Abstract
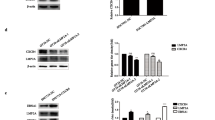
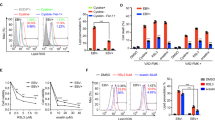
This study aimed to investigate the association of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) with nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1) and the biological function of NRF1 in EBV-associated gastric cancer (EBVaGC). Western blot and qRT-PCR were used to assess the effect of latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) on NRF1 expression after transfection with LMP2A plasmid or siLMP2A. The effects of NRF1 on the migration and apoptosis ability of GC cells were investigated by transwell assay and flow cytometry apoptosis analysis in vitro, respectively. In addition, we determined the regulatory role of NRF1 in EBV latent infection by western blot and droplet digital PCR (ddPCR). LMP2A upregulated NRF1 expression by activating the NF-κB pathway. Moreover, NRF1 upregulated the expression of N-Cadherin and ZEB1 to promote cell migration. NRF1 promoted the expression of Bcl-2 to increase the anti-apoptotic ability of cells. In addition, NRF1 maintained latent infection of EBV by promoting the expression of the latent protein Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) and inhibiting the expression of the lytic proteins. Our data indicated the role of NRF1 in EBVaGC progression and the maintenance of EBV latent infection. This provided a new theoretical basis for further NRF1-based anti-cancer therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Cui X, Snapper CM (2021) Epstein barr virus: development of vaccines and immune cell therapy for EBV-associated diseases. Front Immunol 12:734471. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.734471
Milano AF (2019) 20-Year comparative survival and mortality of cancer of the stomach by age, sex, race, stage, grade, cohort entry time-period, disease duration & selected ICD-O-3 oncologic phenotypes: a systematic review of 157,258 cases for diagnosis years 1973–2014: (SEER*Stat 8.3.4). J Insur Med 48(1):5–23. https://doi.org/10.17849/insm-48-1-1-19.1
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries [published correction appears in CA Cancer J Clin. 2020 Jul;70(4):313]. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Sun K, Jia K, Lv H et al (2020) EBV-positive gastric cancer: current knowledge and future perspectives. Front Oncol 10:583463. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.583463
Yang J, Liu Z, Zeng B, Hu G, Gan R (2020) Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer: a distinct subtype. Cancer Lett 495:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.09.019
Strong MJ, Xu G, Coco J et al (2013) Differences in gastric carcinoma microenvironment stratify according to EBV infection intensity: implications for possible immune adjuvant therapy. PLoS Pathog 9(5):e1003341. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003341
Ashrafizadeh M, Najafi M, Ang HL et al (2020) PTEN, a barrier for proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells: from molecular pathways to targeting and regulation. Biomedicines 8(8):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8080264
Hino R, Uozaki H, Murakami N et al (2009) Activation of DNA methyltransferase 1 by EBV latent membrane protein 2A leads to promoter hypermethylation of PTEN gene in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res 69(7):2766–2774. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3070
Shaw LM, Rabinovitz I, Wang HH, Toker A, Mercurio AM (1997) Activation of phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase by the alpha6beta4 integrin promotes carcinoma invasion. Cell 91(7):949–960. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80486-9
Portis T, Longnecker R (2004) Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) LMP2A mediates B-lymphocyte survival through constitutive activation of the Ras/PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncogene 23(53):8619–8628. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207905
Mancao C, Hammerschmidt W (2007) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A is a B-cell receptor mimic and essential for B-cell survival. Blood 110(10):3715–3721. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-05-090142
Yuan J, Zhang F, Niu R (2015) Multiple regulation pathways and pivotal biological functions of STAT3 in cancer. Sci Rep 5:17663. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17663
Pal AD, Basak NP, Banerjee AS, Banerjee S (2014) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-2A alters mitochondrial dynamics promoting cellular migration mediated by Notch signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis 35(7):1592–1601. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgu069
