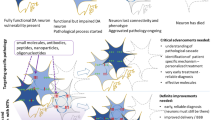
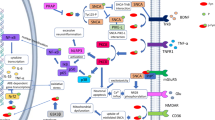
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a chronic and progressive neurodegenerative disease of the brain. PD is characterized by motor and non-motor symptoms. The p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) is a functional receptor for different growth factors including pro-brain derived neurotrophic factor (pro-BDNF), neurotrophin 3 (NT-3), and neurotrophin 4 (NT-4). Consequently, this review aimed to illustrate the detrimental and beneficial role of p75NTR in PD. Diverse studies showed that p75NTR and its downstream signaling are intricate in the pathogenesis of PD. Nevertheless, pro-apoptotic and pro-survival pathways mediated by p75NTR in PD were not fully clarified. Of note, p75NTR plays a critical role in the regulation of dopaminergic neuronal survival and apoptosis in the CNS. Particularly, p75NTR can induce selective apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons and progression of PD. In addition, p75NTR signaling inhibits the expression of transcription factors which are essential for the survival of dopaminergic neurons. Also, p75NTR expression is connected with the severity of dopaminergic neuronal injury. These verdicts implicate p75NTR signaling in the pathogenesis of PD, though the underlying mechanistic pathways remain not elucidated. Collectively, the p75NTR signaling pathway induces a double-sword effect either detrimental or beneficial depending on the ligands and status of PD neuropathology. Therefore, p75NTR signaling seems to be protective via phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT and Bcl-2 and harmful via activation of JNK, caspase 3, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), and RhoA pathways.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Underwood CK, Coulson EJ (2008) The p75 neurotrophin receptor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40(9):1664–1668
Kuhn K, Edamura K, Bhatia N, Cheng I, Clark S, Haynes C et al (2020) Molecular dissection of TNFR-TNFα bidirectional signaling reveals both cooperative and antagonistic interactions with p75 neurotrophic factor receptor in axon patterning. Mol Cell Neurosci 103:103467
Paudel YN, Angelopoulou E, Jones NC, O’Brien TJ, Kwan P, Piperi C et al (2019) Tau related pathways as a connecting link between epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 10(10):4199–4212
Manti S, Xerra F, Spoto G, Butera A, Gitto E, Di Rosa G et al (2023) Neurotrophins: expression of brain–lung axis development. Int J Mol Sci 24(8):7089
Scuri M, Samsell L, Piedimonte G (2010) The role of neurotrophins in inflammation and allergy. Inflamm Allergy-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-Inflammation & Allergy)(Discontinued) 9(3):173–80
Ismail NA, Leong Abdullah MFI, Hami R, Ahmad Yusof H (2020) A narrative review of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) on cognitive performance in Alzheimer’s disease. Growth Factors 38(3–4):210–225
Bao X, Shi J, Xie F, Liu Z, Yu J, Chen W et al (2018) Proteolytic release of the p75NTR intracellular domain by ADAM10 promotes metastasis and resistance to anoikis. Cancer Res 78(9):2262–2276
Skeldal S, Matusica D, Nykjaer A, Coulson EJ (2011) Proteolytic processing of the p75 neurotrophin receptor: a prerequisite for signalling? Neuronal life, growth and death signalling are crucially regulated by intra-membrane proteolysis and trafficking of p75NTR. BioEssays 33(8):614–625. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201100036
Goncharuk SA, Artemieva LE, Nadezhdin KD, Arseniev AS, Mineev KS (2020) Revising the mechanism of p75NTR activation: intrinsically monomeric state of death domains invokes the “helper” hypothesis. Sci Rep 10(1):13686
Sankorrakul K, Qian L, Thangnipon W, Coulson EJ (2021) Is there a role for the p75 neurotrophin receptor in mediating degeneration during oxidative stress and after hypoxia? J Neurochem 158(6):1292–1306
Wei Z, Yang C, Feng K, Guo S, Huang Z, Wang Y et al (2023) p75NTR enhances cognitive dysfunction in a mouse Alzheimer’s disease model by inhibiting microRNA-210-3p-mediated PCYT2 through activation of NF-κB. Int J Biol Macromol 225:404–415
