Abstract
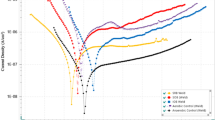
Microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) is closely associated with the metabolism of microorganisms, and organic nitrogen sources (ONS) are some of the key nutrients for bacterial metabolism. However, the influence of the amount of ONS on MIC and the corresponding mechanisms involved are still elusive. In this study, the MIC behavior of aluminum alloy 6061 in aqueous media with different amounts of ONS was investigated. Microbial activity and metabolism, which influenced the environment, were analyzed by optical density, pH, and NH4+ ion concentration. Pitting corrosion was analyzed by scanning electronic microscopy and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Bacillus aerius inhibited the development of pitting corrosion in aluminum alloy 6061 because of the NH4+ and NH3·H2O in their metabolites, which provided a pH buffering effect that suppressed the autocatalysis alkalinization around intermetallic inclusions. The inhibitory effect was positively correlated with microbial activity. Therefore, a higher concentration of ONS contributed to the inhibition of pitting corrosion because ONS was beneficial to the propagation and proliferation of bacteria.










Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
29 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06446-0
References
M. Zhu, B.Z. Zhao, Y.F. Yuan, S.Y. Guo and J. Pan, Effect of Solution Temperature on the Corrosion Behavior of 6061–T6 Aluminum Alloy in NaCl Solution, J. Mater. Eng. and Perform., 2020, 29(7), p 4725–4732.
J. Wang, H. Yang, M. Du, J. Hou, W. Peng and C. Lin, Corrosion Mechanism of 5083 Aluminum Alloy in Seawater Containing Phosphate, J. Ocean Univ. China, 2021, 20(2), p 372–382.
M.X. Milagre, U. Donatus, R.M.P. Silva, A.M. Betancor-Abreu, O.M.P. Ramirez, C.S.C. Machado, J.V.S. Araujo, R.M. Souto and I. Costa, Galvanic Coupling Effects on the Corrosion Behavior of the 6061 Aluminum Alloy Used in Research Nuclear Reactors, J. Nucl. Mater., 2020, 541, p 152440.
N. Li, C. Dong, C. Man and J. Yao, In Situ Electrochemical Atomic Force Microscopy and Auger Electro Spectroscopy Study on the Passive Film Structure of 2024–T3 Aluminum Alloy Combined with a Density Functional Theory Calculation, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2019, 21(12), p 1900386.
Y. Ji, C. Dong, D. Kong and X. Li, Design Materials Based on Simulation Results of Silicon Induced Segregation at AlSi10Mg Interface Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2020, 46, p 145–155.
S. Zhang, T. Zhang, Y. He, D. Liu, J. Wang, X. Du and B. Ma, Long-Term Atmospheric Corrosion of Aluminum Alloy 2024–T4 in Coastal Environment: Surface and Sectional Corrosion Behavior, J. Alloy. and Compd., 2019, 789, p 460–471.
C. Alvarado G., M. Sancy, J.M. Blamey, C. Galarce, A. Monsalve, F. Pineda, N. Vejar, and M. Páez, Electrochemical Characterization of Aluminum Alloy AA2024 − T3 Influenced by Bacteria from Antarctica, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 247, p 71–79.
K. Nishchitha, M.K. Deepa, B.G. Prakashaiah, J.N. Balaraju and B.E. Amitha rani, Effect of Surface Treatment on Bio-Corrosion in Aluminum Alloy 2024–T3, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2018, 27(11), p 5778–5787.
H. Liu, B. Zheng, D. Xu, C. Fu and Y. Luo, Effect of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Iron-Oxidizing Bacteria on the Rate of Corrosion of an Aluminum Alloy in a Central Air-Conditioning Cooling Water System, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, 53(19), p 7840–7846.
X. Li, H. Wang, C. Hu, M. Yang, H. Hu and J. Niu, Characteristics of Biofilms and Iron Corrosion Scales with Ground and Surface Waters in Drinking Water Distribution Systems, Corros. Sci., 2015, 90, p 331–339.
