Abstract
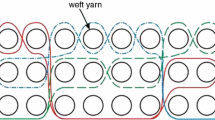
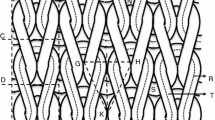
Clothing plays vital role to maintain heat balance between human body and environment. Heat balance must be maintained to keep a person comfortable. Several factors contribute to the thermal properties of textile material, including structure of yarn and fabric which are the key parameters in deciding fabric thermal behaviour. This paper deals with the study of thermal properties of herringbone weave produced with or without structurally modified wool/polyester yarns in the weft. Experimental results are then compared with results obtained through finite element analysis. In the fabric unit, air occupies more volume as compared to fibre volume. Therefore, air should be considered during finite element analysis to obtain good results. In this research, fabric unit cell used for analysis of thermal resistance consists of two domains i.e, air domain and yarn domain. In steady state thermal study, boundary condition was set as 22 °C at one face as it approaches to a comfortable indoor temperature and other face of fabric was set at 35 °C as it directly contacts human skin, and its temperature is nearly equal to skin temperature. The results obtained through finite element analysis show a good co-relation between experimental and predicted values of thermal resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. N. Yoon and A. Buckley, Text. Res. J., 54, 289 (1984).
G. J. Morris, J. Text. Inst. Trans., 44, 449 (1953).
D. Bhatia and U. Malhotra, J. Fashion Technol. Text. Eng., doi: https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-9568.1000128 (2016).
A. Das, S. M. Ishtiaque, and R. P. Singh, J. Text. Inst., 100, 207 (2009).
N. Sharma, P. Kumar, D. Bhatia, and S. K. Sinha J. Inst. Eng. (India): Series E, 97, 123 (2016).
V. Chandrasekaran, P. Senthilkumar, and J. C. Sakthivel, J. Text. Inst., 109, 1458 (2018).
P. Kumar, S. K. Sinha, and S. Ghosh, Fiber. Polym., 17, 1898 (2016).
D. Bhatia and S. K. Sinha, J. Inst. Eng. (India): Series E, 101, 115 (2020).
D. Bhatia and S. K. Sinha, Tekstilec, 63, 138 (2020).
V. K. Kothari and D. Bhattacharjee, J. Text. Inst., 99, 421 (2008).
D. Bhattacharjee and V. K. Kothari, Text. Res. J., 77, 4 (2007).
M. O. R. Siddiqui and D. Sun, Comput. Mater. Sci., 75, 45 (2013).
Y. Sun, X. Chen, Z. Cheng, and X. Feng, Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol., 22, 161 (2010).
M. Wang, J. He, J. Yu, and N. Pan, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 46, (2007).
J. J. Wu, H. Tang, and Y. X. Wu, Therm. Sci., 21, 1627 (2017).
Z. Zheng, N. Zhang, and X. Zhao, Therm. Sci., 22, 2815 (2018).
M. O. R. Siddiqui, Ph. D. Dissertation, Heriot-Watt University, Scotland, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, D., Sinha, S.K. Geometrical Modelling of Herringbone Twill Fabric for Prediction of Thermal Resistance Using Finite Element Method. Fibers Polym 22, 2885–2891 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-021-0774-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-021-0774-7