Abstract
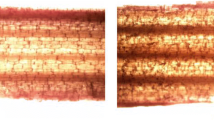
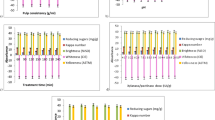
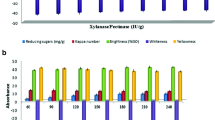
The aim of this study was to evaluate the potential of xylanase-pectinase enzymes in bleaching of wheat straw pulp, just to cut down the toxic wastes, in order to manage the environmental pollution. The appropriate parameters of bleaching were evaluated, and best conditions were xylanase and pectinase dose of 5.0 and 1.66 IU/g of pulp, respectively, along with material to liquid ratio of 1:7.5 (g/ml), temperature 55 °C, treatment time 3 h, Tween-80 1%, and pH 8.5. The release of reducing sugar and other non-cellulosic impurities, phenolic-hydrophobic-lignin was maximum at best bleaching conditions. Prebleaching of wheat straw pulp using these enzymes showed 14.75% decline in kappa number. Enzymatic bleaching plus 100% chemical bleaching also led to 27.90% reduction in yellowness. Using this methodology, the consumption of active chlorine was reduced up to 25%, along with an increase in burst index (7.98%), tear index (3.42%), breaking length (5.30%), viscosity (11.22%), gurley porosity (12.50%), and double-fold number (23.08%), which exhibits a remarkable enhancement in all the properties of pulp treated with enzymes. Microscopic images also confirm the effectiveness of enzymatic treatment in bleaching of wheat straw pulp. BOD and COD values of effluent also decreased by 20.74 and 17.87%, respectively. This research focussing on producing better grade paper using an eco-friendly approach would certainly benefit the paper and pulp industry. This is the first report, depicting bleaching capability of xylanase-pectinase enzymes for soda-anthraquinone pulp of wheat straw.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- BOD:
-
Biochemical oxygen demand
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- SAQ:
-
Soda-anthraquinone
- CEH:
-
C—chlorination, E—alkaline extraction, H—hypochlorite
- TAPPI:
-
Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry
- TSS:
-
Total suspended solids
- TDS:
-
Total dissolved solids
References
Singh, S., Dutt, D., & Tyagi, C. H. (2011). Environmentally friendly totally chlorine free bleaching of wheat straw pulp using novel cellulase-poor xylanases of wild strains of Coprinellus disseminates. BioResources, 6(4), 3876–3882.
Soni, M., Mathur, C., Soni, A., Solanki, M. K., Kashyap and B. K., Kamboj, D. V. (2020). Xylanase in waste management and its industrial applications. In: Kashyap B. K., Solanki M. K., Kamboj D. V., Pandey A. K. (eds.) Waste to energy: Prospects and applications. Springer, Singapore. 393–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4347-4_16
Marin, N., Puitel, A. C., Chesca, A., & Gavrilescu, D. (2017). Response surface modeling of wheat straw pulping using sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide mixtures. Cellulose Chem. Technol., 51(7–8), 745–753.
Ramadas, S., Kumar, T. M. K. and Singh, G. P. (2019). Wheat production in India: Trends and prospects, recent advances in grain crops research, farooq shah, zafar khan, amjad iqbal, metin turan and murat olgun, intechopen. 1–16. https://www.intechopen.com/books/recent-advances-in-grain-crops-research/wheat-production-in-india-trends-and-prospects
Fang, G. and Shen, K. (2018). Wheat straw pulping for paper and paperboard production. 1–19. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.77274
Tufail, T., Saeed, F., Imran, M., Arshad, U. M., Anjum, F. M., Afzaal, M., Ain, H. B. U., Shahbaz, M., Gondal, T. A., & Hussain, S. (2018). Biochemical characterization of wheat straw cell wall with special reference to bioactive profile. International Journal of Food Properties, 21(1), 1303–1310.
Kaur, D., Bhardwaj, N. K., & Lohchab, R. K. (2018). A study on pulping of rice straw and impact of incorporation of chlorine dioxide during bleaching on pulp properties and effluents characteristics. Journal of Cleaner Production, 170, 174–182.
