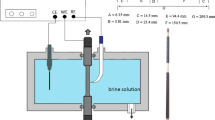
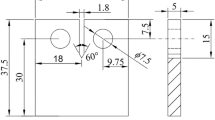
Abstract
Round tensile specimens of modified 9Cr-1Mo steel were subjected to slow strain rate tests in 1-4 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solutions at 473 K to evaluate their susceptibility to caustic stress corrosion cracking (CSCC). The results obtained in NaOH solutions were compared with specimen tested in de-mineralized (DM) water. Secondary stress corrosion cracks were observed in all specimens tested in 1-4 M NaOH, the number of secondary cracks increased with increase in concentration up to 3 M. Tensile test data showed that ductility (%TE) decreased with increasing concentration of NaOH up to 3 M and nearly remained the same for 4 M NaOH. Time to failure was highest for specimen exposed in DM water and decreased with increasing concentration up to 3 M and remained constant thereafter. Crack velocity showed a trend of increasing velocity with increasing concentration of caustic media up to 3 M and remained same for 4 M NaOH. Laser Raman spectroscopic (LRS) analysis confirmed dissolution of protective magnetite and accelerated corrosion on the specimens exposed to 1-4 M NaOH solutions, leading to the formation of a number of oxides and oxyhydroxides. Fractographic studies showed typical surface oxide cracking with decohesions in all specimens. The studies showed that P91 steel is susceptible to CSCC in the concentrations from 1 to 4 M NaOH solutions at 473 K at a strain rate of 10−6 s−1. The evidence for dissolution of magnetite and the presence of decohesions indicated an important role for hydrogen in caustic cracking of P91 steel.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caustic Stress Corrosion Cracking, No. 13, Technical Awareness Bulletin, Materials Technology Institute Inc. 2012
W. Lee Williams, Chloride and Caustic Stress Corrosion of Austenitic Stainless Steel in Hot Water and Steam, Corrosion, 1957, 13, p 67–73
T.V. Vinoy, H. Shaikh, H.S. Khatak, N. Sivaibharasi, and J.B. Gnanamoorthy, Stress Corrosion Crack Growth Studies on AISI Type Stainless Steel in Boiling Acidified Sodium Chloride Solution, J. Nucl. Mater., 1996, 238, p 278–284
W. Yang, G. Zhao, M. Zhang, and J. Congleton, An AES Investigation of the Surface Films Formed on Stress Corrosion Test Specimens of Type 304 Stainless Steel in High Temperature Water, Corros. Sci., 1992, 33, p 89–102
S.L. Mannan, S.C. Chetal, B. Raj, S.B. Bhoje, Selection of materials for prototype fast breeder reactor, in Proceedings of the Materials R&D for PFBR, IGCAR, Kalpakkam, 2003, pp. 9–44
S. Kishore, F. Beauchamp, A. Alexandre, A. Ashok Kumar, S. Chandramouli, and K.K. Rajan, Impingement Wastage Experiments with 9Cr-1Mo Steel, Nucl. Eng. Des., 2016, 297, p 104–110
J.R. Donati, M. Grand, and P. Spiteri, Etude des phenomenes de corrosion consecutifs a une micro-reaction sodium-eau dansune fissure traversante d’un tube de generateur de vapeur de reagteurrapide, J. Nucl. Mater., 1974, 542, p 217–223
C.M. Younes, F.H. Morrissey, G.C. Allen, and P. McIntyre, Effect of Heat TREATMENT on Grain Boundary Chemistry and Resistance to Intergranular CORROSION of Alloys 600 and 690, Br. Corros. J., 1997, 32, p 185–192
J.-Y. Jeong, J.-M. Kim, T.-J. Kim, J.-H. Choi, B.-H. Kim, Y. Lee, Wastage of steam generator tubes by sodium-water reaction, in: Transactions of the Korean Nuclear Society Autumn Meeting, Jeju, Korea, 2010, pp. 41–42
B. Poulson, Caustic Cracking of 9Cr 1Mo Steel at 300 °C, Corros. Sci., 1982, 22, p 473–486
DOE-HDBK-1015, DOE fundamentals handbook, Chemistry module 2, Corrosion, U.S. DOE, Washington, 1993, pp. 1–93
