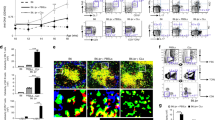
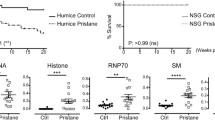
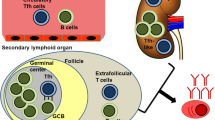
Abstract
Biases in the distribution and phenotype of T, B, and antigen-presenting cell populations are strongly connected to mechanisms of disease development in mouse models of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Here, we describe longitudinal changes in lymphoid and antigen-presenting cell subsets in bone marrow, blood and spleen from two lupus-prone strains (MRL/lpr and B6.Sle1.Sle2.Sle3 tri-congenic mice), and how they integrate in our present understanding of the pathogenesis of the disease. In particular, we focus on (autoreactive) T cell activation patterns in lupus-prone mice. Break of T cell tolerance to chromatin constituents (histone peptides) is key to the development of the disease and is related to T cell intrinsic defects, contributed by genetic susceptibility factors and by extrinsic amplificatory mechanisms, in particular over-stimulation by antigen-presenting cells. We also describe shifts in B cell sub-populations, going from skewed immature B cell populations as an indication of disturbed central and peripheral tolerance checkpoints, to enriched long-lived plasma cells, which are key to persistent autoantibody production in the disease. B cell activation mechanisms in SLE are both T cell-dependent (break of tolerance and production of specific autoantibodies) and -independent (polyclonal B cell activation, production of autoantibodies by long-lived plasma cells). By providing a comprehensive evaluation of B and T cell surface markers in two major mouse models of SLE and a description of their changes before and after disease onset, this review illustrates how the study of lymphoid cell phenotype delivers key information regarding pathogenic pathways and supplies tools to assess the beneficial effects of novel therapeutic interventions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wandstrat A, Wakeland E (2001) The genetics of complex autoimmune diseases: non-MHC susceptibility genes. Nat Immunol 2(9):802–809. doi:10.1038/ni0901-802
Lauwerys BR, Wakeland EK (2005) Genetics of lupus nephritis. Lupus 14(1):2–12
Limaye N, Belobrajdic KA, Wandstrat AE, Bonhomme F, Edwards SV, Wakeland EK (2008) Prevalence and evolutionary origins of autoimmune susceptibility alleles in natural mouse populations. Genes Immun 9(1):61–68. doi:10.1038/sj.gene.6364446
Konsta OD, Le Dantec C, Charras A, Brooks WH, Arleevskaya MI, Bordron A, Renaudineau Y (2015) An in silico approach reveals associations between genetic and epigenetic factors within regulatory elements in B cells from primary Sjogren’s syndrome patients. Front Immunol 6:437. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2015.00437
Konsta OD, Le Dantec C, Brooks WH, Renaudineau Y (2015) Genetics and Epigenetics of Autoimmune Diseases. eLS:1–9. doi: 10.1002/9780470015902.a0023593
Renaudineau Y, Ballestar E (2016) Epigenetics: DNA methylation signatures in Sjogren syndrome. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12(10):565–566. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2016.144
Charras A, Konsta OD, Le Dantec C, Bagacean C, Kapsogeorgou EK, Tzioufas AG, Pers JO, Bordron A, Renaudineau Y (2017) Cell-specific epigenome-wide DNA methylation profile in long-term cultured minor salivary gland epithelial cells from patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 76(3):625–628. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210167
Morel L, Rudofsky UH, Longmate JA, Schiffenbauer J, Wakeland EK (1994) Polygenic control of susceptibility to murine systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 1(3):219–229
Morel L, Yu Y, Blenman KR, Caldwell RA, Wakeland EK (1996) Production of congenic mouse strains carrying genomic intervals containing SLE-susceptibility genes derived from the SLE-prone NZM2410 strain. Mammalian genome : official journal of the International Mammalian Genome Society 7(5):335–339
Morel L, Croker BP, Blenman KR, Mohan C, Huang G, Gilkeson G, Wakeland EK (2000) Genetic reconstitution of systemic lupus erythematosus immunopathology with polycongenic murine strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(12):6670–6675
