Abstract
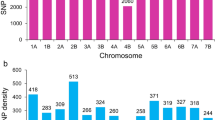
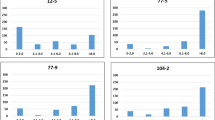
Myrtle rust (caused by Austropuccinia psidii Beenken) is exotic to Australia, yet specific resistance is present in a range of naïve myrtaceous host plants. Resistance to myrtle rust is primarily quantitative in nature and controlled by multiple interacting loci. We undertook a genome-wide association study (GWAS) to discover relationships between nuclear genomic sequence variation and multiple aspects of resistance to A. psidii in Eucalyptus obliqua, a representative species from subgenus Eucalyptus. Sequence variation was assessed with respect to numeric severity, binary symptomatic, hypersensitive, and pustulation responses to inoculation of seedlings with A. psidii. A total of 1.13 million, single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were tested for association with the rust resistance responses of 637 phenotyped E. obliqua seedlings, each from different, single mother tree seedlots. Thirty-three highly significant SNP-trait associations were detected, of which 26 associated with the binary symptomatic/asymptomatic response to A. psidii. Comparison of the genomic position of these SNPs with rust resistance loci (Ppr1-5), previously reported in species from subgenus Symphyomyrtus, suggested that several were positioned near the major Ppr1 locus and other Ppr loci. This study provides the first integrated genomic view of A. psidii resistance across the Eucalyptus subgenera and provides the foundation for discovering key resistance genes for use in marker-based resistance breeding.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its electronic supplementary material.
References
ABARES (2019) Australia’s forests at a glance 2019. Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Sciences (ABARES), Canberra
Alvares CA, Sentelhas PC, Mattos EM, Miranda AC, Moraes WB, Silva PHM, Furtado EL, Stape JL (2017) Climatic favourability zones for Eucalyptus rust in Brazil. For Pathol 47:e12301. https://doi.org/10.1111/efp.12301
Alves AA, Rosado CCG, Faria DA, Guimaraes LMD, Lau D, Brommonschenkel SH, Grattapaglia D, Alfenas AC (2012) Genetic mapping provides evidence for the role of additive and non-additive QTLs in the response of inter-specific hybrids of Eucalyptus to Puccinia psidii rust infection. Euphytica 183:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0455-5
Barbosa-da-Silva A, Wanderley-Nogueira AC, Silva RRM, Berlarmino LC, Soares-Cavalcanti NM, Benko-Iseppon AM (2005) In silico survey of resistance (R) genes in Eucalyptus transcriptome. Genet Mol Biol 28:562–574. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572005000400011
Bayly MJ, Rigault P, Spokevicius A, Ladiges PY, Ades PK, Anderson C, Bossinger G, Merchant A, Udovicic F, Woodrow IE, Tibbits J (2013) Chloroplast genome analysis of Australian eucalypts - Eucalyptus, Corymbia, Angophora, Allosyficarpia and Stockwellia (Myrtaceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 69:704–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2013.07.006
Beenken L (2017) Austropuccinia: a new genus name for the myrtle rust Puccinia psidii placed within the redefined family Sphaerophragmiaceae (Pucciniales). Phytotaxa 297:53–61. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.297.1.5
Beresford RM, Turner R, Tait A, Paul V, Macara G, Yu ZD, Lima L, Martin R (2018) Predicting the climatic risk of myrtle rust during its first year in New Zealand. NZ Plant Prot 71:332–347. https://doi.org/10.30843/nzpp.2018.71.176
Berthon KA, Winzer LF, Sandhu K, Cuddy W, Manea A, Carnegie AJ, Leishman MR (2019) Endangered species face an extra threat: susceptibility to the invasive pathogen Austropuccinia psidii (myrtle rust) in Australia. Australas Plant Pathol 48:385–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-019-00640-4
Bigeard J, Colcombet J, Hirt H (2015) Signaling mechanisms in pattern-triggered immunity (PTI). Mol Plant 8:521–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.022
Boutrot F, Zipfel C (2017) Function, discovery, and exploitation of plant pattern recognition receptors for broad-spectrum disease resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 55:257–286. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-080614-120106
