Abstract
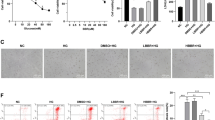
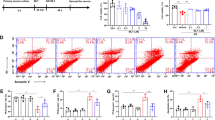
Hypoglycemia has emerged as a prominent complication in anti-diabetic drug therapy or negative energy balance of animals, which causes brain damage, cognitive impairment, and even death. Brain injury induced by hypoglycemia is closely related to oxidative stress and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The intracellular accumulation of ROS leads to neuronal damage, even death. Ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate (BHBA) not only serves as alternative energy source for glucose in extrahepatic tissues, but is also involved in cellular signaling transduction. Previous studies showed that BHBA reduces apoptosis by inhibiting the excessive production of ROS and activation of caspase-3. However, the effects of BHBA on apoptosis induced by glucose deprivation and its related molecular mechanisms have been seldom reported. In the present study, PC12 cells and primary cortical neurons were used to establish a low glucose injury model. The effects of BHBA on the survival and apoptosis in a glucose deficient condition and related molecular mechanisms were investigated by using flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, and western blotting. PC12 cells were incubated with 1 mM glucose for 24 h as a low glucose cell model, in which ROS accumulation and cell mortality were significantly increased. After 24 h and 48 h treatment with different concentrations of BHBA (0 mM, 0.05 mM, 0.5 mM, 1 mM, 2 mM), ROS production was significantly inhibited. Moreover, cell apoptosis rate was decreased and survival rate was significantly increased in 1 mM and 2 mM BHBA groups. In primary cortical neurons, at 24 h after treatment with 2 mM BHBA, the injured length and branch of neurites were significantly improved. Meanwhile, the intracellular ROS level, the proportion of c-Fos+ cells, apoptosis rate, and nuclear translocation of NF-κB protein after treatment with BHBA were significantly decreased when compared with that in low glucose cells. Importantly, the expression of p38, p-p38, NF-κB, and caspase-3 were significantly decreased, while the expression of p-ERK was significantly increased in both PC12 cells and primary cortical neurons. Our results demonstrate that BHBA decreased the accumulation of intracellular ROS, and further inhibited cell apoptosis by mediating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway and caspase-3 apoptosis cascade during glucose deprivation. In addition, BHBA inhibited apoptosis by activating ERK phosphorylation and alleviated the damage of low glucose to PC12 cells and primary cortical neurons. These results provide new insight into the anti-apoptotic effect of BHBA in a glucose deficient condition and the related signaling cascade.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- LG-CM:
-
Low glucose complete medium
- MG-CM:
-
5 MM medium glucose complete medium
- HG-CM:
-
25 MM high glucose complete medium
- BHBA:
-
β-Hydroxybutyrate
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- MTT:
-
Methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium bromide.
References
AAmiel S, Aschner P, Childs B et al (2019) Hypoglycaemia, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in diabetes: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. Lancet Diabet Endocrinol 7:385–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(18)30315-2
Achanta LB, Rae CD (2017) β-Hydroxybutyrate in the Brain: One Molecule. Multiple Mech Neurochem Res 42:35–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2099-2
Amador-Alvarado L, Montiel T, Massieu L (2014) Differential production of reactive oxygen species in distinct brain regions of hypoglycemic mice. Metab Brain Dis 29:711–719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9508-5
Amiel SA (2021) The consequences of hypoglycaemia. Diabetologia 64:963–970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-020-05366-3
Auer RN (2004) Hypoglycemic brain damage. Metab Brain Dis 19:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:mebr.0000043967.78763.5b
Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG (2009) Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 40:e331-339. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.108.531632
Chen H, Yoshioka H, Kim GS et al (2011) Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: mechanisms of cell death and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:1505–1517. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3576
Cheng B, Lu H, Bai B et al (2013) d-β-Hydroxybutyrate inhibited the apoptosis of PC12 cells induced by H2O2 via inhibiting oxidative stress. Neurochem Int 62:620–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2012.09.011
Choi IY, Lee SP, Kim SG et al (2001) In vivo measurements of brain glucose transport using the reversible Michaelis-Menten model and simultaneous measurements of cerebral blood flow changes during hypoglycemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:653–663. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004647-200106000-00003
Dąbek A, Wojtala M, Pirola L et al (2020) Modulation of cellular biochemistry, epigenetics and metabolomics by ketone bodies. Implications of the ketogenic diet in the physiology of the organism and pathological states. Nutrients. 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030788
De Angelis LC, Brigati G, Polleri G et al (2021) Neonatal hypoglycemia and brain vulnerability Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 12 634305. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.634305
Florez CM, Lukankin V, Sugumar S et al (2015) Hypoglycemia-induced alterations in hippocampal intrinsic rhythms: decreased inhibition, increased excitation, seizures and spreading depression. Neurobiol Dis 82:213–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.06.005
