Abstract
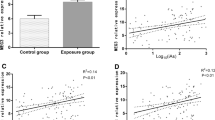
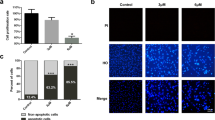
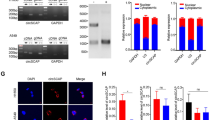
As a class I carcinogen, arsenic has been reported to cause diseases accompanied by circRNAs regulating proliferation and apoptosis at the molecular level, but whether circP50 (circBase ID: hsa_circ_0008012) does the same has not been demonstrated. The aim of this study is to provide the basis for anti-lung cancer mechanism research, by studying the expression of circP50 under arsenic-induced conditions, and the effect and mechanism on the proliferation and apoptosis of A549 cells based on the circP50 knockdown models. To explore whether the circP50 is responsive to arsenic exposure, the qRT-PCR was applied to discover that the relative expression of circP50 in A549 cells increased only with increasing NaAsO2 dose and independent of its metabolites. We further determined the mechanism of circP50 by establishing circP50 knockdown models. The results of cell viability and EdU assays indicated the proliferation of A549 cells. According to the western blotting, phosphorylation of p53 at Ser15, Ser376, and Ser392 and acetylation of p53 at Lys370 and Lys382 were inhibited, resulting in the deficiency of p53 expression. Subsequently, the expression of genes downstream of p53 was reduced, including p21, PUMA, Caspase3, and Bcl-xS. Furthermore, the expressions of IKB-α, p65, and p50 decreased, but C-myc expression did not change significantly, referring to the NF-κB pathway was not dominant. The results suggest that circP50 mainly functions through the p53 pathway to mediate apoptosis in response to arsenic exposure.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Appella E, Anderson CW (2000) Signaling to p53: breaking the posttranslational modification code. Pathol Biol (Paris) 48:227–245
Bjorklund G, Oliinyk P et al (2020) Arsenic intoxication: general aspects and chelating agents. Arch Toxicol 94:1879–1897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02739-w
Bozack AK, Saxena R et al (2018) Nutritional influences on one-carbon metabolism: effects on arsenic methylation and toxicity. Annu Rev Nutr 38:401–429. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-082117-051757
Chen LL (2020) The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21:475–490. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0243-y
Chen QY, Costa M (2021) Arsenic: a global environmental challenge. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 61:47–63. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-030220-013418
Chen L, Liu S et al (2020) Regulating tumor suppressor genes: post-translational modifications. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5:90. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-0196-9
Chung SK, Zhu S et al (2014) Functional analysis of the acetylation of human p53 in DNA damage responses. Protein Cell 5:544–551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-014-0048-x
Concetti J, Wilson CL (2018) NFKB1 and cancer: friend or foe? Cells 7:133. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7090133
Dai X, Chen C et al (2018) Exosomal circRNA_100284 from arsenite-transformed cells, via microRNA-217 regulation of EZH2, is involved in the malignant transformation of human hepatic cells by accelerating the cell cycle and promoting cell proliferation. Cell Death Dis 9:454. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0485-1
Dai M, Hu S et al (2019) BPTF cooperates with p50 NF-kappaB to promote COX-2 expression and tumor cell growth in lung cancer. Am J Transl Res 11:7398–7409
Dong H, Zhou J et al (2021) Biogenesis, functions, and role of CircRNAs in lung cancer. Cancer Manag Res 13:6651–6671. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S324812
Du WW, Zhang C et al (2017) Identifying and characterizing circRNA-protein interaction. Theranostics 7:4183–4191. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.21299
Fan X, Weng X et al (2017) Circular RNAs in cardiovascular disease: an overview. Biomed Res Int 2017:5135781. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5135781
Ferragut Cardoso AP, Udoh KT et al (2020) Arsenic-induced changes in miRNA expression in cancer and other diseases. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 409:115306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2020.115306
Giridharan S, Srinivasan M (2018) Mechanisms of NF-kappaB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation. J Inflamm Res 11:407–419. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S140188
Glazar P, Papavasileiou P et al (2014) circBase: a database for circular RNAs. RNA 20:1666–1670. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.043687.113
Han CY, Patten DA et al (2021) Nuclear HKII-P-p53 (Ser15) Interaction is a prognostic biomarker for chemoresponsiveness and glycolytic regulation in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancers (Basel) 13:3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143399