Khamashta M, Merrill JT, Werth VP, Furie R, Kalunian K, Illei GG, Drappa J, Wang L, Greth W, investigators CDs (2016) Sifalimumab, an anti-interferon-alpha monoclonal antibody, in moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Ann Rheum Dis 75(11):1909–1916. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208562
Peng L, Oganesyan V, Wu H, Dall’Acqua WF, Damschroder MM (2015) Molecular basis for antagonistic activity of anifrolumab, an anti-interferon-alpha receptor 1 antibody. MAbs 7(2):428–439. doi:10.1080/19420862.2015.1007810
Lauwerys BR, Hachulla E, Spertini F, Lazaro E, Jorgensen C, Mariette X, Haelterman E, Grouard-Vogel G, Fanget B, Dhellin O, Vandepapeliere P, Houssiau FA (2013) Down-regulation of interferon signature in systemic lupus erythematosus patients by active immunization with interferon alpha-kinoid. Arthritis & Rheumatism 65(2):447–456. doi:10.1002/art.37785
Ducreux J, Houssiau FA, Vandepapeliere P, Jorgensen C, Lazaro E, Spertini F, Colaone F, Roucairol C, Laborie M, Croughs T, Grouard-Vogel G, Lauwerys BR (2016) Interferon alpha kinoid induces neutralizing anti-interferon alpha antibodies that decrease the expression of interferon-induced and B cell activation associated transcripts: analysis of extended follow-up data from the interferon alpha kinoid phase I/II study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 55(10):1901–1905. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kew262
Liu Z, Bethunaickan R, Huang W, Lodhi U, Solano I, Madaio MP, Davidson A (2011) Interferon-alpha accelerates murine systemic lupus erythematosus in a T cell-dependent manner. Arthritis & Rheumatism 63(1):219–229. doi:10.1002/art.30087
Mathian A, Weinberg A, Gallegos M, Banchereau J, Koutouzov S (2005) IFN-alpha induces early lethal lupus in preautoimmune (New Zealand black x New Zealand White) F1 but not in BALB/c mice. J Immunol 174(5):2499–2506
Fairhurst AM, Mathian A, Connolly JE, Wang A, Gray HF, George TA, Boudreaux CD, Zhou XJ, Li QZ, Koutouzov S, Banchereau J, Wakeland EK (2008) Systemic IFN-alpha drives kidney nephritis in B6.Sle123 mice. Eur J Immunol 38(7):1948–1960. doi:10.1002/eji.200837925
Vidal S, Kono DH, Theofilopoulos AN (1998) Loci predisposing to autoimmunity in MRL-Fas lpr and C57BL/6-Faslpr mice. J Clin Invest 101(3):696–702. doi:10.1172/JCI1817
Ichii O, Konno A, Sasaki N, Endoh D, Hashimoto Y, Kon Y (2008) Autoimmune glomerulonephritis induced in congenic mouse strain carrying telomeric region of chromosome 1 derived from MRL/MpJ. Histol Histopathol 23(4):411–422
Santiago-Raber ML, Haraldsson MK, Theofilopoulos AN, Kono DH (2007) Characterization of reciprocal Lmb1-4 interval MRL-Faslpr and C57BL/6-Faslpr congenic mice reveals significant effects from Lmb3. J Immunol 178(12):8195–8202
Kong PL, Morel L, Croker BP, Craft J (2004) The centromeric region of chromosome 7 from MRL mice (Lmb3) is an epistatic modifier of Fas for autoimmune disease expression. J Immunol 172(5):2785–2794
Yamada A, Miyazaki T, Lu LM, Ono M, Ito MR, Terada M, Mori S, Hata K, Nozaki Y, Nakatsuru S, Nakamura Y, Onji M, Nose M (2003) Genetic basis of tissue specificity of vasculitis in MRL/lpr mice. Arthritis & Rheumatism 48(5):1445–1451. doi:10.1002/art.10952
Kamogawa J, Terada M, Mizuki S, Nishihara M, Yamamoto H, Mori S, Abe Y, Morimoto K, Nakatsuru S, Nakamura Y, Nose M (2002) Arthritis in MRL/lpr mice is under the control of multiple gene loci with an allelic combination derived from the original inbred strains. Arthritis & Rheumatism 46(4):1067–1074
Nishihara M, Terada M, Kamogawa J, Ohashi Y, Mori S, Nakatsuru S, Nakamura Y, Nose M (1999) Genetic basis of autoimmune sialadenitis in MRL/lpr lupus-prone mice: additive and hierarchical properties of polygenic inheritance. Arthritis & Rheumatism 42(12):2616–2623. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199912)42:12<2616::AID-ANR16>3.0.CO;2-O
Subramanian S, Tus K, Li QZ, Wang A, Tian XH, Zhou J, Liang C, Bartov G, McDaniel LD, Zhou XJ, Schultz RA, Wakeland EK (2006) A Tlr7 translocation accelerates systemic autoimmunity in murine lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(26):9970–9975. doi:10.1073/pnas.0603912103
