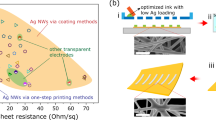
Abstract
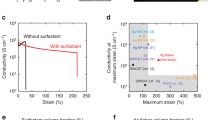
A printable conductive ink that is both highly conductive and stretchable is desired for flexible and wearable electronics. This can be achieved by using silver nanowires as the conductive filler instead of the typically used silver flakes or nanoparticles. It is shown here that long, thin nanowires, lower metal fills and employing plasma sintering rather than thermal annealing leads to the best stretchability. The optimized silver nanowire ink with a 5% metal fill can have resistivity as low as 9.3 × 10−6 Ω cm, increases resistance by only 5× after 250 cycles of 30% strain, and remains conductive to at least 500% strain. It is significantly more stretchable and conductive than commercial stretchable inks, especially at the low sintering temperatures often used in flexible electronics. Moreover, this ink represents the best combination of stretchability and conductivity of all printable inks in the literature. It is found that the reason for the high stretchability of nanowire inks is both its low metal fill and high mechanical strength.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Karim, S. Afroj, A. Malandraki, S. Butterworth, C. Beach, M. Rigout, K.S. Novoselov, A.J. Casson, and S.G. Yeates, All inkjet-printed graphene-based conductive patterns for wearable e-textile applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 11640 (2017).
R. Cao, X. Pu, X. Du, W. Yang, J. Wang, H. Guo, S. Zhao, Z. Yuan, C. Zhang, C. Li, and Z.L. Wang, Screen-printed washable electronic textiles as self-powered touch/gesture tribo-sensors for intelligent human–machine interaction. ACS Nano 12, 5190 (2018).
P. Wei, X. Yang, Z. Cao, X.L. Guo, H. Jiang, Y. Chen, M. Morikado, X. Qiu, and D. Yu, Flexible and stretchable electronic skin with high durability and shock resistance via embedded 3D printing technology for human activity monitoring and personal healthcare. Adv. Mater. Technol. 4, 1 (2019).
S. Wang, J. Xu, W. Wang, G.J.N. Wang, R. Rastak, F. Molina-Lopez, J.W. Chung, S. Niu, V.R. Feig, J. Lopez, T. Lei, S.K. Kwon, Y. Kim, A.M. Foudeh, A. Ehrlich, A. Gasperini, Y. Yun, B. Murmann, J.B.H. Tok, and Z. Bao, Skin electronics from scalable fabrication of an intrinsically stretchable transistor array. Nature 555, 83 (2018).
Y.F. Wang, T. Sekine, Y. Takeda, J. Hong, A. Yoshida, H. Matsui, D. Kumaki, T. Nishikawa, T. Shiba, T. Sunaga, and S. Tokito, Printed strain sensor with high sensitivity and wide working range using a novel brittle-stretchable conductive network. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 35282 (2020).
S. Yao and Y. Zhu, Wearable multifunctional sensors using printed stretchable conductors made of silver nanowires. Nanoscale 6, 2345 (2014).
M. Amjadi, A. Pichitpajongkit, S. Lee, S. Ryu, and I. Park, Highly stretchable and sensitive strain sensor based on silver nanowire–elastomer nanocomposite. ACS Nano 8, 5154 (2014).
C. Zhou, X. Zhang, N. Tang, Y. Fang, H. Zhang, and X. Duan, Rapid response flexible humidity sensor for respiration monitoring using nano-confined strategy. Nanotechnology 31, 125302 (2020).
S. Yaragalla, S. Dussoni, M. Zahid, M. Maggiali, G. Metta, A. Athanasiou, and I.S. Bayer, Stretchable graphene and carbon nanofiber capacitive touch sensors for robotic skin applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 101, 348 (2021).
Z. Cui, F.R. Poblete, G. Cheng, S. Yao, X. Jiang, and Y. Zhu, Design and operation of silver nanowire based flexible and stretchable touch sensors. J. Mater. Res. 30, 79 (2014).
C.K. Jeong, J. Lee, S. Han, J. Ryu, G.T. Hwang, D.Y. Park, J.H. Park, S.S. Lee, M. Byun, S.H. Ko, and K.J. Lee, A hyper-stretchable elastic-composite energy harvester. Adv. Mater. 27, 2866 (2015).
Q. Chen, G. Liu, G. Chen, T. Mi, and J. Tai, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with glucose for conductivity enhancement of conductive ink. BioResources 12, 608 (2017).
L. Mo, Z. Guo, L. Yang, Q. Zhang, Y. Fang, Z. Xin, Z. Chen, K. Hu, L. Han, and L. Li, Silver nanoparticles based ink with moderate sintering in flexible and printed electronics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 2124 (2019).
