Abstract
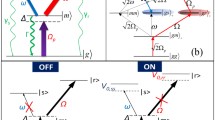
In this paper, we propose a scheme for implementing the nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation (NHQC+) of two Rydberg atoms by using invariant-based reverse engineering (IBRE). The scheme is based on Förster resonance induced by strong dipole-dipole interaction between two Rydberg atoms, which provides a selective coupling mechanism to simply the dynamics of system. Moreover, for improving the fidelity of the scheme, the optimal control method is introduced to enhance the gate robustness against systematic errors. Numerical simulations show the scheme is robust against the random noise in control fields, the deviation of dipole-dipole interaction, the Förster defect, and the spontaneous emission of atoms. Therefore, the scheme may provide some useful perspectives for the realization of quantum computation with Rydberg atoms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. K. Grover, Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack, Phys. Rev. Lett. 79(2), 325 (1997)
G. L. Long, Grover algorithm with zero theoretical failure rate, Phys. Rev. A 64(2), 022307 (2001)
B. Paredes, F. Verstraete, and J. I. Cirac, Exploiting quantum parallelism to simulate quantum random many-body systems, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(14), 140501 (2005)
Y. J. Fan, Z. F. Zheng, Y. Zhang, D. M. Lu, and C. P. Yang, One-step implementation of a multi-target-qubit controlled phase gate with cat-state qubits in circuit QED, Front. Phys. 14(2), 21602 (2019)
H. Fan and X. Zhu, 12 superconducting qubits for quantum walks, Front. Phys. 14(6), 61201 (2019)
E. Sjöqvist, D. M. Tong, L. Mauritz Andersson, B. Hessmo, M. Johansson, and K. Singh, Non-adiabatic holonomic quantum computation, New J. Phys. 14(10), 103035 (2012)
G. F. Xu, J. Zhang, D. M. Tong, E. Sjöqvist, and L. C. Kwek, Nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation in decoherence-free subspaces, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109(17), 170501 (2012)
P. Z. Zhao, G. F. Xu, and D. M. Tong, Nonadiabatic holonomic multiqubit controlled gates, Phys. Rev. A 99(5), 052309 (2019)
P. Z. Zhao, K. Z. Li, G. F. Xu, and D. M. Tong, General approach for constructing Hamiltonians for nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation, Phys. Rev. A 101(6), 062306 (2020)
T. H. Xing, X. Wu, and G. F. Xu, Nonadiabatic holonomic three-qubit controlled gates realized by one-shot implementation, Phys. Rev. A 101(1), 012306 (2020)
P. Z. Zhao, X. Wu, T. H. Xing, G. F. Xu, and D. M. Tong, Nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation with Rydberg superatoms, Phys. Rev. A 98(3), 032313 (2018)
G. F. Xu, P. Z. Zhao, T. H. Xing, E. Sjöqvist, and D. M. Tong, Composite nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation, Phys. Rev. A 95(3), 032311 (2017)
T. Chen, J. Zhang, and Z. Y. Xue, Nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation on coupled transmons with ancillaries, Phys. Rev. A 98(5), 052314 (2018)
Y. Xu, Z. Hua, T. Chen, X. Pan, X. Li, J. Han, W. Cai, Y. Ma, H. Wang, Y. P. Song, Z. Y. Xue, and L. Sun, Experimental implementation of universal nonadiabatic geometric quantum gates in a superconducting circuit, Phys. Rev. Lett. 124(23), 230503 (2020)
S. Li, P. Shen, T. Chen, and Z. Y. Xue, Noncyclic nonadiabatic holonomic quantum gates via shortcuts to adiabaticity, Front. Phys. 16(5), 51502 (2021)
