Abstract
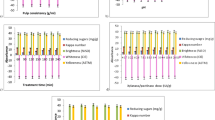
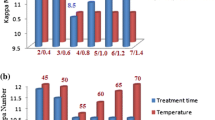
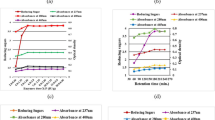
In this study, action of ultrafiltered xylano-pectinolytic enzymes from a bacterial strain has been evaluated for bleaching of rice straw soda-anthraquinone pulp. Maximum bio-bleaching effect and release of non-cellulosic impurities were noticed with xylano:pectinolytic enzymes dose of 6.0:2.1-IU/g pulp, treatment time of 180 min at 10% pulp consistency, pH 8.5, and temperature 55 °C. Microscopic images of bio-bleached rice straw pulp also confirmed the efficacy of ultrafiltered enzymes, as bleaching agent. This bio-bleaching treatment resulted in 15.38% and 32% reduction in kappa number and active chlorine dioxide dose, respectively, along with increase in various physical properties, burst index (12.50%), tear index (19.07%), breaking length (14.30%), double fold number (26.31%), Gurley porosity (45.32%) and viscosity (16.17%). This bio-bleaching approach not only improved the pulp quality but also reduced environmental pollution load by decreasing effluent parameters values of BOD and COD by 23.67% and 27.44%, respectively. This study indicates that use of ultrafiltered xylano-pectinolytic synergism for rice straw pulp bleaching will ultimately help in making the process eco-friendly, along with better quality pulp. This is the first report on use of ultrafiltered xylanase and pectinase, produced from a bacterial isolate, for bleaching of rice straw pulp.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not Applicable.
References
Adhyaru DN, Bhatt NS, Modi HA, Divecha J (2017) Cellulase-free-thermo-alkali-solvent-stable xylanase from Bacillus altitudinis DHN8: over-production through statistical approach, purification and bio-deinking/bio-bleaching potential. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 12:220–227
Agrawal S, Yadav RD, Mahajan R (2016) Synergistic effect of xylano-pectinolytic enzymes produced by a bacterial isolate in bleaching of plywood industrial waste. J Clean Prod 118:229–233
Akpor OB, Muchie B (2011) Environmental and public health implications of wastewater quality. Afr J Biotechnol 10(13):2379–2387
APHA (2017a) In: Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (eds) Method 2120: standard methods for the examination of colour of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, United Book Press, Inc, Baltimore
APHA (2017b) In: Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (eds) Method 5550: standard methods for the examination of colour of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, United Book Press, Inc, Baltimore
Bajpai P (2014) Microbial xylanolytic system and their properties. In: Xylanolytic enzymes. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 19–36
Bhagat DD, Dudhagara PR, Desai PV (2019) Statistical approach for pectinase production by Bacillus firmus SDB9 and evaluation of pectino-xylanolytic enzymes for pretreatment of kraft pulp. J Microbiol Biotechnol Food Sci 2019:396–406
Central Pulp and Paper Research Institute (2011) Current awareness services, bimonthly publication of central pulp and paper research institute. 10(3)
Ghosh UK (2006) Short sequence environment friendly bleaching of wheat straw pulp. J Sci Ind Res 65(1):68–71
Gupta S, Bhushan B, Hoondal GS (2000) Isolation, purification and characterization of xylanase from Staphylococcus sp. SG-13 and its application in biobleaching of kraft pulp. J Appl Microbiol 88:325–334
Gupta V, Garg S, Capalash N, Gupta N, Sharma P (2015) Production of thermo-alkali-stable laccase and xylanase by co-culturing of Bacillus sp. and B. halodurans for biobleaching of kraft pulp and deinking of waste paper. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 3:947–956
Gurjar BR, Ravindra K, Nagpure AS (2016) Air pollution trends over Indian megacities and their local-to-global implications. Atmos Environ 142:475–495
Hise R (1996) Chlorination. In: Dence CW, Reeve DW (eds) Pulp bleaching: principles and practice. Tappi Press, Atlanta, Georgia, pp 241–259
Hossain K, Ismail N (2015) Bioremediation and detoxification of pulp and paper mill effluent: a review. Res J Environ Toxicol 9(3):113–134
Hossain K, Rao AR (2014) Environmental change and it’s affect. Eu J Sus Dev 3(2):89
Igbinttosa EO, Odjadjare EE, Chigor VN, Igbinosa IH, Emoghene AO, Ekhaise FO, Idemudia OG (2013) Toxicological profile of chlorophenols and their derivatives in the environment: the public health perspective. Sci World J 2013:11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/460215
Kaur A, Mahajan R, Singh A, Garg G, Sharma J (2010) Application of cellulase-free xylano-pectinolytic enzymes from the same bacterial isolate in biobleaching of kraft pulp. Bioresour Technol 101(23):9150–9155
Kaur D, Bhardwaj NK, Lohchab RK (2016) Prospects of rice straw as a raw material for paper making. Waste Manag 60:127–139
Kaur A, Singh A, Dua A, Mahajan R (2017) Cost-effective and concurrent production of industrially valuable xylano-pectinolytic enzymes by a bacterial isolate Bacillus pumilus AJK. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 47(1):8–18
