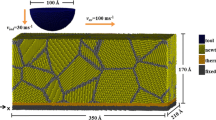
Abstract
In this work, molecular dynamics simulations are performed to investigate the nanoscale wear behavior of SiC particle-reinforced aluminum matrix composites (SiC/Al NCs) through nanoscratching using a spherical diamond indenter. A series of simulations are conducted to explore the effects of scratching depth, scratching speed, temperature, indenter size, and particle size during the nanoscratching process. We find the dislocation strengthening in the nanoscratching of SiC/Al NCs. It is also found that the frictional force and normal force increase with the increase of scratching depth, indenter size, and nanoparticle size. Moreover, the friction coefficient increases with the scratching depth. However, the friction coefficient declines with the increase of indenter size and nanoparticle size. Furthermore, for a larger scratching speed, the frictional force becomes smaller, while the normal force becomes larger, which is mainly determined by the competition between strain rate hardening and thermal softening. We also find that both the frictional force and normal force become smaller for a higher temperature resulting from thermal softening effect. The insights into the nanoscale wear properties of SiC/Al NCs lay a foundation for the wide applications of SiC/Al NCs.
Graphical Abstract























Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Sahin, Y., Kilicli, V.: Abrasive wear behaviour of SiCp/Al alloy composite in comparison with ausferritic ductile iron. Wear. 271, 2766–2774 (2011)
Ghias, A.S.A., VijayaRamnath, B.: Investigation of tensile property of aluminumSiC metal matrix composite. Appl. Mech. Mater. 3996, 252–256 (2015)
Hunt, M.: Automotive MMCs: better and cheapter. J. Mater. Eng. 106, 45–53 (1989)
Wu, S., He, F., Xie, G.X., Bian, Z.L., Luo, J.B., Wen, S.Z.: Black phosphorus: degradation favors lubrication. Nano Lett. 18, 5618–5627 (2018)
Wang, W., Xie, G.X., Luo, J.B.: Black phosphorus as a new lubricant. Friction 6, 116–142 (2018)
Xie, G.X., Luo, J.B., Guo, D., Liu, S.H.: Nanoconfined ionic liquids under electric fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 043112 (2010)
Cao, L., Wang, Y., Yao, C.K.: The wear properties of a SiC-whisker-reinforced aluminum composite. Wear 140, 273–277 (1990)
El-Kady, O., Fathy, A.: Effect of SiC particle size on the physical and mechanical properties of extruded Al matrix nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 54, 348–353 (2014)
Youssef, Y., El-Sayed, M.: Effect of reinforcement particle size and weight fraction on the mechanical properties of SiC particle reinforced Al metal matrix composites. Intl. Rev. Mech. Eng. 10, 261–265 (2016)
Penchal Reddy, M., Shakoor, R.A., Parande, G., Manakari, V., Ubaid, F., Mohamed, A.M.A., Gupta, M.: Enhanced performance of nano-sized SiC reinforced Al metal matrix nanocomposites synthesized through microwave sintering and hot extrusion techniques. Prog. Nat. Sci. 27, 606–614 (2017)
Rahman, M.H., Rashed, H.M.M.A.: Characterization of silicon carbide reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Proc. Eng. 90, 103–109 (2014)
Liu, Q.Y., Wang, F., Wu, W.W., et al.: Enhanced mechanical properties of SiC/Al composites at cryogenic temperatures. Ceram. Int. 45, 4099–4102 (2019)
Kong, X., Wang, B., Wang, M., et al.: Microscratch characteristic and deformation mechanism of SiC particle-reinforced composites at elevated temperatures. Adv. Compos. Lett. 29, 1–11 (2020)
Jiang, C.X., Ruan, S.L., Yang, C.Q.: Molecular dynamics simulations of mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline β-SiC/Al composites. Dongbei Daxue xuebao/Journal of Northeastern University. 34, 194–198 (2013)
