Abstract
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a significant cause of death in the very elderly (≥ 75 years) population. Ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis (USCDT) emerges to improve thrombolysis safety and efficacy. However, outcomes in very elderly patients are unknown, as randomized controlled trials exclude this population. Recently, we demonstrated acute kidney injury (AKI) and ischemic hepatitis in an octogenarian intermediate-risk PE patient treated with USCDT. Considering the lack of evidence, we undertook a systematic review to evaluate the clinical outcomes in very elderly PE patients treated with USCDT. We searched for very elderly PE patients treated with USCDT from 2008 to 2019. Additionally, we conducted another systematic review without age restriction to update previous evidence and compare both populations. We also did an exploratory analysis to determine if thrombolysis was followed based on current guidelines or impending clinical deterioration factors. We identified 18 very elderly patients (age 79.2, 75–86), mostly female and with intermediate-risk PE. We found an intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), and a right pulmonary artery rupture. Additionally, two significant bleedings complicated with transient AKI, and one case of AKI and ischemic hepatic injury. The patients who survived all had clinical and echocardiographic in-hospital improvement. Despite low rt-PA doses, ICH and major bleeding remain as feared complications. Thrombolysis decision was driven by impending clinical deterioration factors instead of international guideline recommendations. Our data do not suggest prohibitive risk associated with USCDT in very elderly intermediate and high-risk PE patients. Despite long-term infusions and right ventricular dysfunction, AKI and ischemic hepatic injury were infrequent.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jerjes-Sánchez C, Fajardo P (2015) Patients for thrombolysis. Thrombolysis in pulmonary embolism. Springer, Cham, pp 107–130
Jerjes-Sanchez C, Rodriguez D, Navarrete A et al (2017) Inferior vena cava filters in pulmonary embolism: a historic controversy. Arch Cardiol Mex 87:155–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acmx.2017.01.007
Miano TA, Cuker A, Christie JD et al (2018) Comparative effectiveness of enoxaparin vs dalteparin for thromboprophylaxis after traumatic injury. Chest 153:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2017.08.008
Rodriguez D, Jerjes-Sanchez C, Fonseca S et al (2020) Thrombolysis in massive and submassive pulmonary embolism during pregnancy and the puerperium: a systematic review. J Thromb Thrombolysis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02122-7
Polo Friz H, Molteni M, Del Sorbo D et al (2015) Mortality at 30 and 90 days in elderly patients with pulmonary embolism: a retrospective cohort study. Intern Emerg Med 10:431–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-014-1179-z
Kucher N, Boekstegers P, Müller OJ et al (2014) Randomized, controlled trial of ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis for acute intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. Circulation 129:479–486. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005544
Piazza G, Hohlfelder B, Jaff MR et al (2015) A prospective, single-arm, multicenter trial of ultrasound-facilitated, catheter-directed, low-dose fibrinolysis for acute massive and submassive pulmonary embolism. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 8:1382–1392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2015.04.020
Tapson VF, Sterling K, Jones N et al (2018) A randomized trial of the optimum duration of acoustic pulse thrombolysis procedure in acute intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 11:1401–1410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2018.04.008
Shenoy P, Harugeri A (2015) Elderly patients’ participation in clinical trials. Perspect Clin Res 6:184. https://doi.org/10.4103/2229-3485.167099
Cesari M, Calvani R, Marzetti E (2017) Frailty in older persons. Clin Geriatr Med 33:293–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cger.2017.02.002
Capodanno D, Angiolillo DJ (2010) Antithrombotic therapy in the elderly. J Am Coll Cardiol 56:1683–1692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2010.04.063
Shah KJ, Scileppi RM, Franz RW (2011) Treatment of pulmonary embolism using ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis directly into pulmonary arteries. Vasc Endovasc Surg 45:541–548. https://doi.org/10.1177/1538574411407085
Paredes-Vázquez JG, Sanchez-Diaz C, Valdes F et al (2019) successful ultrasound assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis complicated with renal and hepatic failure in massive pulmonary embolism octogenarian patient. J Am Coll Cardiol 73:2176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0735-1097(19)32782-2
Avgerinos ED, Saadeddin Z, Abou Ali AN et al (2018) A meta-analysis of outcomes of catheter-directed thrombolysis for high- and intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. J Vasc Surg 6:530–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvsv.2018.03.010
Pei DT, Liu J, Yaqoob M et al (2019) Meta-analysis of catheter directed ultrasound-assisted thrombolysis in pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.07.040
Engelberger RP, Kucher N (2014) Ultrasound-assisted thrombolysis for acute pulmonary embolism: a systematic review. Eur Heart J 35:758–764. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehu029
