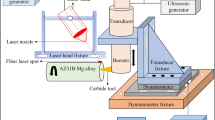
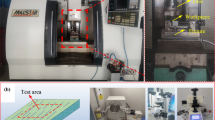
Abstract
The use of cryogenic coolants as an alternative cooling technique has been applied widely in recent years because of the many problems associated with conventional cutting fluids. No paper has been published to date on the milling of AZ31 magnesium alloy under dipped cryogenic cooling approach. The comprehensive results from the experimental study have practical importance and provide valuable information for industrial production processes. In this study, milling tests were carried out on AZ31B magnesium alloy under various cutting speeds, feed rates, and depths of cut. During milling, the effects of liquid nitrogen on milling forces, chip formation, and surface roughness were examined and a damage analysis was also carried out. This study introduced a novel cryogenic approach in the milling of AZ31B magnesium alloy using a liquid nitrogen bath. A new experimental setup was prepared for performing milling tests with the approach. Based on the experimental results, it was concluded that using the dipped cryogenic approach improved (approximately 2–34%) the surface quality of the workpiece and provided shorter chip formation. In addition to these, in the tests carried out under dry cutting conditions, lower milling forces (approximately 16–88%) were formed compared to the cryogenic conditions. A surface damage analysis was also performed.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Mg :
-
Magnesium
- LN2 :
-
Liquid nitrogen
- HB:
-
Hardness
- PVD:
-
Physical vapor deposition
- AlCrN:
-
Aluminum chromium nitride
- SEM :
-
Scanning electron microscope
- Fx :
-
Milling force in the X direction (N)
- Fy :
-
Milling force in the Y direction (N)
- Fz :
-
Milling force in the Z direction (N)
- Vc :
-
Cutting speed (m/min)
- f :
-
Feed rate (mm/min)
- ap :
-
Depth of cut (mm)
- CL :
-
Cutting length
- MRR :
-
Material removal rate (mm3/min)
- µ:
-
Micron (µ)
References
Guo, Y., Quan, G., Jiang, Y., Ren, L., Fan, L., & Pan, H. (2020). Formability, Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Wire arc Additively Manufactured AZ80M Magnesium Alloy Using Gas Tungsten Arc Welding. J. Magnes. Alloys.
N. Anandan and M. Ramulu, Study of Machining Induced Surface Defects and Its Effect on Fatigue Performance of AZ91/15% SiCp Metal Matrix Composite, J. Magnes. Alloys, 2020, 8(2), p 387–395.
J.A. Gonsalves, S.N. Nayak and G. Bolar, Experimental Investigation on the Performance of Helical Milling for Hole Processing in AZ31 Magnesium Alloy, J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci., 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2020.10.004
F. Xu, L. Luo, L. Xiong and Y. Liu, Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of ALD Al2O3 Film on AZ31 Magnesium Alloy With Different Surface Roughness, J. Magnes. Alloys, 2020, 2(8), p 480.
A.T. Abbas, D.Y. Pimenov, I.N. Erdakov, M.A. Taha, M.S. Soliman and M.M. El Rayes, ANN Surface Roughness Optimization of AZ61 Magnesium Alloy Finish Turning: Minimum Machining Times at Prime Machining Costs, Mater., 2018, 11(5), p 808.
S.C. Cagan, C.I. Pruncu and B.B. Buldum, An Investigation into Ball Burnishing Process of Magnesium Alloy on CNC Lathe Using Different Environments, J. Magnes. Alloys, 2020, 8(4), p 1061–1070.
M. Jamil, W. Zhao, N. He, M.K. Gupta, M. Sarikaya, A.M. Khan and D.Y. Pimenov, Sustainable Milling of Ti–6Al–4V: A Trade-Off Between Energy Efficiency, Carbon Emissions and Machining Characteristics Under MQL and Cryogenic Environment, J. Clean. Prod., 2021, 281, p 125374.
M. Jebaraj and M. Pradeep Kumar, Effect of Cryogenic CO2 and LN2 Coolants in Milling of Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2019, 34(5), p 511–520.
M. Sarikaya, M.K. Gupta, I. Tomaz, M. Danish, M. Mia, S. Rubaiee and N. Khanna, Cooling Techniques to Improve the Machinability and Sustainability of Light-Weight Alloys: A State-of-the-Art Review, J. Manuf. Process., 2021, 62, p 179–201.
Pimenov, D. Y., Mia, M., Gupta, M. K., Machado, A. R., Tomaz, Í. V., Sarikaya, M., ... & Kapłonek, W. (2021). Improvement of Machinability of Ti and its Alloys Using Cooling-Lubrication Techniques: A Review and Future Prospect. J. Mater. Res. Technol.