Fu SP, Wang JF, Xue WJ et al (2015) Anti-inflammatory effects of BHBA in both in vivo and in vitro Parkinson’s disease models are mediated by GPR109A-dependent mechanisms. J Neuroinflammation 12:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-014-0230-3
Green DR, Llambi F (2015) Cell death signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a006080
Isaev NK, Stel’mashuk EV, Zorov DB (2007) Cellular mechanisms of brain hypoglycemia. Biochemistry (mosc) 72:471–478. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0006297907050021
Jackson DA, Michael T, Vieira de Abreu A et al (2018) Prevention of severe hypoglycemia-induced brain damage and cognitive impairment with verapamil. Diabetes 67:2107–2112. https://doi.org/10.2337/db18-0008
Julio-Amilpas A, Montiel T, Soto-Tinoco E et al (2015) Protection of hypoglycemia-induced neuronal death by β-hydroxybutyrate involves the preservation of energy levels and decreased production of reactive oxygen species. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 35:851–860. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2015.1
Kauppinen TM, Chan WY, Suh SW et al (2006) Direct phosphorylation and regulation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 by extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:7136–7141. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508606103
Kilic E, Kilic U, Soliz J et al (2005) Brain-derived erythropoietin protects from focal cerebral ischemia by dual activation of ERK-1/-2 and Akt pathways. Faseb j 19:2026–2028. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.05-3941fje
Kittah NE, Vella A (2017) Management of endocrine disease: pathogenesis and management of hypoglycemia. Eur J Endocrinol 177:R37-r47. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje-16-1062
Kuo WT, Shen L, Zuo L et al (2019) Inflammation-induced occludin downregulation limits epithelial apoptosis by suppressing caspase-3 expression. Gastroenterology 157:1323–1337. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.058
Lacy ME, Gilsanz P, Eng C et al (2020) Severe hypoglycemia and cognitive function in older adults with type 1 diabetes: the study of longevity in diabetes (SOLID). Diabetes Care 43:541–548. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-0906
Lamichhane S, Bastola T, Pariyar R et al (2017) ROS production and ERK activity are involved in the effects of d-β-hydroxybutyrate and metformin in a glucose deficient Condition Int J Mol Sci 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030674
Liu Y, Song XD, Liu W et al (2003) Glucose deprivation induces mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in PC12 cell line. J Cell Mol Med 7:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2003.tb00202.x
Ma YL, Zhang LX, Liu GL et al (2017) N-Myc Downstream-regulated gene 2 (Ndrg2) Is Involved in ischemia-hypoxia-induced Astrocyte Apoptosis: a Novel Target for Stroke Therapy. Mol Neurobiol 54:3286–3299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9814-5
Maalouf M, Sullivan PG, Davis L et al (2007) Ketones inhibit mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species production following glutamate excitotoxicity by increasing NADH oxidation. Neuroscience 145:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.11.065
McNay EC, McCarty RC, Gold PE (2001) Fluctuations in brain glucose concentration during behavioral testing: dissociations between brain areas and between brain and blood. Neurobiol Learn Mem 75:325–337. https://doi.org/10.1006/nlme.2000.3976
Medina MG, Ledesma MD, Domínguez JE et al (2005) Tissue plasminogen activator mediates amyloid-induced neurotoxicity via Erk1/2 activation. Embo j 24:1706–1716. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600650
Mohseni S (2001) Hypoglycemic neuropathy. Acta Neuropathol 102:413–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010100459
Moley KH, Mueckler MM (2000) Glucose transport and apoptosis. Apoptosis 5:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1009697908332
Najm NA, Zimmermann L, Dietrich O et al (2020) Associations between motion activity, ketosis risk and estrus behavior in dairy cattle. Prev Vet Med 175:104857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed.2019.104857
Newman JC, Verdin E (2017) β-Hydroxybutyrate: a signaling metabolite. Annu Rev Nutr 37:51–76. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064916
Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Du XL et al (2000) Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature 404:787–790. https://doi.org/10.1038/35008121
Páramo B, Montiel T, Hernández-Espinosa DR et al (2013) Calpain activation induced by glucose deprivation is mediated by oxidative stress and contributes to neuronal damage. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45:2596–2604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2013.08.013
Pierozan P, Cattani D, Karlsson O (2020) Hippocampal neural stem cells are more susceptible to the neurotoxin BMAA than primary neurons: effects on apoptosis, cellular differentiation, neurite outgrowth, and DNA methylation. Cell Death Dis 11:910. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03093-6
Puchalska P, Crawford PA (2017) Multi-dimensional roles of ketone bodies in fuel metabolism, signaling, and therapeutics. Cell Metab 25:262–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.12.022
Qi S, Feng Z, Li Q et al (2018) Inhibition of ROS-mediated activation Src-MAPK/AKT signaling by orientin alleviates H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:3973–3984. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.S178217
Rehni AK, Dave KR (2018) Impact of hypoglycemia on brain metabolism during diabetes. Mol Neurobiol 55:9075–9088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1044-6
Sánchez-Temprano A, Relova JL, Camiña JP et al (2021) Concurrent Akt, ERK1/2 and AMPK activation by obestatin inhibits apoptotic signaling cascades on nutrient-deprived PC12 cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. Epub ahead of print 2021/01/06. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-01025-8
