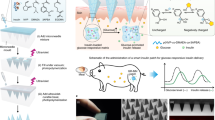
Abstract
Glucose-responsive insulin delivery systems show great promise to improve therapeutic outcomes and quality of life for people with diabetes. Herein, a new microneedle-array patch containing pH-sensitive insulin-loaded nanoparticles (NPs) (SNP(I)) together with glucose oxidase (GOx)- and catalase (CAT)-loaded pH-insensitive NPs (iSNP(G+C)) is constructed for transcutaneous glucose-responsive insulin delivery. SNP(I) are prepared via double emulsion from a pH-sensitive amphiphilic block copolymer, and undergo rapid dissociation to promote insulin release at a mild acidic environment induced by GOx in iSNP(G+C) under hyperglycemic conditions. CAT in iSNP(G+C) can further consume excess H2O2 generated during GOx oxidation, and thus reduce the risk of inflammation toward the normal skin. The in vivo study on type 1 diabetic mice demonstrates that the platform can effectively regulate blood glucose levels within normal ranges for a prolonged period.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chatterjee, S.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M. J. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet, 2017, 389, 2239–2251.
Atkinson, M. A.; Eisenbarth, G. S.; Michels, A. W. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet, 2014, 383, 69–82.
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition 2019 [Online]. Brussels, Belgium: Internationa Diabetes Federation, 2019. https://www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed Oct 10, 2020).
Owens, D. R.; Zinman, B.; Bolli, G. B. Insulins today and beyond. Lancet, 2001, 358, 739–746.
Bluestone, J. A.; Herold, K.; Eisenbarth, G. Genetics, pathogenesis and clinical interventions in type 1 diabetes. Nature, 2010, 464, 1293–1300.
Karges, B.; Binder, E.; Rosenbauer, J. Complications with insulin pump therapy vs insulin injection therapy-reply. JAMA, 2018, 319, 503–504.
Yeh, H. C.; Brown, T. T.; Maruthur, N.; Ranasinghe, P.; Berger, Z.; Suh, Y. D.; Wilson, L. M.; Haberl, E. B.; Brick, J.; Bass, E. B. et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of methods of insulin delivery and glucose monitoring for diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med., 2012, 157, 336–347.
Writing Team for the Diabetes Control; Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions; Complications Research Group. Sustained effect of intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus on development and progression of diabetic nephropathy: The epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications (EDIC) study. JAMA, 2003, 290, 2159–2167.
Donnelly, L. A.; Morris, A. D.; Frier, B. M.; Ellis, J. D.; Donnan, P. T.; Durrant, R.; Band, M. M.; Reekie, G.; Leese, G. P.; DARTS/MEMO Collaboration. Frequency and predictors of hypoglycaemia in Type 1 and insulin-treated Type 2 diabetes: A population-based study. Diabet. Med., 2005, 22, 749–755.
Shen, D.; Yu, H. J.; Wang, L.; Khan, A.; Haq, F.; Chen, X.; Huang, Q.; Teng, L. S. Recent progress in design and preparation of glucose-responsive insulin delivery systems. J. Control. Release, 2020, 321, 236–258.
Yu, J. C.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Yan, J. J.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Gu, Z. Advances in bioresponsive closed-loop drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm., 2018, 544, 350–357.
Bakh, N. A.; Cortinas, A. B.; Weiss, M. A.; Langer, R. S.; Anderson, D. G.; Gu, Z.; Dutta, S.; Strano, M. S. Glucose-responsive insulin by molecular and physical design. Nat. Chem., 2017, 9, 937–944.
Ravaine, V.; Ancla, C.; Catargi, B. Chemically controlled closed-loop insulin delivery. J. Control. Release, 2008, 132, 2–11.
Jamaledin, R.; Makvandi, P.; Yiu, C. K. Y.; Agarwal, T.; Vecchione, R.; Sun, W. J.; Maiti, T. K.; Tay, F. R.; Netti, P. A. Engineered microneedle patches for controlled release of active compounds: recent advances in release profile tuning. Adv. Ther., 2020, in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/adtp.202000171.
Jamaledin, R.; Yiu, C. K. Y.; Zare, E. N.; Niu, L. N.; Vecchione, R.; Chen, G. J.; Gu, Z.; Tay, F. R.; Makvandi, P. Advances in antimicrobial microneedle patches for combating infections. Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 2002129.
Steil, G M.; Rebrin, K.; Darwin, C.; Hariri, F.; Saad, M. F. Feasibility of automating insulin delivery for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes, 2006, 55, 3344–3350.
Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, H. J.; Li, C. J.; Feng, J. Y.; Haq, F.; Khan, A.; Khan, R. U. Preparation, properties and challenges of the microneedles-based insulin delivery system. J. Control. Release, 2018, 288, 173–188.
