Abstract
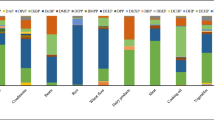
Grain, vegetable, and fruit samples were collected from Xi’an City in Northwest China and analyzed for the characteristics, bio-accessibility, and dietary exposure of 22 phthalic acid esters (PAEs). All the studied PAEs were ubiquitously detected, except for diethyl phthalate in vegetables and fruits. In grains, the sum of detectable PAEs (∑22PAEs) varied between 0.0840 and 40.0 µg/g, with a mean of 4.19 µg/g, presenting rice > > beans > flour, and the major PAEs were di-n-butyl phthalate (DnBP) and bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP). In vegetables, the ∑21PAEs ranged from 0.190 to 56.8 µg/g, with a mean of 8.07 µg/g, exhibiting leafy vegetables > root vegetables > fruits-vegetables > fungus > cauliflower > beans, and the main PAEs were di-iso-butyl phthalate (DiBP), DnBP, DEHP, di-iso-nonyl phthalate (DiNP), and di-iso-decyl phthalate (DiDP). In fruits, the ∑21PAEs varied between 0.300 and 12.6 µg/g, with a mean of 3.97 µg/g, presenting spring-winter season fruits > summer-autumn season fruits and shell-less fruits > shelled fruits, and the predominant PAEs were DiBP, DnBP, DEHP, DiNP, and DiDP. The bio-accessibility of PAEs in the gastrointestinal fluid simulant was higher than that in the single gastric or intestinal fluid simulant. The bio-accessibility of PAEs was correlated with the physiochemical properties of PAEs. The estimated daily intakes (EDIs) of human dietary exposure to PAEs were lower than the reference doses of United States Environmental Protection Agency and the tolerable dairy intakes (TDIs) of European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), except for the EDI of DnBP in the grains and DiBP in the vegetables higher than or close to the TDI of the EFSA. The research suggested that special attention should be paid to human dietary exposure to DnBP and DiBP, especially for children and adolescents.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Baloyi ND, Tekere M, Maphangwa KW, Masindi V (2021) Insights into the prevalence and impacts of phthalate esters in aquatic ecosystems. Front Environ Sci 9:684190
Bradley EL, Burden RA, Bentayeb K, Driffield M, Harmer N, Mortimer DN, Speck DR, Ticha J, Castle L (2013) Exposure to phthalic acid, phthalate diesters and phthalate monoesters from foodstuffs: UK total diet study results. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 30:735–742
Cao YR, Li J, Wu RB, Lin HJ, Lao JY, Ruan YF, Zhang K, Wu JX, Leung KMY, Lam PKS (2021) Phthalate esters in seawater and sediment of the northern South China Sea: occurrence, distribution, and ecological risks. Sci Total Environ 811:151412
Chen Q, Yang H, Zhou NY, Sun L, Bao HQ, Tan L, Chen HQ, Ling X, Zhang GW, Huang LP, Li LB, Ma MF, Yang H, Wang XG, Zou P, Peng KG, Liu TX, Shi XF, Feng DJ, Zhou ZY, Ao L, Cui ZH, Cao J (2017) Phthalate exposure, even below US EPA reference doses, was associated with semen quality and reproductive hormones: prospective MARHCS study in general population. Environ Int 104:58–68
Cheng Z, Li HH, Wang HS, Zhu XM, Suthipong S, Kim KW, Mohamed Y, Jamal H, Wong MH (2016) Dietary exposure and human risk assessment of phthalate esters based on total diet study in Cambodia. Environ Res 150:423–430
Cho SC, Bhang SY, Hong YC, Shin MS, Kim BN, Kim JW, Yoo HJ, Cho IH, Kim HW (2010) Relationship between environmental phthalate exposure and the intelligence of school-age children. Environ Health Perspect 118:1027–1032
Cirillo T, Fasano E, Castaldi E, Montuori P, Cocchieri RA (2011) Children’s exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and dibutyl phthalate plasticizers from school meals. J Agric Food Chem 59:10532–10538
Dewalque L, Charlier C, Pirard C (2014) Estimated daily intake and cumulative risk assessment of phthalate diesters in a Belgian general population. Toxicol Lett 231:161–168
Duan XL, Zhao XG, Wang BB, Chen YT, Cao SZ (2014) Highlights of the Chinese Exposure Factors Handbook (Adults). Science Press, Beijing, pp 24–25
Duan XL, Zhao XG, Wang BB, Chen HG, Cao SZ (2016) Highlights of the Chinese Exposure Factors Handbook (Children). China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, pp 55–64, 166–169
