Abstract
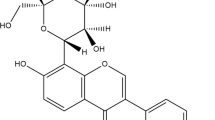
Ergothioneine (ET) is a naturally occurring antioxidant and cytoprotective agent that is synthesized by fungi and certain bacteria. Recent studies have shown a beneficial effect of ET on neurological functions, including cognition and animal models of depression. The aim of this study is to elucidate a possible effect of ET in rodent models of stroke. Post-ischemic intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) infusion of ET significantly reduced brain infarct volume by as early as 1 day after infusion in rats, as shown by triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) assay. There was a dose-dependent increase in protection, from 50 to 200 ng of ET infusion. These results suggest that ET could have a protective effect on CNS neurons. We next elucidated the effect of systemic ET on brain infarct volume in mice after stroke. Daily i.p. injection of 35 mg/kg ET (the first dose being administered 3 h after stroke) had no significant effect on infarct volume. However, daily i.p. injections of 70 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, 125 mg/kg and 150 mg/kg ET, with the first dose administered 3 h after stroke, significantly decreased infarct volume at 7 days after vessel occlusion in mice. In order to elucidate at what time interval during the 7 days there could be effective protection, a second set of experiments was carried out in mice, using one of the effective loading protocols, i.e. 125 mg/kg i.p. ET but the brains were analyzed at 1, 4 and 7 days post-stroke by MRI. We found that ET was already protective against neuronal injury and decreased the size of the brain infarct from as early as 1 day post-stroke. Behavioral experiments carried out on a third set of mice (using 125 mg/kg i.p. ET) showed that this was accompanied by significant improvements in certain behaviors (pole test) at 1 day after stroke. Together, results of this study indicate that i.c.v. and systemic ET are effective in reducing brain infarct volume after stroke in rodent models.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akanmu, D., Cecchini, R., Aruoma, O. I., & Halliwell, B. (1991). The antioxidant action of ergothioneine. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 288(1), 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(91)90158-f
Bedirli, A., Sakrak, O., Muhtaroglu, S., Soyuer, I., Guler, I., Riza Erdogan, A., et al. (2004). Ergothioneine pretreatment protects the liver from ischemia–reperfusion injury caused by increasing hepatic heat shock protein 70. Journal of Surgical Research, 122(1), 96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2004.06.016
Beelman, R. B., Phillips, A. T., Richie, J. P., Jr., Ba, D. M., Duiker, S. W., & Kalaras, M. D. (2022). Health consequences of improving the content of ergothioneine in the food supply. FEBS Letters, 596(10), 1231–1240. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.14268
Behof, W. J., Whitmore, C. A., Haynes, J. R., Rosenberg, A. J., Tantawy, M. N., Peterson, T. E., et al. (2022). Improved synthesis of an ergothioneine PET radioligand for imaging oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. FEBS Letters, 596(10), 1279–1289. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.14303
Brouns, R., & De Deyn, P. P. (2009). The complexity of neurobiological processes in acute ischemic stroke. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery, 111(6), 483–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2009.04.001
Butterfield, D. A., & Halliwell, B. (2019). Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 20(3), 148–160. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-019-0132-6
Cheah, I. K., Feng, L., Tang, R. M. Y., Lim, K. H. C., & Halliwell, B. (2016). Ergothioneine levels in an elderly population decrease with age and incidence of cognitive decline; a risk factor for neurodegeneration? Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 478(1), 162–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.07.074
Cheah, I. K., & Halliwell, B. (2021). Ergothioneine, recent developments. Redox Biology, 42, 101868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.101868
Cheah, I. K., Tang, R. M., Yew, T. S., Lim, K. H., & Halliwell, B. (2017). Administration of pure ergothioneine to healthy human subjects: Uptake, metabolism, and effects on biomarkers of oxidative damage and inflammation. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 26(5), 193–206. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2016.6778
Dare, A., Elrashedy, A. A., Channa, M. L., & Nadar, A. (2022). Cardioprotective effects and in-silico antioxidant mechanism of l-ergothioneine in experimental type-2 diabetic rats. Cardiovascular & Hematological Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 20(2), 133–147. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871525719666210809122541
Gokce, G., & Arun, M. Z. (2014). Ergothioneine produces relaxation in isolated rat aorta by inactivating superoxide anion. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 18(21), 3339–3345.