Fudalej E, Justyniarska M, Kasarełło K, Dziedziak J, Szaflik JP, Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska A (2021) Neuroprotective factors of the retina and their role in promoting survival of retinal ganglion cells: a review. Ophthalmic Res 64(3):345–355
Eggert S, Kins S, Endres K, Brigadski T (2022) Brothers in arms: proBDNF/BDNF and sAPPα/Aβ-signaling and their common interplay with ADAM10, TrkB, p75NTR, sortilin, and sorLA in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Biol Chem 403(1):43–71
Riolo G, Ricci C, De Angelis N, Marzocchi C, Guerrera G, Borsellino G et al (2022) BDNF and pro-BDNF in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a new perspective for biomarkers of neurodegeneration. Brain Sci 12(5):617
Blondy S, Christou N, David V, Verdier M, Jauberteau M-O, Mathonnet M et al (2019) Neurotrophins and their involvement in digestive cancers. Cell Death Dis 10(2):123
Dave BP, Shah KC, Shah MB, Chorawala MR, Patel VN, Shah PA et al (2023) Unveiling the modulation of Nogo receptor in neuroregeneration and plasticity: novel aspects and future horizon in a new frontier. Biochem Pharmacol 210:115461
Zhang N, Kisiswa L, Ramanujan A, Li Z, Sim EW, Tian X et al (2021) Structural basis of NF-κB signaling by the p75 neurotrophin receptor interaction with adaptor protein TRADD through their respective death domains. J Biol Chem 297(2):100916
Schmidt SI, Blaabjerg M, Freude K, Meyer M (2022) RhoA signaling in neurodegenerative diseases. Cells 11(9):1520
Rashidbenam Z, Ozturk E, Pagnin M, Theotokis P, Grigoriadis N, Petratos S (2023) How does Nogo receptor influence demyelination and remyelination in the context of multiple sclerosis? Front Cell Neurosci 17:1197492
Zarneshan SN, Fakhri S, Khan H (2022) Targeting Akt/CREB/BDNF signaling pathway by ginsenosides in neurodegenerative diseases: a mechanistic approach. Pharmacol Res 177:106099
Chen L, Yung K, Chan Y, Shum D, Bolam J (2008) The proNGF-p75NTR-sortilin signalling complex as new target for the therapeutic treatment of Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders) 7(6):512–23
Liu Z, Yan A, Zhao J, Yang S, Song L, Liu Z (2021) The p75 neurotrophin receptor as a novel intermediate in L-dopa-induced dyskinesia in experimental Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 342:113740
Al‐kuraishy HM, Al‐Gareeb AI, Kaushik A, Kujawska M, Ahmed EA, Batiha GES (2023) SARS‐COV‐2 infection and Parkinson’s disease: possible links and perspectives. J Neurosci Res
Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Kaushik A, Kujawska M, Ahmed EA, Batiha GES (2023) SARS-COV-2 infection and Parkinson’s disease: possible links and perspectives. J Neurosci Res 101(6):952–975
Alrouji M, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2023) A story of the potential effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in Parkinson’s disease: beneficial or detrimental effects. Inflammopharmacology 31(2):673–688
Alrouji M, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Ashour NA, Jabir MS, Negm WA, et al (2023) Metformin role in Parkinson’s disease: a double-sword effect. Mol Cell Biochem:1–17.
Batiha GE-S, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Elekhnawy E (2023) SIRT1 pathway in Parkinson’s disease: a faraway snapshot but so close. Inflammopharmacology 31(1):37–56
Alrouji M, Al‐kuraishy HM, Al‐Gareeb AI, Alexiou A, Papadakis M, Jabir MS, et al (2023) NF‐κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis and risk of Parkinson’s disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a narrative review and new perspective. J Cell Mol Med
Alrouji M, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Buhadily AK, Al-Gareeb AI, Elekhnawy E, Batiha GE-S (2023) DPP-4 inhibitors and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Parkinson’s disease: a mutual relationship. Pharmacol Rep 1–14
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Alsayegh AA, Abusudah WF, Almohmadi NH, Eldahshan OA, et al (2023) Insights on benzodiazepines’ potential in Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci 121532
Alrouji M, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2023) A story of the potential effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in Parkinson’s disease: beneficial or detrimental effects. Inflammopharmacology 2023/03/24