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) (2005a) Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) on a request from the Commission related to di-butyl phthalate (DBP) for use in food contact materials (EFSA-Q-2003-192). The EFSA Journal 242:1–17
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) (2005b) Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) on a request from the Commission related to bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) for use in food contact materials (EFSA-Q-2003-191). The ESFA Journal 243:1–20
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) (2005c) Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) on a request from the Commission related to butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP) for use in food contact materials (EFSA-Q-2003-190). The ESFA Journal 241:1–14
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) (2005d) Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) on a request from the Commission related to di-isononyl phthalate (DiNP) for use in food contact materials (EFSA-Q-2003-194). The ESFA Journal 244:1–18
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) (2005e) Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) on a request from the Commission related to di-isodecyl phthalate (DiDP) for use in food contact materials (EFSA-Q-2003-195). The ESFA Journal 245:1–14
Feng YX, Feng NX, Zeng LJ, Chen X, Xiang L, Li YW, Cai QY, Mo CH (2020) Occurrence and human health risks of phthalates in indoor air of laboratories. Sci Total Environ 707:135609
Fierens T, Servaes K, Holderbeke MV, Geerts L, Henauw DS, Sioen I, Vanermen G (2012) Analysis of phthalates in food products and packaging materials sold on the Belgian market. Food Chem Toxicol 50:2575–2583
Fromme H, Gruber L, Schlummer M, Wolz G, Böhmer S, Angerer J, Mayer R, Liebl B, Bolte G (2007) Intake of phthalates and di(2-ethylhexyl) adipate: results of the integrated exposure assessment survey based on duplicate diet samples and biomonitoring data. Environ Int 33:1012–1020
Guo Y, Zhang Z, Liu L, Li Y, Ren N, Kannan K (2012) Occurrence and profiles of phthalates in foodstuffs from China and their implications for human exposure. J Agric Food Chem 60:6913–6919
He MJ, Lu JF, Wang J, Wei SQ, Hageman KJ (2020) Phthalate esters in biota, air and water in an agricultural area of western china, with emphasis on bioaccumulation and human exposure. Sci Total Environ 698:134264
Heinemeyer G, Sommerfeld C, Springer A, Heiland A, Lindtner O, Greiner M, Heuer T, Krems C, Conrad A (2013) Estimation of dietary intake of bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) by consumption of food in the German population. Int J Hyg Environ Health 216:472–480
Holderbeke MV, Geerts L, Vanermen G, Servaes K, Sioen I, Henauw SD, Fierens T (2014) Determination of contamination pathways of phthalates in food products sold on the Belgian market. Environ Res 134:345–352
Huang L, Zhu X, Zhou S, Cheng Z, Shi K, Zhang C, Shao H (2021) Phthalic acid esters: natural sources and biological activities. Toxins (basel) 13:495
Jamarani R, Erythropel H, Nicell J, Leask R, Marić M (2018) How green is your plasticizer? Polymers (Basel) 10:834
Ji Y, Wang F, Zhang L, Shan C, Bai Z, Sun ZR, Liu LL, Shen BX (2014) A comprehensive assessment of human exposure to phthalates from environmental media and food in Tianjin, China. J Hazard Mater 279:133–140
Johns LE, Cooper GS, Galizia A, Meeker JD (2015) Exposure assessment issues in epidemiology studies of phthalates. Environ Int 85:27–39
Koch HM, Lorber M, Christensen KL, Palmke C, Koslitz S, Bruning T (2013) Identifying sources of phthalate exposure with human biomonitoring: results of a 48h fasting study with urine collection and personal activity patterns. Int J Hyg Environ Health 216:672–681
Koniecki D, Wang R, Moody RP, Zhu J (2011) Phthalates in cosmetic and personal care products: concentrations and possible dermal exposure. Environ Res 111:329–336