F. Jiang, T. Zhang and L. Yan, Estimation of Temperature-Dependent Heat Transfer Coefficients in Near-Dry Cutting, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2016, 86(5), p 1207–1218.
Koklu, U., Morkavuk, S., Featherston, C., Haddad, M., Sanders, D., Aamir, M., ... & Giasin, K. (2021). The Effect of Cryogenic Machining of S2 Glass Fibre Composite on the Hole form and Dimensional Tolerances. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 1-16.
A. Shokrani, V. Dhokia, P. Muñoz-Escalona and S.T. Newman, State-of-the-Art Cryogenic Machining and Processing, Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf., 2013, 26(7), p 616–648.
U. Koklu and H. Çoban, Effect of Dipped Cryogenic Approach on Thrust Force, Temperature, Tool Wear and Chip Formation in Drilling of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy, J. Market. Res., 2020, 9(3), p 2870–2880.
A.H. Kheireddine, A.H. Ammouri, T. Lu, I.S. Jawahir and R.F. Hamade, An FEM Analysis with Experimental Validation to Study the Hardness of In-Process Cryogenically Cooled Drilled Holes in Mg AZ31b, Procedia Cirp, 2013, 8, p 588–593.
A.H. Kheireddine, A.H. Ammouri, T. Lu, O.W. Dillon, R.F. Hamade and I.S. Jawahir, An Experimental and Numerical Study of the Effect of Cryogenic Cooling on the Surface Integrity of Drilled Holes in AZ31B Mg Alloy, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2015, 78(1–4), p 269–279.
Z. Pu, J.C. Outeiro, A.C. Batista, O.W. Dillon Jr., D.A. Puleo and I.S. Jawahir, Enhanced Surface Integrity of AZ31B Mg Alloy by Cryogenic Machining Towards Improved Functional Performance of Machined Components, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 2012, 56, p 17–27.
Z. Pu, D. Umbrello, O.W. Dillon Jr., T. Lu, D.A. Puleo and I.S. Jawahir, Finite Element Modeling of Microstructural Changes in Dry and Cryogenic Machining of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy, J. Manuf. Process., 2014, 16(2), p 335–343.
M.N. Nasr and J.C. Outeiro, Sensitivity Analysis of Cryogenic Cooling on Machining of Magnesium Alloy AZ31B-O, Procedia Cirp, 2015, 31, p 264–269.
S. Dinesh, V. Senthilkumar and P. Asokan, Experimental Studies on the Cryogenic Machining of Biodegradable ZK60 Mg Alloy Using Micro-Textured Tools, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2017, 32(9), p 979–987.
R. Bertolini, S. Bruschi, A. Ghiotti, L. Pezzato and M. Dabalà, The Effect of Cooling Strategies and Machining Feed Rate on the Corrosion Behavior and Wettability of AZ31 Alloy for Biomedical Applications, Procedia Cirp, 2017, 65, p 7–12.
A. Shokrani, V. Dhokia and S.T. Newman, Investigation of the Effects of Cryogenic Machining on Surface Integrity in CNC end Milling of Ti–6Al–4V Titanium Alloy, J. Manuf. Process., 2016, 21, p 172–179.
D. Kumar, S. Gururaja and I.S. Jawahir, Machinability and Surface Integrity of Adhesively Bonded Ti/CFRP/Ti Hybrid Composite Laminates Under Dry and Cryogenic Conditions, J. Manuf. Process., 2020, 58, p 1075–1087.
K.K. Kumar and S.K. Choudhury, Investigation of Tool Wear and Cutting Force in Cryogenic Machining Using Design of Experiments, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 203(1–3), p 95–101.
M. Dhananchezian and M.P. Kumar, Cryogenic Turning of the Ti–6Al–4V Alloy with Modified Cutting Tool Inserts, Cryog., 2011, 51(1), p 34–40.
M. Dhananchezian, M.P. Kumar and T. Sornakumar, Cryogenic Turning of AISI 304 Stainless Steel with Modified Tungsten Carbide Tool Inserts, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2011, 26(5), p 781–785.
A.H. Musfirah, J.A. Ghani and C.C. Haron, Tool Wear and Surface Integrity of Inconel 718 in Dry and Cryogenic Coolant at High Cutting Speed, Wear, 2017, 376, p 125–133.
S. Ravi and M.P. Kumar, Experimental Investigations on Cryogenic Cooling by Liquid Nitrogen in the End Milling of Hardened Steel, Cryog., 2011, 51(9), p 509–515.
Çiçek, A., Ekici, E., Kıvak, T., Kara, F., & Ucak, N. (2021). Performance of Multilayer Coated and Cryo-treated Uncoated Tools in Machining of AISI H13 Tool Steel—Part 2: HSS End Mills. J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 1-12.