Butler JB, Freeman JS, Vaillancourt RE, Potts BM, Glen M, Lee DJ, Pegg GS (2016) Evidence for different QTL underlying the immune and hypersensitive responses of Eucalyptus globulus to the rust pathogen Puccinia psidii. Tree Genet Genomes 12:39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-0987-x
Butler JB, Potts BM, Vaillancourt RE, Lee DJ, Pegg GS, Freeman JS (2019) Independent QTL underlie resistance to the native pathogen Quambalaria pitereka and the exotic pathogen Austropuccinia psidii in Corymbia. Tree Genet Genomes 15:72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-019-1378-x
Carnegie AJ (2015) First report of Puccinia psidii (myrtle rust) in Eucalyptus plantations in Australia. Plant Dis 99:161. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-09-14-0901-PDN
Carnegie AJ, Cooper K (2011) Emergency response to the incursion of an exotic myrtaceous rust in Australia. Australas Plant Pathol 40:346–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-011-0066-6
Carnegie AJ, Lidbetter JR (2012) Rapidly expanding host range for Puccinia psidii sensu lato in Australia. Australas Plant Pathol 41:13–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-011-0082-6
Carnegie AJ, Pegg GS (2018) Lessons from the incursion of myrtle rust in Australia. Annu Rev Phytopathol 56:457–478. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-080516-035256
Carnegie AJ, Lidbetter JR, Walker J, Horwood MA, Tesoriero L, Glen M, Priest MJ (2010) Uredo rangelii, a taxon in the guava rust complex, newly recorded on Myrtaceae in Australia. Australas Plant Pathol 39:463–466. https://doi.org/10.1071/AP10102
Carnegie AJ, Kathuria A, Pegg GS, Entwistle P, Nagel M, Giblin FR (2016) Impact of the invasive rust Puccinia psidii (myrtle rust) on native Myrtaceae in natural ecosystems in Australia. Biol Invasions 18:127–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-015-0996-y
Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ (2006) Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 124:803–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.008
Christie N, Tobias PA, Naidoo S, Külheim C (2016) The Eucalyptus grandis NBS-LRR gene family: physical clustering and expression hotspots. Front Plant Sci 6:1238. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01238
Core Team R (2016) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical computing, Vienna, Austria Available at https://www.r-project.org
Coutinho TA, Wingfield MJ, Alfenas AC, Crous PW (1998) Eucalyptus rust: a disease with the potential for serious international implications. Plant Dis 82:819–825. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS.1998.82.7.819
Crisp M, Cook L, Steane D (2004) Radiation of the Australian flora: what can comparisons of molecular phylogenies across multiple taxa tell us about the evolution of diversity in present-day communities? Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 359:1551–1571. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2004.1528
Cui H, Tsuda K, Parker JE (2015) Effector-triggered immunity: from pathogen perception to robust defense. Annu Rev Plant Biol 66:487–511. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-040012
Dianese JC, Moraes TSA, Silva AR (1986) Screening Eucalyptus species for rust resistance in Bahia, Brazil. Trop Pest Manage 32:292–295. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670878609371082
Dodds PN, Rathjen JP (2010) Plant immunity: towards an integrated view of plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Genet 11:539–548. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2812
Dodds PN, Lawrence GJ, Catanzariti AM, Teh T, Wang CIA, Ayliffe MA, Kobe B, Ellis JG (2006) Direct protein interaction underlies gene-for-gene specificity and coevolution of the flax resistance genes and flax rust avirulence genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:8888–8893. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0602577103
Doughty RW (2000) The Eucalyptus: a natural and commercial history of the gum tree. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore and London