Grigat, S., Harlfinger, S., Pal, S., Striebinger, R., Golz, S., Geerts, A., et al. (2007). Probing the substrate specificity of the ergothioneine transporter with methimazole, hercynine, and organic cations. Biochemical Pharmacology, 74(2), 309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2007.04.015
Grundemann, D., Harlfinger, S., Golz, S., Geerts, A., Lazar, A., Berkels, R., et al. (2005). Discovery of the ergothioneine transporter. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(14), 5256–5261. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0408624102
Gründemann, D., Hartmann, L., & Flögel, S. (2022). The ergothioneine transporter (ETT): Substrates and locations, an inventory. FEBS Letters, 596(10), 1252–1269. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.14269
Halliwell, B. (2006). Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: Where are we now? Journal of Neurochemistry, 97(6), 1634–1658. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03907.x
Halliwell, B., & Cheah, I. (2022). Ergothioneine, where are we now? FEBS Letters, 596(10), 1227–1230. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.14350
Halliwell, B., Cheah, I. K., & Tang, R. M. Y. (2018). Ergothioneine—A diet-derived antioxidant with therapeutic potential. FEBS Letters, 592(20), 3357–3366. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13123
Ishimoto, T., & Kato, Y. (2022). Ergothioneine in the brain. FEBS Letters, 596(10), 1290–1298. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.14271
Ishimoto, T., Masuo, Y., Kato, Y., & Nakamichi, N. (2019). Ergothioneine-induced neuronal differentiation is mediated through activation of S6K1 and neurotrophin 4/5-TrkB signaling in murine neural stem cells. Cellular Signalling, 53, 269–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.10.012
Ishimoto, T., Nakamichi, N., Hosotani, H., Masuo, Y., Sugiura, T., & Kato, Y. (2014). Organic cation transporter-mediated ergothioneine uptake in mouse neural progenitor cells suppresses proliferation and promotes differentiation into neurons. PLoS ONE, 9(2), e89434. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089434
Jang, J. H., Aruoma, O. I., Jen, L. S., Chung, H. Y., & Surh, Y. J. (2004). Ergothioneine rescues PC12 cells from beta-amyloid-induced apoptotic death. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 36(3), 288–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2003.11.005
Kato, Y., Kubo, Y., Iwata, D., Kato, S., Sudo, T., Sugiura, T., et al. (2010). Gene knockout and metabolome analysis of carnitine/organic cation transporter OCTN1. Pharmaceutical Research, 27(5), 832–840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0076-z
Koh, S. S., Ooi, S. C., Lui, N. M., Qiong, C., Ho, L. T., Cheah, I. K., et al. (2021). Effect of ergothioneine on 7-ketocholesterol-induced endothelial injury. Neuromolecular Medicine, 23(1), 184–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-020-08620-4
Li, R. W., Yang, C., Sit, A. S., Kwan, Y. W., Lee, S. M., Hoi, M. P., et al. (2014). Uptake and protective effects of ergothioneine in human endothelial cells. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 350(3), 691–700. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.114.214049
Li, W. W., Wei, Y. H., Li, H., Lai, D. M., & Lin, T. N. (2013). Isolation and characterization of a novel strain of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse umbilical cord: Potential application in cell-based therapy. PLoS ONE, 8(8), e74478. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0074478
Lin, H., Lin, T. N., Cheung, W. M., Nian, G. M., Tseng, P. H., Chen, S. F., et al. (2002a). Cyclooxygenase-1 and bicistronic cyclooxygenase-1/prostacyclin synthase gene transfer protect against ischemic cerebral infarction. Circulation, 105(16), 1962–1969. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000015365.49180.05
Lin, T. N., He, Y. Y., Wu, G., Khan, M., & Hsu, C. Y. (1993). Effect of brain edema on infarct volume in a focal cerebral ischemia model in rats. Stroke, 24(1), 117–121. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.24.1.117
Lin, T. N., Sun, S. W., Cheung, W. M., Li, F., & Chang, C. (2002b). Dynamic changes in cerebral blood flow and angiogenesis after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Evaluation with serial magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke, 33(12), 2985–2991. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.0000037675.97888.9d
Mehta, S. L., Manhas, N., & Raghubir, R. (2007). Molecular targets in cerebral ischemia for developing novel therapeutics. Brain Research Reviews, 54(1), 34–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2006.11.003
Moncaster, J. A., Walsh, D. T., Gentleman, S. M., Jen, L. S., & Aruoma, O. I. (2002). Ergothioneine treatment protects neurons against N-methyl-d-aspartate excitotoxicity in an in vivo rat retinal model. Neuroscience Letters, 328(1), 55–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(02)00427-5
Nagarajan, S., Chellappan, D. R., Chinnaswamy, P., & Thulasingam, S. (2015). Ferulic acid pretreatment mitigates MPTP-induced motor impairment and histopathological alterations in C57BL/6 mice. Pharmaceutical Biology, 53(11), 1591–1601. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.993041
Nakamichi, N., Nakao, S., Nishiyama, M., Takeda, Y., Ishimoto, T., Masuo, Y., et al. (2021). Oral administration of the food-derived hydrophilic antioxidant ergothioneine enhances object recognition memory in mice. Current Molecular Pharmacology, 14(2), 220–233. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874467213666200212102710