O. Pereira, A. Celaya, G. Urbikaín, A. Rodríguez, A. Fernández-Valdivielso and L.N.L. de Lacalle, CO2 Cryogenic Milling of Inconel 718: Cutting Forces and Tool Wear, J. Market. Res., 2020, 9(4), p 8459–8468.
W. Zhao, F. Ren, A. Iqbal, L. Gong, N. He and Q. Xu, Effect of Liquid Nitrogen Cooling on Surface Integrity in Cryogenic Milling of Ti–6al–4v Titanium Alloy, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2020, 106(3), p 1497–1508.
Chhetri, S., Tariq, M., Mohapatra, S. D., Sumi, V. V., Zhimomi, A. P., Davis, R., & Singh, A. (2020, December). Surface Characteristics Enhancement of Biocompatible Mg Alloy AZ31B by Cryogenic Milling. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 1004, No. 1, p. 012011). IOP Publishing.
G.R. Li, H.M. Wang, Y. Cai, Y.T. Zhao, J.J. Wang and S.P. Gill, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ91 Magnesium Alloy Subject to Deep Cryogenic Treatments, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2013, 20(9), p 896–901.
R. Shishir, A.R. Shebeer and T. Hanas, Studies on Effect of Cryogenic Treatment on Bio-corrosion of Low Calcium Containing Mg-Ca Alloy, Mater. Today: Proc., 2020, 22, p 2877–2882.
http://www.matweb.com/search/datasheet.aspx?matguid=d1e286e1ac0742358544b953bbf3c2e9&ckck=1
M. Aamir, M. Tolouei-Rad, K. Giasin and A. Vafadar, Feasibility of Tool Configuration and the Effect of Tool Material, and Tool Geometry in Multi-Hole Simultaneous Drilling of Al2024, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2020, 111(3), p 861–879.
I. Hanafi, A. Khamlichi, F.M. Cabrera, P.J.N. López and A. Jabbouri, Fuzzy Rule Based Predictive Model for Cutting Force in Turning of Reinforced PEEK Composite, Meas., 2012, 45(6), p 1424–1435.
Çiçek, A., Kıvak, T., Ekici, E., Kara, F., & Ucak, N. (2021). Performance of Multilayer Coated and Cryo-Treated Uncoated Tools in Machining of AISI H13 Tool Steel—Part 1: Tungsten Carbide End Mills. J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 1-10.
U. Koklu, S. Morkavuk and L. Urtekin, Effects of the Drill Flute Number on Drilling of a Casted AZ91 Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Test., 2019, 61(3), p 260–266.
Z. Zhao and S.Y. Hong, Cooling Strategies for Cryogenic Machining from a Materials Viewpoint, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 1992, 1(5), p 669–678.
U. Koklu and S. Morkavuk, Cryogenic Drilling of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Composite (CFRP), Surf. Rev. Lett., 2019, 26(09), p 1950060.
G. Basmaci, A.S. Yoruk, U. Koklu and S. Morkavuk, Impact of Cryogenic Condition and Drill Diameter on Drilling Performance of CFRP, Appl. Sci., 2017, 7(7), p 667.
S. Morkavuk, U. Köklü, M. Bağcı and L. Gemi, Cryogenic Machining of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic (CFRP) Composites and the Effects of Cryogenic Treatment on Tensile Properties: a Comparative Study, Compos. B Eng., 2018, 147, p 1–11.
Giasin, K., Barouni, A., Dhakal, H. N., Featherson, C., Redouane, Z., Morkavuk, S., & Koklu, U. (2020). Microstructural Investigation and Hole Quality Evaluation in S2/FM94 Glass-Fibre Composites Under Dry and Cryogenic Conditions. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., 0731684420958479.
F. Kara, M. Karabatak, M. Ayyıldız and E. Nas, Effect of Machinability, Microstructure and Hardness of Deep Cryogenic Treatment in Hard Turning of AISI D2 Steel with Ceramic Cutting, J. Market. Res., 2020, 9(1), p 969–983.
J.P. Costes, Y. Guillet, G. Poulachon and M. Dessoly, Tool-Life and Wear Mechanisms of CBN Tools in Machining of Inconel 718, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf, 2007, 47(7–8), p 1081–1087.
U.A. Dabade and S.S. Joshi, Analysis of Chip Formation Mechanism in Machining of Al/SiCp Metal Matrix Composites, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209(10), p 4704–4710.
B.R. Sunil, K.V. Ganesh, P. Pavan, G. Vadapalli, C. Swarnalatha, P. Swapna and G.P.K. Reddy, Effect of Aluminum Content on Machining Characteristics of AZ31 and AZ91 Magnesium Alloys During Drilling, J. Magnes. Alloys, 2016, 4(1), p 15–21.