Heras-Garvin A, Stefanova N (2020) From synaptic protein to prion: the long and controversial journey of α-synuclein. Front Synaptic Neurosci 12:584536
Al-Kuraishy HM, Abdulhadi MH, Hussien NR, Al-Niemi MS, Rasheed HA, Al-Gareeb AI (2020) Involvement of orexinergic system in psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders: a scoping review. Brain Circulation 6(2):70
Xu B, Fan F, Liu Y, Liu Y, Zhou L, Yu H (2023) Distinct effects of familial Parkinson’s disease-associated mutations on α-synuclein phase separation and amyloid aggregation. Biomolecules 13(5):726
Airavaara M, Parkkinen I, Konovalova J, Albert K, Chmielarz P, Domanskyi A (2020) Back and to the future: from neurotoxin-induced to human Parkinson’s disease models. Curr Protoc Neurosci 91(1):e88
Chung SJ, Yoo HS, Lee YH, Lee PH, Sohn YH (2019) Heterogeneous patterns of striatal dopamine loss in patients with young-versus old-onset Parkinson’s disease: impact on clinical features. J Mov Disord 12(2):113
Johnson ME, Stecher B, Labrie V, Brundin L, Brundin P (2019) Triggers, facilitators, and aggravators: redefining Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Trends Neurosci 42(1):4–13
Consonni A, Miglietti M, De Luca CMG, Cazzaniga FA, Ciullini A, Dellarole IL et al (2022) Approaching the gut and nasal microbiota in Parkinson’s disease in the era of the seed amplification assays. Brain Sci 12(11):1579
Liu Z, Shen C, Li H, Tong J, Wu Y, Ma Y et al (2023) NOD-like receptor NLRC5 promotes neuroinflammation and inhibits neuronal survival in Parkinson’s disease models. J Neuroinflammation 20(1):1–21
Hou X, Watzlawik JO, Fiesel FC, Springer W (2020) Autophagy in Parkinson’s disease. J Mol Biol 432(8):2651–2672
Kung H-C, Lin K-J, Kung C-T, Lin T-K (2021) Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuroprotection of polyphenols with respect to resveratrol in Parkinson’s disease. Biomedicines 9(8):918
Tang J-J, Feng S, Chen X-D, Huang H, Mao M, Wang H-Y et al (2021) The effects of P75NTR on learning memory mediated by hippocampal apoptosis and synaptic plasticity. Curr Pharm Des 27(4):531–539
Xiong LL, Chen L, Deng IB, Zhou XF, Wang TH (2022) P75 neurotrophin receptor as a therapeutic target for drug development to treat neurological diseases. Eur J Neurosci 56(8):5299–5318
Simmons DA, Mills BD, Butler RR III, Kuan J, McHugh TL, Akers C et al (2021) Neuroimaging, urinary, and plasma biomarkers of treatment response in Huntington’s disease: preclinical evidence with the p75 NTR ligand LM11A-31. Neurotherapeutics 18:1039–1063
Suelves N, Miguez A, López-Benito S, Barriga GG-D, Giralt A, Alvarez-Periel E et al (2019) Early downregulation of p75 NTR by genetic and pharmacological approaches delays the onset of motor deficits and striatal dysfunction in Huntington’s disease mice. Mol Neurobiol 56:935–953
Feldman EL, Goutman SA, Petri S, Mazzini L, Savelieff MG, Shaw PJ et al (2022) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet 400(10360):1363–1380
Shu Y-H, Lu X-M, Wei J-X, Xiao L, Wang Y-T (2015) Update on the role of p75NTR in neurological disorders: a novel therapeutic target. Biomed Pharmacother 76:17–23
Küst B, Brouwer N, Mantingh I, Boddeke H, Copray J (2003) Reduced p75NTR expression delays disease onset only in female mice of a transgenic model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 4(2):100–105
Turner BJ, Murray SS, Piccenna LG, Lopes EC, Kilpatrick TJ, Cheema SS (2004) Effect of p75 neurotrophin receptor antagonist on disease progression in transgenic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mice. J Neurosci Res 78(2):193–199
Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2022) Benzodiazepines in Alzheimer’s disease: beneficial or detrimental effects. Inflammopharmacology 2022/11/23
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Alsayegh AA, Hakami ZH, Khamjan NA, Saad HM, et al (2022) A potential link between visceral obesity and risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res 2022/11/21
Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2023) Long-term use of metformin and Alzheimer’s disease: beneficial or detrimental effects. Inflammopharmacology 2023/02/28
AlAnazi FH, Al-Kuraishy HM, Alexiou A, Papadakis M, Ashour MHM, Alnaaim SA, et al (2023) Primary hypothyroidism and Alzheimer’s disease: a tale of two. Cell Mol Neurobiol 1–12