Downham R, Gavran M (2018) Australian plantation statistics 2018 update. Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Sciences (ABARES), Canberra
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Eitas TK, Dangl JL (2010) NB-LRR proteins: pairs, pieces, perception, partners, and pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:472–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2010.04.007
Eldridge K, Davidson J, Harwood C, van Wyk G (1993) Eucalypt domestication and breeding. Oxford Science Publications, New York
Falconer DS, Mackay TFC (1996) Introduction to quantitative genetics, 4th edn. Pearson Prentice Hall, New York
Florence RG (1996) Ecology and silviculture of eucalypt forests. CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood
Freeman JS, Potts BM, Vaillancourt RE (2008) Few Mendelian genes underlie the quantitative response of a forest tree, Eucalyptus globulus, to a natural fungal epidemic. Genetics 178:563–571. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.107.081414
Freeman JS, Hamilton MG, Lee DJ, Pegg GS, Brawner JT, Tilyard PA, Potts BM (2019) Comparison of host susceptibilities to native and exotic pathogens provides evidence for pathogen-imposed selection in forest trees. New Phytol 221:2261–2272. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15557
Furtado EL, Marino CL (2003) Eucalyptus rust management in Brazil. In: Proceedings of Second IUFRO Rust Forest Trees W.P. Conference. International Union of Forest Research Organizations (IUFRO), Vienna, Austria, pp 118-124
Giblin F, Carnegie AJ (2014) Puccinia psidii (myrtle rust): Australian host list. Australian Network for Plant Conservation, Canberra http://www.anpc.asn.au/myrtle-rust. Accessed 20 November 2019
González-Orozco CE, Thornhill AH, Knerr N, Laffan S, Miller JT (2014) Biogeographical regions and phytogeography of the eucalypts. Divers Distrib 20:46–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.12129
Graça RN, Aun CP, Guimarães LMS, Rodrigues BVA, Zauza EAV, Alfenas AC (2011) A new race of Puccinia psidii defeats rust resistance in eucalypt. Australas Plant Pathol 40:442–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-011-0056-8
Grattapaglia D, Vaillancourt RE, Shepherd M, Thumma BR, Foley W, Külheim C, Potts BM, Myburg AA (2012) Progress in Myrtaceae genetics and genomics: Eucalyptus as the pivotal genus. Tree Genet Genomes 8:463–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-012-0491-x
Gururani MA, Venkatesh J, Upadhyaya CP, Nookaraju A, Pandey SK, Park SW (2012) Plant disease resistance genes: current status and future directions. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 78:51–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2012.01.002
Harwood C (2011) Introductions: doing it right. In: Walker J (ed) Developing a eucalypt resource: learning from Australia and elsewhere. University of Canterbury, Christchurch, Wood Technology Research Centre, pp 43–54
Heim RHJ, Wright IJ, Chang HC, Carnegie AJ, Pegg GS, Lancaster EK, Falster DS, Oldeland J (2018) Detecting myrtle rust (Austropuccinia psidii) on lemon myrtle trees using spectral signatures and machine learning. Plant Pathol 67:1114–1121. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12830
Hulbert SH, Webb CA, Smith SM, Sun Q (2001) Resistance gene complexes: evolution and utilization. Annu Rev Phytopathol 39:285–312. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.39.1.285
Iglesias-Trabado G, Carballeira-Tenreiro R, Folgueira-Lozano J (2009) Eucalyptus universalis: global cultivated eucalypt forests map version 1.2. In: Eucalyptologics: information resources on eucalypt cultivation worldwide. http://www.git-forestry.com. Accessed 20 November 2019
Jacobs MR (1981) Eucalypts for planting, FAO forestry series, volume 11. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), Rome
Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05286
Junghans DT, Alfenas AC, Brommonschenkel SH, Oda S, Mello EJ, Grattapaglia D (2003) Resistance to rust (Puccinia psidii Winter) in Eucalyptus: mode of inheritance and mapping of a major gene with RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 108:175–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1415-9