Latini G, De Felice C, Presta G, Del Vecchio A, Paris I, Ruggieri F, Mazzeo A (2003) In utero exposure to di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and duration of human pregnancy. Environ Health Perspect 111:1783–1785
Le TM, Nguyen HMN, Nguyen VK, Nguyen AV, Vu ND, Yen NTH, Hoang AQ, Minh TB, Kannan K, Tran TM (2021) Profiles of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) in bottled water, tap water, lake water, and wastewater samples collected from Hanoi, Vietnam. Sci Total Environ 788:147831
Lee ST, Lin C, Vu CT, Chen YC, Chen KS, Villanueva MC (2019) How human activities in commercial areas contribute to phthalate ester pollution in street dust of Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 647:619–626
Liu B, Ai S, Naeem S, Ding J, Ji W, Zhang Y (2018) Metal bioaccessibility in a wastewater irrigated soil-wheat system and associated human health risks: implications for regional thresholds. Ecol Ind 94:305–311
Lu H, Zhu Z (2021) Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk of atmospheric phthalate esters in a multi-function area of Hangzhou, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:8615–8625
Ma BB, Wang LJ, Tao WD, Liu MM, Zhang PQ, Zhang SW, Li XP, Lu XW (2020) Phthalate esters in atmospheric PM2.5 and PM10 in the semi-arid city of Xi’an, Northwest China: pollution characteristics, sources, health risks, and relationships with meteorological factors. Chemosphere 242:125226
Ma G, Ma BB, Wang LJ, Tao WD (2022) Occurrence and dietary exposure risks of phthalate esters in food in the typical valley city Xi’an, Northwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:31426–31440
Martine B, Marie-Jeanne T, Cendrine D, Fabrice A, Marc C (2013) Assessment of adult human exposure to phthalate esters in the urban centre of Paris (France). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90:91–96
Net S, Sempere R, Delmont A, Paluselli A, Ouddane B (2015) Occurrence, fate, behavior and ecotoxicological state of phthalates in different environmental matrices. Environ Sci Technol 49:4019–4035
Page BD, Lacroix GM (1995) The occurrence of phthalate ester and di-2-ethylhexyl adipate plasticizers in Canadian packaging and food sampled in 1985–1989: a survey. Food Addit Contam 12:129–151
Sakhi AK, Lillegaard IT, Voorspoels S, Carlsen MH, Loken EB, Brantsaeter AL, Haugen B, Meltzer HM, Thomsen C (2014) Concentrations of phthalates and bisphenol A in Norwegian foods and beverages and estimated dietary exposure in adults. Environ Int 73:259–269
Schecter A, Lorber M, Guo Y, Wu Q, Yun SH, Kannan K, Hommel M, Imran N, Hynan LS, Cheng DL, Colacino JA, Birnbaum LS (2013) Phthalate concentrations and dietary exposure from food purchased in New York state. Environ Health Perspect 121:473–494
Schettler T (2006) Human exposure to phthalates via consumer products. Int J Androl 29:134–139
Schiedek T (1995) Impact of plasticizers (phthalic acid esters) on soil and groundwater quality. Groundwater Quality: Remediation and Protection. LAHS Press, Wallingford, pp 149–156
Selvaraj KK, Mubarakali H, Rathinam M, Harikumar L, Sampath S, Shanmugam G, Ramaswamy BR (2016) Cumulative exposure and dietary risk assessment of phthalates in bottled water and bovine milk samples: a preliminary case study in Tamil Nadu, India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 22:1166–1182
Shen C, Wu T, Zang X (2018) Hollow fiber stir bar sorptive extraction combined with GC–MS for the determination of phthalate esters from children’s food. Chromatography 82:683–693
Silva M, Reidy J, Samandar E (2005) Detection of phthalate metabolites in human saliva. Arch Toxicol 79:647–652
Sui HX, Zhang L, Wu PG, Song Y, Yong L, Yang DJ, Jiang DG, Liu ZP (2014) Concentration of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) in foods and its dietary exposure in China. Int J Hyg Environ Health 217:695–701
Talsness CE, Andrade AJ, Kuriyama SN, Taylor JA, vom Saal FS (2009) Components of plastic: experimental studies in animals and relevance for human health. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 364:2079–2096
Tao H, Wang Y, Liang H, Zhang X, Liu X, Li J (2020) Pollution characteristics of phthalate acid esters in agricultural soil of Yinchuan, northwest China, and health risk assessment. Environ Geochem Health 42:4313–4326