Y.L. Tai and Z.G. Yang, Facile and scalable preparation of solid silver nanoparticles (<10 nm) for flexible electronics. Surf. Interface Anal. 44, 529 (2012).
W. Li, X. Xu, W. Li, Y. Zhao, and M. Chen, Green synthesis of micron-sized silver flakes and their application in conductive ink. J. Mater. Sci. 53, 6424 (2018).
J.Y. Park, W.J. Lee, B.S. Kwon, S.Y. Nam, and S.H. Choa, Highly stretchable and conductive conductors based on Ag flakes and polyester composites. Microelectron. Eng. 199, 16 (2018).
T. Zhong, N. Jin, W. Yuan, C. Zhou, W. Gu, and Z. Cui, Printable stretchable silver ink and application to printed RFID tags for wearable electronics. Materials (Basel) 12, 1 (2019).
T. Lee and H. Park, The effect of MWCNTs on the electrical properties of a stretchable carbon composite electrode. Compos. Sci. Technol. 114, 11 (2015).
A. Claypole, J. Claypole, L. Kilduff, D. Gethin, and T. Claypole, Stretchable carbon and silver inks for wearable applications. Nanomaterials 11, 1200 (2021).
L. Lo, J. Zhao, H. Wan, Y. Wang, S. Chakrabartty, and C. Wang, An inkjet-printed PEDOT: PSS-based stretchable conductor for wearable health monitoring device applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 13, 21693 (2021).
D. Li, X. Liu, X. Chen, W.Y. Lai, and W. Huang, A simple strategy towards highly conductive silver-nanowire inks for screen-printed flexible transparent conductive films and wearable energy-storage devices. Adv. Mater. Technol. 4, 1 (2019).
X. Wu, Z. Zhou, Y. Wang, and J. Li, Syntheses of silver nanowires ink and printable flexible transparent conductive film: a review. Coatings 10, 865 (2020).
Y. Yang, S. Duan, and H. Zhao, Advances in constructing silver nanowire-based conductive pathways for flexible and stretchable electronics. Nanoscale 14, 11484 (2022).
K.K. Krawczyk, J. Groten, O. Glushko, M. Krivec, M. Frühwirth, G. Schulz, C. Wolf, D. Hartmann, M. Moser, M.J. Cordill, B. Stadlober, and T. Griesser, Self-reducing silver ink on polyurethane elastomers for the manufacture of thin and highly stretchable electrical circuits. Chem. Mater. 33, 2742 (2021).
J.F. Kurniawan, B. Tjhia, V.M. Wu, A. Shin, N.L.J. Sit, T. Pham, A. Nguyen, C. Li, R. Kumar, M. Aguilar-Rivera, I. Lerman, D.C. Kunkel, and T.P. Coleman, An adhesive-integrated stretchable silver–silver chloride electrode array for unobtrusive monitoring of gastric neuromuscular activity. Adv. Mater. Technol. 6, 1 (2021).
N. Zavanelli and W.H. Yeo, Advances in screen printing of conductive nanomaterials for stretchable electronics. ACS Omega 6, 9344 (2021).
A.J. Galante, B.C. Pilsbury, M. Li, M. Lemieux, Q. Liu, and P.W. Leu, Achieving highly conductive, stretchable, and washable fabric from reactive silver ink and increased interfacial adhesion. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 4, 5253 (2022).
Y. Shi, L. He, Q. Deng, Q. Liu, L. Li, W. Wang, Z. Xin, and N. Tce, Synthesis and applications of silver nanowires for transparent conductive films. Micromachines 10, 330 (2019).
H. Jang, B. Hwang, K. Lee, Y. Kim, J. Kim, H. Jang, B. Hwang, K. Lee, and Y. Kim, Controlling the size of silver nanowires produced by a tetrabutylammonium dichlorobromide salt-based polyol process : kinetics of silver crystal growth. AIP Adv. 8, 025303 (2018).
H.D. Yun, D.M. Seo, M.Y. Lee, S.Y. Kwon, and L.S. Park, Effective synthesis and recovery of silver nanowires flexible and transparent conducting electrode. Metals (Basel) 6, 14 (2016).
J. Liang, K. Tong, and Q. Pei, A water-based silver-nanowire screen-print ink for the fabrication of stretchable conductors and wearable thin-film transistors. Adv. Mater. 28, 5986 (2016).
W. Li, S. Yang, and A. Shamim, Screen printing of silver nanowires: balancing conductivity with transparency while maintaining flexibility and stretchability. NPJ Flex. Electron. 3, 13 (2019).