Fairhurst AM, Hwang SH, Wang A, Tian XH, Boudreaux C, Zhou XJ, Casco J, Li QZ, Connolly JE, Wakeland EK (2008) Yaa autoimmune phenotypes are conferred by overexpression of TLR7. Eur J Immunol 38(7):1971–1978. doi:10.1002/eji.200838138
Hanrotel-Saliou C, Segalen I, Le Meur Y, Youinou P, Renaudineau Y (2011) Glomerular antibodies in lupus nephritis. Clinical reviews in allergy & immunology 40(3):151–158. doi:10.1007/s12016-010-8204-4
Seret G, Canas F, Pougnet-Di Costanzo L, Hanrotel-Saliou C, Jousse-Joulin S, Le Meur Y, Saraux A, Valeri A, Putterman C, Youinou P, Rojas-Villarraga A, Anaya JM, Renaudineau Y (2015) Anti-alpha-actinin antibodies are part of the anti-cell membrane antibody spectrum that characterize patients with lupus nephritis. J Autoimmun 61:54–61. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2015.05.009
Renaudineau Y, Croquefer S, Jousse S, Renaudineau E, Devauchelle V, Gueguen P, Hanrotel C, Gilburd B, Saraux A, Shoenfeld Y, Putterman C, Youinou P (2006) Association of alpha-actinin-binding anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies with lupus nephritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 54(8):2523–2532. doi:10.1002/art.22015
Xie C, Zhou XJ, Liu X, Mohan C (2003) Enhanced susceptibility to end-organ disease in the lupus-facilitating NZW mouse strain. Arthritis & Rheumatism 48(4):1080–1092. doi:10.1002/art.10887
Li QZ, Zhou J, Yang R, Yan M, Ye Q, Liu K, Liu S, Shao X, Li L, Zhou XJ, Wakeland EK, Mohan C (2009) The lupus-susceptibility gene kallikrein downmodulates antibody-mediated glomerulonephritis. Genes Immun 10(5):503–508. doi:10.1038/gene.2009.7
Mohan C, Adams S, Stanik V, Datta SK (1993) Nucleosome: a major immunogen for pathogenic autoantibody-inducing T cells of lupus. J Exp Med 177(5):1367–1381
Lu L, Kaliyaperumal A, Boumpas DT, Datta SK (1999) Major peptide autoepitopes for nucleosome-specific T cells of human lupus. J Clin Invest 104(3):345–355. doi:10.1172/JCI6801
Wofsy D, Seaman WE (1985) Successful treatment of autoimmunity in NZB/NZW F1 mice with monoclonal antibody to L3T4. J Exp Med 161(2):378–391
Wofsy D, Seaman WE (1987) Reversal of advanced murine lupus in NZB/NZW F1 mice by treatment with monoclonal antibody to L3T4. J Immunol 138(10):3247–3253
Carteron NL, Wofsy D, Schimenti C, Ermak TH (1990) F(ab’)2 anti-CD4 and intact anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies inhibit the accumulation of CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and B cells in the kidneys of lupus-prone NZB/NZW mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 56(3):373–383
Connolly K, Roubinian JR, Wofsy D (1992) Development of murine lupus in CD4-depleted NZB/NZW mice. Sustained inhibition of residual CD4+ T cells is required to suppress autoimmunity. J Immunol 149(9):3083–3088
Santoro TJ, Portanova JP, Kotzin BL (1988) The contribution of L3T4+ T cells to lymphoproliferation and autoantibody production in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. J Exp Med 167(5):1713–1718
Merino R, Iwamoto M, Fossati L, Izui S (1993) Polyclonal B cell activation arises from different mechanisms in lupus-prone (NZB x NZW)F1 and MRL/MpJ-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol 151(11):6509–6516
Chesnutt MS, Finck BK, Killeen N, Connolly MK, Goodman H, Wofsy D (1998) Enhanced lymphoproliferation and diminished autoimmunity in CD4-deficient MRL/lpr mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 87(1):23–32
Mohan C, Alas E, Morel L, Yang P, Wakeland EK (1998) Genetic dissection of SLE pathogenesis. Sle1 on murine chromosome 1 leads to a selective loss of tolerance to H2A/H2B/DNA subnucleosomes. J Clin Invest 101(6):1362–1372
Sobel ES, Satoh M, Chen Y, Wakeland EK, Morel L (2002) The major murine systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility locus Sle1 results in abnormal functions of both B and T cells. J Immunol 169(5):2694–2700
Sobel ES, Mohan C, Morel L, Schiffenbauer J, Wakeland EK (1999) Genetic dissection of SLE pathogenesis: adoptive transfer of Sle1 mediates the loss of tolerance by bone marrow-derived B cells. J Immunol 162(4):2415–2421
Wandstrat AE, Nguyen C, Limaye N, Chan AY, Subramanian S, Tian XH, Yim YS, Pertsemlidis A, Garner HR Jr, Morel L, Wakeland EK (2004) Association of extensive polymorphisms in the SLAM/CD2 gene cluster with murine lupus. Immunity 21(6):769–780. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2004.10.009