Bruno F, Abondio P, Montesanto A, Luiselli D, Bruni AC, Maletta R (2023) The nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR/p75NTR): a major player in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 24(4):3200
Sáez ET, Pehar M, Vargas MR, Barbeito L, Maccioni RB (2006) Production of nerve growth factor by β-amyloid-stimulated astrocytes induces p75NTR-dependent tau hyperphosphorylation in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Res 84(5):1098–1106
Costantini C, Weindruch R, Della Valle G, Puglielli L (2005) A TrkA-to-p75NTR molecular switch activates amyloid β-peptide generation during aging. Biochem J 391(1):59–67
Rabizadeh S, Bitler CM, Butcher LL, Bredesen DE (1994) Expression of the low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor enhances beta-amyloid peptide toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91(22):10703-10706
Hu Y, Lee X, Shao Z, Apicco D, Huang G, Gong B, et al (2013) A DR6/p75NTR complex is responsible for β-amyloid-induced cortical neuron death. Cell Death Dis 4(4):e579-e
Fombonne J, Rabizadeh S, Banwait S, Mehlen P, Bredesen DE (2009) Selective vulnerability in Alzheimer’s disease: amyloid precursor protein and p75NTR interaction. Ann Neurol: Off J Am Neurol Assoc Child Neurol Soc 65(3):294–303
Frade JM, López-Sánchez N (2010) A novel hypothesis for Alzheimer disease based on neuronal tetraploidy induced by p75NTR. Cell Cycle 9(10):1934–1941
Zeng F, Lu J-J, Zhou X-F, Wang Y-J (2011) Roles of p75NTR in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: a novel therapeutic target. Biochem Pharmacol 82(10):1500–1509
Jiao S, Bu X, Liu Y, Wang Q, Liu C, Yao X, et al (2015) Differential levels of p75NTR ectodomain in CSF and blood in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a novel diagnostic marker. Transl Psychiatr 5(10):e650-e
Yao X, Jiao S, Saadipour K, Zeng F, Wang Q, Zhu C et al (2015) p75NTR ectodomain is a physiological neuroprotective molecule against amyloid-beta toxicity in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 20(11):1301–1310
Wang Y-J, Wang X, Lu J-J, Li Q-X, Gao C-Y, Liu X-H et al (2011) p75NTR regulates Aβ deposition by increasing Aβ production but inhibiting Aβ aggregation with its extracellular domain. J Neurosci 31(6):2292–2304
Zhou X-F, Wang Y-J (2011) The p75NTR extracellular domain: a potential molecule regulating the solubility and removal of amyloid-β. Prion 5(3):161–163
Alavian KN, Sgadò P, Alberi L, Subramaniam S, Simon HH (2009) Elevated P75 NTR expression causes death of engrailed-deficient midbrain dopaminergic neurons by Erk1/2 suppression. Neural Dev 4:1–13
Wang Y-Q, Bian G-L, Bai Y, Cao R, Chen L-W (2008) Identification and kainic acid-induced up-regulation of low-affinity p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) in the nigral dopamine neurons of adult rats. Neurochem Int 53(3–4):56–62
Savall ASP, Fidelis EM, de Mello JD, Quines CB, Denardin CC, Marques LS et al (2023) Neuroprotective effect of Eugenia uniflora against intranasal MPTP-induced memory impairments in rats: the involvement of pro-BDNF/p75NTR pathway. Life Sci 324:121711
Radomski SA (2022) Assay development for investigating the contributions of p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) signaling to neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease
Chen Y, Hou Y, Yang J, Du R, Chen C, Chen F et al (2018) P75 involved in the ubiquitination of α-synuclein in Rotenone-based Parkinson’s disease models. Neuroscience 388:367–373
Xu X-M, Dong M-X, Feng X, Liu Y, Pan J-X, Jia S-Y et al (2018) Decreased serum proNGF concentration in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci 39:91–96
Li W-W, Shen Y-Y, Chen D-W, Li H-Y, Shi Q-Q, Mei J et al (2019) Genetic association between NGFR, ADAM17 gene polymorphism, and Parkinson’s disease in the Chinese Han population. Neurotox Res 36:463–471
Lange J, Lunde KA, Sletten C, Møller SG, Tysnes O-B, Alves G et al (2015) Association of a BACE1 gene polymorphism with Parkinson’s disease in a Norwegian population. Parkinson’s Dis 2015:973298. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/973298
Shepheard SR, Chataway T, Schultz DW, Rush RA, Rogers M-L (2014) The extracellular domain of neurotrophin receptor p75 as a candidate biomarker for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One 9(1):e87398