He W, Zhang Y et al (2020) LncRNA NNT-AS1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through regulating miR-22-3p/YAP1 axis. Thorac Cancer 11:549–560. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13280
Huang J, Yu S et al (2021) The dual role of circular RNAs as miRNA sponges in breast cancer and colon cancer. Biomedicines 9:1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111590
Islam MM, Takeyama N (2021) Inorganic arsenic administration suppresses human neutrophil function in vitro. Hum Exp Toxicol 40:725–734. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327120966040
Januszyk K, Januszyk P et al (2020) The influence of salinomycin on the expression profile of mRNAs encoding selected caspases and MiRNAs regulating their expression in endometrial cancer cell line. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 21:1505–1515. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389201021666200514095043
Jiang M, Qi L et al (2020) The caspase-3/GSDME signal pathway as a switch between apoptosis and pyroptosis in cancer. Cell Death Dis 6:112. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-020-00349-0
Kon N, Churchill M et al (2021) Robust p53 stabilization is dispensable for its activation and tumor suppressor function. Cancer Res 81:935–944. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1804
Lai L, Shin GY et al (2020) The role of cell cycle regulators in cell survival-dual functions of cyclin-dependent kinase 20 and p21(Cip1/Waf1). Int J Mol Sci 21:8504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228504
Lin XL, Li K et al (2020) Dulcitol suppresses proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating SIRT1/p53 pathway. Phytomedicine 66:153112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153112
Liu Y, Tavana O et al (2019) p53 Modifications: exquisite decorations of the powerful guardian. J Mol Cell Biol 11:564–577. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjz060
Ma J, Feng Y et al (2016) PUMA and survivin are involved in the apoptosis of HepG2 cells induced by microcystin-LR via mitochondria-mediated pathway. Chemosphere 157:241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.051
Mar Wai K, Umezaki M et al (2019) Arsenic exposure through drinking water and oxidative stress status: a cross-sectional study in the Ayeyarwady region, Myanmar. J Trace Elem Med Biol 54:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.04.009
Martinez-Reyes I, Chandel NS (2021) Cancer metabolism: looking forward. Nat Rev Cancer 21:669–680. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-021-00378-6
Medda N, De SK et al (2021) Different mechanisms of arsenic related signaling in cellular proliferation, apoptosis and neo-plastic transformation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111752
Meng S, Zhou H et al (2017) CircRNA: functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker for cancer. Mol Cancer 16:94. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0663-2
Mitchell S, Vargas J et al (2016) Signaling via the NFkappaB system. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 8:227–241. https://doi.org/10.1002/wsbm.1331
Nan A, Chen L et al (2017) A novel regulatory network among LncRpa, CircRar1, MiR-671 and apoptotic genes promotes lead-induced neuronal cell apoptosis. Arch Toxicol 91:1671–1684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1837-1
Pietrzak S, Wojcik J et al (2021) Influence of the levels of arsenic, cadmium, mercury and lead on overall survival in lung cancer. Biomolecules 11:1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081160
Pospisilova S, Brazda V et al (2004) Activation of the DNA-binding ability of latent p53 protein by protein kinase C is abolished by protein kinase CK2. Biochem J 378:939–947. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20030662
Prats AC, David F et al (2020) Circular RNA, the key for translation. Int J Mol Sci 21:8591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228591
Rahman M, Sohel N et al (2019) Arsenic exposure and young adult's mortality risk: a 13-year follow-up study in Matlab, Bangladesh. Environ Int 123:358–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.006
Stevens M, Oltean S (2019) Modulation of the apoptosis gene Bcl-x function through alternative splicing. Front Genet 10:804. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00804
Sun DZ, Song CQ et al (2020) Role of the MAPK pathway in human lung epithelial-like A549 cells apoptosis induced by paraquat. Genet Mol Biol 43:e20190137. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2019-0137
Sun M, Tan J et al (2021) Inorganic arsenic-mediated upregulation of AS3MT promotes proliferation of nonsmall cell lung cancer cells by regulating cell cycle genes. Environ Toxicol 36:204–212. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.23026