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2012) Regional screening level (RSL) summary table. United State Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Wang J, Chen G, Christie P, Zhang M, Luo Y, Teng Y (2015) Occurrence and risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in vegetables and soils of suburban plastic film greenhouses. Sci Total Environ 523:129–137
Wang W, Themelis NJ, Sun K, Bourtsalas AC, Huang Q, Zhang Y, Zhang W (2019) Current influence of China’s ban on plastic waste imports. Waste Disposal Sustain Energy 1:67–78
Wittassek M, Koch HM, Angerer J, Brüning T (2011) Assessing exposure to phthalates-the human biomonitoring approach. Mol Nutr Food Res 55:7–31
Wu S, Li B, Liang JM, Peng SQ (2015) Distribution characteristics of phthalic acid esters in soils and vegetables in vegetable producing areas of Shantou city, China. J Agron Environ Sci 34:1889–1896 (In Chinese)
Xiao KE, Mo CH, Cai QY (2012) Concentrations of PAEs in vegetable fields of Pearl River Delta. Sichuan Environ 31:49–55 (In Chinese)
Yang X, Chen DW, Lv B, Miao H, Wu YN, Zhao YF (2018) Dietary exposure of the Chinese population to phthalate esters by a Total Diet Study. Food Control 89:314–321
Yen TH, Lin-Tan DT, Lin JL (2011) Food safety involving ingestion of foods and beverages prepared with phthalate-plasticizer-containing clouding agents. J Formos Med Assoc 110:671–684
Yu YJ, Ye H, Yang Y, Zhao J (2014) The bioaccessibility and exposure of PAEs via oral media in Taihu Lake basin of south Jiangsu Province. Environ Chem 33:194–205 (In Chinese)
Zhai ZL, Lu SG, Zhang W (2014) Investigation on contents of phthalate acid esters in grain. China Chin J Health Lab Technol 24:207–272 (In Chinese)
Zhang SM, Li MY, Wang JY, Wang QJ, Mo CH (2009) Occurrence of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) in vegetable fields of Dongguan City. Guangdong Agric Sci 6:172–175 (In Chinese)
Zhang WP, Xu L, Guo CS, Xu J (2021) Spatial distribution, historical trend, and ecological risk assessment of phthalate esters in sediment from Taihu Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:25207–25217
Zhang X, Wang Q, Qiu T, Tang S, Li J, Giesy JP, Zhu Y, Hu XJ, Xu DQ (2019) PM2.5 bound phthalates in four metropolitan cities of China: concentration, seasonal pattern and health risk via inhalation. Sci Total Environ 696:133982
Zhao X, Shen JM, Zhang H, Li X, Chen ZL, Wang XC (2020) The occurrence and spatial distribution of phthalate esters (PAEs) in the Lanzhou section of the Yellow river. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:19724–19735
Zhou B, Zhao L, Sun Y, Li X, Weng L, Li Y (2021) Contamination and human health risks of phthalate esters in vegetable and crop soils from the Huang-Huai-Hai region of China. Sci Total Environ 778:146281
Zhu J, Phillips S, Feng Y (2006) Phthalate esters in human milk: concentration variations over a 6-month postpartum time. Environ Sci Technol 40:5276–5281
Zhu Q, Xu L, Wang W, Liu W, Liao C, Jiang G (2022) Occurrence, spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of phthalate esters in water, soil and sediment from Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci Total Environ 806:150966
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China through grant 41877516.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tong Zhang: writing—original draft preparation, formal analysis, and visualization; Bianbian Ma: methodology, data curation, and investigation; Lijun Wang: conceptualization; resources; writing—review and editing; supervision; project administration; and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ester Heath
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Ma, B. & Wang, L. Phthalic acid esters in grains, vegetables, and fruits: concentration, distribution, composition, bio-accessibility, and dietary exposure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 2787–2799 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22415-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22415-z