Kohler A, Rinaldi C, Duplessis S, Baucher M, Geelen D, Duchaussoy F, Meyers BC, Boerjan W, Martin F (2008) Genome-wide identification of NBS resistance genes in Populus trichocarpa. Plant Mol Biol 66:619–636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9293-9
Kriticos DJ, Morin L, Leriche A, Anderson RC, Caley P (2013) Combining a climatic niche model of an invasive fungus with its host species distributions to identify risks to natural assets: Puccinia psidii sensu lato in Australia. PLoS One 8:e64479. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0064479
Kthiri D, Loladze A, N’Diaye A, Nilsen KT, Walkowiak S, Dreisigacker S, Ammar K, Pozniak CJ (2019) Mapping of genetic loci conferring resistance to leaf rust from three globally resistant durum wheat sources. Front Plant Sci 10:1247. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01247
L’Héritier CL (1788) Sertum Anglicum, seu, Plantae rariores quae in hortis juxta Londinum: imprimis in horto regio Kewensi excoluntur, ab anno 1786 ad annum 1787 observatae (in Latin). Petri Francisci Didot, Paris
Labate CA, de Assis TF, Oda S, de Mello EJ, González ER, Zauza EAV, Mori ES, de Moraes MLT, Cid LPB, Alfenas AC, Foelkel C, Moon DH, de Carvalho MCCG, Caldas DGG, Carneiro RT, de Andrade A, Salvatierra GR (2009) Eucalyptus. In: Kole C, Hall TC (eds) Compendium of transgenic crop plants, part 9: transgenic forest tree species. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., New Jersey, pp 35–108
Ladiges PY, Udovicic F, Nelson G (2003) Australian biogeographical connections and the phylogeny of large genera in the plant family Myrtaceae. J Biogeogr 30:989–998. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2699.2003.00881.x
Lee DJ, Brawner JT, Pegg GS (2015) Screening Eucalyptus cloeziana and E. argophloia populations for resistance to Puccinia psidii. Plant Dis 99:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-04-14-0353-RE
Lipka AE, Tian F, Wang Q, Peiffer J, Li M, Bradbury PJ, Gore MA, Buckler ES, Zhang Z (2012) GAPIT: genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics 28:2397–2399. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts444
Liu H, Zhan J, Li J, Lu X, Liu J, Wang Y, Zhao Q, Ye G (2020) Genome-wide association study (GWAS) for mesocotyl elongation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under multiple culture conditions. Genes 11:49. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010049
Mamani EMC, Bueno NW, Faria DA, Guimarães LMS, Lau D, Alfenas AC, Grattapaglia D (2010) Positioning of the major locus for Puccinia psidii rust resistance (Ppr1) on the Eucalyptus reference map and its validation across unrelated pedigrees. Tree Genet Genomes 6:953–962. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0304-z
Marone D, Russo MA, Laidò G, De Leonardis AM, Mastrangelo AM (2013) Plant nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) genes: active guardians in host defense responses. Int J Mol Sci 14:7302–7326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14047302
Michelmore RW, Meyers BC (1998) Clusters of resistance genes in plants evolve by divergent selection and a birth-and-death process. Genome Res 8:1113–1130. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.8.11.1113
Mirlohi A, Brueggeman R, Drader T, Nirmala J, Steffenson BJ, Kleinhofs A (2008) Allele sequencing of the barley stem rust resistance gene Rpg1 identifies regions relevant to disease resistance. Phytopathology 98:910–918. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-98-8-0910
Misra G, Badoni S, Anacleto R, Graner A, Alexandrov N, Sreenivasulu N (2017) Whole genome sequencing-based association study to unravel genetic architecture of cooked grain width and length traits in rice. Sci Rep 7:12478. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12778-6
Moon DH, Salvatierra GR, Caldas DGG, de Carvalho MCCG, Carneiro RT, Franceschini LM, Oda S, Labate CA (2007) Comparison of the expression profiles of susceptible and resistant Eucalyptus grandis exposed to Puccinia psidii Winter using SAGE. Funct Plant Biol 34:1010–1018. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP07094