B. J. Liu, X. K. Song, Z. Y. Xue, X. Wang, and M. H. Yung, Plug-and-play approach to nonadiabatic geometric quantum gates, Phys. Rev. Lett. 123(10), 100501 (2019)
M. V. Berry, Transitionless quantum driving, J. Phys. A 42(36), 365303 (2009)
X. Chen, I. Lizuain, A. Ruschhaupt, D. Guéry-Odelin, and J. G. Muga, Shortcut to adiabatic passage in two- and three-level atoms, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(12), 123003 (2010)
A. del Campo, Shortcuts to adiabaticity by counterdiabatic driving, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111(10), 100502 (2013)
S. Qi and J. Jing, Berry-phase-based quantum gates assisted by transitionless quantum driving, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 37(3), 682 (2020)
K. Khodjasteh and D. A. Lidar, Fault-tolerant quantum dynamical decoupling, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(18), 180501 (2005)
A. M. Souza, G. A. Álvarez, and D. Suter, Robust dynamical decoupling for quantum computing and quantum memory, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106(24), 240501 (2011)
G. T. Genov, D. Schraft, N. V. Vitanov, and T. Halfmann, Arbitrarily accurate pulse sequences for robust dynamical decoupling, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118(13), 133202 (2017)
D. Daems, A. Ruschhaupt, D. Sugny, and S. Guérin, Robust quantum control by a single-shot shaped pulse, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111(5), 050404 (2013)
X. T. Yu, Q. Zhang, Y. Ban, and X. Chen, Fast and robust control of two interacting spins, Phys. Rev. A 97(6), 062317 (2018)
H. R. Jr Lewis and W. B. Riesenfeld, An exact quantum theory of the time-dependent harmonic oscillator and of a charged particle in a time-dependent electromagnetic field, J. Math. Phys. 10(8), 1458 (1969)
X. Chen, E. Torrontegui, and J. G. Muga, Lewis-Riesenfeld invariants and transitionless quantum driving, Phys. Rev. A 83(6), 062116 (2011)
S. Li, T. Chen, and Z. Y. Xue, Fast holonomic quantum computation on superconducting circuits with optimal control, Adv. Quantum Technol. 3(3), 2000001 (2020)
T. Yan, B. J. Liu, K. Xu, C. Song, S. Liu, Z. Zhang, H. Deng, Z. Yan, H. Rong, K. Huang, M. H. Yung, Y. Chen, and D. Yu, Experimental realization of nonadiabatic shortcut to non-Abelian geometric gates, Phys. Rev. Lett. 122(8), 080501 (2019)
J. Xu, S. Li, T. Chen, and Z. Y. Xue, Nonadiabatic geometric quantum computation with optimal control on superconducting circuits, Front. Phys. 15(4), 41503 (2020)
Y. H. Kang, Z. C. Shi, B. H. Huang, J. Song, and Y. Xia, Flexible scheme for the implementation of nonadiabatic geometric quantum computation, Phys. Rev. A 101(3), 032322 (2020)
C. Zhang, T. Chen, S. Li, X. Wang, and Z. Y. Xue, High-fidelity geometric gate for silicon-based spin qubits, Phys. Rev. A 101(5), 052302 (2020)
C. Y. Guo, L. L. Yan, S. Zhang, S. L. Su, and W. Li, Optimized geometric quantum computation with a mesoscopic ensemble of Rydberg atoms, Phys. Rev. A 102(4), 042607 (2020)
Y. H. Kang, Z. C. Shi, J. Song, and Y. Xia, Heralded atomic nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation with Rydberg blockade, Phys. Rev. A 102(2), 022617 (2020)
B. J. Liu, S. L. Su, and M. H. Yung, Nonadiabatic non-cyclic geometric quantum computation in Rydberg atoms, Phys. Rev. Research 2(4), 043130 (2020)