Hayek G, McDaniel M, Liberman H et al (2016) Ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis in the treatment of high risk pulmonary embolism: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 68(18S):B311–B311
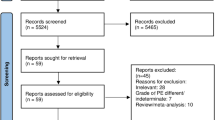
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Konstantinides SV, Meyer G, Becattini C et al (2019) 2019 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur Heart J 41(4):543–603. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz405
Greenhalgh T, Peacock R (2005) Effectiveness and efficiency of search methods in systematic reviews of complex evidence: audit of primary sources. BMJ 331:1064–1065. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38636.593461.68
Schulman S, Kearon C, The Subcommittee on Control of Anticoagulation of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (2005) Definition of major bleeding in clinical investigations of antihemostatic medicinal products in non-surgical patients: definitions of major bleeding in clinical studies. J Thromb Haemost 3:692–694. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01204.x
Jerjes-Sanchez C, Ramirez-Rivera A, Arriaga-Nava R et al (2001) High dose and short-term streptokinase infusion in patients with pulmonary embolism: prospective with seven-year follow-up trial. J Thromb Thrombolysis 12:237–247
Jerjes-Sánchez C, Villarreal-Umaña S, Ramírez-Rivera A et al (2009) Improving adjunctive treatment in pulmonary embolism and fibrinolytic therapy. The role of enoxaparin and weight-adjusted unfractionated heparin. J Thromb Thrombolysis 27:154–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-008-0192-3
Obi M, Packer CD (2019) Submassive pulmonary embolism: a re-evaluation of hemodynamic instability. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.4644
Zuin M, Rigatelli G, Zonzin P et al (2018) Short- and long-term prognostic role of diastolic blood pressure in intermediate-high risk patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Eur J Intern Med 55:e23–e24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2018.07.016
Kearon C, Akl EA, Ornelas J et al (2016) Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease. Chest 149:315–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2015.11.026
Jaff MR, McMurtry MS, Archer SL et al (2011) Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis, and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 123:1788–1830. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0b013e318214914f
Barco S, Vicaut E, Klok FA et al (2018) Improved identification of thrombolysis candidates amongst intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism patients: implications for future trials. Eur Respir J 51:1701775. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01775-2017
Kwak MK, Kim WY, Lee CW et al (2013) The impact of saddle embolism on the major adverse event rate of patients with non-high-risk pulmonary embolism. BJR 86:20130273. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20130273
Engelberger RP, Kucher N (2011) Catheter-based reperfusion treatment of pulmonary embolism. Circulation 124:2139–2144. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.023689
Porres-Aguilar M, Burgos JD, Munoz OC et al (2013) Successful pharmacomechanical intervention with ultrasonic-accelerated thrombolytic catheter for massive pulmonary embolism. Indian Heart J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ihj.2013.10.007
Salerno A, Latib A, Ballarotto C et al (2013) Trombolisi intra-arteriosa associata ad ultrasuoni nell’embolia polmonare submassiva: primo caso italiano. Giornale Italiano di Cardiologia doi. https://doi.org/10.1714/1257.13887
Jain SKA, Patel B, David W et al (2014) Unloading of right ventricle and clinical improvement after ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis in patients with submassive pulmonary embolism. Case Rep Med 2014:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/297951
Eryilmaz U, Tas Gulen S, Akgullu C et al (2015) Ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism. Anatol J Cardiol 15:512–513. https://doi.org/10.5152/akd.2015.6175
Schreinlechner M, Theurl M, Kirchmain R et al (2016) Anticoagulation with rivaroxaban after ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis in patients with intermediate high-risk pulmonary embolism: a case series. Interv Cardiol. https://doi.org/10.4172/Interventional-Cardiology.1000545
Yadlapati A, Sweis R, Schimmel D (2016) Ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis in patients with intracardiac thrombi: a case series. J Invasive Cardiol 28:30–33
Bethea BT, Elliot JW, Richardson JB, Ahmed MI (2017) Treatment of pulmonary embolism with argatroban and ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis with alteplase in a patient with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Am J Health Syst Pharm 74:1153–1157. https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp160368
Boshara A, Edla S, Neupane S et al (2017) Ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis in pulmonary embolism in transit. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 10:e135–e137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2017.05.024
Ganatra S, Majithia A, Yeh Y-TE, Levy MS (2017) Intracranial hemorrhage in a patient with sub-massive pulmonary embolism treated with EkoSonic endovascular system directed thrombolysis: ICH with EkoSonic system directed thrombolysis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 90:476–479. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccd.27045
Fernandez Romero G, Riyaz B, Gupta R et al (2019) Pulmonary artery rupture after ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 199:e30–e32. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201805-0947IM