V. Pozzobon, W. Levasseur, C. Guerin and P. Perré, Nitrate and Nitrite as Mixed Source of Nitrogen for Chlorella Vulgaris: Fast Nitrogen Quantification Using Spectrophotometer and Machine Learning, J. Appl. Phycol., 2021 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-021-02422-2
Y. Hu, K. Xiao, D. Zhang, P. Yi, R. Xiong, C. Dong, J. Wu and X. Li, Corrosion Acceleration of Printed Circuit Boards With an Immersion Silver Layer Exposed to Bacillus Cereus in an Aerobic Medium, Front. Microbiol., 2019, 10, p 1493.
F. Guan, X. Zhai, J. Duan, J. Zhang, K. Li and B. Hou, Influence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on the Corrosion Behavior of 5052 Aluminum Alloy, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2017, 316, p 171–179.
J.S. de Andrade, M.R.S. Vieira, S.H. Oliveira, S.K. de Melo Santos and S.L. Urtiga Filho, Study of Microbiologically Induced Corrosion of 5052 Aluminum Alloy by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria in Seawater, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2020, 241, p 122296.
J. Wang, F. Xiong, H. Liu, T. Zhang, Y. Li, C. Li, W. Xia, H. Wang and H. Liu, Study of the Corrosion Behavior of Aspergillus Niger on 7075–T6 Aluminum Alloy in a High Salinity Environment, Bioelectrochemistry, 2019, 129, p 10–17.
M. Sancy, A. Abarzúa, M.I. Azócar, J.M. Blamey, F. Boehmwald, G. Gómez, N. Vejar and M. Páez, Biofilm Formation on Aluminum Alloy 2024: A Laboratory Study, J. of Electroanal. Chem., 2015, 737, p 212–217.
X. Dai, H. Wang, L.-K. Ju, G. Cheng, H. Cong and B.Z. Newby, Corrosion of Aluminum Alloy 2024 Caused by Aspergillus Niger, Int. Biodeter. Biodegr., 2016, 115, p 1–10.
E. Juzeliūnas, R. Ramanauskas, A. Lugauskas, M. Samulevičienė and K. Leinartas, Microbially Influenced Corrosion Acceleration and Inhibition. EIS Study of Zn and Al Subjected for Two Years to Influence of Penicillium Frequentans, Aspergillus Niger and Bacillus Mycoides, Electrochem. Commun., 2005, 7(3), p 305–311.
T. Tran Thi Thuy, K. Kannoorpatti, A. Padovan, S. Thennadil, and N. Nguyen Dang, Effect of Nickel on the Adhesion and Corrosion Ability of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa on Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2019, 28(9), p 5797–5805.
R. Xiong, K. Xiao, P. Yi, Y. Hu, C. Dong, J. Wu and X. Li, The Influence of Bacillus Subtilis on Tin-Coated Copper in an Aqueous Environment, RSC Adv., 2018, 8(9), p 4671–4679.
Q. Liu, Z. Li, Z.Y. Liu, X.G. Li and S.Q. Wang, Effects of H2S/HS− on Stress Corrosion Cracking Behavior of X100 Pipeline Steel Under Simulated Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Metabolite Conditions, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26(6), p 2763–2775.
A. Rajasekar and Y.-P. Ting, Role of Inorganic and Organic Medium in the Corrosion Behavior of Bacillus Megaterium and Pseudomonas Sp in Stainless Steel SS 304, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2011, 50(22), p 12534–12541.
M.A. Javed, P.R. Stoddart, E.A. Palombo, S.L. McArthur and S.A. Wade, Inhibition or Acceleration: Bacterial Test Media Can Determine the Course of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion, Corros. Sci., 2014, 86, p 149–158.
Z.Y. Cui, X.G. Li, C. Man, K. Xiao, C.F. Dong, X. Wang and Z.Y. Liu, Corrosion Behavior of Field-Exposed 7A04 Aluminum Alloy in the Xisha Tropical Marine Atmosphere, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24(8), p 2885–2897.
F. Guan, J. Duan, X. Zhai, N. Wang, J. Zhang, D. Lu and B. Hou, Interaction between Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Aluminum Alloys—Corrosion Mechanisms of 5052 and Al-Zn-In-Cd Aluminum Alloys, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2020, 36, p 55–64.
L. Wen, Y.M. Wang, Y. Liu, Y. Zhou, L.X. Guo, J.H. Ouyang and D.C. Jia, EIS Study of a Self-Repairing Microarc Oxidation Coating, Corros. Sci., 2011, 53(2), p 618–623.