Huo, S.Y., Xie, L.J., Xiang, J.F., Pang, S.Q., Hu, F., Umer, U.: Atomic-level study on mechanical properties and strengthening mechanisms of SiC/Al nano-composites. Appl. Phys. A 124, 209.1-209.12 (2018)
Mohammadi, S., Montazeri, A., Urbassek, H.M.: Geometrical aspects of nanofillers influence the tribological performance of Al-based nanocomposites. Wear 444–445, 203117 (2020)
Alhafez, I.A., Urbassek, H.M.: Influence of tip adhesion on nanoindentation and scratching. Modell. Simulat. Mater. Sci. Eng. 27, 065014 (2019)
Fang, Q.H., Wang, Q., Li, J., et al.: Mechanisms of subsurface damage and material removal during high speed grinding processes in Ni/Cu multilayers using a molecular dynamics study. RSC Adv. 7, 42047–42055 (2017)
Zhu, P.Z., Qiu, C., Fang, F.Z., Yuan, D.D., Shen, X.C.: Molecular dynamics simulations of nanometric cutting mechanisms of amorphous alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 317, 432–442 (2014)
Li, B.Z., Li, J.Y., Zhu, P.Z., Xu, J.H., Li, R., Yu, J.X.: Influence of crystal anisotropy on deformation behaviors in nanoscratching of AlN. Appl. Surf. Sci. 487, 1068–1076 (2019)
Zhu, P.Z., Fang, F.Z.: Molecular dynamics simulations of nanoindentation of monocrystalline germanium. Appl. Phys. A. 108, 415–421 (2012)
Zhu, P.Z., Hu, Y.Z., Ma, T.B., Wang, H.: Molecular dynamics study on friction due to ploughing and adhesion in nanometric scratching process. Tribol. Lett. 41, 41–46 (2011)
Xu, F.F., Fang, F.Z., Zhang, X.D.: Hard particle effect on surface generation in nano-cutting. Appl. Surf. Sci. 425, 1020–1027 (2017)
Lu, S., Li, Z., Zhang, J., et al.: Finite element investigation of the influence of SiC particle distribution on diamond cutting of SiCp/Al composites. Nanomanuf. Metrol. 3, 1–9 (2020)
Lu, S.J., Zhang, J.J., Li, Z.Q., et al.: Cutting path-dependent machinability of SiCp/Al composite under multi-step ultra-precision diamond cutting. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 34(4), 241–252 (2020)
Shao, J.C., Xiao, B.L., Wang, Q.Z., et al.: An enhanced FEM model for particle size dependent flow strengthening and interface damage in particle reinforced metal matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 71(1), 39–45 (2011)
Mendelev, M.I., Kramer, M.J., Becker, C.A., Asta, M.: Analysis of semi-empirical interatomic potentials appropriate for simulation of crystalline and liquid Al and Cu. Phil. Mag. 88, 1723–1750 (2008)
Tersoff, J.: Modeling solid-state chemistry: interatomic potentials for multicomponent systems. Phys. Rev. B. 39, 5566–5568 (1989)
Fang, T.H., Weng, C.I., Chang, J.G.: Molecular dynamics simulation of nano-lithography process using atomic force microscopy. Surf. Sci. 501, 138–147 (2002)
Peng, P., Liao, G.L., Shi, T.L., et al.: Molecular dynamic simulations of nanoindentation in aluminum thin film on silicon substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 6284–6290 (2010)
Liu, Y., Li, B.Z., Kong, L.F.: A molecular dynamics investigation into nanoscale scratching mechanism of polycrystalline silicon carbide. Comput. Mater. Sci. 148, 76–86 (2018)
Dandekar, C.R., Shin, Y.C.: Molecular dynamics based cohesive zone law for describing Al–SiC interface mechanics. Compos. Part A. 42, 355–363 (2011)
Plimpton, S.: Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 117, 1–19 (1995)
Stukowski, A.: Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO: the Open Visualization Tool. Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18, 15012 (2010)
Doan, D.Q., Fang, T.H., Tran, A.S., Chen, T.S.: Residual stress and elastic recovery of imprinted Cu-Zr metallic glass films using molecular dynamic simulation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 170, 109162 (2019)