Knox MF, Langholz DE, Berjaoui WK, Eberhart L (2019) Preservation of cardiopulmonary function in patients treated with ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis in the setting of submassive pulmonary embolism. J Vasc Interv Radiol 30:734–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2018.08.027
Taha A, Mohammedzein A, Carthel K, Brabham D (2019) Impella RP: a promising intervention for hemodynamic support in acute right ventricular failure caused by massive pulmonary embolism. J Am Coll Cardiol 73:2427. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0735-1097(19)33033-5
Rao G, Xu H, Wang JJ et al (2019) Ultrasound-assisted versus conventional catheter-directed thrombolysis for acute pulmonary embolism: a multicenter comparison of patient-centered outcomes. Vasc Med 24:241–247. https://doi.org/10.1177/1358863X19838334
Rothschild DP, Goldstein JA, Ciacci J, Bowers TR (2019) Ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis (USAT) versus standard catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT) for treatment of pulmonary embolism: a retrospective analysis. Vasc Med 24:234–240. https://doi.org/10.1177/1358863X19838350
Sharifi M, Awdisho A, Schroeder B et al (2019) Retrospective comparison of ultrasound facilitated catheter-directed thrombolysis and systemically administered half-dose thrombolysis in treatment of pulmonary embolism. Vasc Med 24:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1177/1358863X18824159
Visco E, Adamo M, Locantore E et al (2019) EkoSonic endovascular system for patients with acute pulmonary embolism and contraindication to systemic fibrinolysis. J Cardiovasc Med 20:131–136. https://doi.org/10.2459/JCM.0000000000000751
Kuo WT, Banerjee A, Kim PS et al (2015) Pulmonary embolism response to fragmentation, embolectomy, and catheter thrombolysis (PERFECT). Chest 148:667–673. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.15-0119
Ozcinar E, Cakici M, YAMAN ND et al (2017) Thrombus resolution and right ventricular functional recovery using ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis in acute massive and submassive pulmonary embolism. Int Angiol 36(5):428–437. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0392-9590.17.03775-0
Chamsuddin A, Nazzal L, Kang B et al (2008) Catheter-directed thrombolysis with the endowave system in the treatment of acute massive pulmonary embolism: a retrospective multicenter case series. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19:372–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2007.10.019
Lin PH, Annambhotla S, Bechara CF et al (2009) Comparison of percutaneous ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis versus catheter-directed thrombolysis in patients with acute massive pulmonary embolism. Vascular 17:S137–S147. https://doi.org/10.2310/6670.2009.00063
Engelhardt TC, Taylor AJ, Simprini LA, Kucher N (2011) Catheter-directed ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis for the treatment of acute pulmonary embolism. Thromb Res 128:149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2011.05.014
Kennedy RJ, Kenney HH, Dunfee BL (2013) Thrombus resolution and hemodynamic recovery using ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis in acute pulmonary embolism. J Vasc Interv Radiol 24:841–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2013.02.023
Quintana D, Salsamendi J, Fourzali R, Narayanan G (2014) Ultrasound-assisted thrombolysis in submassive and massive pulmonary embolism: assessment of lung obstruction before and after catheter-directed therapy. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37:420–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0696-x
Dumantepe M, Uyar I, Teymen B et al (2014) Improvements in pulmonary artery pressure and right ventricular function after ultrasound-accelerated catheter-directed thrombolysis for the treatment of pulmonary embolism: endovascular treatment of pulmonary embolism. J Card Surg 29:455–463. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocs.12354
Bagla S, Smirniotopoulos JB, van Breda A et al (2015) Ultrasound-accelerated catheter-directed thrombolysis for acute submassive pulmonary embolism. J Vasc Interv Radiol 26:1001–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2014.12.017
George B, Wallace EL, Charnigo R et al (2015) A retrospective analysis of catheter-based thrombolytic therapy for acute submassive and massive pulmonary embolism. Vasc Med 20:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1177/1358863X14568135
McCabe JM, Huang P-H, Riedl L et al (2015) Usefulness and safety of ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis for submassive pulmonary emboli. Am J Cardiol 115:821–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.12.050
Nykamp M, VandenHull A, Remund T et al (2015) Safety and efficacy of ultrasound-accelerated catheter-directed lytic therapy in acute pulmonary embolism with and without hemodynamic instability. J Vasc Surg 3:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvsv.2015.03.001
Liang NL, Chaer RA, Marone LK et al (2017) Midterm outcomes of catheter-directed interventions for the treatment of acute pulmonary embolism. Vascular 25:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1177/1708538116654638
Bloomer TL, El-Hayek GE, McDaniel MC et al (2017) Safety of catheter-directed thrombolysis for massive and submassive pulmonary embolism: results of a multicenter registry and meta-analysis: safety of catheter-directed thrombolysis. Cathet Cardiovasc Interv 89:754–760. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccd.26900