Wong EB, Khan TN, Mohan C, Rahman ZS (2012) The lupus-prone NZM2410/NZW strain-derived Sle1b sublocus alters the germinal center checkpoint in female mice in a B cell-intrinsic manner. J Immunol 189(12):5667–5681. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1201661
Simpson N, Gatenby PA, Wilson A, Malik S, Fulcher DA, Tangye SG, Manku H, Vyse TJ, Roncador G, Huttley GA, Goodnow CC, Vinuesa CG, Cook MC (2010) Expansion of circulating T cells resembling follicular helper T cells is a fixed phenotype that identifies a subset of severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis & Rheumatism 62(1):234–244. doi:10.1002/art.25032
Jacquemin C, Schmitt N, Contin-Bordes C, Liu Y, Narayanan P, Seneschal J, Maurouard T, Dougall D, Davizon ES, Dumortier H, Douchet I, Raffray L, Richez C, Lazaro E, Duffau P, Truchetet ME, Khoryati L, Mercie P, Couzi L, Merville P, Schaeverbeke T, Viallard JF, Pellegrin JL, Moreau JF, Muller S, Zurawski S, Coffman RL, Pascual V, Ueno H, Blanco P (2015) OX40 ligand contributes to human lupus pathogenesis by promoting T follicular helper response. Immunity 42(6):1159–1170. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2015.05.012
Mohan C, Yu Y, Morel L, Yang P, Wakeland EK (1999) Genetic dissection of Sle pathogenesis: Sle3 on murine chromosome 7 impacts T cell activation, differentiation, and cell death. J Immunol 162(11):6492–6502
Bethunaickan R, Berthier CC, Zhang W, Eksi R, Li HD, Guan Y, Kretzler M, Davidson A (2014) Identification of stage-specific genes associated with lupus nephritis and response to remission induction in (NZB x NZW)F1 and NZM2410 mice. Arthritis & Rheumatology 66(8):2246–2258. doi:10.1002/art.38679
Bethunaickan R, Berthier CC, Zhang W, Kretzler M, Davidson A (2013) Comparative transcriptional profiling of 3 murine models of SLE nephritis reveals both unique and shared regulatory networks. PLoS One 8(10):e77489. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077489
Deane JA, Pisitkun P, Barrett RS, Feigenbaum L, Town T, Ward JM, Flavell RA, Bolland S (2007) Control of toll-like receptor 7 expression is essential to restrict autoimmunity and dendritic cell proliferation. Immunity 27(5):801–810. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.09.009
Hwang SH, Lee H, Yamamoto M, Jones LA, Dayalan J, Hopkins R, Zhou XJ, Yarovinsky F, Connolly JE, Curotto de Lafaille MA, Wakeland EK, Fairhurst AM (2012) B cell TLR7 expression drives anti-RNA autoantibody production and exacerbates disease in systemic lupus erythematosus-prone mice. J Immunol 189(12):5786–5796. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1202195
Scalapino KJ, Tang Q, Bluestone JA, Bonyhadi ML, Daikh DI (2006) Suppression of disease in New Zealand black/New Zealand White lupus-prone mice by adoptive transfer of ex vivo expanded regulatory T cells. J Immunol 177(3):1451–1459
Humrich JY, Morbach H, Undeutsch R, Enghard P, Rosenberger S, Weigert O, Kloke L, Heimann J, Gaber T, Brandenburg S, Scheffold A, Huehn J, Radbruch A, Burmester GR, Riemekasten G (2010) Homeostatic imbalance of regulatory and effector T cells due to IL-2 deprivation amplifies murine lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(1):204–209. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903158107
Yang CH, Tian L, Ling GS, Trendell-Smith NJ, Ma L, Lo CK, Stott DI, Liew FY, Huang FP (2008) Immunological mechanisms and clinical implications of regulatory T cell deficiency in a systemic autoimmune disorder: roles of IL-2 versus IL-15. Eur J Immunol 38(6):1664–1676. doi:10.1002/eji.200838190
Divekar AA, Dubey S, Gangalum PR, Singh RR (2011) Dicer insufficiency and microRNA-155 overexpression in lupus regulatory T cells: an apparent paradox in the setting of an inflammatory milieu. J Immunol 186(2):924–930. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1002218
Cuda CM, Wan S, Sobel ES, Croker BP, Morel L (2007) Murine lupus susceptibility locus Sle1a controls regulatory T cell number and function through multiple mechanisms. J Immunol 179(11):7439–7447
Wan S, Xia C, Morel L (2007) IL-6 produced by dendritic cells from lupus-prone mice inhibits CD4+CD25+ T cell regulatory functions. J Immunol 178(1):271–279
