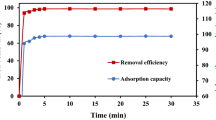
Abstract
The thorny problem of adsorption is the disposing of spent adsorbent. In this manuscript, the exhaust adsorbent of efficient capture Cu(II) over ZSM-5 that supported zero-valent iron (nZVI) was reused as a catalyst for eliminating Rhodamine B (RhB). Batch experiments were used to evaluate the removal performance of Cu2+ and RhB. The results demonstrated that the Cu2+ adsorption process obeyed pseudo-second-order kinetics, and the adsorption performance was dependent on solution pH. The maximum adsorption capacity at the optimal pH 4.0 was 375.9 mg/g; equilibrium was reached rapidly within 35 min. From XPS, the reduction-oxidation between Fe0 and Cu2+ was occurred in the adsorption process, and Fe2+, Fe3+, and Cu0 was formed. In the recycling experiments, RhB was removed by the spent Cu adsorbent, with the removal performance being dependent on the initial Cu concentration, in the order of 5 mg/L > 20 mg/L > 0 mg/L > 100 mg/L > 500 mg/L. RhB removal also improved with increasing H2O2 concentration. More than 99.9% of the RhB was degraded within 8 min using 1.75 mM H2O2, which was a large improvement over the previously used catalyst. The hydroxyl radical was found to be the main free radical responsible for RhB degradation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Monaem EM, Elshishini HM, Bakr SS et al (2023) A comprehensive review on LDH-based catalysts to activate persulfates for the degradation of organic pollutants, npj Clean. Water 6:34. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-023-00245-x
Abdelfatah AM, Fawzy M, El-Khouly ME et al (2021a) Efficient adsorptive removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution using phytosynthesized nano-zero valent iron. J Saudi Chem Soc 25:101365. https://doi.org/10.1016/jscs.2021.101365
Abdelfatah AM, Fawzy M, Eltaweil AS et al (2021b) Green synthesis of nano-zero-valent iron using Ricinus communis seeds extract: characterization and application in the treatment of methylene blue-polluted water. ACS Omega 6:25397–25411. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c03355
Al-Gheethi AA, Azhar QM, Kumar PS et al (2020) Sustainable approaches for removing Rhodamine B dye using agricultural waste adsorbents: a review. Chemosphere 287:132080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132080
Azzam AM, El-Wakeel ST, Mostafa BB et al (2016) Removal of Pb, Cd, Cu and Ni from aqueous solution using nano scale zero valent iron particles, Journal of Environmental. Chem Eng 4(2):2196–2206. https://doi.org/10.1016/jece.2016.03.048
Brillas E, SireS I, Oturan MA (2009) Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chem Rev 109(12):6570–6631. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900136g
Brion D (1980) Etude par spectroscopie de photoelectrons de la degradation superficielle de FeS2, CuFeS2, ZnS et PbS a l’air et dans l’eau. Appl Surf Sci 5(2):133–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5963(80)90148-8
Chawla SK, Sankarraman N, Payer JH (1992) Diagnostic spectra for XPS analysis of Cu-O-S-H compounds. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 61(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/0368-2048(92)80047-C
Chen H, Yang M, Shang W et al (2018a) Organosilane surfactant-directed synthesis of hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites with improved catalytic performance in methanol-to-propylene reaction. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:10956–10966. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b00849
Chen N, Shang H, Tao S et al (2018b) Visible light driven organic pollutants degradation with hydrothermally carbonized sewage sludge and oxalate via molecular oxygen activation. Environ Sci Technol 52:12656–12666. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b03882
Chen Z, Tang B, Niu Y et al (2021) Synthesis of silica supported thiosemicarbazide for Cu(II) and Zn(II) adsorption from ethanol: a comparison with aqueous solution. Fuel 286:119287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119287
Chen Z, Zheng R, Wei W et al (2022) Recycling spent water treatment adsorbents for efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation reaction. Resour Conserv Recycl 178:106037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.106037
Connor JA, Derrick LMR, Hillier IH (1974) High energy photoelectron spectroscopy of transition metal complexes. Part 4.-bis(arene) and related complexes of chromium manganese and iron. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans II(70):941–944. https://doi.org/10.1039/F29747000941
Ding D, Liu C, Ji Y et al (2017) Mechanism insight of degradation of norfloxacin by magnetite nanoparticles activated persulfate: identification of radicals and degradation pathway. Chem Eng J 308:330–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.077
Eltaweil AS, Bakr SS, Abd El-Monaem EM et al (2023) Magnetic hierarchical flower-like Fe3O4@ZIF-67/CuNiMn-LDH catalyst with enhanced redox cycle for Fenton-like degradation of Congo red: optimization and mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:75332–75348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27430-2
Ezzatahmadi N, Ayoko GA, Millar GJ et al (2017) Clay-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron composite materials for the remediation of contaminated aqueous solutions: a review. Chem Eng J 312:336–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.154
Fariña AO, Peacock CL, Sarah F et al (2018) A universal adsorption behaviour for Cu uptake by iron (hydr)oxide organo-mineral composites. Chem Geol 479:22–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.12.022
