Abstract
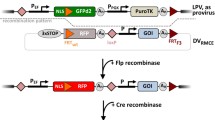
Traditional cell line development is based on random genomic integration of transgenes. Random integration leads to unpredictable expression and results in clonal heterogeneity requiring a tedious screening procedure. Therefore, a new strategy is needed to establish clones that exhibit stable transgene expression. Here, we performed CRISPR/Cas9-mediated site-specific integration (SSI) to incorporate a landing pad (LP; containing mCherry) at a genomic hotspot (Fer1L4) allowing stable and strong expression. Site-specific integration of LP on Fer1L4 was demonstrated by sequencing results representing the swapped sequences in mCherry-expressing cells. We then performed Cre/Lox-based recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE) to exchange LP with a targeting vector (TV; containing GFP) in clones established by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated SSI. The success of Cre/Lox-based RMCE was evidenced by sequencing results representing the swapped sequences in GFP-expressing cells. Furthermore, the swapped clones expressing GFP was enriched up to 80%, indicating that the efficiency of Cre/Lox-based RMCE would be sufficient to swap pre-existing cassettes with gene-of-interest (GOI). Taken together, our study provides a new platform for Cre/Lox-based RMCE to iteratively establish stable clones from existing ones previously established by SSI at a genomic hotspot.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kesik-Brodacka, M. (2018) Progress in biopharmaceutical development. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 65: 306–322.
Lai, T., Y. Yang, and S. K. Ng (2013) Advances in mammalian cell line development technologies for recombinant protein production. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 6: 579–603.
Carvalho, R. J. (2019) Comparison of cationic flocculants for the clarification of CHO-derived monoclonal antibodies. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 24: 754–760.
Li, F., N. Vijayasankaran, A. Y. Shen, R. Kiss, and A. Amanullah (2010) Cell culture processes for monoclonal antibody production. MAbs. 2: 466–479.
Coates, C. J., J. M. Kaminski, J. B. Summers, D. J. Segal, A. D. Miller, and A. F. Kolb (2005) Site-directed genome modification: derivatives of DNA-modifying enzymes as targeting tools. Trends Biotechnol. 23: 407–419.
Hamaker, N. K. and K. H. Lee (2018) Site-specific integration ushers in a new era of precise CHO cell line engineering. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 22: 152–160.
Turan, S., C. Zehe, J. Kuehle, J. Qiao, and J. Bode (2013) Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE) — a rapidly-expanding toolbox for targeted genomic modifications. Gene. 515: 1–27.
Shin, S. W. and J. S. Lee (2020) CHO cell line development and engineering via site-specific integration: Challenges and opportunities. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 25: 633–645.
Gidoni, D., V. Srivastava, and N. Carmi (2008) Site-specific excisional recombination strategies for elimination of undesirable transgenes from crop plants. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant. 44: 457–467.
Schnütgen, F., A. F. Stewart, H. von Melchner, and K. Anastassiadis (2006) Engineering embryonic stem cells with recombinase systems. Methods Enzymol. 420: 100–136.
Aach, J., P. Mali, and G. M. Church (2014) CasFinder: Flexible algorithm for identifying specific Cas9 targets in genomes. bioRxiv. 005074.
Lee, J. S., T. B. Kallehauge, L. E. Pedersen, and H. F. Kildegaard (2015) Site-specific integration in CHO cells mediated by CRISPR/Cas9 and homology-directed DNA repair pathway. Sci. Rep. 5: 8572.
Saraf-Levy, T., S. W. Santoro, H. Volpin, T. Kushnirsky, Y. Eyal, P. G. Schultz, D. Gidoni, and N. Carmi (2006) Site-specific recombination of asymmetric lox sites mediated by a heterotetrameric Cre recombinase complex. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 14: 3081–3089.
Du, Z. W., B. Y. Hu, M. Ayala, B. Sauer, and S. C. Zhang (2009) Cre recombination-mediated cassette exchange for building versatile transgenic human embryonic stem cells lines. Stem Cells. 27: 1032–1041.