Fukuda M, Longnecker R (2007) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A mediates transformation through constitutive activation of the Ras/PI3-K/Akt Pathway. J Virol 81(17):9299–9306. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00537-07
Scarpulla RC (2008) Transcriptional paradigms in mammalian mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Physiol Rev 88(2):611–638. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00025.2007
Satoh J, Kawana N, Yamamoto Y (2013) Pathway analysis of ChIP-Seq-based NRF1 target genes suggests a logical hypothesis of their involvement in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Gene Regul Syst Bio 7:139–152. https://doi.org/10.4137/GRSB.S13204
Tokusumi Y, Zhou S, Takada S (2004) Nuclear respiratory factor 1 plays an essential role in transcriptional initiation from the hepatitis B virus x gene promoter. J Virol 78(20):10856–10864. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.78.20.10856-10864.2004
Wu CH, Hsieh PF, Lee YH et al (2022) Nuclear respiratory factor 1 overexpression inhibits proliferation and migration of PC3 prostate cancer cells. Cancer Genom Proteom 19(5):614–623. https://doi.org/10.21873/cgp.20346
Gao W, Wu M, Wang N et al (2018) Increased expression of mitochondrial transcription factor A and nuclear respiratory factor-1 predicts a poor clinical outcome of breast cancer. Oncol Lett 15(2):1449–1458. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.7487
Miller CL, Lee JH, Kieff E, Burkhardt AL, Bolen JB, Longnecker R (1994) Epstein-Barr virus protein LMP2A regulates reactivation from latency by negatively regulating tyrosine kinases involved in sIg-mediated signal transduction. Infect Agents Dis 3(2–3):128–136
Fukayama M, Hino R, Uozaki H (2008) Epstein-Barr virus and gastric carcinoma: virus-host interactions leading to carcinoma. Cancer Sci 99(9):1726–1733. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00888.x
Morrison JA, Klingelhutz AJ, Raab-Traub N (2003) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A activates beta-catenin signaling in epithelial cells. J Virol 77(22):12276–12284. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.77.22.12276-12284.2003
Miranda S, Foncea R, Guerrero J, Leighton F (1999) Oxidative stress and upregulation of mitochondrial biogenesis genes in mitochondrial DNA-depleted HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 258(1):44–49. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1999.0580
Bhawe K, Roy D (2018) Interplay between NRF1, E2F4 and MYC transcription factors regulating common target genes contributes to cancer development and progression. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 41(5):465–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-018-0395-3
Cam H, Balciunaite E, Blais A et al (2004) A common set of gene regulatory networks links metabolism and growth inhibition. Mol Cell 16(3):399–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2004.09.037
Liu W, Beck BH, Vaidya KS et al (2014) Metastasis suppressor KISS1 seems to reverse the Warburg effect by enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis. Cancer Res 74(3):954–963. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1183
Okoh VO, Garba NA, Penney RB et al (2015) Redox signalling to nuclear regulatory proteins by reactive oxygen species contributes to oestrogen-induced growth of breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 112(10):1687–1702. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.586
Das JK, Felty Q, Poppiti R, Jackson RM, Roy D (2018) Nuclear respiratory factor 1 acting as an oncoprotein drives estrogen-induced breast carcinogenesis. Cells 7(12):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120234
Wang W, Zhang Y, Liu W et al (2020) CXCR4 induces cell autophagy and maintains EBV latent infection in EBVaGC. Theranostics 10(25):11549–11561. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.44251
Suliman HB, Sweeney TE, Withers CM, Piantadosi CA (2010) Co-regulation of nuclear respiratory factor-1 by NFkappaB and CREB links LPS-induced inflammation to mitochondrial biogenesis. J Cell Sci 123(Pt 15):2565–2575. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.064089
Zhang Y, Liu W, Zhang W et al (2019) Constitutive activation of the canonical NF-κB signaling pathway in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma. Virology 532:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2019.03.019
Incrocci R, McAloon J, Montesano M et al (2019) Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A utilizes Syk and PI3K to activate NF-κB in B-cell lymphomas to increase MIP-1α production. J Med Virol 91(5):845–855. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25381