Weigert O, von Spee C, Undeutsch R, Kloke L, Humrich JY, Riemekasten G (2013) CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells prolong drug-induced disease remission in (NZBxNZW) F1 lupus mice. Arthritis research & therapy 15(1):R35. doi:10.1186/ar4188
Yan JJ, Lee JG, Jang JY, Koo TY, Ahn C, Yang J (2017) IL-2/anti-IL-2 complexes ameliorate lupus nephritis by expansion of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Kidney Int 91(3):603–615. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2016.09.022
von Spee-Mayer C, Siegert E, Abdirama D, Rose A, Klaus A, Alexander T, Enghard P, Sawitzki B, Hiepe F, Radbruch A, Burmester GR, Riemekasten G, Humrich JY (2016) Low-dose interleukin-2 selectively corrects regulatory T cell defects in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 75(7):1407–1415. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207776
Yang JQ, Kim PJ, Halder RC, Singh RR (2013) Intrinsic hyporesponsiveness of invariant natural killer T cells precedes the onset of lupus. Clin Exp Immunol 173(1):18–27. doi:10.1111/cei.12079
Yang JQ, Wen X, Kim PJ, Singh RR (2011) Invariant NKT cells inhibit autoreactive B cells in a contact- and CD1d-dependent manner. J Immunol 186(3):1512–1520. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1002373
Wermeling F, Lind SM, Jordo ED, Cardell SL, Karlsson MC (2010) Invariant NKT cells limit activation of autoreactive CD1d-positive B cells. J Exp Med 207(5):943–952. doi:10.1084/jem.20091314
Zeng D, Liu Y, Sidobre S, Kronenberg M, Strober S (2003) Activation of natural killer T cells in NZB/W mice induces Th1-type immune responses exacerbating lupus. J Clin Invest 112(8):1211–1222. doi:10.1172/JCI17165
Yang JQ, Kim PJ, Singh RR (2012) Brief treatment with iNKT cell ligand alpha-galactosylceramide confers a long-term protection against lupus. J Clin Immunol 32(1):106–113. doi:10.1007/s10875-011-9590-y
Karpouzas GA, La Cava A, Ebling FM, Singh RR, Hahn BH (2004) Differences between CD8+ T cells in lupus-prone (NZB x NZW) F1 mice and healthy (BALB/c x NZW) F1 mice may influence autoimmunity in the lupus model. Eur J Immunol 34(9):2489–2499. doi:10.1002/eji.200424978
Ruiz PJ, Zinger H, Mozes E (1996) Effect of injection of anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 monoclonal antibodies on the development of experimental systemic lupus erythematosus in mice. Cell Immunol 167(1):30–37. doi:10.1006/cimm.1996.0004
Kim HJ, Verbinnen B, Tang X, Lu L, Cantor H (2010) Inhibition of follicular T-helper cells by CD8(+) regulatory T cells is essential for self tolerance. Nature 467(7313):328–332. doi:10.1038/nature09370
Kim HJ, Wang X, Radfar S, Sproule TJ, Roopenian DC, Cantor H (2011) CD8+ T regulatory cells express the Ly49 class I MHC receptor and are defective in autoimmune prone B6-Yaa mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(5):2010–2015. doi:10.1073/pnas.1018974108
Tsumiyama K, Hashiramoto A, Takimoto M, Tsuji-Kawahara S, Miyazawa M, Shiozawa S (2013) IFN-gamma-producing effector CD8 T lymphocytes cause immune glomerular injury by recognizing antigen presented as immune complex on target tissue. J Immunol 191(1):91–96. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1203217
Heymann F, Meyer-Schwesinger C, Hamilton-Williams EE, Hammerich L, Panzer U, Kaden S, Quaggin SE, Floege J, Grone HJ, Kurts C (2009) Kidney dendritic cell activation is required for progression of renal disease in a mouse model of glomerular injury. J Clin Invest 119(5):1286–1297. doi:10.1172/JCI38399
Couzi L, Merville P, Deminiere C, Moreau JF, Combe C, Pellegrin JL, Viallard JF, Blanco P (2007) Predominance of CD8+ T lymphocytes among periglomerular infiltrating cells and link to the prognosis of class III and class IV lupus nephritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 56(7):2362–2370. doi:10.1002/art.22654
Taher TE, Muhammad HA, Bariller E, Flores-Borja F, Renaudineau Y, Isenberg DA, Mageed RA (2013) B-lymphocyte signalling abnormalities and lupus immunopathology. Int Rev Immunol 32(4):428–444. doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.788648
Taher TE, Muhammad HA, Rahim A, Flores-Borja F, Renaudineau Y, Isenberg DA, Mageed RA (2013) Aberrant B-lymphocyte responses in lupus: inherent or induced and potential therapeutic targets. Eur J Clin Investig 43(8):866–880. doi:10.1111/eci.12111