T. Chen, P. Shen, and Z. Y. Xue, Robust and fast holonomic quantum gates with encoding on superconducting circuits, Phys. Rev. Appl. 14(3), 034038 (2020)
M. Saffman, T. G. Walker, and K. Mølmer, Quantum information with Rydberg atoms, Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 2313 (2010)
E. Urban, T. A. Johnson, T. Henage, L. Isenhower, D. D. Yavuz, T. G. Walker, and M. Saffman, Observation of Rydberg blockade between two atoms, Nat. Phys. 5(2), 110 (2009)
A. Gaëtan, Y. Miroshnychenko, T. Wilk, A. Chotia, M. Viteau, D. Comparat, P. Pillet, A. Browaeys, and P. Grangier, Observation of collective excitation of two individual atoms in the Rydberg blockade regime, Nat. Phys. 5(2), 115 (2009)
D. Barredo, H. Labuhn, S. Ravets, T. Lahaye, A. Browaeys, and C. S. Adams, Coherent excitation transfer in a spin chain of three Rydberg atoms, Phys. Rev. Lett. 114(11), 113002 (2015)
S. L. Su, Y. Gao, E. Liang, and S. Zhang, Fast Rydberg antiblockade regime and its applications in quantum logic gates, Phys. Rev. A 95(2), 022319 (2017)
Y. H. Kang, Y. H. Chen, Z. C. Shi, B. H. Huang, J. Song, and Y. Xia, Nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation using Rydberg blockade, Phys. Rev. A 97(4), 042336 (2018)
S. L. Su, H. Z. Shen, E. Liang, and S. Zhang, One-step construction of the multiple-qubit Rydberg controlled-phase gate, Phys. Rev. A 98(3), 032306 (2018)
D. X. Li and X. Q. Shao, Directional quantum state transfer in a dissipative Rydberg-atom-cavity system, Phys. Rev. A 99(3), 032348 (2019)
Y. H. Chen, Z. C. Shi, J. Song, Y. Xia, and S. B. Zheng, Accelerated and noise-resistant generation of high-fidelity steady-state entanglement with Rydberg atoms, Phys. Rev. A 97(3), 032328 (2018)
R. H. Zheng, Y. H. Kang, D. Ran, Z. C. Shi, and Y. Xia, Deterministic interconversions between the Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger states and the W states by invariant-based pulse design, Phys. Rev. A 101(1), 012345 (2020)
R. H. Zheng, Y. H. Kang, S. L. Su, J. Song, and Y. Xia, Robust and high-fidelity nondestructive Rydberg parity meter, Phys. Rev. A 102(1), 012609 (2020)
S. L. Su, F. Q. Guo, L. Tian, X. Y. Zhu, L. L. Yan, E. J. Liang, and M. Feng, Nondestructive Rydberg parity meter and its applications, Phys. Rev. A 101(1), 012347 (2020)
X. F. Shi, Rydberg quantum computation with nuclear spins in two-electron neutral atoms, Front. Phys. 16(5), 52501 (2021)
R. H. Zheng, Y. Xiao, S. L. Su, Y. H. Chen, Z. C. Shi, J. Song, Y. Xia, and S. B. Zheng, Fast and dephasing-tolerant preparation of steady Knill-Laflamme-Milburn states via dissipative Rydberg pumping, Phys. Rev. A 103(5), 052402 (2021)
H. D. Yin, X. X. Li, G. C. Wang, and X. Q. Shao, One-step implementation of Toffoli gate for neutral atoms based on unconventional Rydberg pumping, Opt. Express 28(24), 35576 (2020)
D. Jaksch, J. I. Cirac, P. Zoller, S. L. Rolston, R. Côté, and M. D. Lukin, Fast quantum gates for neutral atoms, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(10), 2208 (2000)
M. D. Lukin, M. Fleischhauer, R. Cote, L. M. Duan, D. Jaksch, J. I. Cirac, and P. Zoller, Dipole blockade and quantum information processing in mesoscopic atomic ensembles, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(3), 037901 (2001)
C. Ates, T. Pohl, T. Pattard, and J. M. Rost, Antiblockade in Rydberg excitation of an ultracold lattice gas, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(2), 023002 (2007)
