Abstract
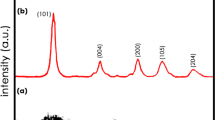
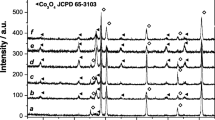
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with reversible redox units and a conjugated molecular skeleton possess novel photoelectrochemical properties. In this work, tris(4-aminophenyl)amine and 4,4-biphenyldiformaldehyde were chosen to synthesize TABP-COF electrochromic film with triphenylamine (TPA) active unit by a solvothermal method in a Teflon-lined reactor. The growth process and reaction time optimization of the TABP-COF were studied. TABP-COF shows a self-assembly growth process from an array of nanosheets to nanospheres. Owing to the redox characteristics of TPA, the TABP-COF film exhibits reversible electrochromic behavior. With a solvothermal reaction time of 72 h, the TABP-COF-3 film exhibits the best electrochromic properties, including contrast of 0.483 and response time of 7.3 s/13.6 s. Considering the abundance of redox-active units that can be chosen, COF materials with different redox units and color changes can be designed for a variety of applications in the field of electrochromic materials.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.X. Guo, Y. Zhang, S. Wang, L. Li, W. Wang, and Q. Sun, In-situ generation of Bi2S3 to construct WO3/BiVO4/Bi2S3 heterojunction for photocathodic protection of 304SS. J. Electroanal. Chem. 907, 116033 (2022).
J.R. Platt, Electrochromism, a possible change of color producible in dyes by an electric field. J. Chem. Phys. 34, 862 (1961).
M. Rozman, L. Bostjanmatoh, F. Regina, S. Argyroula, and E. Urbanluksic, Flexible electrochromic tape using steel foil with WO3 thin film. Electrochim. Acta 330, 135329 (2020).
W.E. Donath, J.C. Powers, W.R. Heller, and J. Kumamoto, Stark effect of phenol blue (electrochromism). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86, 1004 (1964).
E. Hopmann, A.Y. Elezzabi, W. Zhang, and H. Li, Nanostructured inorganic electrochromic materials for light applications. Nanophotonics 10, 825 (2020).
D. Ma, and J. Wang, Inorganic electrochromic materials based on tungsten oxide and nickel oxide nanostructures. Sci. China: Chem. 60, 54 (2017).
B.J. Holliday, Y. Liang, D. Strohecker, V. Lynch, and R.A. Jones, A thiophene-containing conductive metallopolymer using an Fe(II) Bis(terpyridine) core for electrochromic materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 34568 (2016).
F. Li, T.-C. Yen, and G.-S. Liou, Synthesis of high-performance electrochromic material for facile fabrication of truly black electrochromic devices. Electrochim. Acta 367, 137474 (2021).
N. Huang, L.P. Zhai, D.E. Coupry, M.A. Addicoat, K. Okushita, K. Nishimura, T. Heine, and D.L. Jiang, Multiple-component covalent organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 7, 12325 (2016).
S. Ding, W. Wang, S. Ding, and W. Wang, Covalent organic frameworks (COFs): from design to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 548 (2013).
C.J. Kang, Z.Q. Zhang, A.K. Usadi, D.C. Calabro, L.S. Baugh, K.X. Yu, Y.X. Wang, and D. Zhao, Aggregated structures of two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 7, 144 (2022).
Y.H. Zhu, S.Y. Jiang, X.C. Jing, and X. Feng, Electrically conductive 2D covalent organic frameworks. Trends Chem. 4, 128 (2021).
L. Jianguo, W. Nan, and Ma. Longlong, Recent advances in covalent organic frameworks for catalysis. Chem.-Asian J. 15, 338 (2020).
W.-K. Qin, C.-H. Tung, and L.-Z. Wu, Covalent organic framework and hydrogen-bonded organic framework for solar-driven photocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 11, 12521 (2023).
S. Das, J. Feng, and W. Wang, Covalent organic frameworks in separation. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 11, 112019 (2020).
R. Iqbal, An electrochemically stable 2D covalent organic framework for high-performance organic supercapacitors. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 38, 8 (2020).
C.J. Yao, Z.Z. Wu, J. Xie, F. Yu, W. Guo, Z.C.J. Xu, S.Q. Zhang, and Q.C. Zhang, Two-dimensional (2D) covalent organic framework as efficient cathode for binder-free lithium-ion battery. Chemsuschem 13, 2457 (2020).
M.S. Lohse, and T. Bein, Covalent organic frameworks: structures, synthesis, and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1705553 (2018).
L. Liu, D. Cui, S.R. Zhang, W. Xie, C. Yao, and Y.H. Xu, Integrated carbon nanotube and triazine-based covalent organic framework composites for high capacitance performance. Dalton Trans. 52, 2762 (2023).
S.X. Xiong, Y.K. Zhang, J.J. Zhang, X.Q. Wang, J. Chu, R.L. Zhang, M. Gong, B.H. Wu, and G.Q. Liu, Solvothermal synthesis and enhanced electrochromic properties of covalent organic framework/functionalized carbon nanotubes composites electrochromic materials with anthraquinonoid active unit. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 235, 111489 (2022).
S.X. Xiong, Y.C. Wang, X.Q. Wang, J. Chu, R.L. Zhang, M. Gong, B.H. Wu, and Z. Li, Schiff base type conjugated organic framework nanofibers: solvothermal synthesis and electrochromic properties. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 209, 110438 (2021).
Q. Hao, Z.J. Li, C. Lu, B. Sun, Y.W. Zhong, L.J. Wan, and D. Wang, Oriented two-dimensional covalent organic framework films for near-infrared electrochromic application. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 19831 (2019).
