Abstract
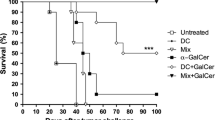
CD1d presents glycolipid antigens such as α-galactosylceramide (αGalCer) to invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT). We have reported that activated iNKTs inhibit IL-10-producing autoreactive B cells, while promoting or leaving intact the normal B cell responses, making iNKT modulation an attractive therapeutic modality. Here, we report that a brief treatment of young lupus-prone (NZB/NZW)F1 (BWF1) mice with two injections of αGalCer conferred a long-term protection against lupus. Long-term repeated administrations of αGalCer, however, afforded no clinical benefit. These disparate clinical effects correlated with iNKT responsiveness. While a brief treatment with αGalCer enhanced iNKT responses upon in vitro recall, the long-term αGalCer treatment resulted in reduced iNKT responses in BWF1 mice. The improvement in disease with αGalCer treatment was associated with the reduced IL-10 production. Furthermore, iNKTs directly inhibited IL-10-secreting cells in vivo in reconstituted SCID mice and inhibited IL-10-secreting B cells in vitro in co-cultures. Thus, a brief treatment with a CD1d-binding glycolipid enhances iNKT responses, reduces IL-10 production, and delays the onset of lupus, whereas long-term repeated treatments induce marked iNKT hyporesponsiveness and do not affect disease outcome in BWF1 mice. Identifying glycolipid regimens that can modulate iNKT responsiveness will have important implications for developing iNKT-based therapies for autoimmune diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendelac A. CD1: presenting unusual antigens to unusual T lymphocytes. Science. 1995;269:185–6.
Godfrey DI, MacDonald HR, Kronenberg M, Smyth MJ, Van Kaer L. NKT cells: what's in a name? Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:231–7.
Kronenberg M. Toward an understanding of NKT cell biology: progress and paradoxes. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:877–900.
Yang JQ, Wen X, Kim PJ, Singh RR. Invariant NKT cells inhibit autoreactive B cells in a contact- and CD1d-dependent manner. J Immunol. 2011;186:1512–20.
Yang JQ, Wen X, Liu H, Folayan G, Dong X, Zhou M, et al. Examining the role of CD1d and natural killer T cells in the development of nephritis in a genetically susceptible lupus model. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1219–33.
F. Wermeling, S.M. Lind, E.D. Jordo, S.L. Cardell, M.C. Karlsson, Invariant NKT cells limit activation of autoreactive CD1d-positive B cells. J Exp Med. 2010;207:943–52.
Wither J, Cai YC, Lim S, McKenzie T, Roslin N, Claudio JO, et al. Reduced proportions of natural killer T cells are present in the relatives of lupus patients and are associated with autoimmunity. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10:R108.
Kojo S, Adachi Y, Keino H, Taniguchi M, Sumida T. Dysfunction of T cell receptor AV24AJ18+, BV11+ double-negative regulatory natural killer T cells in autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:1127–38.
van der Vliet HJ, von Blomberg BM, Nishi N, Reijm M, Voskuyl AE, van Bodegraven AA, et al. Circulating V(alpha24+) Vbeta11+ NKT cell numbers are decreased in a wide variety of diseases that are characterized by autoreactive tissue damage. Clin Immunol. 2001;100:144–8.
Oishi Y, Sumida T, Sakamoto A, Kita Y, Kurasawa K, Nawata Y, et al. Selective reduction and recovery of invariant Vα24 JαQ T cell receptor T cells in correlation with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:275–83.
Hahn BH, Singh RR. Animal models of systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Wallace DJ, Hahn BH, editors. Dubois' lupus erythematosus, Lippincott. Philadelphia: Williams and Wilkins; 2007. p. 299–355.
Bendelac A, Hunziker RD, Lantz O. Increased interleukin 4 and immunoglobulin E production in transgenic mice overexpressing NK1 T cells. J Exp Med. 1996;184:1285–93.
Cui J, Shin T, Kawano T, Sato H, Kondo E, Toura I, et al. Requirement for Vα14 NKT cells in IL-12-mediated rejection of tumors. Science. 1997;278:1623–6.
Fan GC, Singh RR. Vaccination with minigenes encoding V(H)-derived major histocompatibility complex class I-binding epitopes activates cytotoxic T cells that ablate autoantibody-producing B cells and inhibit lupus. J Exp Med. 2002;196:731–41.
Yang JQ, Singh AK, Wilson MT, Satoh M, Stanic AK, Park JJ, et al. Immunoregulatory role of CD1d in the hydrocarbon oil-induced model of lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 2003;171:2142–53.