Z.W. Yang, D. Huang, D. Kong, G. Zhao, and J. Congleton, Caustic Stress Corrosion CRACKING of Nickel-Rich, Chromium-Bearing Alloys, Corros. Sci., 2001, 43, p 963–977
D. Singbeil and D. Tromans, Caustic Stress Corrosion Cracking of Mild Steel, Metall. Trans. A, 1982, 13, p 1091–1098
K. Abouswa, F. Elshawesh, and A. Abuargoub, Stress Corrosion Cracking (Caustic Embrittlement) of Super Heater Tubes, Desalination, 2008, 222, p 682–688
M. Yasuda, M. Okada, and F. Hin, Corrosion of Carbon Steel in Hot NaOH Solutions Under Heat Transfer Conditions, Corrosion, 1982, 38, p 256–261
ASTM Standard E8/E8M-13a, Standard test methods for testing of metallic materials. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States, 2013, pp. 1–28
P. Muraleedharan, Metallurgical influences on stress corrosion behaviour of austenitic stainless steels in chloride media, Ph.D. thesis, 1993
E. Henthorne, The Slow Strain Rate Stress Corrosion Cracking Test: a 50 yEAR retrospective M. Henthorne, Corrosion, 2016, 72(12), p 1488–1518
A. Dessert and R. Oltra, The Influence of Plastic Straining on Localized and General Corrosion of Stainless Steels, Corros. Sci., 1980, 20, p 799–820
M.G. Fontana, Eight Forms of Corrosion, Corrosion Engineering, 3rd ed., McGraw Hill Education, New York, 2005, p 112–114
A.R. McIlree and H.T. Michels, Stress Corrosion Behaviour of Fe-Cr-Ni and Other Alloys in High Temperature Caustic Solutions, Corrosion, 1977, 33, p 60–67
V. Thomas Paul, S. Saroja, and M. Vijayalakshmi, Microstructural Stability of Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel During Long Term Exposures at Elevated Temperatures, J. Nucl. Mater., 2008, 378, p 273–281
U. Schwertmann and H. Fechter, The Formation of Green Rust and Its Transformation to Lepidocrocite, Clay Miner., 1994, 29, p 87–92
T.S. Gendler, V.P. Shcherbakov, M.J. Dekkers, A.K. Gapeev, S.K. Gribov, and E. McClell, The Lepidocrocite–Maghemite–Haematite Reaction Chain—I. Acquisition of Chemical Remanent Magnetization by Maghemite, Its Magnetic Properties and Thermal Stability, Geophys. J. Int., 2005, 160, p 815–832
P.M.A. De Bakker, E. De Grave, R.E. Vandenberghe, L.H. Bowen, R.J. Pollard, and M. Persoons, Study of the Thermal Decomposition of Lepidocrocite and Characterization of the Decomposition Products, Phys. Chem. Miner., 1991, 18, p 131–143
O. Ozdemir and S.K. Banerjee, High Temperature Stability of Maghemite, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1984, 11, p 161–164
A. Matthews, Magnetite Formation by the Reduction of Hematite with Iron Under Hydrothermal Condition, Am. Mineral., 1976, 6, p 927–932
A. Matthews, Oxygen isotope geology: experimental calibration of geothermometers with related experimental investigations. Ph.D. thesis, University of Manchester, 1973
Hans-Peter Hermansson, The Stability of Magnetite and its Significance as a Passivating Film in the Repository Environment, in: Studsvik Nuclear AB SE-611 82 Nyköping, Sweden, 2004, vol. 5, pp. 103–109
K. Asami, K. Hashimoto, and S. Shimodaira, An ESCA Study of the Fe2+/Fe3+ Ratio in Passive Films on Iron-Chromium Alloys, Corros. Sci., 1976, 1, p 387–397
K. Sigimoto and Y. Sawada, The Role of Molybdenum Additions to Austenitic Stainless Steels in the Inhibition of Pitting in acid chloride Solutions, Corros. Sci., 1977, 17, p 425–445
O. Monnereau, L. Torte, C.E.A. Grigorescu, D. Savastru, C.R. Iordanescu, F. Guinneton, R. Notonier, A. Tonetto, T. Zhang, I.N. Mihailescu, D. Stanoi, and H.J. Trodahl, Chromium Oxides Mixtures in PLD Films Investigated by Raman Spectroscopy, J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater., 2010, 12, p 1752–1757