Das JK, Deoraj A, Roy D, Felty Q (2022) Brain infiltration of breast cancer stem cells is facilitated by paracrine signaling by inhibitor of differentiation 3 to nuclear respiratory factor 1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 148(10):2881–2891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04026-w
Lin CS, Lee HT, Lee SY et al (2012) High mitochondrial DNA copy number and bioenergetic function are associated with tumor invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Int J Mol Sci 13(9):11228–11246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911228
de Martin R, Schmid JA, Hofer-Warbinek R (1999) The NF-kappaB/Rel family of transcription factors in oncogenic transformation and apoptosis. Mutat Res 437(3):231–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1383-5742(99)00089-7
Li H, Niu N, Yang J et al (2021) Nuclear respiratory factor 1 protects H9C2 cells against hypoxia-induced apoptosis via the death receptor pathway and mitochondrial pathway. Cell Biol Int 45(8):1784–1796. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11619
Niu N, Li Z, Zhu M et al (2019) Effects of nuclear respiratory factor-1 on apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction induced by cobalt chloride in H9C2 cells. Mol Med Rep 19(3):2153–2163. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.9839
Brown HJ, Song MJ, Deng H, Wu TT, Cheng G, Sun R (2003) NF-kappaB inhibits gammaherpesvirus lytic replication. J Virol 77(15):8532–8540. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.77.15.8532-8540.2003
Murata T, Sugimoto A, Inagaki T et al (2021) Molecular basis of Epstein-Barr virus latency establishment and lytic reactivation. Viruses 13(12):2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122344
Zhao J, Jin H, Cheung KF et al (2012) Zinc finger E-box binding factor 1 plays a central role in regulating Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent-lytic switch and acts as a therapeutic target in EBV-associated gastric cancer. Cancer 118(4):924–936. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.26184
Wilson JB, Manet E, Gruffat H, Busson P, Blondel M, Fahraeus R (2018) EBNA1: oncogenic activity, immune evasion and biochemical functions provide targets for novel therapeutic strategies against Epstein-Barr virus—associated cancers. Cancers (Basel) 10(4):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10040109
Avolio-Hunter TM, Frappier L (2003) EBNA1 efficiently assembles on chromatin containing the Epstein-Barr virus latent origin of replication. Virology 315(2):398–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00561-0
Solecki D, Bernhardt G, Lipp M, Wimmer E (2000) Identification of a nuclear respiratory factor-1 binding site within the core promoter of the human polio virus receptor/CD155 gene. J Biol Chem 275(17):12453–12462. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.17.12453
Schaefer BC, Strominger JL, Speck SH (1995) Redefining the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen EBNA-1 gene promoter and transcription initiation site in group I Burkitt lymphoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(23):10565–10569. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.23.10565
Nonkwelo C, Skinner J, Bell A, Rickinson A, Sample J (1996) Transcription start sites downstream of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) Fp promoter in early-passage Burkitt lymphoma cells define a fourth promoter for expression of the EBV EBNA-1 protein. J Virol 70(1):623–627. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.70.1.623-627.1996
Verhoeven RJA, Tong S, Zong J et al (2018) NF-κB signaling regulates Epstein-Barr virus BamHI-Q-driven EBNA1 expression. Cancers (Basel) 10(4):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10040119
Wang FW, Wu XR, Liu WJ et al (2011) Heat shock factor 1 upregulates transcription of Epstein-Barr Virus nuclear antigen 1 by binding to a heat shock element within the BamHI-Q promoter [published correction appears in Virology. 2021 Sep;561:125]. Virology 421(2):184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2011.10.001
Acknowledgements
We thank everyone who helped us with our experiment.
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province [ZR2020MH302; ZR2020MC020].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL, YZ, BL, WL, MZ, DS: designed research. YL, YZ: analyzed data. YL: performed research. YL, YZ: wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Additional information
Edited by Hartmut Hengel.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Y., Liu, W., Zhao, M. et al. Nuclear respiratory factor 1 promotes the progression of EBV-associated gastric cancer and maintains EBV latent infection. Virus Genes 59, 204–214 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-023-01970-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-023-01970-8