Q. Hao, B. Zhi-Juanbai, Y.-W. Xingzhong, and D. Li-Junwang, A covalent organic framework film for three-state near-infrared electrochromism and a molecular logic gate. Angewandte Chemie 60, 12498 (2021).
R. Zheng, J. Zhang, C. Jia, Z. Wan, Y. Fan, X. Weng, J. Xie, and L. Deng, A novel self-healing electrochromic film based on a triphenylamine cross-linked polymer. Polym. Chem. 8, 6981 (2017).
R.Z. Zheng, J.Q. Zhang, C.Y. Jia, Z.Q. Wan, Y.R. Fan, X.L. Weng, J.L. Xie, and L.J. Deng, Synthesis and characterization of stable electrochromic polyimides with quinolin-8-yloxy-substituted triphenylamine units. J. Electroanal. Chem. 801, 388 (2017).
Y. Yan, N.W. Sun, X.T. Jia, X.C. Liu, C. Wang, and D.M. Chao, Electrochromic and electrofluorochromic behavior of novel polyurea bearing oligoaniline and triphenylamine units. Polymer 134, 1 (2018).
S. Cai, S. Wang, D. Wei, H. Niu, W. Wang, and B. Xuduo, Multifunctional polyamides containing pyrrole unit with different triarylamine units owning electrochromic, electrofluorochromic and photoelectron conversion properties. J. Electroanal. Chem. 812, 132 (2018).
L. Cao, I.C. Chen, X.W. Liu, Z. Li, Z.Y. Zhou, and Z.P. Lai, An ionic diode covalent organic framework membrane for efficient osmotic energy conversion. ACS Nano 16, 18910 (2022).
H. Chen, X. Yuan, H. Wang, Yu. Hanbo, and L. Jiang, Nanostructured covalent organic frameworks with elevated crystallization for (electro)photocatalysis and energy storage devices. J. Mater. Sci. 56, 13875 (2021).
S.B. Raoni, R.S. Gonçalves, A.B. de Oliveira, H.C. Sindra, B.S. Archanjo, M.E. Mendoza, L.S. Carneiro, C.D. Buarque, and P. Esteves, Heterogeneous catalysis by covalent organic frameworks (COF): Pd(OAc)2@COF-300 in cross-coupling reactions. Chemcatchem 8, 743 (2016).
D.L. Ma, C. Qian, Q.Y. Qi, Z.R. Zhong, G.F. Jiang, and X. Zhao, Effects of connecting sequences of building blocks on reticular synthesis of covalent organic frameworks. Nano Res. 14, 381 (2020).
F. Lv, S. Xiong, J. Zhang, X. Wang, J. Chu, R. Zhang, M. Gong, B. Wu, G. Liu, and W. Luo, Enhanced electrochromic properties of 2,6-diaminoanthraquinone and 1,3,5-triformylresorcinol (DAAQ-TFP) covalent organic framework/functionalized graphene oxide composites containing anthraquinone active unit. Electrochim. Acta 398, 139301 (2021).
X. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Liu, L.I. Zonglong, L.I. Hui, Q. Fang, and Y. Jin, A covalent organic framework with high surface area for drug delivery. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 40, 1813 (2019).
Y. Ji, H.J. Niu, H.Y. Zhang, W.J. Wu, J.W. Cai, C. Wang, X.D. Bai, and W. Wang, Synthesis and electrochromic properties of polybismaleimides containing triphenylamine units. J. Solid State Electrochem. 18, 1537 (2014).
R. Brooke, J. Edberg, D. Iandolo, M. Berggren, X. Crispin, and I. Engquist, Controlling the electrochromic properties of conductive polymers using UV-light. J. Mater. Chem. C. 6, 4663 (2018).
N.B. Teran, and J.R. Reynolds, Discrete donor-acceptor conjugated systems in neutral and oxidized states: implications toward molecular design for high contrast electrochromics. Chem. Mater. 29, 1290 (2017).
X.Y. Yang, L. Gong, K. Wang, S.H. Ma, W.P. Liu, B.W. Li, N. Li, H.H. Pan, X. Chen, H.L. Wang, J.M. Liu, and J.Z. Jiang, Ionothermal synthesis of fully conjugated covalent organic frameworks for high-capacity and ultrastable potassium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 34, e2207245 (2022).
G. Balamurugan, and J.S. Park, Metallo-terpyridine modified asymmetric viologen exhibiting remarkable optical memory effect in single-layered electrochromic devices. Electrochim. Acta 382, 138308 (2021).
C.-P. Constantin, and M.-D. Damaceanu, A refreshing perspective on electrochromic materials: phenoxazine as an opportune moiety towards stable and efficient electrochromic polyimides. Chem. Eng. J. 465, 142883 (2023).
W. Liu, X. Zhang, J. Liu, X. Ma, J. Zeng, P. Liu, and T. Xu, Electrochromic properties of organic-inorganic composite materials. J. Alloys Compd. 718, 379 (2017).
A.A. Moya, Electrochemical impedance of ion-exchange membranes with interfacial charge transfer resistances. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 6543 (2016).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52073227) and Shaanxi Province Technological Innovation Guidance Special (2021QFY04-01) and for technical support provided by the Analytical Instrumentation Center of XUST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, S., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W. et al. Solvothermal Synthesis and Growth of Covalent Organic Framework Electrochromic Film with Triphenylamine Active Unit. J. Electron. Mater. 53, 2656–2665 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-10937-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-10937-w