M. Uludağ, Ş Yazman, L. Gemi, B. Bakircioğlu, E. Erzi and D. Dispinar, Relationship Between Machinability, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties of Al-7Si Alloy, J. Test. Eval., 2018, 46(6), p 2592–2603.
Ş Yazman, L. Gemı, M. Uludağ, A. Akdemır, M. Uyaner and D. Dişpinar, Correlation Between Machinability and Chip Morphology of Austempered Ductile Iron, J. Test. Eval., 2017, 46(3), p 1012–1021.
H.A. Al-Tameemi, T. Al-Dulaimi, M.O. Awe, S. Sharma, D.Y. Pimenov, U. Koklu and K. Giasin, Evaluation of Cutting-Tool Coating on the Surface Roughness and Hole Dimensional Tolerances During Drilling of Al6061-T651 Alloy, Mater., 2021, 14(7), p 1783.
Ş Yazman, U. Köklü, L. Urtekin, S. Morkavuk and L. Gemi, Experimental Study on the Effects of Cold Chamber Die Casting Parameters on High-Speed Drilling Machinability of Casted AZ91 Alloy, J. Manuf. Process., 2020, 57, p 136–152.
K. Giasin, A. Hodzic, V. Phadnis and S. Ayvar-Soberanis, Assessment of Cutting Forces and Hole Quality in Drilling Al2024 Aluminium Alloy: Experimental and Finite Element Study, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2016, 87(5), p 2041–2061.
Kuram, E., Ozcelik, B., Demirbas, E., & Sik, E. (2010, July). Effects of the cutting fluid types and cutting parameters on surface roughness and thrust force. In Proceedings of the world congress on engineering (Vol. 2, pp. 978-988).
S. Basavarajappa, G. Chandramohan and J.P. Davim, Some Studies on Drilling of Hybrid Metal Matrix Composites Based on Taguchi Techniques, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 196(1–3), p 332–338.
J.P. Davim, V.N. Gaitonde and S.R. Karnik, Investigations into the Effect of Cutting Conditions on Surface Roughness in Turning of Free Machining Steel by ANN Models, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 205(1–3), p 16–23.
M. Aamir, K. Giasin, M. Tolouei-Rad and A. Vafadar, A Review: Drilling Performance and Hole Quality of Aluminium Alloys for Aerospace Applications, J. Market. Res., 2020, 9(6), p 12484–12500.
G. Hebbar, G. D’Mello and P.S. Pai, Surface Roughness Optimization in Machining of Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys, Mater. Today: Proc., 2018, 5(5), p 11787–11793.
Reddy, U., Dubey, D., Panda, S. S., Ireddy, N., Jain, J., Mondal, K., & Singh, S. S. (2021). Effect of Surface Roughness Induced by Milling Operation on the Corrosion Behavior of Magnesium Alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 1-11.
U. Koklu, The Drilling Machinability of 5083 Aluminum Under Shallow and Deep Cryogenic Treatment, Emerg. Mater. Res., 2020, 9(2), p 323–330.
M. Aamir, M. Tolouei-Rad, K. Giasin, A. Vafadar, U. Koklu and W. Keeble, Evaluation of the Surface Defects and Dimensional Tolerances in Multi-Hole Drilling of AA5083, AA6061, and AA2024, Appl. Sci., 2021, 11(9), p 4285.
Y. Yao, H. Zhu, C. Huang, J. Wang, P. Zhang and P. Yao, Investigation on Chip Formation and Surface Integrity in Micro end Milling of Maraging Steel, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2019, 102(5), p 1973–1984.
S.Y. Hong, Lubrication Mechanisms of LN2 in Ecological Cryogenic Machining, Mach. Sci. Technol., 2006, 10(1), p 133–155.
S.Y. Hong, Y. Ding and J. Jeong, Experimental Evaluation of Friction Coefficient and Liquid Nitrogen Lubrication Effect in Cryogenic Machining, Mach. Sci. Technol., 2002, 6(2), p 235–250.
M.K. Gupta, Q. Song, Z. Liu, M. Sarikaya, M. Jamil, M. Mia and G.M. Krolczyk, Experimental Characterisation of the Performance of Hybrid Cryo-Lubrication Assisted Turning of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy, Tribol. Int., 2021, 153, p 106582.
L.S. Ahmed and M.P. Kumar, Cryogenic Drilling of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy Under Liquid Nitrogen Cooling, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2016, 31(7), p 951–959.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Commission of Scientific Research Projects of Karamanoglu Mehmetbey University, Karaman-Turkey (Project No. 08-YL-17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koklu, U., Kayhanlar, H. An Experimental Investigation on Machinability of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy under Dry and Dipped Cryogenic Approaches. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 1285–1296 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06264-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06264-4