Youinou P, Taher TE, Pers JO, Mageed RA, Renaudineau Y (2009) B lymphocyte cytokines and rheumatic autoimmune disease. Arthritis & Rheumatism 60(7):1873–1880. doi:10.1002/art.24665
Renaudineau Y, Pers JO, Bendaoud B, Jamin C, Youinou P (2004) Dysfunctional B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 3(7–8):516–523. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2004.07.035
Jacobi AM, Reiter K, Mackay M, Aranow C, Hiepe F, Radbruch A, Hansen A, Burmester GR, Diamond B, Lipsky PE, Dorner T (2008) Activated memory B cell subsets correlate with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: delineation by expression of CD27, IgD, and CD95. Arthritis & Rheumatism 58(6):1762–1773. doi:10.1002/art.23498
Simonin L, Pasquier E, Leroyer C, Cornec D, Lemerle J, Bendaoud B, Hillion S, Pers J-O, Couturaud F, Renaudineau Y (2016) Lymphocyte disturbances in primary antiphospholipid syndrome and application to venous thromboembolism follow-up. Clinical reviews in allergy & immunology:1–14. doi:10.1007/s12016-016-8568-1
Sims GP, Ettinger R, Shirota Y, Yarboro CH, Illei GG, Lipsky PE (2005) Identification and characterization of circulating human transitional B cells. Blood 105(11):4390–4398. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-11-4284
Garaud S, Le Dantec C, de Mendoza AR, Mageed RA, Youinou P, Renaudineau Y (2009) IL-10 production by B cells expressing CD5 with the alternative exon 1B. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1173:280–285. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04616.x
Youinou P, Renaudineau Y (2011) CD5 expression in B cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Crit Rev Immunol 31(1):31–42
Mohan C, Morel L, Yang P, Wakeland EK (1998) Accumulation of splenic B1a cells with potent antigen-presenting capability in NZM2410 lupus-prone mice. Arthritis & Rheumatism 41(9):1652–1662. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199809)41:9<1652::AID-ART17>3.0.CO;2-W
Xu Z, Morel L (2015) Contribution of B-1a cells to systemic lupus erythematosus in the NZM2410 mouse model. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1362:215–223. doi:10.1111/nyas.12607
Holodick NE, Zeumer L, Rothstein TL, Morel L (2016) Expansion of B-1a cells with germline heavy chain sequence in lupus mice. Front Immunol 7:108. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2016.00108
Xu Z, Butfiloski EJ, Sobel ES, Morel L (2004) Mechanisms of peritoneal B-1a cells accumulation induced by murine lupus susceptibility locus Sle2. J Immunol 173(10):6050–6058
Xu Z, Duan B, Croker BP, Wakeland EK, Morel L (2005) Genetic dissection of the murine lupus susceptibility locus Sle2: contributions to increased peritoneal B-1a cells and lupus nephritis map to different loci. J Immunol 175(2):936–943
Renaudineau Y, Bariller E, Pers JO (2014) B1- and CD5-positive B cells. In: eLS. John Wiley & Sons, ltd. doi:10.1002/9780470015902.a0024242
Ye YL, Chuang YH, Chiang BL (1996) In vitro and in vivo functional analysis of CD5+ and CD5- B cells of autoimmune NZB x NZW F1 mice. Clin Exp Immunol 106(2):253–258
Mageed RA, Garaud S, Taher TE, Parikh K, Pers JO, Jamin C, Renaudineau Y, Youinou P (2012) CD5 expression promotes multiple intracellular signaling pathways in B lymphocyte. Autoimmun Rev. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2012.02.007
Garaud S, Taher TE, Debant M, Burgos M, Melayah S, Berthou C, Parikh K, Pers JO, Luque-Paz D, Chiocchia G, Peppelenbosch M, Isenberg DA, Youinou P, Mignen O, Renaudineau Y, Mageed RA (2016) CD5 expression promotes IL-10 production through activation of the MAPK/Erk pathway and upregulation of TRPC1 channels in B lymphocytes. Cellular & molecular immunology. doi:10.1038/cmi.2016.42
Garaud S, Morva A, Lemoine S, Hillion S, Bordron A, Pers JO, Berthou C, Mageed RA, Renaudineau Y, Youinou P (2011) CD5 promotes IL-10 production in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells through STAT3 and NFAT2 activation. J Immunol 186(8):4835–4844. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1003050
Roy V, Chang NH, Cai Y, Bonventi G, Wither J (2005) Aberrant IgM signaling promotes survival of transitional T1 B cells and prevents tolerance induction in lupus-prone New Zealand black mice. J Immunol 175(11):7363–7371
