Abstract
Objective
Treatment for borderline resectable (cT3br) esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is currently undefined. This study aimed to analyze the outcome of treatment strategies including induction chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil (DCF) against T3br esophageal SCC.
Methods
A total of 32 patients with cT3br esophageal SCC enrolled in this study were treated with two cycles of DCF induction therapy.
Results
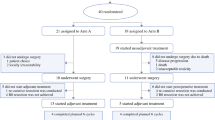
The overall response rate to DCF induction therapy was 62.5%, while the disease control rate was 93.8% (complete response (CR), three; partial response (PR), 17; stable disease (SD), 10; progressive disease (PD), 2). After DCF induction chemotherapy, 27 patients underwent conversion surgery (CS) and five patients underwent definitive chemoradiotherapy (CRT). Out of 27 patients who underwent CS, 17 underwent transthoracic esophagectomy and 10 underwent thoracoscopic esophagectomy. Anastomotic leakage occurred in five patients (18.5%) and pneumonia in four (14.8%). Recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis and arrhythmia were observed in two patients (7.4%). The R0 resection rate was 81.5%. Among the five patients who underwent definitive CRT, only one patient (20.0%) achieved CR. Two patients (40.0%) had PR and two (40.0%) had PD. Salvage esophagectomy was performed in one patient after definitive CRT. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival rates were 75.0, 50.6, and 46.4%, respectively, whereas the 1-, 3-, and 5-year disease-free survival rates were 54.9, 38.8, and 38.8%, respectively.
Conclusion
DCF induction therapy and subsequent CS or definitive CRT are promising treatment strategies for cT3br esophageal SCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Watanabe M, Toh Y, Ishihara R, Kono K, Matsubara H, Miyazaki T, Registration Committee for Esophageal Cancer of the Japan Esophageal Society, et al. Comprehensive registry of esophageal cancer in Japan, 2015. Esophagus. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-022-00950-5.
Saddoughi SA, Reinersman JM, Zhukov YO, Taswell J, Mara K, Harmsen SW, et al. Survival after surgical resection of stage IV esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103:261–6.
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
GLOBOCAN database. http://gco.iarc.fr/ (2020). Accessed 20 Dec 2022.
Watanabe M, Otake R, Kozuki R, Toihata T, Takahashi K, Okamura A, et al. Recent progress in multidisciplinary treatment for patients with esophageal cancer. Surg Today. 2020;50:12–20.
Lee CC, Soon YY, Vellayappan B, Ho F, Tey JCS. Survival rates and safety associated with chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery and chemoradiotherapy alone for patients with T4 esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Oncol. 2022;61:738–48.
Yoon HH, Ou FS, Soori GS, Shi Q, Wigle DA, Sticca RP, et al. Induction versus no induction chemotherapy before neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and surgery in oesophageal adenocarcinoma: a multicentre randomised phase II trial (NCCTG N0849 [Alliance]). Eur J Cancer. 2021;150:214–23.
Saeki H, Nakashima Y, Kudou K, Sasaki S, Jogo T, Hirose K, et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for patients with cT3/nearly T4 esophageal cancer: is sarcopenia correlated with postoperative complications and prognosis? World J Surg. 2018;42:2894–901.
Hamamoto Y, Nojima M, Aoki Y, Suzuki T, Kawasaki K, Hirata K, et al. Inter-evaluator heterogeneity of clinical diagnosis for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Esophagus. 2017;14:324–32.
Kobayashi K, Kanetaka K, Yoneda A, Kobayashi S, Maruya Y, Isagawa Y, et al. Downstaging and histological effects might be reliable predictors of the efficacy of DOC+CDDP+5-FU (DCF) as neoadjuvant therapy for stage III or borderline resectable esophageal cancer: a single institute experience. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2021;52:582–92.
Nakajima M, Muroi H, Kikuchi M, Yamaguchi S, Sasaki K, Tsuchioka T, et al. Salvage esophagectomy combined with partial aortic wall resection following thoracic endovascular aortic repair. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;66:736–43.