Taniguchi K, Karin M (2018) NF-kappaB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol 18:309–324. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.142
Tian F, Wang Y et al (2017) Circular RNA CircHIPK3 promotes NCI-H1299 and NCI-H2170 cell proliferation through miR-379 and its target IGF1. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi 20:459–467. https://doi.org/10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2017.07.04
Van Der Steen N, Lyu Y et al (2020) The circular RNA landscape of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancers (Basel) 12:1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051091
Wang L, Lu YF et al (2020) HB-EGF activates the EGFR/HIF-1alpha pathway to induce proliferation of arsenic-transformed cells and tumor growth. Front Oncol 10:1019. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.01019
Williams LM, Gilmore TD (2020) Looking down on NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Biol 40:e00104–e00120. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00104-20
Wu J, Ferragut Cardoso AP et al (2019) Overexpression of hsa-miR-186 induces chromosomal instability in arsenic-exposed human keratinocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 378:114614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2019.114614
Xiao T, Xue J et al (2018) Circ008913, via miR-889 regulation of DAB2IP/ZEB1, is involved in the arsenite-induced acquisition of CSC-like properties by human keratinocytes in carcinogenesis. Metallomics 10:1328–1338. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8mt00207j
Xue J, Liu Y et al (2017) Circ100284, via miR-217 regulation of EZH2, is involved in the arsenite-accelerated cell cycle of human keratinocytes in carcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis 1863:753–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.12.018
Xue J, Chen C et al (2018) CircLRP6 regulation of ZEB1 via miR-455 is involved in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition during arsenite-induced malignant transformation of human keratinocytes. Toxicol Sci 162:450–461. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfx269
Yang X, Wang J et al (2018) Silica-induced initiation of circular ZC3H4 RNA/ZC3H4 pathway promotes the pulmonary macrophage activation. FASEB J 32:3264–3277. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201701118R
Zang J, Lu D et al (2020) The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: an important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res 98:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24356
Zhang HD, Jiang LH et al (2018) CircRNA: a novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast Cancer 25:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-017-0793-9
Zhang AL, Chen L et al (2020) Role of H3K18ac-regulated nucleotide excision repair-related genes in arsenic-induced DNA damage and repair of HaCaT cells. Hum Exp Toxicol 39:1168–1177. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327120903482
Zhou Q, Yin J et al (2022) Up-regulation of PUMA caused the activation of p53 phosphorylation and acetylation, enhancing the interaction between PUMA and Bcl-X and mediating arsenic-induced apoptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 434:115800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2021.115800
Zhu X, Wang X et al (2017) hsa_circ_0013958: a circular RNA and potential novel biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma. FEBS J 284:2170–2182. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14132
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.82160607), Yunnan Applied Basic Research Projects-Union Foundation, Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department, and Kunming Medical University, China (Grant No.202101AY070001-054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yizhu Mao wrote the first draft of the manuscript and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript; Yizhu Mao and Qian Zhou analyzed and interpreted the present study experiment and data; Jinhua Wang and Ruihuan Zhao performed material preparation; Xuefei Yang, Ya Shi and Jinyao Yin collected and analyzed data; Chenglan Jiang prepared the instrument for the experiment; Yuefeng He had the idea for the article and revised the first version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ludek Blaha
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, Y., Zhou, Q., Wang, J. et al. CircP50 functions through the phosphorylation- and acetylation-activated p53 pathway to mediate inorganic arsenic-induced apoptosis in A549 cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 91232–91240 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22094-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22094-w