S. Król and M. Pietrzyk, Formation of Corrosion Products Protecting Surfaces of the Boiler Proper Tubes from the Combustion Chamber, J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng., 2007, 21, p 45–48
M.G. Fontana, Eight Forms of Corrosion, Corrosion Engineering, 3rd ed., McGraw Hill Education, New York, 2005, p 109–126
D. Singbeil and D. Thomas, Caustic Stress Corrosion Cracking of Mild Steel, Metall. Trans. A, 1982, 13, p 1092–1098
R.K.S. Raman, R. Rihan, and R.N. Ibrahim, Circumferential Notch Tensile Testing, Role of Imposed Electrochemical Potentials in Susceptibility of Steel to caustic Cracking, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2007, 154, p C658–C662
J. Woodtli and R. Kieselbach, Damage Due to Hydrogen Embrittlement and Stress Corrosion Cracking, Eng. Fail. Anal., 2000, 7, p 427–450
E.I. Meletis and R.F. Hochman, A Review of the Crystallography of Stress Corrosion Cracking, Corros. Sci., 1986, 26, p 63–90
N. Eliaz, A. Shachar, B. Tal, and D. Eliezer, Characteristics of Hydrogen Embrittlement, Stress Corrosion Cracking and Tempered Martensite Embrittlement in High Strength Steels, Eng. Fail. Anal., 2002, 9, p 167–184
J. Cwiek, Hydrogen Degradation of High-Strength Steels, J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng., 2009, 37, p 193–212
G. Butler, H.C.K. Ison, and A.D. Mecer, Some Important Aspects of Corrosion in Central Heating Systems, Br. Corros. J., 1971, 6, p 31–38
H.E. Townsend, Jr., Potential-pH Diagrams at Elevated Temperature for the System Fe-H2O, Corros. Sci., 1970, 10, p 343–358
M.R. Louthan, Jr., Hydrogen Embrittlement of Metals: A Primer for the Failure Analyst, J. Fail. Anal. Prev., 2008, 8, p 289–307
G.M.W. Mann, The oxidation of iron base alloys containing less than 12% Cr in high temperature aqueous solutions, high temperature high pressure electrochemistry in aqueous solutions, in: NACE-4, University of Surrey, 1973, pp. 34–47
L. Tomlinson, M.H. Hurdus, C.B. Ashmore, and P.J.B. Silver, Sodium Heated Steam Generator Tubes: Effect of Heat Flux on the Deposition of Magnetite from Solution and Corrosion of the Underlying Steel, Corrosion, 1985, 41, p 257–264
D.R. Harries, J.M. Dupouy, and C.H. Wu, Materials Research and Development for NET, J. Nucl. Mater., 1985, 133, p 25–31
Z. Ahmed, Principles of corrosion engineering and corrosion control, Butterworth-Heinemann, Burlington, 2006, p 604
C. Man, C. Dong, Z. Cui, K. Xiao, Q. Yu, and X. Li, A Comparative Study of Primary and Secondary Passive Films Formed on AM355 Stainless STEEL in 0.1 M NaOH, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 427, p 763–773
M. Islam, Alkaline-type boiler tube failures induced by phosphate water treatment, in: ASM International, Handbook of Case Histories in Failure Analysis, 1993, vol. 2, pp. 141–144
A. Kumari, S.K. Das, and P.K. Srivastava, Impact of Boiler Water Chemistry on Waterside Tube Failures, Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Technol., 2015, 2, p 2349–6010
A. Nagao, M. Dadfarnia, B.P. Somerday, P. Sofronis, and R.O. Ritchie, Hydrogen-Enhanced-Plasticity Mediated Decohesion for Hydrogen-Induced Intergranular and “Quasi-Cleavage” Fracture of Lath Martensitic Steels, J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 2018, 112, p 403–430
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharasi, N.S., Toppo, A., Paul, V.T. et al. Studies on the Susceptibility of Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel to Stress Corrosion Cracking in Sodium Hydroxide Using Slow Strain Rate Testing Technique. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 2172–2184 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04766-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04766-1