Bouabe, H., R. Fässler, and J. Heesemann (2008) Improvement of reporter activity by IRES-mediated polycistronic reporter system. Nucleic Acids Res. 36: e28.
Wang, B., T. Albanetti, G. Miro-Quesada, L. Flack, L. Li, J. Klover, K. Burson, K. Evans, W. Ivory, M. Bowen, R. Schoner, and P. Hawley-Nelson (2018) High-throughput screening of antibody-expressing CHO clones using an automated shaken deep-well system. Biotechnol. Prog. 34: 1460–1471.
West, A. G. and P. Fraser (2005) Remote control of gene transcription. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14 Spec No 1: R101–R111.
Turan, S., M. Galla, E. Ernst, J. Qiao, C. Voelkel, B. Schiedlmeier, C. Zehe, and J. Bode (2011) Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE): traditional concepts and current challenges. J. Mol. Biol. 407: 193–221.
Zhang, L., M. C. Inniss, S. Han, M. Moffat, H. Jones, B. Zhang, W. L. Cox, J. R. Rance, and R. J. Young (2015) Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE) for monoclonal antibody expression in the commercially relevant CHOK1SV cell line. Biotechnol. Prog. 31: 1645–1656.
Crawford, Y., M. Zhou, Z. Hu, J. Joly, B. Snedecor, A. Shen, and A. Gao (2013) Fast identification of reliable hosts for targeted cell line development from a limited-genome screening using combined φC31 integrase and CRE-Lox technologies. Biotechnol. Prog. 29: 1307–1315.
Gaidukov, L., L. Wroblewska, B. Teague, T. Nelson, X. Zhang, Y. Liu, K. Jagtap, S. Mamo, W. A. Tseng, A. Lowe, J. Das, K. Bandara, S. Baijuraj, N. M. Summers, T. K. Lu, L. Zhang, and R. Weiss (2018) A multi-landing pad DNA integration platform for mammalian cell engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 46: 4072–4086.
Donnelly, M. L. L., L. E. Hughes, G. Luke, H. Mendoza, E. Ten Dam, D. Gani, and M. D. Ryan (2001) The ‘cleavage’ activities of foot-and-mouth disease virus 2A site-directed mutants and naturally occurring ‘2A-like’ sequences. J. Gen. Virol. 82: 1027–1041.
Donnelly, M. L. L., G. Luke, A. Mehrotra, X. Li, L. E. Hughes, D. Gani, and M. D. Ryan (2001) Analysis of the aphthovirus 2A/2B polyprotein ‘cleavage’ mechanism indicates not a proteolytic reaction, but a novel translational effect: a putative ribosomal ‘skip’. J. Gen. Virol. 82: 1013–1025.
Geier, M., P. Fauland, T. Vogl, and A. Glieder (2015) Compact multi-enzyme pathways in P. pastoris. Chem. Commun (Camb). 51: 1643–1646.
Xia, T., S. Chen, Z. Jiang, Y. Shao, X. Jiang, P. Li, B. Xiao, and J. Guo (2015) Long noncoding RNA i suppresses cancer cell growth by acting as a competing endogenous RNA and regulating PTEN expression. Sci. Rep. 5: 13445.
Inniss, M. C., K. Bandara, B. Jusiak, T. K. Lu, R. Weiss, L. Wroblewska, and L. Zhang (2017) A novel Bxb1 integrase RMCE system for high fidelity site-specific integration of mAb expression cassette in CHO cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 114: 1837–1846.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by priority Research Centers Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2020R1A6A1A0304195411). This research was also supported by Research Assistance Program (2019) in the Incheon National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KJW, HWK and JTP conceived of and designed the experiments. KJW, YHL, MUK and SYH performed the experiments. KJW and JTP analyzed the data. KJW, HWK and JTP wrote and edited the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Lee, Y.H., Kuk, M.U. et al. Cre/Lox-based RMCE for Site-specific Integration in CHO Cells. Biotechnol Bioproc E 26, 795–803 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0332-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0332-y