T. Amthor, C. Giese, C. S. Hofmann, and M. Weidemüller, Evidence of antiblockade in an ultracold Rydberg gas, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104(1), 013001 (2010)
S. L. Su, Y. Tian, H. Z. Shen, H. Zang, E. Liang, and S. Zhang, Applications of the modified Rydberg antiblockade regime with simultaneous driving, Phys. Rev. A 96(4), 042335 (2017)
M. M. Müller, M. Murphy, S. Montangero, T. Calarco, P. Grangier, and A. Browaeys, Implementation of an experimentally feasible controlled-phase gate on two blockaded Rydberg atoms, Phys. Rev. A 89(3), 032334 (2014)
T. Keating, R. L. Cook, A. M. Hankin, Y. Y. Jau, G. W. Biedermann, and I. H. Deutsch, Robust quantum logic in neutral atoms via adiabatic Rydberg dressing, Phys. Rev. A 91(1), 012337 (2015)
A. Mitra, M. J. Martin, G. W. Biedermann, A. M. Marino, P. M. Poggi, and I. H. Deutsch, Robust Mølmer-Sørensen gate for neutral atoms using rapid adiabatic Rydberg dressing, Phys. Rev. A 101(3), 030301 (2020)
X. R. Huang, Z. X. Ding, C. S. Hu, L. T. Shen, W. Li, H. Wu, and S. B. Zheng, Robust Rydberg gate via Landau-Zener control of Förster resonance, Phys. Rev. A 98(5), 052324 (2018)
I. I. Beterov, G. N. Hamzina, E. A. Yakshina, D. B. Tretyakov, V. M. Entin, and I. I. Ryabtsev, Adiabatic passage of radio-frequency-assisted Förster resonances in Rydberg atoms for two-qubit gates and the generation of Bell states, Phys. Rev. A 97(3), 032701 (2018)
T. Förster, Zwischenmolekulare energiewanderung und fluoreszenz, Ann. Phys. 437(1–2), 55 (1948)
I. I. Ryabtsev, D. B. Tretyakov, I. I. Beterov, and V. M. Entin, Observation of the stark-tuned Förster resonance between two Rydberg atoms, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104(7), 073003 (2010)
H. Gorniaczyk, C. Tresp, P. Bienias, A. Paris-Mandoki, W. Li, I. Mirgorodskiy, H. P. Büchler, I. Lesanovsky, and S. Hofferberth, Enhancement of Rydberg-mediated singlephoton nonlinearities by electrically tuned Förster Resonances, Nat. Commun. 7, 12480 (2016)
S. Ravets, H. Labuhn, D. Barredo, L. Béguin, T. Lahaye, and A. Browaeys, Coherent dipole-dipole coupling between two single Rydberg atoms at an electrically-tuned Förster resonance, Nat. Phys. 10(12), 914 (2014)
H. Z. Wu, Z. B. Yang, and S. B. Zheng, Implementation of a multiqubit quantum phase gate in a neutral atomic ensemble via the asymmetric Rydberg blockade, Phys. Rev. A 82(3), 034307 (2010)
X. Q. Shao, Selective Rydberg pumping via strong dipole blockade, Phys. Rev. A 102(5), 053118 (2020)
I. I. Beterov, M. Saffman, E. A. Yakshina, D. B. Tretyakov, V. M. Entin, S. Bergamini, E. A. Kuznetsova, and I. I. Ryabtsev, Two-qubit gates using adiabatic passage of the Stark-tuned Förster resonances in Rydberg atoms, Phys. Rev. A 94(6), 062307 (2016)
I. I. Beterov, I. N. Ashkarin, E. A. Yakshina, D. B. Tretyakov, V. M. Entin, I. I. Ryabtsev, P. Cheinet, P. Pillet, and M. Saffman, Fast three-qubit Toffoli quantum gate based on three-body Förster resonances in Rydberg atoms, Phys. Rev. A 98(4), 042704 (2018)
D. X. Li and X. Q. Shao, Unconventional Rydberg pumping and applications in quantum information processing, Phys. Rev. A 98(6), 062338 (2018)
W. Li, P. J. Tanner, and T. F. Gallagher, Dipole-dipole excitation and ionization in an ultracold gas of Rydberg atoms, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(17), 173001 (2005)