Nakamichi, N., Nakayama, K., Ishimoto, T., Masuo, Y., Wakayama, T., Sekiguchi, H., et al. (2016). Food-derived hydrophilic antioxidant ergothioneine is distributed to the brain and exerts antidepressant effect in mice. Brain and Behavior: A Cognitive Neuroscience Perspective, 6(6), e00477. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.477
Nakamichi, N., Taguchi, T., Hosotani, H., Wakayama, T., Shimizu, T., Sugiura, T., et al. (2012). Functional expression of carnitine/organic cation transporter OCTN1 in mouse brain neurons: Possible involvement in neuronal differentiation. Neurochemistry International, 61(7), 1121–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2012.08.004
Paul, B. D., & Snyder, S. H. (2010). The unusual amino acid l-ergothioneine is a physiologic cytoprotectant. Cell Death and Differentiation, 17(7), 1134–1140. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.163
Sakrak, O., Kerem, M., Bedirli, A., Pasaoglu, H., Akyurek, N., Ofluoglu, E., et al. (2008). Ergothioneine modulates proinflammatory cytokines and heat shock protein 70 in mesenteric ischemia and reperfusion injury. Journal of Surgical Research, 144(1), 36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2007.04.020
Seo, H. B., Kang, B. K., Kim, J. H., Choi, Y. W., Hong, J. W., Choi, B. T., et al. (2015). Partially purified components of Uncaria sinensis attenuate blood brain barrier disruption after ischemic brain injury in mice. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 15, 157. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0678-4
Shen, Z., Xiang, M., Chen, C., Ding, F., Wang, Y., Shang, C., et al. (2022). Glutamate excitotoxicity: Potential therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 151, 113125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113125
Song, T. Y., Lin, H. C., Chen, C. L., Wu, J. H., Liao, J. W., & Hu, M. L. (2014). Ergothioneine and melatonin attenuate oxidative stress and protect against learning and memory deficits in C57BL/6J mice treated with d-galactose. Free Radical Research, 48(9), 1049–1060. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2014.920954
Stoll, G., & Nieswandt, B. (2019). Thrombo-inflammation in acute ischaemic stroke—Implications for treatment. Nature Reviews. Neurology, 15(8), 473–481. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-019-0221-1
Tang, R. M. Y., Cheah, I. K., Yew, T. S. K., & Halliwell, B. (2018). Distribution and accumulation of dietary ergothioneine and its metabolites in mouse tissues. Science and Reports, 8(1), 1601. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20021-z
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. (1995). Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. New England Journal of Medicine, 333(24), 1581–1587. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199512143332401
Tucker, R. A. J., Cheah, I. K., & Halliwell, B. (2019). Specificity of the ergothioneine transporter natively expressed in HeLa cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 513(1), 22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.02.122
Wei, Z. Z., Chen, D., Lee, M. J. H., Zhao, Y., Gu, X., Yu, S. P., et al. (2021). dl-3-n-butylphthalide increases collateriogenesis and functional recovery after focal ischemic stroke in mice. Aging & Disease, 12(7), 1835–1849. https://doi.org/10.14336/ad.2020.1226
Wu, J. S., Cheung, W. M., Tsai, Y. S., Chen, Y. T., Fong, W. H., Tsai, H. D., et al. (2009). Ligand-activated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma protects against ischemic cerebral infarction and neuronal apoptosis by 14-3-3 epsilon upregulation. Circulation, 119(8), 1124–1134. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.812537
Wu, J. S., Kao, M. H., Tsai, H. D., Cheung, W. M., Chen, J. J., Ong, W. Y., et al. (2018). Clinacanthus nutans mitigates neuronal apoptosis and ischemic brain damage through augmenting the C/EBPβ-driven PPAR-γ transcription. Molecular Neurobiology, 55(7), 5425–5438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0776-z
Wu, L. Y., Cheah, I. K., Chong, J. R., Chai, Y. L., Tan, J. Y., Hilal, S., et al. (2021). Low plasma ergothioneine levels are associated with neurodegeneration and cerebrovascular disease in dementia. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 177, 201–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.10.019
Yang, N. C., Lin, H. C., Wu, J. H., Ou, H. C., Chai, Y. C., Tseng, C. Y., et al. (2012). Ergothioneine protects against neuronal injury induced by beta-amyloid in mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 50(11), 3902–3911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.08.021
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Tetrahedron (Paris, France) for provision of the l-ergothioneine used in these studies. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Singapore (R-181-000-183-114, WYO), HCLA (Catalyst Grant, HLCA21Jan-0019, WYO); and grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology (MoST) and Academia Sinica, Taiwan (TNL). We thank the Animal Image Facility (AIF), Academia Sinica and Taiwan Animal Consortium for the technical support in MRI analysis. We thank Professor Barry Halliwell, Department of Biochemistry, National University of Singapore for valuable discussion and suggestions on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WYO, DMKL, IKMC and TNL wrote and edited the main manuscript text. MHK and WMC prepared figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ong, WY., Kao, MH., Cheung, WM. et al. Protective Effect of Ergothioneine Against Stroke in Rodent Models. Neuromol Med 25, 205–216 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-022-08727-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-022-08727-w