Morin L, Aveyard R, Lidbetter JR, Wilson PG (2012) Investigating the host-range of the rust fungus Puccinia psidii sensu lato across tribes of the family Myrtaceae present in Australia. PLoS One 7:e35434. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035434
Myburg AA, Grattapaglia D, Tuskan GA, Hellsten U, Hayes RD, Grimwood J, Jenkins J, Lindquist E, Tice H, Bauer D, Goodstein DM, Dubchak I, Poliakov A, Mizrachi E, Kullan ARK, Hussey SG, Pinard D, van der Merwe K, Singh P, van Jaarsveld I, Silva-Junior OB, Togawa RC, Pappas MR, Faria DA, Sansaloni CP, Petroli CD, Yang X, Ranjan P, Tschaplinski TJ, Ye CY, Li T, Sterck L, Vanneste K, Murat F, Soler M, Clemente HS, Saidi N, Cassan-Wang H, Dunand C, Hefer CA, Bornberg-Bauer E, Kersting AR, Vining K, Amarasinghe V, Ranik M, Naithani S, Elser J, Boyd AE, Liston A, Spatafora JW, Dharmwardhana P, Raja R, Sullivan C, Romanel E, Alves-Ferreira M, Külheim C, Foley W, Carocha V, Paiva J, Kudrna D, Brommonschenkel SH, Pasquali G, Byrne M, Rigault P, Tibbits J, Spokevicius A, Jones RC, Steane DA, Vaillancourt RE, Potts BM, Joubert F, Barry K, Pappas GJ, Strauss SH, Jaiswal P, Grima-Pettenati J, Salse J, Van de Peer Y, Rokhsar DS, Schmutz J (2014) The genome of Eucalyptus grandis. Nature 510:356–362. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13308
Narouei-Khandan HA, Worner SP, Viljanen SLH, van Bruggen AHC, Jones EE (2020) Projecting the suitability of global and local habitats for myrtle rust (Austropuccinia psidii) using model consensus. Plant Pathol 69:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.13111
Neyland M, Hickey J, Beadle C, Bauhus J, Davidson N, Edwards L (2009) An examination of stocking and early growth in the Warra silvicultural systems trial confirms the importance of a burnt seedbed for vigorous regeneration in Eucalyptus obliqua forest. For Ecol Manag 258:481–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2008.10.039
Nicolle D (2006) Eucalypts of Victoria and Tasmania. Bloomings Books, Melbourne
Nicolle D (2019) Classification of the eucalypts (Angophora, Corymbia and Eucalyptus) version 4. http://www.dn.com.au/Classification-Of-The-Eucalypts.pdf. Accessed 20 November 2019
Pegg GS, Giblin FR, McTaggart AR, Guymer GP, Taylor H, Ireland KB, Shivas RG, Perry S (2014) Puccinia psidii in Queensland, Australia: disease symptoms, distribution and impact. Plant Pathol 63:1005–1021. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12173
Pegg G, Taylor T, Entwistle P, Guymer G, Giblin F, Carnegie A (2017) Impact of Austropuccinia psidii (myrtle rust) on Myrtaceae-rich wet sclerophyll forests in south east Queensland. PLoS One 12:e0188058. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188058
Potts BM, Hamilton M, Pilbeam DJ (2014) Mejoramiento genético de eucaliptos de zonas templadas en Australia (Genetic improvement of temperate eucalypts in Australia, translated into Spanish by editors http://bosques.ciren.cl/handle/123456789/21039, original english version https://ecite.utas.edu.au/98313). In: Ipinza R, Barros S, Gutiérrez B, Borralho N (eds) Mejoramiento genético de eucaliptos de en Chile. INFOR Instituto Forestal, Chile, pp 413–445
Potts BM, Sandhu KS, Wardlaw T, Freeman J, Li H, Tilyard P, Park RF (2016) Evolutionary history shapes the susceptibility of an island tree flora to an exotic pathogen. For Ecol Manag 368:183–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.02.027
Resende RT, Resende MDV, Silva FF, Azevedo CF, Takahashi EK, Silva-Junior OB, Grattapaglia D (2017) Regional heritability mapping and genome-wide association identify loci for complex growth, wood and disease resistance traits in Eucalyptus. New Phytol 213:1287–1300. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14266
Rosado TB, Tomaz RS, Ribeiro Junior MF, Rosado AM, Guimarães LMS, de Araújo EF, Alfenas AC, Cruz CD (2010) Detection of QTL associated with rust resistance using IBD-based methodologies in exogamic Eucalyptus spp. populations. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 10:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-70332010000400006