S.H. Ke, Q.W. Xue, C.Y. Pang, P.W. Guo, W.J. Yao, H.P. Zhu, and W. Wu, Printing the ultra-long Ag nanowires inks onto the flexible textile substrate for stretchable electronics. Nanomaterials 9, 1 (2019).
Y.Z.N. Htwe and M. Mariatti, Printed graphene and hybrid conductive inks for flexible, stretchable, and wearable electronics: progress, opportunities, and challenges. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 7, 100435 (2022).
F. Macionczyk, W. Bruckner, and G. Reiss, Stress–strain curves by tensile testing of thin metallic films on polyimide foils. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 505, 235 (1997).
X. Chen, B.L. Kirsch, R. Senter, S.H. Tolbert, and V. Gupta, Tensile testing of thin films supported on compliant substrates. Mech. Mater. 41, 839 (2009).
T. Filleter, S. Ryu, K. Kang, J. Yin, R.A. Bernal, K. Sohn, S. Li, J. Huang, W. Cai, and H.D. Espinosa, Nucleation-controlled distributed plasticity in penta-twinned silver nanowires. Small 8, 2986 (2012).
K. Cao, Y. Han, H. Zhang, L. Gao, H. Yang, J. Chen, Y. Li, and Y. Lu, Size-dependent fracture behavior of silver nanowires. Nanotechnology 29, 295703 (2018).
S.M. Bergin, Y. Chen, A.R. Rathmell, P. Charbonneau, Z. Li, and B.J. Wiley, Nanoscale the effect of nanowire length and diameter on the properties of transparent, conducting nanowire films. Nanoscale 4, 1996 (2012).
A. Madeira, D.T. Papanastasiou, T. Toupance, L. Servant, M. Tréguer-Delapierre, D. Bellet, and I.A. Goldthorpe, Rapid synthesis of ultra-long silver nanowires for high performance transparent electrodes. Nanoscale Adv. 2, 3804 (2020).
C.F. Guo and Z. Ren, Flexible transparent conductors based on metal nanowire networks. Mater. Today 18, 143 (2015).
Y. Huang, Y. Tian, C. Hang, Y. Liu, S. Wang, M. Qi, and J. Zhao, Self-limited nanosoldering of silver nanowires for high-performance flexible transparent heaters. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(24), 21850 (2019).
R. Wang, H. Zhai, T. Wang, X. Wang, Y. Cheng, L. Shi, and J. Sun, Silver nanowire ink for flexible circuit on textiles. Micromach. Nano Res. 9, 2138 (2016).
K. Elen, H. Penxten, S. Nagels, W. Deferme, L. Lutsen, A. Hardy, and M.K. Van Bael, Screen-printing of flexible semi-transparent electrodes and devices based on silver nanowire networks. Nanotechnology 29, 425201 (2018).
D. Du, X. Yang, Y. Yang, Y. Zhao, and Y. Wang, Silver nanowire ink for flexible circuit on textiles. Micromachines 10, 1 (2019).
S. Ding, J. Ying, F. Chen, L. Fu, Y. Lv, S. Zhao, and G. Ji, Highly stretchable conductors comprising composites of silver nanowires and silver flakes. J. Nanopart. Res. 23, 111 (2021).
A. Mohammed and M. Pecht, A stretchable and screen-printable conductive ink for stretchable electronics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 184101 (2016).
M.R. Ramli, S. Ibrahim, Z. Ahmad, I.S.Z. Abidin, and M.F. Ain, Stretchable conductive ink based on polysiloxane–silver composite and its application as a frequency reconfigurable patch antenna for wearable electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 28033 (2019).
A. Kumar, H. Saghlatoon, T.G. La, M.M. Honari, H. Charaya, H.A. Damis, R. Mirzavand, P. Mousavi, and H.J. Chung, A highly deformable conducting traces for printed antennas and interconnects: silver/fluoropolymer composite amalgamated by triethanolamine. Flex. Print. Electron. 2, 45001 (2017).
N. Matsuhisa, M. Kaltenbrunner, T. Yokota, H. Jinno, K. Kuribara, T. Sekitani, and T. Someya, Printable elastic conductors with a high conductivity for electronic textile applications. Nat. Commun. 6, 7461 (2015).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) (Grant No. RGPIN-2019-04294), a Waterloo Institute of Nanotechnology (WIN) Nanofellowship, an Ontario Graduate Scholarship (OGS), and Bemis Company for providing TPU films.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kayaharman, M., Argasinski, H., Atkinson, J. et al. Enhancing and Understanding the High Stretchability of Printable, Conductive Silver Nanowire Ink. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 4634–4643 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10417-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10417-7