Veiseh, O.; Tang, B. C.; Whitehead, K. A.; Anderson, D. G.; Langer, R. Managing diabetes with nanomedicine: Challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 2015, 14, 45–57.
Weissberg-Benchell J.; Antisdel-Lomaglio J.; Seshadri R. Insulin pump therapy: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care, 2003, 26, 1079–1087.
Wang, J. Q.; Wang, Z. J.; Yu, J. C.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Glucose-responsive insulin and delivery systems: Innovation and translation. Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 1902004.
Zhang, Y. Q.; Yu, J. C.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Wang, J. Q.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Advances in transdermal insulin delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2019, 139, 51–70.
Gordijo, C. R.; Koulajian, K.; Shuhendler, A. J.; Bonifacio, L. D.; Huang, H. Y.; Chiang, S.; Ozin, G. A.; Giacca, A.; Wu, X. Y. Nanotechnology-enabled closed loop insulin delivery device: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of glucose-regulated insulin release for diabetes control. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2011, 21, 73–82.
Jin, X.; Zhu, D. D.; Chen, B. Z.; Ashfaq, M.; Guo, X. D. Insulin delivery systems combined with microneedle technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2018, 127, 119–137.
Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Yu, H. J.; Wang, J. J.; Chen, Z. F. Organization of glucose-responsive systems and their properties. Chem. Rev., 2011, 111, 7855–7875.
Yu, J. C.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Wang, J. Q.; Wen, D.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Glucose-responsive oral insulin delivery for postprandial glycemic regulation. Nano Res., 2019, 12, 1539–1545.
Gu, Z.; Dang, T. T.; Ma, M. L.; Tang, B. C.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, S.; Dong, Y. Z.; Zhang, Y. L.; Anderson, D. G. Glucose-responsive microgels integrated with enzyme nanocapsules for closed-loop insulin delivery. ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 6758–6766.
Gu, Z.; Aimetti, A. A.; Wang, Q.; Dang, T. T.; Zhang, Y. L.; Veiseh, O.; Cheng, H.; Langer, R. S.; Anderson, D. G. Injectable nano-network for glucose-mediated insulin delivery. ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 4194–4201.
Podual, K.; Doyle, F. J.; Peppas, N. A. Glucose-sensitivity of glucose oxidase-containing cationic copolymer hydrogels having poly (ethylene glycol) grafts. J. Control. Release, 2000, 67, 9–17.
Chou, D. H. C.; Webber, M. J.; Tang, B. C.; Lin, A. B.; Thapa, L. S.; Deng, D.; Truong, J. V.; Cortinas, A. B.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. Glucose-responsive insulin activity by covalent modification with aliphatic phenylboronic acid conjugates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2015, 112, 2401–2406.
Huang, Q.; Wang, L.; Yu, H. J.; Ur-Rahman, K. Advances in phenylboronic acid-based closed-loop smart drug delivery system for diabetic therapy. J. Control. Release, 2019, 305, 50–64.
Yu, J. C.; Wang, J. Q.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Chen, G. J.; Mao, W. W.; Ye, Y. Q.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Buse, J. B.; Langer, R.; Gu, Z. Glucose-responsive insulin patch for the regulation of blood glucose in mice and minipigs. Nat. Biomed. Eng., 2020, 4, 499–506.
Matsumoto, A.; Tanaka, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Ochi, K.; Moro-oka, Y.; Kuwata, H.; Yamada, H.; Shirakawa, I.; Miyazawa, T.; Ishii, H. et al. Synthetic “smart gel” provides glucose-responsive insulin delivery in diabetic mice. Sci. Adv., 2017, 3, eaaq0723.
Matsumoto, A.; Ishii, T.; Nishida, J.; Matsumoto, H.; Kataoka, K.; Miyahara, Y. A synthetic approach toward a self-regulated insulin delivery system. Angew. Chem, Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 2124–2128.
Wu, S. S.; Huang, X.; Du, X. Z. Glucose-and pH-responsive controlled release of cargo from protein-gated carbohydrate-functionalized mesoporous silica nanocontainers. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 5580–5584.
Wang, J. Q.; Yu, J. C.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Zhang, X. D.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Chen, G. J.; Wang, Z. J.; Sun, W. J.; Cai, L. L.; Chen, Z. W. et al. Charge-switchable polymeric complex for glucose-responsive insulin delivery in mice and pigs. Sci. Adv., 2019, 5, eaaw4357.
Yu, J. C.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Sun, W. J.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Wang, J. Q.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Insulin-responsive glucagon delivery for prevention of hypoglycemia. Small, 2017, 13, 1603028.