Doheny C, Gonzalez L, Duchman SM et al (2018) Echocardiographic assessment with right ventricular function improvement following ultrasound-accelerated catheter-directed thrombolytic therapy in submassive pulmonary embolism. Vascular 26:271–277. https://doi.org/10.1177/1708538117733645
Fuller TJ, Paprzycki CM, Zubair MH et al (2017) Initial experiences with endovascular management of submassive pulmonary embolism: is it safe? Ann Vasc Surg 38:158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2016.09.002
Graif A, Grilli CJ, Kimbiris G et al (2017) Comparison of ultrasound-accelerated versus pigtail catheter-directed thrombolysis for the treatment of acute massive and submassive pulmonary embolism. J Vasc Interv Radiol 28:1339–1347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2017.07.004
Lee KA, Cha A, Kumar MH et al (2017) Catheter-directed, ultrasound-assisted thrombolysis is a safe and effective treatment for pulmonary embolism, even in high-risk patients. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord 5:165–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvsv.2016.10.075
Edla S, Rosman H, Neupane S et al (2018) Early versus delayed use of ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis in patients with acute submassive pulmonary embolism. J Invasive Cardiol 30:157–162
Hennemeyer C, Khan A, McGregor H et al (2019) Outcomes of catheter-directed therapy plus anticoagulation versus anticoagulation alone for submassive and massive pulmonary embolism. Am J Med 132:240–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.10.015
Kaymaz C, Akbal OY, Hakgor A et al (2018) A five-year, single-centre experience on ultrasound-assisted, catheter-directed thrombolysis in patients with pulmonary embolism at high risk and intermediate to high risk. EuroIntervention 14:1136–1143. https://doi.org/10.4244/EIJ-D-18-00371
Mohan PP, Manov JJ, Contreras F et al (2018) Ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis for submassive pulmonary embolism. Vasc Endovascular Surg 52:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1177/1538574418757400
Schissler AJ, Gylnn RJ, Sobieszczyk PS, Waxman AB (2018) Ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis compared with anticoagulation alone for treatment of intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. Pulm Circ 8:204589401880026. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045894018800265
Valerio L, Klok FA, Barco S (2019) Immediate and late impact of reperfusion therapies in acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J Suppl 21:I1–I13. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/suz222
Chopard R, Ecarnot F, Meneveau N (2019) Catheter-directed therapy for acute pulmonary embolism: navigating gaps in the evidence. Eur Heart J Suppl 21:I23–I30. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/suz224
Chang C-H, Fu C-M, Fan P-C et al (2017) Acute kidney injury in patients with pulmonary embolism: a population-based cohort study. Medicine 96:e5822. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000005822
Aslan S, Meral M, Akgun M et al (2007) Liver dysfunction in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Hepatol Res 37:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1872-034X.2007.00014.x
de Winter MA, Vlachojannis GJ, Ruigrok D et al (2019) Rationale for catheter-based therapies in acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J Suppl 21:I16–I22. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/suz223
Mostafa A, Briasoulis A, Telila T et al (2016) Treatment of massive or submassive acute pulmonary embolism with catheter-directed thrombolysis. Am J Cardiol 117:1014–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.12.041
Tafur AJ, Shamoun FE, Patel SI et al (2017) Catheter-directed treatment of pulmonary embolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis of modern literature. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 23:821–829. https://doi.org/10.1177/1076029616661414
Ungvari Z, Tarantini S, Kiss T et al (2018) Endothelial dysfunction and angiogenesis impairment in the ageing vasculature. Nat Rev Cardiol 15:555–565. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-018-0030-z
Wayne NB, Davis GA, Macaulay TE et al (2020) Reduced dose thrombolysis with ultrasound-facilitated catheter-directed administration for acute pulmonary embolism reduces length of stay. J Thromb Thrombolysis 49:540–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-019-02009-2
Patel H, Shih JA, Gardner R et al (2019) Hemodynamic decompensation in normotensive patients admitted to the ICU with pulmonary embolism. J Crit Care 54:105–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2019.07.017
Keller K, Beule J, Balzer JO, Dippold W (2015) Blood pressure for outcome prediction and risk stratification in acute pulmonary embolism. Am J Emerg Med 33:1617–1621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2015.07.009
Quezada A, Jiménez D, Bikdeli B et al (2020) Systolic blood pressure and mortality in acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Int J Cardiol 302:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.11.102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclosure.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castillo-Perez, M., Jerjes-Sánchez, C., Rodríguez, D. et al. Clinical outcomes of very elderly patients treated with ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism: a systematic review. J Thromb Thrombolysis 52, 260–271 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-021-02409-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-021-02409-3