Abstract
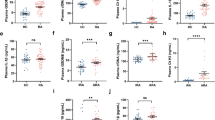
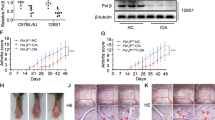
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints and is associated with excessive immune cell infiltration. However, the complex interactions between the immune cell populations in the RA synovium remain unknown. Here, we demonstrate that inflammatory macrophages in the synovium exacerbate neutrophil-driven joint damage in RA through ADP/P2Y1 signaling. We show that extracellular ADP (eADP) and its receptors are obviously increased in synovial tissues of RA patients as well as collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice, and eADP enhances neutrophil infiltration into joints through macrophages producing the chemokine CXCL2, aggravating disease development. Accordingly, the arthritis mouse model had more neutrophils in inflamed joints following ADP injection, whereas P2Y1 deficiency and pharmacologic inhibition restored arthritis severity to basal levels, suggesting a dominant role of ADP/P2Y1 signaling in RA pathology. Moreover, cellular activity of ADP/P2Y1-mediated CXCL2 production was dependent on the Gαq/Ca2+-NF-κB/NFAT pathway in macrophages. Overall, this study reveals a non-redundant role of eADP as a trigger in the pathogenesis of RA through neutrophil recruitment and disrupted tissue homeostasis and function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben Addi, A., Cammarata, D., Conley, P.B., Boeynaems, J.M., and Robaye, B. (2010). Role of the P2Y12 receptor in the modulation of murine dendritic cell function by ADP. J Immunol 185, 5900–5906.
Bevaart, L., Vervoordeldonk, M.J., and Tak, P.P. (2010). Collagen-induced arthritis in mice. In: Proetzel, G., and Wiles, M., eds. Mouse Models for Drug Discovery. Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols). New York: Humana Press. 181–192.
Cauli, A., Yanni, G., and Panayi, G.S. (1997). Interleukin-1, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and macrophage populations in rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane. Rheumatology 36, 935–940.
Chatterjee, C., and Sparks, D.L. (2014). P2X receptors regulate adenosine diphosphate release from hepatic cells. Purinergic Signal 10, 587–593.
Czepielewski, R.S., Porto, B.N., Rizzo, L.B., Roesler, R., Abujamra, A.L., Pinto, L.G., Schwartsmann, G., Cunha, F.D.Q., and Bonorino, C. (2012). Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR) mediates chemotaxis in neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 547–552.
da Silva, J.L.G., Passos, D.F., Bernardes, V.M., and Leal, D.B.R. (2019). ATP and adenosine: Role in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Lett 214, 55–64.
Firestein, G.S., and McInnes, I.B. (2017). Immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunity 46, 183–196.
Gachet, C. (2006). Regulation of platelet functions by P2 receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 46, 277–300.
Gang, X., Sun, Y., Li, F., Yu, T., Jiang, Z., Zhu, X., Jiang, Q., and Wang, Y. (2017). Identification of key genes associated with rheumatoid arthritis with bioinformatics approach. Medicine 96, e7673.
Hamilton, J.A., Filonzi, E.L., and Ianches, G. (1993). Regulation of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) production in cultured human synovial fibroblasts. Growth Factors 9, 157–165.
Hollopeter, G., Jantzen, H.M., Vincent, D., Li, G., England, L., Ramakrishnan, V., Yang, R.B., Nurden, P., Nurden, A., Julius, D., et al. (2001). Identification of the platelet ADP receptor targeted by antithrombotic drugs. Nature 409, 202–207.
Idzko, M., Dichmann, S., Ferrari, D., Di Virgilio, F., la Sala, A., Girolomoni, G., Panther, E., and Norgauer, J. (2002). Nucleotides induce chemotaxis and actin polymerization in immature but not mature human dendritic cells via activation of pertussis toxin-sensitive P2y receptors. Blood 100, 925–932.