Kaur, D., Bhardwaj, N. K., & Lohchab, R. K. (2016). Prospects of rice straw as a raw material for paper making. Waste Management, 60, 127–139.
Zhao, D. Q., Chen, K. F., Mo, L. H., Li, J., Xu, J., Yang, R. D., & Yang, F. (2010). Chlorine dioxide bleaching reinforced by alkaline extraction and corresponding ECF bleaching sequences for wheat straw pulp. J. South China Univ. Technol., 38, 45–50.
Gangwar, A. K., Prakash, N. T., & Prakash, R. (2014). Applicability of microbial xylanase in paper pulp bleaching: A review. BioResources, 9(2), 3733–3754.
Zhang, X., Renaud, S., & Paice, M. (2008). Cellulase deinking of fresh and aged recycled newsprint/magazines (ONP/OMG). Enyzme and Microbial Technology, 43(2), 103–108.
Nathan, V. K., Rani, M. E., Rathinasamy, G., & Dhirviam, K. N. (2017). Low molecular weight xylanase from trichoderma viride vkf3 for bio-bleaching of newspaper pulp. BioResources, 12(3), 5264–5278.
Raj, A., Kumar, S., Singh, S. K., & Prakash, J. (2018). Production and purification of xylanase from alkaliphilic Bacillus licheniformis and its pretreatment of eucalyptus kraft pulp. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 15, 199–209.
Kaur, D., Bhardwaj, N. K., & Lohchab, R. K. (2019). Impact of modifying conventional chlorine dioxide stage to hot chlorine dioxide during rice straw pulp bleaching on pulp, paper and effluent characteristics. Cellulose, 26(1), 7469–7482.
Silva, L. A. O., Terrasan, C. R. F., & Carmona, E. C. (2015). Purification and characterization of xylanases from Trichoderma inhamatum. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 18, 307–313.
Adesina, F. C., Onilude, A. A., Oluboyede, O. A., Olajide, A., Bamkefa, B., & Abiola-Olagunju, A. (2017). Production and application of xylanase by Fusarium Sp. using wood shavings as substrate. EC Microbiogy, 6(1), 4–13.
Viikari, L., Tenkanen, M. and Suurnakki, A. (2001). Biotechnology in the pulp and paper industry. 523–546.
Ahlawat, S., Battan, B., Dhiman, S. S., Sharma, J., & Mandhan, R. P. (2007). Production of thermostable pectinase and xylanase for their potential application in bleaching of kraft pulp. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 34, 763–770.
Zhao, Y., Meng, K., Luo, H., Huang, H., Yuan, T., Yang, P., & Yao, B. (2013). Molecular and biochemical characterization of a new alkaline active multidomain xylanase from alkaline wastewater sludge. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 29(2), 327–334.
Kaur, A., Singh, A., Dua, A., & Mahajan, R. (2017). Cost-effective and concurrent production of industrially valuable xylano-pectinolytic enzymes by a bacterial isolate Bacillus pumilus AJK. Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 47(1), 8–18.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry, 31(3), 426–428.
Kaur, A., Mahajan, R., Singh, A., Garg, G., & Sharma, J. (2010). Application of cellulase-free xylano-pectinolytic enzymes from the same bacterial isolate in biobleaching of kraft pulp. Bioresource Technology, 101(23), 9150–9155.
Patel, R. N., Grabski, A. C., & Jeffries, T. W. (1993). Chromophore release from kraft pulp by purified Streptomyces roseiscleroticus xylanases. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 39, 405–412.
Khandeparkar, R., & Bhosle, N. B. (2007). Application of thermoalkalophilic xylanase from Arthrobacter sp. MTCC 5214 in biobleaching of kraft pulp. Bioresource Technology, 98(4), 897–903.
Hise, R. (1996). Chlorination. In C. W. Dence & D. W. Reeve (Eds.), Pulp bleaching–Principles and practice (pp. 241–259). Tappi Press Atlanta.
TAPPI T205 sp-02. (2002). Forming handsheets for physical tests of pulp. TAPPI Press.