Goel, S., Luo, X., Reuben, R.L.: Molecular dynamics simulation model for the quantitative assessment of tool wear during single point diamond turning of cubic silicon carbide. Comput. Mater. Sci. 51, 402–408 (2012)
Sharma, A., Datta, D., Balasubramaniam, R.: A molecular dynamics simulation of wear mechanism of diamond tool in nanoscale cutting of copper beryllium. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 102, 731–745 (2019)
Alexander, S., Vasily, V.B., Athanasios, A.: Automated identification and indexing of dislocations in crystal interfaces. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 20, 085007 (2012)
Porter, D.A., Easteling, K.E.: Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys. Chapman Hall, London (1981)
Walsh, P., Omeltchenko, A., Kalia, R.K., Nakano, A., Vashishta, P., Saini, S.: Nanoindentation of silicon nitrid: a multi-million atom molecular dynamics study. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 118–120 (2003)
Dai, H.F., Li, S.B., Chen, G.Y.: Molecular dynamics simulation of subsurface damage mechanism during nanoscratching of single crystal silicon. Proc. IMechE Part J. 233, 61–73 (2018)
Zhang, Z.B., Urbassek, H.M.: Dislocation-based strengthening mechanisms in metal-matrix nanocomposites: a molecular dynamics study of the influence of reinforcement shape in the Al-Si system. Comput. Mater. Sci. 45, 109–115 (2018)
Chen, S., Aitken, Z.H., Wu, Z., et al.: Hall-Petch and inverse Hall-Petch relations in high-entropy CoNiFeAlxCu1-x alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 773, 138873 (2019)
Patil, R.P., Doan, D., Aitken, Z.H., et al.: Hardening in Au-Ag nanoboxes from stacking fault-dislocation interactions. Nat. Commun. 11(1), 2923 (2020)
Li, J., Fang, Q.H., Liu, Y.W., et al.: Scratching of copper with rough surfaces conducted by diamond tip simulated using molecular dynamics. Intl. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 77, 1057–1070 (2015)
Chen, D.K., Costello, L.L., Geller, C.B., Zhu, T., McDowell, D.L.: Atomistic modeling of dislocation cross-slip in nickel using free-end nudged elastic band method. Acta Mater. 168, 436–447 (2019)
Zhu, P., Fang, F.: Study of the minimum depth of material removal in nanoscale mechanical machining of single crystalline copper. Comput. Mater. Sci. 118, 192–202 (2016)
Pei, Q.X., Lu, C., Lee, H.P.: Large scale molecular dynamics study of nanometric machining of copper. Comput. Mater. Sci. 41, 177–185 (2007)
Zhu, P.Z., Hu, Y.Z., Ma, T.B., Wang, H.: Study of AFM-based nanometric cutting process using molecular dynamics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 7160–7165 (2010)
Alhafez, I.A., Ruestes, I.A., Urbasse, H.M.: Size of the plastic zone produced by nanoscratching. Tribol. Lett. 66, 1–12 (2017)
Wang, J., Chen, S., Cui, K., et al.: Approach and coalescence of gold nanoparticles driven by surface thermodynamic fluctuations and atomic interaction forces. ACS Nano 10(2), 2893–2902 (2016)
Yaghoobi, M., Voyiadjis, G.Z.: The effects of temperature and strain rate in fcc and bcc metals during extreme deformation rates. Acta Mater. 151, 1–10 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The results described in this paper are obtained on the China National Grid (http://www.cngrid.org) / China Scientific Computing Grid (http://www.scgrid.cn)
Funding
This work is supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 3202024), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51405337 and 51875405), and Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (No. 15JCQNJC04800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, Z., Zhu, P. & Li, B. Study of Nanoscale Wear of SiC/Al Nanocomposites Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Tribol Lett 69, 38 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01414-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01414-0