Idzko, M., Ferrari, D., and Eltzschig, H.K. (2014). Nucleotide signalling during inflammation. Nature 509, 310–317.
Janossy, G., Duke, O., Poulter, L.W., Panayi, G., Bofill, M., and Goldstein, G. (1981). Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of T-lymphocyte/macrophage immunoregulation. Lancet 318, 839–842.
Kang, J.H., Lim, H., Lee, D.S., and Yim, M. (2018). Montelukast inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and bone loss via CysLTR1 and P2Y12. Mol Med Report 18, 2387–2389.
Khavrutskii, I.V., Grant, B., Taylor, S.S., and McCammon, J.A. (2009). A transition path ensemble study reveals a linchpin role for Mg2+ during rate-limiting ADP release from protein kinase A. Biochemistry 48, 11532–11545.
Kumahashi, N., Naitou, K., Nishi, H., Oae, K., Watanabe, Y., Kuwata, S., Ochi, M., Ikeda, M., and Uchio, Y. (2011). Correlation of changes in pain intensity with synovial fluid adenosine triphosphate levels after treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee with high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid. Knee 18, 160–164.
Lenain, N., Freund, M., Léon, C., Cazenave, J.P., and Gachet, C. (2003). Inhibition of localized thrombosis in P2Y1-deficient mice and rodents treated with MRS2179, a P2Y1 receptor antagonist. J Thromb Haemost 1, 1144–1149.
McDonald, B., Pittman, K., Menezes, G.B., Hirota, S.A., Slaba, I., Waterhouse, C.C.M., Beck, P.L., Muruve, D.A., and Kubes, P. (2010). Intravascular danger signals guide neutrophils to sites of sterile inflammation. Science 330, 362–366.
McInnes, I.B., and Schett, G. (2007). Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol 7, 429–442.
McInnes, I.B., and Schett, G. (2011). The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 365, 2205–2219.
Medzhitov, R. (2008). Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 454, 428–435.
Mohr, W., Westerhellweg, H., and Wessinghage, D. (1981). Polymorphonuclear granulocytes in rheumatic tissue destruction. III. an electron microscopic study of PMNs at the pannus-cartilage junction in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 40, 396–399.
Muller, W.A. (2011). Sorting the signals from the signals in the noisy environment of inflammation. Sci Signal 4, pe23.
Nahrendorf, M., and Swirski, F.K. (2015). Neutrophil-macrophage communication in inflammation and atherosclerosis. Science 349, 237–238.
Nanki, T. (2016). Treatment for rheumatoid arthritis by chemokine blockade. Jpn J Clin Immunol 39, 172–180.
Nefla, M., Holzinger, D., Berenbaum, F., and Jacques, C. (2016). The danger from within: alarmins in arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12, 669–683.
Pelus, L.M., and Fukuda, S. (2006). Peripheral blood stem cell mobilization: The CXCR2 ligand GROβ rapidly mobilizes hematopoietic stem cells with enhanced engraftment properties. Exp Hematol 34, 1010–1020.
Scott, D.L., Wolfe, F., and Huizinga, T.W. (2010). Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 376, 1094–1108.
Siouti, E., and Andreakos, E. (2019). The many facets of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Pharmacol 165, 152–169.
Swamydas, M., Luo, Y., Dorf, M.E., and Lionakis, M.S. (2015). Isolation of mouse neutrophils. Curr Protoc Immunol 110, 3.20.21–23.
Symmons, D., Turner, G., Webb, R., Asten, P., Barrett, E., Lunt, M., Scott, D., and Silman, A. (2002). The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the United Kingdom: new estimates for a new century. Rheumatology 41, 793–800.
Tak, P.P., and Bresnihan, B. (2000). The pathogenesis and prevention of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: advances from synovial biopsy and tissue analysis. Arthritis Rheum 43, 2619–2633.
Teixeira, V.H., Olaso, R., Martin-Magniette, M.L., Lasbleiz, S., Jacq, L., Oliveira, C.R., Hilliquin, P., Gut, I., Cornelis, F., and Petit-Teixeira, E. (2009). Transcriptome analysis describing new immunity and defense genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of rheumatoid arthritis patients. PLoS ONE 4, e6803.
