Abstract
Purpose
Very few studies have sought prognostic factors after adrenalectomy for metastasis. The aim of this study was to assess prognostic factors for oncological outcomes after adrenalectomy for adrenal metastasis.
Methods
All adrenalectomies for metastases performed in seven centers between 2006 and 2016 were included in a retrospective study. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) were estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method. Prognostic factors for CSS and RFS were sought by Cox regression analyses.
Results
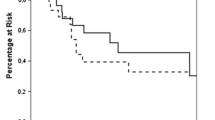
106 patients were included. The primary tumors were mostly renal (47.7%) and pulmonary (32.3%). RFS and CSS estimated rates at 5 years were 20.7% and 63.7%, respectively. In univariate analysis, tumor size (HR 3.83; p = 0.04) and the metastasis timing (synchronous vs. metachronous; HR 0.47; p = 0.02) were associated with RFS. In multivariate analysis, tumor size (HR 8.28; p = 0.01) and metastasis timing (HR 18.60; p = 0.002) were significant factors for RFS. In univariate analysis, the renal origin of the primary tumor (HR 0.1; p < 0.001) and the disease-free interval (DFI; HR 0.12; p = 0.02) were associated with better CSS, positive surgical margins with poorer CSS (HR 3.4; p = 0.01). In multivariate analysis, the renal origin of the primary tumor vs. pulmonary (HR 0.13; p = 0.03) and vs. other origins (HR 0.10; p = 00.4) and the DFI (HR 0.01; p = 0.009) were prognostic factors for CSS.
Conclusion
In this study, tumor size and synchronous occurrence of the adrenal metastasis were associated with poorer RFS. Renal origin of the primary tumor and longer DFI were associated with better CSS. These prognostic factors might help for treatment decision in the management of adrenal metastasis.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LA:
-
Laparoscopic adrenalectomy
- CT scan:
-
Computed tomography
- CSS:
-
Cancer-specific survival
- RFS:
-
Recurrence-free survival
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- DFI:
-
Disease-free interval
References
Bullock WK, Hirst AE (1953) Metastatic carcinoma of the adrenal. Am J Med Sci 226(5):521–524
Fassnacht M, Arlt W, Bancos I, Dralle H, Newell-Price J, Sahdev A et al (2016) Management of adrenal incidentalomas: European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline in collaboration with the European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors. Eur J Endocrinol 175(2):G1–G34
Gunjur A, Duong C, Ball D, Siva S (2014) Surgical and ablative therapies for the management of adrenal ‘oligometastases’—a systematic review. Cancer Treat Rev 40(7):838–846
Sancho JJ, Triponez F, Montet X, Sitges-Serra A (2012) Surgical management of adrenal metastases. Langenbecks Arch Surg 397(2):179–194
Romero Arenas MA, Sui D, Grubbs EG, Lee JE, Perrier ND (2014) Adrenal metastectomy is safe in selected patients. World J Surg 38(6):1336–1342
Solaini L, Ministrini S, Tomasoni M, Merigo G, Gaverini G, Bertoloni GP et al (2015) Adrenalectomy for metastasis: long-term results and predictors of survival. Endocrine 50(1):187–192
Smith CD, Weber CJ, Amerson JR (1999) Laparoscopic adrenalectomy: new gold standard. World J Surg 23(4):389–396
Gryn A, Peyronnet B, Manunta A, Beauval J-B, Bounasr E, Nouhaud F-X et al (2015) Patient selection for laparoscopic excision of adrenal metastases: a multicenter cohort study. Int J Surg 24:75–80
Sebag F, Calzolari F, Harding J, Sierra M, Palazzo FF, Henry JF (2006) Isolated adrenal metastasis: the role of laparoscopic surgery. World J Surg 30(5):888–892
Crenn G, Delaunay B, Salloum A, Vezzosi D, Bellec L, Thoulouzan M et al (2011) Carcinological results of laparoscopic adrenalectomy for adrenal metastasis. Progres En Urol J Assoc Francaise Urol Soc Francaise Urol 21(9):607–614
Muth A, Persson F, Jansson S, Johanson V, Ahlman H, Wängberg B (2010) Prognostic factors for survival after surgery for adrenal metastasis. Eur J Surg Oncol 36(7):699–704
Cho JW, Lee Y, Sung T-Y, Yoon JH, Chung K-W, Hong SJ (2018) Factors related to improved clinical outcomes associated with adrenalectomy for metachronous adrenal metastases from solid primary carcinomas. Surg Oncol 27(1):18–22