Giltiay NV, Chappell CP, Sun X, Kolhatkar N, Teal TH, Wiedeman AE, Kim J, Tanaka L, Buechler MB, Hamerman JA, Imanishi-Kari T, Clark EA, Elkon KB (2013) Overexpression of TLR7 promotes cell-intrinsic expansion and autoantibody production by transitional T1 B cells. J Exp Med 210(12):2773–2789. doi:10.1084/jem.20122798
Kumar KR, Li L, Yan M, Bhaskarabhatla M, Mobley AB, Nguyen C, Mooney JM, Schatzle JD, Wakeland EK, Mohan C (2006) Regulation of B cell tolerance by the lupus susceptibility gene Ly108. Science 312(5780):1665–1669. doi:10.1126/science.1125893
Batten M, Groom J, Cachero TG, Qian F, Schneider P, Tschopp J, Browning JL, Mackay F (2000) BAFF mediates survival of peripheral immature B lymphocytes. J Exp Med 192(10):1453–1466
Teague BN, Pan Y, Mudd PA, Nakken B, Zhang Q, Szodoray P, Kim-Howard X, Wilson PC, Farris AD (2007) Cutting edge: transitional T3 B cells do not give rise to mature B cells, have undergone selection, and are reduced in murine lupus. J Immunol 178(12):7511–7515
Hoyer BF, Moser K, Hauser AE, Peddinghaus A, Voigt C, Eilat D, Radbruch A, Hiepe F, Manz RA (2004) Short-lived plasmablasts and long-lived plasma cells contribute to chronic humoral autoimmunity in NZB/W mice. J Exp Med 199(11):1577–1584. doi:10.1084/jem.20040168
Mumtaz IM, Hoyer BF, Panne D, Moser K, Winter O, Cheng QY, Yoshida T, Burmester GR, Radbruch A, Manz RA, Hiepe F (2012) Bone marrow of NZB/W mice is the major site for plasma cells resistant to dexamethasone and cyclophosphamide: implications for the treatment of autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 39(3):180–188. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2012.05.010
Cheng Q, Mumtaz IM, Khodadadi L, Radbruch A, Hoyer BF, Hiepe F (2013) Autoantibodies from long-lived 'memory' plasma cells of NZB/W mice drive immune complex nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis 72(12):2011–2017. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203455
Neubert K, Meister S, Moser K, Weisel F, Maseda D, Amann K, Wiethe C, Winkler TH, Kalden JR, Manz RA, Voll RE (2008) The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib depletes plasma cells and protects mice with lupus-like disease from nephritis. Nat Med 14(7):748–755. doi:10.1038/nm1763
Khodadadi L, Cheng Q, Alexander T, Sercan-Alp O, Klotsche J, Radbruch A, Hiepe F, Hoyer BF, Taddeo A (2015) Bortezomib plus continuous B cell depletion results in Sustained plasma cell depletion and amelioration of lupus nephritis in NZB/W F1 mice. PLoS One 10(8):e0135081. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0135081
Taddeo A, Khodadadi L, Voigt C, Mumtaz IM, Cheng Q, Moser K, Alexander T, Manz RA, Radbruch A, Hiepe F, Hoyer BF (2015) Long-lived plasma cells are early and constantly generated in New Zealand black/New Zealand White F1 mice and their therapeutic depletion requires a combined targeting of autoreactive plasma cells and their precursors. Arthritis research & therapy 17:39. doi:10.1186/s13075-015-0551-3
Seret G, Hanrotel C, Bendaoud B, Le Meur Y, Renaudineau Y (2013) Homozygous FCGR3A-158F mutation is associated with delayed B-cell depletion following rituximab but with preserved efficacy in a patient with refractory lupus nephritis. Clin Kidney J 6(1):74–76. doi:10.1093/ckj/sfs162
Devauchelle-Pensec V, Morvan J, Rat AC, Jousse-Joulin S, Pennec Y, Pers JO, Jamin C, Renaudineau Y, Quintin-Roue I, Cochener B, Youinou P, Saraux A (2011) Effects of rituximab therapy on quality of life in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29(1):6–12
Renaudineau Y, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Hanrotel C, Pers JO, Saraux A, Youinou P (2009) Monoclonal anti-CD20 antibodies: mechanisms of action and monitoring of biological effects. Joint Bone Spine 76(5):458–463. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2009.03.010
Jousse-Joulin S, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Morvan J, Guias B, Pennec Y, Pers JO, Daridon C, Jamin C, Renaudineau Y, Roue IQ, Cochener B, Bressollette L, Youinou P, Saraux A (2007) Ultrasound assessment of salivary glands in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome treated with rituximab: quantitative and Doppler waveform analysis. Biologics : targets & therapy 1(3):311–319