T. Amthor, M. Reetz-Lamour, S. Westermann, J. Denskat, and M. Weidemüller, Mechanical effect of van der Waals interactions observed in real time in an ultracold Rydberg gas, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(2), 023004 (2007)
T. Amthor, M. Reetz-Lamour, C. Giese, and M. Weidemüller, Modeling many-particle mechanical effects of an interacting Rydberg gas, Phys. Rev. A 76(5), 054702 (2007)
A. Ruschhaupt, X. Chen, D. Alonso, and J. G. Muga, Optimally robust shortcuts to population inversion in two-level quantum systems, New J. Phys. 14(9), 093040 (2012)
T. G. Walker and M. Saffman, Zeros of Rydberg-Rydberg Föster interactions, J. Phys. B 38(2), S309 (2005)
T. G. Walker and M. Saffman, Consequences of Zeeman degeneracy for the van der Waals blockade between Rydberg atoms, Phys. Rev. A 77(3), 032723 (2008)
D. F. James and J. Jerke, Effective Hamiltonian theory and its applications in quantum information, Can. J. Phys. 85(6), 625 (2007)
S. Ravets, H. Labuhn, D. Barredo, T. Lahaye, and A. Browaeys, Measurement of the angular dependence of the dipole-dipole interaction between two individual Rydberg atoms at a Förster resonance, Phys. Rev. A 92(2), 020701 (2015)
P. Zanardi and D. A. Lidar, Purity and state fidelity of quantum channels, Phys. Rev. A 70(1), 012315 (2004)
L. H. Pedersen, N. M. Møller, and K. Mølmer, Fidelity of quantum operations, Phys. Lett. A 367(1–2), 47 (2007)
Z. Y. Xue, J. Zhou, and Z. D. Wang, Universal holonomic quantum gates in decoherence-free subspace on superconducting circuits, Phys. Rev. A 92(2), 022320 (2015)
Z. Y. Xue, J. Zhou, Y. M. Chu, and Y. Hu, Nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation with all-resonant control, Phys. Rev. A 94(2), 022331 (2016)
Z. Y. Xue, F. L. Gu, Z. P. Hong, Z. H. Yang, D. W. Zhang, Y. Hu, and J. Q. You, Nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation with dressed-state qubits, Phys. Rev. Appl. 7(5), 054022 (2017)
P. Z. Zhao, X. D. Cui, G. F. Xu, E. Sjöqvist, and D. M. Tong, Rydberg-atom-based scheme of nonadiabatic geometric quantum computation, Phys. Rev. A 96(5), 052316 (2017)
Y. Xu, W. Cai, Y. Ma, X. Mu, L. Hu, T. Chen, H. Wang, Y. P. Song, Z. Y. Xue, Z. Q. Yin, and L. Sun, Single-loop realization of arbitrary nonadiabatic holonomic single-qubit quantum gates in a superconducting circuit, Phys. Rev. Lett. 121(11), 110501 (2018)
M. D. Reed, L. DiCarlo, S. E. Nigg, L. Sun, L. Frunzio, S. M. Girvin, and R. J. Schoelkopf, Realization of three-qubit quantum error correction with superconducting circuits, Nature 482(7385), 382 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 11575045, 11874114, and 11674060, the Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar of Fujian Province under Grant 2020J06011 and Project from Fuzhou University under Grant JG202001-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
arXiv: 2107.14486. This article can also be found at http://journal.hep.com.cn/fop/EN/10.1007/s11467-021-1108-3.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Shen, JH., Zheng, RH. et al. Optimized nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation based on Förster resonance in Rydberg atoms. Front. Phys. 17, 21502 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-021-1108-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-021-1108-3