Wang, C.; Ye, Y. Q.; Sun, W. J.; Yu, J. C.; Wang, J. Q.; Lawrence, D. S.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Red blood cells for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1606617.
Wang, J. Q.; Yu, J. C.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Wang, Z. J.; Fang, J.; Whitelegge, J. P.; Li, S.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Glucose transporter inhibitor-conjugated insulin mitigates hypoglycemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2019, 116, 10744–10748.
Bankar, S. B.; Bule, M. V.; Singhal, R. S.; Ananthanarayan, L. Glucose oxidase-An overview. Biotechnol. Adv., 2009, 27, 489–501.
Zhang, G. Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, X. L.; Wang, X. Y.; Song, M. M.; Gou, H. L.; Gao, S.; Jia, X. D. Polymer-covalent organic frameworks composites for glucose and pH dual-responsive insulin delivery in mice. Adv. Healthc. Mater., 2020, 9, 2000221.
Zuo, M. Z.; Qian, W. R.; Xu, Z. Q.; Shao, W.; Hu, X. Y.; Zhang, D. M.; Jiang, J. L.; Sun, X. Q.; Wang, L. Y. Multiresponsive supramolecular theranostic nanoplatform based on pillar[5]arene and diphenylboronic acid derivatives for integrated glucose sensing and insulin delivery. Small, 2018, 14, 1801942.
Hu, X. L.; Yu, J. C.; Qian, C. G; Lu, Y.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Xie, Z. G.; Jing, X. B.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. H2O2-responsive vesicles integrated with transcutaneous patches for glucose-mediated insulin delivery. ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 613–620.
Zhang, Y. Q.; Wang, J. Q.; Yu, J. C.; Wen, D.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X. D.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Bioresponsive microneedles with a sheath structure for H2O2 and pH cascade-triggered insulin delivery. Small, 2018, 14, 1704181.
Wang, J. Q.; Ye, Y. Q.; Yu, J. C.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Zhang, X. D.; Wang, C.; Sun, W. J.; Corder, R. D.; Chen, Z. W.; Khan, S. A. et al. Core-shell microneedle gel for self-regulated insulin delivery. ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 2466–2473.
Yu, J. C.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Ye, Y. Q.; DiSanto, R.; Sun, W. J.; Ranson, D.; Ligler, F. S.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Microneedle-array patches loaded with hypoxia-sensitive vesicles provide fast glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2015, 112, 8260–8265.
Yu, J. C.; Qian, C. G.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Cui, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Q. D.; Ligler, F. S.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Hypoxia and H2O2 dual-sensitive vesicles for enhanced glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Nano Lett., 2017, 17, 733–739.
Zhang, C.; Hong, S.; Liu, M. D.; Yu, W. Y.; Zhang, M. K.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, X. Z. pH-sensitive MOF integrated with glucose oxidase for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. J. Control. Release, 2020, 320, 159–167.
Wu, W. T.; Mitra, N.; Yan, E. C. Y.; Zhou, S. Q. Multifunctional hybrid nanogel for integration of optical glucose sensing and self-regulated insulin release at physiological pH. ACS Nano, 2010, 4, 4831–4839.
Volpatti, L. R.; Matranga, M. A.; Cortinas, A. B.; Delcassian, D.; Daniel, K. B.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. Glucose-responsive nanoparticles for rapid and extended self-regulated insulin delivery. ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 488–497.
Zhou, K. J.; Wang, Y. G.; Huang, X. N.; Luby-Phelps, K.; Sumer, B. D.; Gao, J. M. Tunable, ultrasensitive pH-responsive nanoparticles targeting specific endocytic organelles in living cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 6109–6114.
Loncar, N.; Fraaije, M. W. Catalases as biocatalysts in technical applications: current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2015, 99, 3351–3357.
Chen, G. J.; Chen, Z. T.; Wen, D.; Wang, Z. J.; Li, H. J.; Zeng, Y.; Dotti, G.; Wirz, R. E.; Gu, Z. Transdermal cold atmospheric plasmamediated immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2020, 117, 3687–3692.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFA0205600), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31771091 and 51922043), Guangdong Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar (No. 2017A030306018), Guangdong Provincial Programs (Nos. 2017ZT07S054 and 2017GC010304), Outstanding Scholar Program of Bioland Laboratory (Guangzhou Regenerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory) (No. 2018GZR110102001), Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (No. 2018A030310285), Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (Nos. 201902020018, 201804020060, and 201904010398), and Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities, National Science Foundation (No. 1919285) and American Diabetes Association (No. 1-15-ACE-21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, FQ., Chen, G., Xu, W. et al. Microneedle-array patch with pH-sensitive formulation for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Nano Res. 14, 2689–2696 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3273-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3273-z