Rosado CCG, Guimarães LMS, Faria DA, de Resende MDV, Cruz CD, Grattapaglia D, Alfenas AC (2016) QTL mapping for resistance to Ceratocystis wilt in Eucalyptus. Tree Genet Genomes 12:72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-1029-4
Roux J, Granados GM, Shuey L, Barnes I, Wingfield MJ, McTaggart AR (2016) A unique genotype of the rust pathogen, Puccinia psidii, on Myrtaceae in South Africa. Australas Plant Pathol 45:645–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-016-0447-y
Sandhu KS, Park RF (2013) Genetic basis of pathogenicity in Uredo rangelii, National Myrtle Rust Transition to Management (T2M) Program Final Report. The University of Sydney, Cobbitty, New South Wales
Sandhu KS, Karaoglu H, Zhang P, Park RF (2016) Simple sequence repeat markers support the presence of a single genotype of Puccinia psidii in Australia. Plant Pathol 65:1084–1094. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12501
Santos MR, Guimarães LMS, de Resende MDV, Rosse LN, Zamprogno KC, Alfenas AC (2014) Resistance of Eucalyptus pellita to rust (Puccinia psidii). Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 14:244–250. https://doi.org/10.1590/1984-70332014v14n4a38
Santos IB, Lopes MS, Bini AP, Augusto B, Tschoeke P, Verssani BAW, Figueredo EF, Cataldi TR, Marques JPR, Silva LD, Labate CA, Quecine MC (2019) The Eucalyptus cuticular waxes contribute in preformed defense against Austropuccinia psidii. Front Plant Sci 9:1978. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01978
Santos SA, Vidigal PMP, Guimarães LMS, Mafia RG, Templeton MD, Alfenas AC (2020) Transcriptome analysis of Eucalyptus grandis genotypes reveals constitutive overexpression of genes related to rust (Austropuccinia psidii) resistance. Plant Mol Biol 104:339–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-020-01030-x
Simpson JA, Thomas K, Grgurinovic CA (2006) Uredinales species pathogenic on species of Myrtaceae. Australas Plant Pathol 35:549–562. https://doi.org/10.1071/AP06057
Soewarto J, Carriconde F, Hugot N, Bocs S, Hamelin C, Maggia L (2018) Impact of Austropuccinia psidii in New Caledonia, a biodiversity hotspot. For Pathol 48:e12402. https://doi.org/10.1111/efp.12402
Stahl EA, Dwyer G, Mauricio R, Kreitman M, Bergelson J (1999) Dynamics of disease resistance polymorphism at the Rpm1 locus of Arabidopsis. Nature 400:667–671. https://doi.org/10.1038/23260
Stewart JE, Ross-Davis AL, Graça RN, Alfenas AC, Peever TL, Hanna JW, Uchida JY, Hauff RD, Kadooka CY, Kim MS, Cannon PG, Namba S, Simeto S, Pérez CA, Rayamajhi MB, Lodge DJ, Arguedas M, Medel-Ortiz R, López-Ramirez MA, Tennant P, Glen M, Machado PS, McTaggart AR, Carnegie AJ, Klopfenstein NB (2018) Genetic diversity of the myrtle rust pathogen (Austropuccinia psidii) in the Americas and Hawaii: global implications for invasive threat assessments. For Pathol 48:e12378. https://doi.org/10.1111/efp.12378
Szatmári Á, Zvara Á, Móricz ÁM, Besenyei E, Szabó E, Ott PG, Puskás LG, Bozsó Z (2014) Pattern triggered immunity (PTI) in tobacco: isolation of activated genes suggests role of the phenylpropanoid pathway in inhibition of bacterial pathogens. PLoS One 9:e102869. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0102869
Tang Y, Liu X, Wang J, Li M, Wang Q, Tian F, Su Z, Pan Y, Liu D, Lipka AE, Buckler ES, Zhang Z (2016) GAPIT version 2: an enhanced integrated tool for genomic association and prediction. Plant Genome 9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2015.11.0120
Thornhill AH, Ho SYW, Külheim C, Crisp MD (2015) Interpreting the modern distribution of Myrtaceae using a dated molecular phylogeny. Mol Phylogenet Evol 93:29–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2015.07.007
Thumma B, Pegg G, Warburton P, Brawner J, Macdonell P, Yang X, Southerton S (2013) Molecular tagging of rust resistance genes in eucalypts, Final Report PHA_6.2. Plant Health Australia Limited, Canberra
Tibbits JFG, McManus LJ, Spokevicius AV, Bossinger G (2006) A rapid method for tissue collection and high-throughput isolation of genomic DNA from mature trees. Plant Mol Biol Report 24:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02914048