TAPPI T217 wd-77. (2004). Brightness of pulp. TAPPI Press.
TAPPI T403 om-10. (2010). Burst strength of paper. TAPPI Press.
TAPPI T494 om-01. (2001). Tensile breaking properties of paper and paperboard. TAPPI Press.
TAPPI T414 om-04. (2004). Internal tearing resistance of paper (Elmendorf-type method). TAPPI Press.
TAPPI T230 om-99. (1976). Viscosity of pulp (capillary viscometer method). TAPPI Press.
TAPPI T511 om-02. (2002). Folding endurance of paper (MIT tester). TAPPI Press.
SCAN-C 19:65 (1999). Pulps determination of drainability-part 1 (Schopper-Riegler method)
TAPPI T460 om-02. (2002). Air resistance of paper. TAPPI Press.
Li, X., She, Y., Sun, B., Song, H., Zhu, Y., Lv, Y., & Song, H. (2010). Purification and characterization of a cellulase-free, thermostable xylanase from Streptomyces rameus L2001 and its biobleaching effect on wheat straw pulp. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 52, 71–78.
Garg, G., Dhiman, S. S., Mahajan, R., Kaur, A., & Sharma, J. (2011). Bleach-boosting effect of crude xylanase from Bacillus Stearothermophilus SDX on wheat straw pulp. New Biotechnology, 28(1), 1–7.
Comlekcioglu, U., Tutus, A., Cicekler, M., Gunes, M., & Aygan, A. (2014). Application of recombinant xylanase from Orpinomyces sp. in elemental chlorine-free bleaching of kraft pulps. Romanian Biotechnological Letters, 19(1), 1–10.
Walia, A., Mehta, P., Guleria, S. and Shirkot, C. K. (2015). Modification in the properties of paper by using cellulase-free xylanase in biobleaching of wheat straw pulp produced from alkalophilic Cellulosimicrobium cellulans CKMX1. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 1–25
Agrawal, S., Yadav, R. D., & Mahajan, R. (2016). Synergistic effect of xylano-pectinolytic enzymes produced by a bacterial isolate in bleaching of plywood industrial waste. Journal of Cleaner Production, 118, 229–233.
Nagar, S., Jain, R. K., Thakur, V. V., & Gupta, V. K. (2013). Biobleaching application of cellulase poor and alkali stable xylanase from Bacillus pumilus SV-85S. 3 Biotech, 3, 277–285.
Ozer, A., Canakci, S., Gocmen, G., Denij, I., Kirci, H., Okan, O. T., & Belduz, A. O. (2018). Distinctive delignification with consecutive application of geobacillus sp. 71 xylanase and Rhodococcus jostii rha1 lignin peroxidase. Maderas. Ciencia y tecnología, 20(3), 505–518.
Sharma, A., Balda, S., Gupta, N., Capalash, N., & Sharma, P. (2020). Enzyme cocktail: An opportunity for greener agro-pulp biobleaching in paper industry. Journal of Cleaner Production., 271(1), 122573.
Boruah, P., Dowarah, P., Hazarika, R., Yadav, A., Barkakati, P., & Goswami, T. (2016). Xylanase from Penicillium meleagrinum var. viridiflavum-A potential source for bamboo pulp bleaching. Journal of Cleaner Production, 116, 259–267.
Torres, C. E., Negro, C., Fuente, E., & Blanco, A. (2012). Enzymatic approaches in paper industry for pulp refining and biofilm control. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 96, 327–344.
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author would like to thank Avantha Centre for Industrial Research and Development (ACIRD), Yamuna Nagar, for providing their laboratory facilities.
Funding
The financial support provided by Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science & Technology, Government of India (Grant Number: BT/PR 20438/BCE/8/1220/2016 for 3 years).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, D., Nagpal, R., Agrawal, S. et al. Eco-friendly Bleaching of Agrowaste Wheat Straw Using Crude Alkalo-Thermotolerant Cellulase-Free Xylano-Pectinolytic Enzymes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 620–634 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03641-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03641-6