Giles C, Smith D, Huitson A (1974) A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm. I. Theoretical. J Colloid Interface Sci 47:755–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(74)90252-5
Han C, Li H, Pu H et al (2013) Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous alumina and their performances for removing arsenic(V). Chem Eng J 217:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.087
Han C, Liu H, Zhang L et al (2017) Effectively uptake arsenate from water by mesoporous sulphated zirconia: characterization, adsorption, desorption, and uptake mechanism, The Canadian Journal Of. Chem Eng 95:543–549. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.22704
Han C, Yang L, Yu H et al (2020) The adsorption behavior and mechanism of Cr(VI) on facile synthesized mesoporous NH-SiO2. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:2455–2463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3599-1
Han C, Yang T, Liu H et al (2019) Characterizations and mechanisms for synthesis of chitosan-coated Na–X zeolite from fly ash and As(V) adsorption study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:10106–10116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04466-x
Humayun M, He M, Feng W et al (2021) Enhanced photocatalytic performance of novel MIL53Sr metal-organic framework (MOF) for RhB dye degradation and H2 evolution by coupling MIL53Fe. Sol Energy 215:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2020.12.025
Li S, Wang W, Liang F et al (2016) Heavy metal removal using nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): theory and application. J Hazard Mater 322:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.032
Li Z, Guo Z, Zhang T et al (2021) Fabrication of in situ ZIF-67 grown on alginate hydrogels and its application for enhancing Cu (II) adsorption from aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 207:112036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.112036
Liang L, Lia X, Guo Y et al (2021) The removal of heavy metal cations by sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-nZVI): the reaction mechanisms and the role of sulfur. J Hazard Mater 404:124057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124057
Liu A, Liu J, Zhang W (2015) Transformation and composition evolution of nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI) synthesized by borohydride reduction in static water. Chemosphere 119:1068–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.026
Liu CM, Diao ZH, Huo WY et al (2018) Simultaneous removal of Cu2+ and bisphenol A by a novel biochar-supported zero valent iron from aqueous solution: synthesis, reactivity and mechanism. Environ Pollut 239:698–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.084
Liu F, Peng G, Li T et al (2019) Au(III) adsorptionand reduction to gold particles on cost-effective tannin acid immobilized dialdehyde corn starch. Chem Eng J 370:228–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.208
Liu N, Zhu X, Hua S et al (2016) A facile strategy for preparation of phosphorus modified HZSM-5 shape-selective catalysts and its performances in disproportionation of toluene. Catal Commun 77:60–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2016.01.027
Ma J, Zhou B, Zhang H et al (2019) Activated municipal wasted sludge biochar supported by nanoscale Fe/Cu composites for tetracycline removal from water. Chem Eng Res Des 149:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2019.07.013
Min X, Han C, Yang L, Zhou C (2021) Enhancing As(V) and As(III) adsorption performance of low alumina fly ash with ferric citrate modification: role of FeSiO3 and monosodium citrate. J Environ Manag 287:112302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112302
Mohan D, Pittman CU Jr (2007) Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents-a critical review. J Hazard Mater 142:1–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.006
Mukherjee J, Dutta DP, Ramakumar J (2016) A comprehensive study on the uptake of dyes, Cu(II) and radioactive 137Cs(I) by sonochemically synthesized strontium/yttrium tungstate and molybdate nanoparticles. J Environ Chem Eng 4(3):3050–3064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.06.015
Mwafya EA, Mostafa AM (2020) Tailored MWCNTs/SnO2 decorated cellulose nanofiber adsorbent for the removal of Cu (II) from waste water. Radiat Phys Chem 177:109172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.109172
Natividad E, Lataste E, Lahaye M et al (2004) Chemical and morphological study of the sensitisation, activation and Cu electroless plating of Al2O3 polycrystalline substrate. Surf Sci 557(1-3):129–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2004.03.026
Nguyen L, Van HT, Ngo QN et al (2021) Improving Fenton-like oxidation of Rhodamin B using a new catalyst based on magnetic/iron-containing waste slag composite. Environ Techn Inn 23:101582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101582
Papas BN, Whitten JL (2016) Adsorption of copper on a γ-alumina support. Surf Sci 651:22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2016.03.019
Ren LM, Wu QM, Yang CG et al (2012) Solvent-free synthesis of zeolites from solid raw materials. J Am Chem Soc 134(37):15173–15176. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja3044954
Renock D, Gallegos T, Utsunomiya S et al (2009) Chemical and structural characterization of As immobilization by nanoparticles of mackinawite (FeSm). Chem Geol 268:116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.08.003