Shen T, Huang Z, Shi C et al (2020) Pancreatic cancer-derived exosomes induce apoptosis of T lymphocytes through the p38 MAPK-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress. Faseb J 34:8442–8458. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201902186R
Sheng M, Greenberg ME (1990) The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron 4:477–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-6273(90)90106-p
Shimazu T, Hirschey MD, Newman J et al (2013) Suppression of oxidative stress by β-hydroxybutyrate, an endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science 339:211–214. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1227166
Shippy DC, Wilhelm C, Viharkumar PA et al (2020) β-hydroxybutyrate inhibits inflammasome activation to attenuate Alzheimer’s disease pathology. J Neuroinflammation 17:280. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01948-5
Stanley S, Moheet A, Seaquist ER (2019) Central mechanisms of glucose sensing and counterregulation in defense of hypoglycemia. Endocr Rev 40:768–788. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2018-00226
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L et al (2014) p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Lett 344:174–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.11.019
Tajima T, Yoshifuji A, Matsui A et al (2019) β-hydroxybutyrate attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through its anti-pyroptotic effects. Kidney Int 95:1120–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2018.11.034
Ułamek-Kozioł M, Czuczwar SJ, Januszewski S et al (2019) Ketogenic diet and epilepsy Nutrients 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102510
Uzdensky AB (2019) Apoptosis regulation in the penumbra after ischemic stroke: expression of pro- and antiapoptotic proteins. Apoptosis 24:687–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-019-01556-6
Wang S, Li X, Zhang Q et al (2020) Nyap1 regulates multipolar-bipolar transition and morphology of migrating neurons by fyn phosphorylation during corticogenesis. Cereb Cortex 30:929–941. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhz137
Wesley UV, Sutton IC, Cunningham K et al (2021) Galectin-3 protects against ischemic stroke by promoting neuro-angiogenesis via apoptosis inhibition and Akt/Caspase regulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 41:857–873. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678x20931137
White H, Venkatesh B (2011) Clinical review: ketones and brain injury. Crit Care 15:219. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc10020
Wiatrak B, Kubis-Kubiak A, Piwowar A et al (2020) PC12 cell line: cell types, coating of culture vessels, differentiation and other culture conditions Cells 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040958
Wu DM, Zhang YT, Lu J et al (2018) Effects of microRNA-129 and its target gene c-Fos on proliferation and apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in rats with epilepsy via the MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 233:6632–6643. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26297
Wu L, Xiong X, Wu X et al (2020a) Targeting oxidative stress and inflammation to prevent ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Mol Neurosci 13:28. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2020.00028
Wu Y, Gong Y, Luan Y et al (2020b) BHBA treatment improves cognitive function by targeting pleiotropic mechanisms in transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Faseb j 34:1412–1429. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201901984R
Yao Y, Cui L, Ye J et al (2020) Dioscin facilitates ROS-induced apoptosis via the p38-MAPK/HSP27-mediated pathways in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci 16:2883–2894. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.45710
Yoshinaga A, Kajihara N, Kukidome D et al (2021) Hypoglycemia induces mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production through increased fatty acid oxidation and promotes retinal vascular permeability in diabetic mice. Antioxid Redox Signal 34:1245–1259. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2019.8008
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31802154), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFE0127000), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 2019T120957), Shaanxi Provincial Regional Innovation Capability Guiding Plan Project (No. 2020QFY10-04), and General Project of Basic Research of Shaanxi Province (No. 2021JM-492).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cixia Li: writing — original draft, methodology, investigation, data curation; Xuejun Chai: writing — review and editing, validation, investigation; Jiarong Pan: methodology, visualization, investigation, data curation, Jian Huang: validation, investigation; Yongji Wu: methodology, investigation; Yuhuan Xue: investigation; Wentai Zhou: data curation; Jiping Yang: methodology; Xiaoyan Zhu: conceptualization, writing — review and editing, funding acquisition, supervision; Shanting Zhao: writing — review and editing, funding acquisition, resources, project administration.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
No human studies were carried out by the authors for this article. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained for each participant.
Consent for Publication
All participants consented to publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Chai, X., Pan, J. et al. β-Hydroxybutyrate Alleviates Low Glucose–Induced Apoptosis via Modulation of ROS-Mediated p38 MAPK Signaling. J Mol Neurosci 72, 923–938 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-01974-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-01974-3