Japan Esophageal Society. Japanese classification of esophageal cancer, 11th edition: part II and III. Esophagus. 2017;14:37–65.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:228–47.
Nakajima M, Muroi H, Kikuchi M, Takahashi M, Ihara K, Shida Y, et al. Adverse prognostic factors of advanced esophageal cancer in patients undergoing induction therapy with docetaxel, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:911–8.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240:205–13.
Kitagawa Y, Uno T, Oyama T, Kato K, Kato H, Kawakubo H, et al. Esophageal cancer practice guidelines 2017 edited by the Japan Esophageal Society: part 1. Esophagus. 2019;16:1–24.
Ajani JA, D’Amico TA, Bentrem DJ, Cooke D, Corvera C, Das P, et al. NCCN clinical practice guideline in oncology (NCCN guidelinesⓇ) esophageal and esophagogastric junction cancers version 5. www.nccn.org/patients (2022). Accessed 20 Dec 2022.
Suzuki T, Okamura A, Watanabe M, Chin K. ASO author reflections: how should we approach borderline resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma? Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27:1518–9.
Ishikura S, Kondo T, Murai T, Ozawa Y, Yanagi T, Sugie C, et al. A single-arm, multicenter, phase II clinical study of tislelizumab plus albumin-bound paclitaxel/cisplatin as neoadjuvant therapy for borderline resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Radiat Res. 2020;61:464–9.
Suzuki T, Okamura A, Watanabe M, Mine S, Imamura Y, Asari T, et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy with cisplatin plus fluorouracil for borderline resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27:1510–7.
Wang Z, Hu M, Hu Y, Li Q, Wu J, Fong WP, et al. Paclitaxel plus cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil induction chemotherapy for locally advanced borderline-resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a phase II clinical trial. Esophagus. 2022;19:120–8.
Shiraishi O, Yasuda T, Kato H, Momose K, Hiraki Y, Yasuda A, et al. Comparison of aggressive planned salvage surgery versus neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery for borderline resectable T4 squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021;28:6366–75.
Li X, Xu C, Qiu H, Chen D, Zhu K, Zhang B, et al. A single-arm, multicenter, phase II clinical study of tislelizumab plus albumin-bound paclitaxel/cisplatin as neoadjuvant therapy for borderline resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10:263.
Ando N, Kato H, Igaki H, Shinoda M, Ozawa S, Shimizu H, et al. A randomized trial comparing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil versus preoperative chemotherapy for localized advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus (JCOG9907). Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:68–74.
Matsuda S, Kitagawa Y, Takemura R, Okui J, Okamura A, Kawakubo H, et al. Real-world evaluation of the efficacy of neoadjuvant DCF over CF in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: propensity score matched analysis from 85 authorized institutes for esophageal cancer in Japan. Ann Surg. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000005533.
Hirohata R, Hamai Y, Hihara J, Emi M, Kurokawa T, Yoshikawa T, et al. Evaluation of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery for borderline resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg. 2022;46:1934–43.
Sugase T, Sugimura K, Kanemura T, Takeoka T, Yamamoto M, Shinno N, et al. Recurrence pattern comparing preoperative chemoradiotherapy and preoperative chemotherapy with docetaxel plus 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin for advanced esophageal cancer. Oncology. 2022;100:655–65.
Makino T, Yamasaki M, Tanaka K, Miyazaki Y, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, et al. Treatment and clinical outcome of clinical T4 esophageal cancer: a systematic review. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2018;3:169–80.
Yokota T, Kato K, Hamamoto Y, Tsubosa Y, Ogawa H, Ito Y, et al. Phase II study of chemoselection with docetaxel plus cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil induction chemotherapy and subsequent conversion surgery for locally advanced unresectable oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2016;115:1328–34.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception, design, data analysis, and interpretation: NM, MH, KM, IK, and NM. Clinical data acquisition: IN, KT. Precision management: MS, NT, KK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nakajima, M., Muroi, H., Kikuchi, M. et al. Therapeutic strategy aiming at R0 resection for borderline-resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using induction chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 71, 584–590 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-023-01934-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-023-01934-7