Tobias PA, Guest DI, Külheim C, Hsieh JF, Park RF (2016) A curious case of resistance to a new encounter pathogen: myrtle rust in Australia. Mol Plant Pathol 17:783–788. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12331
Wilkinson GR (2008) Population differentiation within Eucalyptus obliqua: implications for regeneration success and genetic conservation in production forests. Aust For 71:4–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/00049158.2008.10676266
Williams J, Woinarski J (1997) Overview and outlook. In: Williams J, Woinarski J (eds) Eucalypt ecology: individuals to ecosystems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 402–410
Winter G (1884) Repertorium. Rabenhorstii fungi europaei et extraeuropaei exsiccati cura Dr. G. Winter, Centuria XXXI et XXXII. Hedwigia 23:164–172
Winzer LF, Berthon KA, Carnegie AJ, Pegg GS, Leishman MR (2019) Austropuccinia psidii on the move: survey based insights to its geographical distribution, host species, impacts and management in Australia. Biol Invasions 21:1215–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-018-1891-0
Xavier AA, Sanfuentes EV, Junghans DT, Alfenas AC (2007) Resistance of Eucalyptus globulus and E. nitens to rust. Rev Árvore 31:731–735. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-67622007000400018
Yong WTL, Ades PK, Bossinger G, Runa FA, Sandhu KS, Potts BM, Tibbits JFG (2019) Geographical patterns of variation in susceptibility of Eucalyptus globulus and Eucalyptus obliqua to myrtle rust. Tree Genet Genomes 15:31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-019-1338-5
Acknowledgements
WTLY received a scholarship from the Malaysian government via the Academic Training Scheme of Public Higher Education Institutions (Skim Latihan Akademik Institut Pengajian Tinggi Awam, SLAI). The authors would like to thank Alice Gower, Hossein Valipour Kahrood and Agnieszka Wujeska-Klause for their excellent technical support and Robert Park for having made available the specialized rust glasshouse facilities at the University of Sydney.
Code availability
All code for data analysis associated with this study is available in its electronic supplementary material.
Funding
This project was supported by Australian Research Council ARC-Linkage Project LP13010045 and associated partners.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WTLY, PKA, GB, and JFGT conceived this research and designed experiments; WTLY, PKA, BMP, and JFGT participated in the design and interpretation of the data; WTLY, FAR, and KSS performed experiments and analysis; WTLY wrote the first draft of the manuscript and all authors participated in the revisions of it. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by C. Kulheim
Data archiving statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its electronic supplementary material.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key message
This is the first report of GWAS for myrtle rust resistance of a subgenus Eucalyptus species and the results highlight the potential of marker-based resistance breeding across Eucalyptus subgenera.
Supplementary Information
ESM S1
Phenotype data (TXT 73 kb)
ESM A
(XLSX 45 kb)
ESM S2
Genotype data (TXT 73267 kb)
ESM B
(TXT 128135 kb)
ESM C
(TXT 149839 kb)
ESM D
(TXT 70836 kb)
ESM E
(TXT 148796 kb)
ESM F
(TXT 87386 kb)
ESM G
(TXT 95853 kb)
ESM H
(TXT 144191 kb)
ESM I
(TXT 62821 kb)
ESM J
(TXT 62871 kb)
ESM K
(TXT 77811 kb)
ESM S3
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (TXT 70712 kb)
ESM L
(TXT 100749 kb)
ESM M
(TXT 86457 kb)
ESM N
(TXT 64969 kb)
ESM O
(TXT 81454 kb)
ESM P
(TXT 101193 kb)
ESM Q
(TXT 69745 kb)
ESM R
(TXT 112169 kb)
ESM S
(TXT 65022 kb)
ESM T
(TXT 68813 kb)
ESM U
(TXT 80021 kb)
ESM S4
R code for data analysis (R 2 kb)
ESM V
(R 5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yong, W.T.L., Ades, P.K., Runa, F.A. et al. Genome-wide association study of myrtle rust (Austropuccinia psidii) resistance in Eucalyptus obliqua (subgenus Eucalyptus). Tree Genetics & Genomes 17, 31 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-021-01511-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-021-01511-0