Mufson EJ, Presley LN, Kordower JH (1991) Nerve growth factor receptor immunoreactivity within the nucleus basalis (Ch4) in Parkinson’s disease: reduced cell numbers and co-localization with cholinergic neurons. Brain Res 539(1):19–30
Long H-Z, Cheng Y, Zhou Z-W, Luo H-Y, Wen D-D, Gao L-C (2021) PI3K/AKT signal pathway: a target of natural products in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Front Pharmacol 12:648636
Jing P-B, Cao D-L, Li S-S, Zhu M, Bai X-Q, Wu X-B et al (2018) Chemokine receptor CXCR3 in the spinal cord contributes to chronic itch in mice. Neurosci Bull 34:54–63
Gong J, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Li X, Xia X-J, Liu Y-Y et al (2018) Lentiviral vector-mediated SHC3 silencing exacerbates oxidative stress injury in nigral dopamine neurons by regulating the PI3K-AKT-FoxO signaling pathway in rats with Parkinson’s disease. Cell Physiol Biochem 49(3):971–984
Costantini C, Della-Bianca V, Formaggio E, Chiamulera C, Montresor A, Rossi F (2005) The expression of p75 neurotrophin receptor protects against the neurotoxicity of soluble oligomers of β-amyloid. Exp Cell Res 311(1):126–134
Wang W, Ma C, Mao Z, Li M (2004) JNK inhibition as a potential strategy in treating Parkinson’s disease. Drug News Perspect 17(10):646–654
Hunot S, Vila M, Teismann P, Davis RJ, Hirsch EC, Przedborski S et al (2004) JNK-mediated induction of cyclooxygenase 2 is required for neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(2):665–670
Wang S, Zhang C, Sheng X, Zhang X, Wang B, Zhang G (2014) Peripheral expression of MAPK pathways in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. J Clin Neurosci 21(5):810–814
Oliveira MA, Heimfarth L, Passos FRS, Miguel-dos-Santos R, Mingori MR, Moreira JCF et al (2020) Naringenin complexed with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin improves the sciatic nerve regeneration through inhibition of p75NTR and JNK pathway. Life Sci 241:117102
Akao Y, Maruyama W, Yi H, Shamoto-Nagai M, Youdim MB, Naoi M (2002) An anti-Parkinson’s disease drug, N-propargyl-1 (R)-aminoindan (rasagiline), enhances expression of anti-apoptotic bcl-2 in human dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci Lett 326(2):105–108
Batiha GE, Al-Gareeb AI, Rotimi D, Adeyemi OS, Al-Kuraishy HM (2022) Common NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors and COVID-19: divide and conquer. Scientific African e01407
Hartmann A, Hunot S, Michel PP, Muriel M-P, Vyas S, Faucheux BA, et al. (2000) Caspase-3: a vulnerability factor and final effector in apoptotic death of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(6):2875-2880
Yamada M, Kida K, Amutuhaire W, Ichinose F, Kaneki M (2010) Gene disruption of caspase-3 prevents MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 402(2):312–318
Tatton NA (2000) Increased caspase 3 and Bax immunoreactivity accompany nuclear GAPDH translocation and neuronal apoptosis in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 166(1):29–43
Jellinger K (2000) Cell death mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 107:1–29
Bradshaw JM, Nguyen L, Wallace W, Li C, Sauer J-M, Bard F et al (2012) Monitoring signaling by the p75NTR receptor utilizing a caspase-3 activation assay amenable to small-molecule screening. Assay Drug Dev Technol 10(4):353–364
Song W, Volosin M, Cragnolini AB, Hempstead BL, Friedman WJ (2010) ProNGF induces PTEN via p75NTR to suppress Trk-mediated survival signaling in brain neurons. J Neurosci 30(46):15608–15615
Imbriani P, Tassone A, Meringolo M, Ponterio G, Madeo G, Pisani A et al (2019) Loss of non-apoptotic role of caspase-3 in the PINK1 mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 20(14):3407
Sekar S, Taghibiglou C (2018) Elevated nuclear phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and altered insulin signaling in substantia nigral region of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 666:139–143
Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu H (2020) Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):209
Barnabei L, Laplantine E, Mbongo W, Rieux-Laucat F, Weil R (2021) NF-κB: at the borders of autoimmunity and inflammation. Front Immunol 12:716469
Zhang T, Ma C, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu H (2021) NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. MedComm 2(4):618–653