Yang JQ, Saxena V, Xu H, Van Kaer L, Wang CR, Singh RR. Repeated alpha-galactosylceramide administration results in expansion of NK T cells and alleviates inflammatory dermatitis in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol. 2003;171:4439–46.
Van Kaer L. alpha-Galactosylceramide therapy for autoimmune diseases: prospects and obstacles. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:31–42.
Major AS, Singh RR, Joyce S, Van Kaer L. The role of invariant natural killer T cells in lupus and atherogenesis. Immunol Res. 2006;34:49–66.
Coppieters K, Van Beneden K, Jacques P, Dewint P, Vervloet A, Vander Cruyssen B, et al. A single early activation of invariant NK T cells confers long-term protection against collagen-induced arthritis in a ligand-specific manner. J Immunol. 2007;179:2300–9.
Dombrowicz D. Exploiting the innate immune system to control allergic asthma. Eur J Immunol. 2005;35:2786–8.
Morishima Y, Ishii Y, Kimura T, Shibuya A, Shibuya K, Hegab AE, et al. Suppression of eosinophilic airway inflammation by treatment with alpha-galactosylceramide. Eur J Immunol. 2005;35:2803–14.
Yang JQ, Chun T, Liu H, Hong S, Bui H, Van Kaer L, et al. CD1d deficiency exacerbates inflammatory dermatitis in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34:1723–32.
Singh AK, Yang JQ, Parekh VV, Wei J, Wang CR, Joyce S, et al. The natural killer T cell ligand alpha-galactosylceramide prevents or promotes pristane-induced lupus in mice. Eur J Immunol. 2005;35:1143–54.
Sireci G, Russo D, Dieli F, Porcelli SA, Taniguchi M, La Manna MP, et al. Immunoregulatory role of Jalpha281 T cells in aged mice developing lupus-like nephritis. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:425–33.
Zeng D, Lee MK, Tung J, Brendolan A, Strober S. Cutting edge: a role for CD1 in the pathogenesis of lupus in NZB/NZW mice. J Immunol. 2000;164:5000–4.
Zeng D, Liu Y, Sidobre S, Kronenberg M, Strober S. Activation of natural killer T cells in NZB/W mice induces Th1-type immune responses exacerbating lupus. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:1211–22.
Morshed SR, Takahashi T, Savage PB, Kambham N, Strober S. Beta-galactosylceramide alters invariant natural killer T cell function and is effective treatment for lupus. Clin Immunol. 2009;132:321–33.
Chiba A, Kaieda S, Oki S, Yamamura T, Miyake S. The involvement of V(alpha)14 natural killer T cells in the pathogenesis of arthritis in murine models. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:1941–8.
Chiba A, Oki S, Miyamoto K, Hashimoto H, Yamamura T, Miyake S. Suppression of collagen-induced arthritis by natural killer T cell activation with OCH, a sphingosine-truncated analog of alpha-galactosylceramide. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:305–13.
Jahng AW, Maricic I, Pedersen B, Burdin N, Naidenko O, Kronenberg M, et al. Activation of natural killer T cells potentiates or prevents experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 2001;194:1789–99.
Van Kaer L. Natural killer T cells as targets for immunotherapy of autoimmune diseases. Immunol Cell Biol. 2004;82:315–22.
Furlan R, Bergami A, Cantarella D, Brambilla E, Taniguchi M, Dellabona P, et al. Activation of invariant NKT cells by alphaGalCer administration protects mice from MOG35-55-induced EAE: critical roles for administration route and IFN-gamma. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33:1830–8.
Singh AK, Wilson MT, Hong S, Olivares-Villagomez D, Du C, Stanic AK, et al. Natural killer T cell activation protects mice against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 2001;194:1801–11.
Llorente L, Zou W, Levy Y, Richaud-Patin Y, Wijdenes J, Alcocer-Varela J, et al. Role of interleukin 10 in the B lymphocyte hyperactivity and autoantibody production of human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1995;181:839–44.
Ishida H, Muchamuel T, Sakaguchi S, Andrade S, Menon S, Howard M. Continuous administration of anti-interleukin 10 antibodies delays onset of autoimmunity in NZB/W F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1994;179:305–10.
Llorente L, Richaud-Patin Y, Garcia-Padilla C, Claret E, Jakez-Ocampo J, Cardiel MH, et al. Clinical and biologic effects of anti-interleukin-10 monoclonal antibody administration in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:1790–800.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from National Institutes of Health (AR47322, AR50797, AR56465, and AI80778) and the American Heart Association (Beginning-Grant-in-Aid to PJK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, JQ., Kim, P.J. & Singh, R.R. Brief Treatment with iNKT Cell Ligand α-Galactosylceramide Confers a Long-term Protection Against Lupus. J Clin Immunol 32, 106–113 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-011-9590-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-011-9590-y