B. Wang, L. Zhang, H. Jiang, X. Li and X. Mu, Atmospheric Corrosion Comparison of Antirust Aluminum Exposed to Industrial and Coastal Atmospheres, Mater. Corros., 2018, 69(11), p 1516–1525.
Q. Zhao, C. Guo, K. Niu, J. Zhao, Y. Huang and X. Li, Long-Term Corrosion Behavior of the 7A85 Aluminum Alloy in an Industrial-Marine Atmospheric Environment, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, 12, p 1350–1359.
D. Chaofang, X. Kui, X. Lin, S. Hai, A. Yinghui and L. Xiaogang, Characterization of 7A04 Aluminum Alloy Corrosion under Atmosphere with Chloride Ions Using Electrochemical Techniques, Rare. Metal. Mat. Eng., 2011, 40(S2), p 275–179.
K. Ding, S. Liu, W. Cheng, J. Du, L. Fan, J. Hou and L. Xu, Corrosion Behavior of T2 and B30 Cu-Ni Alloy at Different Seawater Depths of the South China Sea, J. Mater. Eng Perform., 2021 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05790-5
K. Xiao, X. Gao, L. Yan, P. Yi, D. Zhang, C. Dong, J. Wu and X. Li, Atmospheric Corrosion Factors of Printed Circuit Boards in a Dry-Heat Desert Environment: Salty Dust and Diurnal Temperature Difference, Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 336, p 92–101.
R. Zuo, E. Kus, F. Mansfeld and T.K. Wood, The importance of live biofilms in corrosion protection, Corros. Sci., 2005, 47(2), p 279–287.
C. Blanc and G. Mankowski, Susceptibility to Pitting Corrosion of 6056 Aluminium Alloy, Corros. Sci., 1997, 39(5), p 949–959.
J.H.W. de Wit, New Knowledge on Localized Corrosion Obtained from Local Measuring Techniques, Electrochim. Acta, 2001, 46(24), p 3641–3650.
D. Zander, C. Schnatterer, C. Altenbach and V. Chaineux, Microstructural Impact on Intergranular Corrosion and the Mechanical Properties of Industrial Drawn 6056 Aluminum Wires, Mat. Design, 2015, 83, p 49–59.
W. Tian, S. Li, X. Chen, J. Liu and M. Yu, Intergranular Corrosion of Spark Plasma Sintering Assembled Bimodal Grain Sized AA7075 Aluminum Alloys, Corros. Sci., 2016, 107, p 211–224.
J. Ryl, J. Wysocka, M. Jarzynka, A. Zielinski, J. Orlikowski and K. Darowicki, Effect of Native Air-Formed Oxidation on the Corrosion Behavior of AA 7075 Aluminum Alloys, Corros. Sci., 2014, 87, p 150–155.
N. Birbilis and R.G. Buchheit, Investigation and Discussion of Characteristics for Intermetallic Phases Common to Aluminum Alloys as a Function of Solution PH, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2008, 155(3), p C117.
J.O. Park, C.-H. Paik and R.C. Alkire, Scanning Microsensors for Measurement of Local PH Distributions at the Microscale, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, 143(8), p L174.
M. Büchler, T. Watari and W.H. Smyrl, Investigation of the Initiation of Localized Corrosion on Aluminum Alloys by Using Fluorescence Microscopy, Corros. Sci., 2000, 42(9), p 1661–1668.
A.F. Forte Giacobone, S.A. Rodriguez, A.L. Burkart and R.A. Pizarro, Microbiological Induced Corrosion of AA 6061 Nuclear Alloy in Highly Diluted Media by Bacillus Cereus RE 10, Int. Biodeter. Biodegr., 2011, 65(8), p 1161–1168.
Z. Li, H. Wan, D. Song, X. Liu, Z. Li and C. Du, Corrosion Behavior of X80 Pipeline Steel in the Presence of Brevibacterium Halotolerans in Beijing Soil, Bioelectrochemistry, 2019, 126, p 121–129.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51971032 and 51771027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised: In the originally published article, Figure 5 showed a copy of Figure 4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Z., Xiao, K., Yao, Q. et al. Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of AA 6061 with Bacillus Species in an Environment Containing an Organic Nitrogen Source. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 1870–1880 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06379-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06379-8