.; Wang, L.; Peng, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, Q. Y.; Bi, Y. J.; Gao, B.; Zhang, X. M. Mesoporous hollow nanospheres consisting of carbon coated silica nanoparticles for robust lithium-ion battery anodes. J. Power Sources 2017, 345, 227–236.
Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Liu, B. H.; Liang, M. F.; Lv, Z. L.; Adair, K. R.; Sun, X. L. Few-layer MoSe2 nanosheets with expanded (002) planes confined in hollow carbon nanospheres for ultrahigh-performance Na-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1707480.
Wang, J. J.; Luo, C.; Gao, T.; Langrock, A.; Mignerey, A. C.; Wang, C. S. An advanced MoS2/carbon anode for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Small 2015, 11, 473–481.
Dong, C.; Yu, Q.; Ye, R. P.; Su, P. P.; Liu, J.; Wang, G. H. Hollow carbon sphere nanoreactors loaded with PdCu nanoparticles: Voidconfinement effects in liquid-phase hydrogenations. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 18532–18537.
Yao, D. W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y. J.; Lv, J.; Ma, X. B. A highperformance nanoreactor for carbon-oxygen bond hydrogenation reactions achieved by the morphology of nanotube-assembled hollow spheres. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 1218–1226.
Yao, D. W.; Wang, Y.; Hassan-Legault, K.; Li, A. T.; Zhao, Y. J.; Lv, J.; Huang, S. Y.; Ma, X. B. Balancing effect between adsorption and diffusion on catalytic performance inside hollow nanostructured catalyst. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 2969–2976.
Yang, Q. H.; Yang, C. C.; Lin, C. H.; Jiang, H. L. Metal-organic-framework-derived hollow N-doped porous carbon with ultrahigh concentrations of single Zn atoms for efficient carbon dioxide conversion. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3511–3515
Zhang, L. H.; Sun, Q.; Liu, D. H.; Lu, A. H. Magnetic hollow carbon nanospheres for removal of chromium ions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 9477–9483.
Acknowledgements
The research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 20873014 and 21073026), National Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 21225312) and the Cheung Kong Scholars Program of China (No. T2015036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, RP., Li, WC., Hao, GP. et al. Confined nanospace pyrolysis: A versatile strategy to create hollow structured porous carbons. Nano Res. 14, 3159–3173 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3425-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3425-9