Devauchelle-Pensec V, Pennec Y, Morvan J, Pers JO, Daridon C, Jousse-Joulin S, Roudaut A, Jamin C, Renaudineau Y, Roue IQ, Cochener B, Youinou P, Saraux A (2007) Improvement of Sjogren’s syndrome after two infusions of rituximab (anti-CD20). Arthritis & Rheumatism 57(2):310–317. doi:10.1002/art.22536
Pers JO, Devauchelle V, Daridon C, Bendaoud B, Le Berre R, Bordron A, Hutin P, Renaudineau Y, Dueymes M, Loisel S, Berthou C, Saraux A, Youinou P (2007) BAFF-modulated repopulation of B lymphocytes in the blood and salivary glands of rituximab-treated patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. Arthritis & Rheumatism 56(5):1464–1477. doi:10.1002/art.22603
Mahevas M, Patin P, Huetz F, Descatoire M, Cagnard N, Bole-Feysot C, Le Gallou S, Khellaf M, Fain O, Boutboul D, Galicier L, Ebbo M, Lambotte O, Hamidou M, Bierling P, Godeau B, Michel M, Weill JC, Reynaud CA (2013) B cell depletion in immune thrombocytopenia reveals splenic long-lived plasma cells. J Clin Invest 123(1):432–442. doi:10.1172/JCI65689
Mahevas M, Michel M, Vingert B, Moroch J, Boutboul D, Audia S, Cagnard N, Ripa J, Menard C, Tarte K, Megret J, Le Gallou S, Patin P, Thai L, Galicier L, Bonnotte B, Godeau B, Noizat-Pirenne F, Weill JC, Reynaud CA (2015) Emergence of long-lived autoreactive plasma cells in the spleen of primary warm auto-immune hemolytic anemia patients treated with rituximab. J Autoimmun 62:22–30. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2015.05.006
Morell M, Varela N, Maranon C (2017) Myeloid populations are altered in systemic autoimmune diseases. Clinical reviews in allergy & immunology
Baumann I, Kolowos W, Voll RE, Manger B, Gaipl U, Neuhuber WL, Kirchner T, Kalden JR, Herrmann M (2002) Impaired uptake of apoptotic cells into tingible body macrophages in germinal centers of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis & Rheumatism 46(1):191–201. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200201)46:1<191::AID-ART10027>3.0.CO;2-K
Sisirak V, Ganguly D, Lewis KL, Couillault C, Tanaka L, Bolland S, D’Agati V, Elkon KB, Reizis B (2014) Genetic evidence for the role of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med 211(10):1969–1976. doi:10.1084/jem.20132522
Blanco P, Palucka AK, Gill M, Pascual V, Banchereau J (2001) Induction of dendritic cell differentiation by IFN-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Science 294(5546):1540–1543. doi:10.1126/science.1064890
Celhar T, Hopkins R, Thornhill SI, De Magalhaes R, Hwang SH, Lee HY, Yasuga H, Jones LA, Casco J, Lee B, Thamboo TP, Zhou XJ, Poidinger M, Connolly JE, Wakeland EK, Fairhurst AM (2015) RNA sensing by conventional dendritic cells is central to the development of lupus nephritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(45):E6195–E6204. doi:10.1073/pnas.1507052112
Zhu J, Liu X, Xie C, Yan M, Yu Y, Sobel ES, Wakeland EK, Mohan C (2005) T cell hyperactivity in lupus as a consequence of hyperstimulatory antigen-presenting cells. J Clin Invest 115(7):1869–1878. doi:10.1172/JCI23049
Sahu R, Bethunaickan R, Singh S, Davidson A (2014) Structure and function of renal macrophages and dendritic cells from lupus-prone mice. Arthritis & Rheumatology 66(6):1596–1607. doi:10.1002/art.38410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique. A. De Groof is supported by the “Chaire UCB/UCL sur les rhumatismes inflammatoires et systémiques”. B. Lauwerys is supported in part by the Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique (Communauté française de Belgique), and P. Hemon by a SATT Ouest Valorisation grant.
Ethical Approval
All animal experiments reported in this manuscript were approved by the ethical committee of the Université catholique de Louvain (Secteur des Sciences de la Santé), and by the ethical committee of the Université de Bretagne Occidentale (Brest).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Groof, A., Hémon, P., Mignen, O. et al. Dysregulated Lymphoid Cell Populations in Mouse Models of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 53, 181–197 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-017-8605-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-017-8605-8