Khandeparkar R, Bhosle NB (2007) Application of thermoalkalophilic xylanase from Arthrobacter sp. MTCC 5214 in biobleaching of kraft pulp. Bioresour Technol 98:897–903
Kumar S, Saha T, Sharma S (2015) Treatment of pulp and paper mill effluents using novel biodegradable polymeric flocculants based on anionic polysaccharides: a new way to treat the waste water. IRJET 2(4):1415–1428
Kumar S, Haq I, Prakash J, Singh SK, Mishra S, Raj A (2017) Purification, characterization and thermostability improvement of xylanase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its application in pre-bleaching of kraft pulp. 3 Biotech 7(1):20
Mamo G (2019) Alkaline active hemicellulases. In: Mamo G, Mattiasson B (eds) Alkaliphiles in biotechnology, Adv Biochem Eng Biot, vol 172, pp 1–47
Mengesha A, Mamo W, Tesfaye T (2004) Sanitary survey in Gondar town. Ethiop Med J 18(1):39–43
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31(1):426–428
Nissen AM, Anker L, Munk N, Lange K (1992) In: Xylanase for the pulp and paper industry, (Visser J, Beldman G, Kustersvan someren MA, Voragen AGJ Eds.). Biotechnol Prog 7:325–337
Patel RN, Grabski AC, Jeffries TW (1993) Chromophore release from kraft pulp by purified Streptomyces roseiscleroticus xylanases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:405–412
Raj A, Kumar S, Haq I, Singh SK (2014) Bioremediation and toxicity reduction in pulp and paper mill effluent by newly isolated ligninolytic Paenibacillus sp. Ecol Eng 71:355–362
SCAN-C 19:65 (1999) Pulps determination of drainability-part 1 (Schopper-Riegler method). TAPPI press, Atlanta
Sharma D, Agrawal S, Yadav RD, Mahajan R (2017) Improved efficacy of ultrafiltered xylanase–pectinase concoction in biobleaching of plywood waste soda pulp. 3 biotech 7(1):2
TAPPI T205 sp-02 (2002) Forming handsheets for physical tests of pulp. TAPPI Press, Atlanta
TAPPI T21 wd-77 (2004) Brightness of pulp. TAPPI Press, Atlanta
TAPPI T217 wd-77 (2004) Brightness of pulp. TAPPI Press, Atlanta, GA
TAPPI T230 om-99 (1976) Viscosity of pulp (capillary viscometer method). TAPPI Press, Atlanta
TAPPI T236 om-99 (2004) Kappa number of pulp. TAPPI Press, Atlanta
TAPPI T403 om-10 (2010) Burst strength of paper. TAPPI Press, Atlanta
TAPPI T414 om-04 (2004) Internal tearing resistance of paper (Elmendorf-type method). TAPPI Press, Atlanta
TAPPI T460 om-02 (2002) Air resistance of paper (Gurley method). TAPPI Press, Atlanta
TAPPI T494 om-01 (2001) Tensile breaking properties of paper and paperboard. TAPPI Press, Atlanta
TAPPI T511 om-02 (2002) Folding endurance of paper (MIT tester). TAPPI Press, Atlanta
Teh CY, Budiman PM, Shak KPY, Wu TY (2016) Recent advancement of coagulation–flocculation and its application in wastewater treatment. Ind Eng Chem Res 55(16):4363–4389
Tutus A (2004) Bleaching of rice straw pulps with hydrogen peroxide. PJBS 7(8):1327–1329
Tutuş AH, Eroğlu HÜ (2003) A practical solution to silica problem in straw pulping. Appita J 56(2):111–115
Walia A, Mehta P, Guleria S, Shirkot CK (2015) Modification in the properties of paper by using cellulase-free xylanase in biobleaching of wheat straw pulp produced from alkalophilic Cellulosimicrobium cellulans CKMX1. Can J Microbiol 61(9):671–681
Yang JL, Eriksson KEL (1992) Use of hemicellulolytic enzymes as one stage in bleaching of kraft pulps. Holzforschung-Int J Biol Chem Phys Technol Wood 46(6):481–488
Acknowledgements
The authors thankfully acknowledge the financial support provided by Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science & Technology, Government of India (Grant Number: BT/ PR 20438 / BCE /8 /1220 / 2016 for 3 years). The corresponding author is also thankful to Avantha Centre for Industrial Research and Development (ACIRD), Yamuna Nagar, for providing laboratory facilities. First author is thankful to Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra for providing the financial support in the form of University Research Scholarship.
Funding
The financial support was provided by Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science & Technology, Government of India (Grant Number: BT/PR20438/BCE/8/1220/2016 for 3 years).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ritu Mahajan (Corresponding Author): Idea of concept, planning and designing of various experiments done for this manuscript. Experimental work done by the first author for this manuscript under the corresponding author’s supervision. Raksha Nagpal (First Author): All experimental work mentioned in this manuscript done, both at Research laboratory and Paper Industry level, and also whole manuscript written by first author under the supervision of corresponding author. Nishi Kant Bhardwaj: Research work done, by first author, at Paper Industry level under his supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent to publication
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagpal, R., Bhardwaj, N.K. & Mahajan, R. Synergistic approach using ultrafiltered xylano-pectinolytic enzymes for reducing bleaching chemical dose in manufacturing rice straw paper. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 44637–44646 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11104-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11104-4