Udalova, I.A., Mantovani, A., and Feldmann, M. (2016). Macrophage heterogeneity in the context of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12, 472–485.
Uderhardt, S., Martins, A.J., Tsang, J.S., Lämmermann, T., and Germain, R. N. (2019). Resident macrophages cloak tissue microlesions to prevent neutrophil-driven inflammatory damage. Cell 177, 541–555.e17.
Wang, X., Sun, L., He, N., An, Z., Yu, R., Li, C., Li, Y., Li, Y., Liu, X., Fang, X., et al. (2021). Increased expression of CXCL2 in ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis and its role in osteoclastogenesis. Clin Exp Immunol 203, 194–208.
Weinmann, P., Moura, R.A., Caetano-Lopes, J.R., Pereira, P.A., Canhao, H., Queiroz, M.V., and Fonseca, J.E. (2007). Delayed neutrophil apoptosis in very early rheumatoid arthritis patients is abrogated by methotrexate therapy. Clin Experimental Rheumatol 25, 885–887.
Weyand, C.M., and Goronzy, J.J. (2017). Immunometabolism in early and late stages of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 13, 291–301.
Wittkowski, H., Foell, D., af Klint, E., De Rycke, L., De Keyser, F., Frosch, M., Ulfgren, A.K., and Roth, J. (2007). Effects of intra-articular corticosteroids and anti-TNF therapy on neutrophil activation in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66, 1020–1025.
Woetzel, D., Huber, R., Kupfer, P., Pohlers, D., Pfaff, M., Driesch, D., Häupl, T., Koczan, D., Stiehl, P., Guthke, R., et al. (2014). Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther 16, R84.
Wolpe, S.D., Sherry, B., Juers, D., Davatelis, G., Yurt, R.W., and Cerami, A. (1989). Identification and characterization of macrophage inflammatory protein 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86, 612–616.
Wright, H.L., Moots, R.J., and Edwards, S.W. (2014). The multifactorial role of neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 10, 593–601.
Yarilina, A., Park-Min, K.H., Antoniv, T., Hu, X., and Ivashkiv, L.B. (2008). TNF activates an IRF1-dependent autocrine loop leading to sustained expression of chemokines and STAT1-dependent type I interferon-response genes. Nat Immunol 9, 378–387.
Yegutkin, G.G. (2008). Nucleotide- and nucleoside-converting ectoenzymes: Important modulators of purinergic signalling cascade. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783, 673–694.
Zhang, X., Qin, J., Zou, J., Lv, Z., Tan, B., Shi, J., Zhao, Y., Ren, H., Liu, M., Qian, M., et al. (2018). Extracellular ADP facilitates monocyte recruitment in bacterial infection via ERK signaling. Cell Mol Immunol 15, 58–73.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFA0507001), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570896, 31770969, 81672811, 81871250, 81830083, 81902892 and 82001729), Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (2017-01-07-00-05-E00011), Shenzhen Municipal Government of China (KQTD20170810160226082), Shanghai Super Postdoctoral Incentive Program, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M640364), and Shanghai Sailing Program (19YF1414400). The authors thank Dr. Ningli Li (Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China) for the gift of the synovial tissues from RA and OA patients; Dr. Juling Liu (Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China) for the gift of P2Y12 knockout mice. We thank East China Normal University Multifunctional Platform for Innovation (011) and Flow Cytometry Core Facility of School of Life Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest. All animal experiments conformed to the regulations drafted by the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care in Shanghai and were approved by the East China Normal University Center for Animal Research Committee (No. AR2013/08002). The clinical studies were approved by the respective Ethics Committees and informed patient consent was obtained.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhao, W., Zhao, Y. et al. Inflammatory macrophages exacerbate neutrophil-driven joint damage through ADP/P2Y1 signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 953–968 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1957-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1957-8