Salem DB, Ouakouak A, Touahra F et al (2023) Easy separable, floatable, and recyclable magnetic-biochar/alginate bead as super-adsorbent for adsorbing copper ions in water media. Bioresour Technol 383:129225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129225
Shahrashoub M, Bakhtiari S (2021) The efficiency of activated carbon/magnetite nanoparticles composites in copper removal: industrial waste recovery, green synthesis, characterization, and adsorption-desorption studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 311:110692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110692
Shih PY, Chin TS (1999) Effect of redox state of copper on the properties of P2O5–Na2O–CuO glasses. Mater Chem Phys 60(1):50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(99)00070-X
Sun X, Zhang J, You Y (2021) Enhancement of Cu(II) removal by carbon disulfide modified black wattle tannin gel. Colloids and Surfaces A 608:125594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020
Sun Y, Wang X, Xia S et al (2022) Cu(II) adsorption on poly(lactic acid) microplastics: significance of microbial colonization and degradation. Chem Eng J 429:132306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132306
Tan P (2018) The catalytic performance of Mo-impregnated HZSM-5 zeolite in CH4 aromatization: strong influence of Mo loading and pretreatment conditions. Catal Commun 103:101–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2017.10.008
Velempini T, Ahamed MEH, Pillay K (2023) Heavy-metal spent adsorbents reuse in catalytic, energy and forensic applications- a new approach in reducing secondary pollution associated with adsorption. Results in Chemistry 5:100901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2023.100901
Verbinnen B, Block C, Caneghem JV et al (2015) Recycling of spent adsorbents for oxyanions and heavy metal ions in the production of ceramics. Waste Manag 45:407–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.07.006
Witoon T, Chalorngtham J, Dumrongbunditkul P et al (2016) CO2 hydrogenation to methanol over Cu/ZrO2 catalysts: effects of zirconia phases. Chem Eng J 293:327–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.069
Wu Y, Pang H, Liu Y et al (2019) Environmental remediation of heavy metal ions by novel-nanomaterials: a review. Environ Pollut 246:608–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.12.076
Xiong C, Ren Q, Liu X et al (2021) Fenton activity on RhB degradation of magnetic g-C3N4/diatomite/Fe3O4 composites. Appl Surf Sci 543:148844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148844
Yang T, Han C, Tang J, Luo Y (2020) Removal performance and mechanisms of Cr(VI) by an in-situ self-improvement of mesoporous biochar derived from chicken bone. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:5018–5029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07116-4
Ye Y, Yang H, Wang X, Feng W (2018) Photocatalytic, Fenton and photo-Fenton degradation of RhB over Z-scheme g-C3N4/LaFeO3 heterojunction photocatalysts. Mater Sci Semicond Process 82:14–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2018.03.033
Zhang L, Yang F, Zhao Y et al (2021) Preparation of thiosemicarbazide-modified polyvinyl alcohol and its selective adsorption of Cu(II). Coll Inter Sci Commun 43:100377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100377
Zhi Y, Shi H, Mu L et al (2015) Dehydration pathways of 1-propanol on HZSM-5 in the presence and absence of water. J Am Chem Soc 137:15781–15794. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b09107
Zhou Y, Min L, Zhang Z et al (2018) Iron doped cobalt sulfide derived boosted electrocatalyst for water oxidation. Appl Surf Sci 448:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.04.080
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the support of this work by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Minzu University (Grant No: 2022KJQD27), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 22066013), and the Young Academic Raising Team Foundation of Guangxi Minzu University (Grant No: 2022GXUNXSHQN03).
Funding
Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Minzu University (Grant No: 2022KJQD27), Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 22066013), and Young Academic Raising Team Foundation of Guangxi Minzu University (Grant No: 2022GXUNXSHQN03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing—original draft and data analysis: Jing Xie; experiment, writing–original draft, conceptualization, validation, and conceptualization: Caiyun Han; writing—reviewing and editing: Qin Shi; investigation and writing—reviewing: Liying Liang; experiment, methodology, and software: Ting Yang; characterization, analysis, and writing—reviewing: Sufang He. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This research does not involve human participants and/or animals.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of this paper was obtained from the Guangxi Minzu University and all authors. We confirm that this manuscript is approved by all authors for publication, and publication has been approved by all co-authors and the responsible authorities at the institute where the work has been carried out.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
(i) We confirm that the work described has not been published before; (ii) it is not under consideration for publication anywhere else.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, ., Xie, J., Shi, Q. et al. Capturing Cu2+ and recycling spent Cu-adsorbents as catalyst for eliminating Rhodamine B: reactivity and mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 110352–110362 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29942-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29942-3