Dolatshahi M, Ranjbar Hameghavandi MH, Sabahi M, Rostamkhani S (2021) Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) in pathophysiology of Parkinson disease: diverse patterns and mechanisms contributing to neurodegeneration. Eur J Neurosci 54(1):4101–4123
Bai Y, Li Q, Yang J, Zhou X, Yin X, Zhao D (2008) p75NTR activation of NF-κB is involved in PrP106-126-induced apoptosis in mouse neuroblastoma cells. Neurosci Res 62(1):9–14
Iyer M, Subramaniam MD, Venkatesan D, Cho S-G, Ryding M, Meyer M et al (2021) Role of RhoA-ROCK signaling in Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol 894:173815
Wang Q, Song L-J, Ding Z-B, Chai Z, Yu J-Z, Xiao B-G et al (2022) Advantages of Rho-associated kinases and their inhibitor fasudil for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res 17(12):2623
Yang B, Wang L, Nie Y, Wei W, Xiong W (2021) proBDNF expression induces apoptosis and inhibits synaptic regeneration by regulating the RhoA-JNK pathway in an in vitro post-stroke depression model. Transl Psychiatry 11(1):578
Miguez A, Garcia-Diaz Barriga G, Brito V, Straccia M, Giralt A, Ginés S et al (2015) Fingolimod (FTY720) enhances hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory in Huntington’s disease by preventing p75NTR up-regulation and astrocyte-mediated inflammation. Hum Mol Genet 24(17):4958–4970
Nordvall G, Forsell P, Sandin J (2022) Neurotrophin-targeted therapeutics: a gateway to cognition and more? Drug Discov Today
Conroy JN, Coulson EJ (2022) High-affinity TrkA and p75 neurotrophin receptor complexes: a twisted affair. J Biol Chem 298(3)
Numakawa T, Odaka H (2022) The role of neurotrophin signaling in age-related cognitive decline and cognitive diseases. Int J Mol Sci 23(14):7726
Zainullina L, Vakhitova YV, Lusta AY, Gudasheva T, Seredenin S (2021) Dimeric mimetic of BDNF loop 4 promotes survival of serum-deprived cell through TrkB-dependent apoptosis suppression. Sci Rep 11(1):7781
Zhang F, Lin X, Liu A, Chen J, Shan Z, Teng W et al (2021) Maternal subclinical hypothyroidism in rats impairs spatial learning and memory in offspring by disrupting balance of the TrkA/p75NTR signal pathway. Mol Neurobiol 58(9):4237–4250
Abdolahi S, Zare-Chahoki A, Noorbakhsh F, Gorji A (2022) A review of molecular interplay between neurotrophins and miRNAs in neuropsychological disorders. Mol Neurobiol 59(10):6260–6280
Khan N, Smith MT (2015) Neurotrophins and neuropathic pain: role in pathobiology. Molecules 20(6):10657–10688
Wang M, Xie Y, Qin D (2021) Proteolytic cleavage of proBDNF to mBDNF in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Bull 166:172–184
Siegel GJ, Chauhan NB (2000) Neurotrophic factors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease brain. Brain Res Rev 33(2–3):199–227
Daviaud N, Garbayo E, Sindji L, Martínez-Serrano A, Schiller PC, Montero-Menei CN (2015) Survival, differentiation, and neuroprotective mechanisms of human stem cells complexed with neurotrophin-3-releasing pharmacologically active microcarriers in an ex vivo model of Parkinson’s disease. Stem Cells Transl Med 4(6):670–684
Santos NAG, Martins NM, Sisti FM, Fernandes LS, Ferreira RS, Queiroz RHC et al (2015) The neuroprotection of cannabidiol against MPP+-induced toxicity in PC12 cells involves trkA receptors, upregulation of axonal and synaptic proteins, neuritogenesis, and might be relevant to Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol in Vitro 30(1):231–240
Salahuddin P, Fatima MT, Uversky VN, Khan RH, Islam Z, Furkan M (2021) The role of amyloids in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Int J Biol Macromol 1(190):44–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NHA, HMA-K, and AIA conceptualized the manuscript, wrote, edited, and reviewed the main text, and approved the final edition of the manuscript. SAA, HMS, and GE-SB prepared the figures, wrote, corrected, amended, and approved the final edition of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, N.H., Al-kuraishy, H.M., Al-Gareeb, A.I. et al. The Molecular Pathway of p75 Neurotrophin Receptor (p75NTR) in Parkinson’s Disease: The Way of New Inroads. Mol Neurobiol 61, 2469–2480 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03727-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03727-8