Conzo G, Tartaglia E, Gambardella C, Esposito D, Sciascia V, Mauriello C et al (2016) Minimally invasive approach for adrenal lesions: systematic review of laparoscopic versus retroperitoneoscopic adrenalectomy and assessment of risk factors for complications. Int J Surg 28:S118–S123
Di Buono G, Buscemi S, Lo Monte AI, Geraci G, Sorce V, Citarrella R et al (2019) Laparoscopic adrenalectomy: preoperative data, surgical technique and clinical outcomes. BMC Surg. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-018-0456-6
Goto T, Inoue T, Kobayashi T, Yamasaki T, Ishitoya S, Segawa T et al (2020) Feasibility of laparoscopic adrenalectomy for metastatic adrenal tumors in selected patients: a retrospective multicenter study of Japanese populations. Int J Clin Oncol 25:126–134
Moreno P, de la Quintana Basarrate A, Musholt TJ, Paunovic I, Puccini M, Vidal O et al (2013) Adrenalectomy for solid tumor metastases: results of a multicenter European study. Surgery 154(6):1215–1222 (discussion 1222–1223)
Vazquez BJ, Richards ML, Lohse CM, Thompson GB, Farley DR, Grant CS et al (2012) Adrenalectomy improves outcomes of selected patients with metastatic carcinoma. World J Surg 36(6):1400–1405
Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP (2014) Colorectal cancer. Lancet 383(9927):1490–1502
Vartolomei MD, Matei DV, Renne G, Tringali VM, Crisan N, Musi G et al (2019) Long-term oncologic and functional outcomes after robot-assisted partial nephrectomy in elderly patients. Minerva Urol Nefrol. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0393-2249.18.03006-0
Woodard GA, Jones KD, Jablons DM (2016) Lung cancer staging and prognosis. In: Reckamp KL (ed) Lung cancer [Internet]. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 47–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40389-2_3
Favini F, Sultan I, Meazza C, Casanova M, Ferrari A (2009) Prognostic role of tumor size in childhood cancer. Future Oncol Lond Engl 5(10):1605–1613
Kozminski MA, Palapattu GS, Mehra R, Montgomery JS, Weizer AZ, Skolarus TA et al (2014) Understanding the relationship between tumor size, gland size, and disease aggressiveness in men with prostate cancer. Urology 84(2):373–378
Alimi Q, Peyronnet B, Sebe P, Cote J-F, Kammerer-Jacquet S-F, Khene Z-E et al (2018) Comparison of short-term functional, oncological, and perioperative outcomes between laparoscopic and robotic partial nephrectomy beyond the learning curve. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech 28(9):1047–1052
Larcher A, Muttin F, Peyronnet B, De Naeyer G, Khene Z-E, Dell’Oglio P et al (2019) The learning curve for robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: impact of surgical experience on perioperative outcomes. Eur Urol 75(2):253–256
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AG: project development, data collection, and manuscript writing. NS: project development, data collection, and data analysis. RB: project development and data collection. MT: project development and data collection. VV: data collection. SO: data collection. NB: data collection. BP: project development and data analysis. MR: data collection. AR: project development and data collection. MS: project development and data collection. GF: project development. KB: project development. FB: project development. PG: project development and data collection. VJ: project development and data collection. AM: project development and manuscript writing. FS: project development and data collection. EH: project development and data collection. F-XN: project development and data collection. BP: project development, data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Availability of data and material (data transparency)
Data are available at CHU de Rennes.
Ethical approval retrospective studies
The study received approval of the local committees.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goujon, A., Schoentgen, N., Betari, R. et al. Prognostic factors after adrenalectomy for adrenal metastasis. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 1869–1876 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02496-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02496-w