Abstract
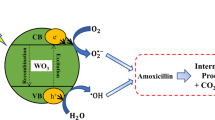
This research aims to investigate the simulation of a pilot-scale photocatalytic reactor based on cobalt-doped ZnO films, where the photocatalyst films were initially assessed on a lab scale for the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB) under visible light. ZnO and cobalt-doped ZnO catalyst films were firstly synthesized by means of the spray pyrolysis technique. The catalyst films were then characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electronic microscopy (SEM), and diffuse spectroscopy (EDS) (DRS). The lattice parameters of cobalt-doped ZnO films, as well as their bandgap values and structures, have been computed applying the density functional theory (DFT). Box-Behnken Design (BBD) was used to assess the effect of the main operating parameters (contact time, RhB concentration, and cobalt doping percentage) on the photocatalytic activity that achieved 93% using 10% of cobalt doping ZnO within 120 min. Aspen Plus was used to model and design the photocatalysis process at the pilot scale based on the lab-scale results. The findings of this study suggest that cobalt-doped ZnO films could be effectively used for the photodegradation of organic pollutants and offer potential perspectives on their large-scale application for the treatment of real liquid effluents using solar light.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Naciri Y, Hsini A, Bouziani A et al (2021) Photocatalytic oxidation of pollutants in gas-phase via Ag3PO4-based semiconductor photocatalysts: recent progress, new trends, and future perspectives. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2021.1877977
Brini L, Hsini A, Naciri Y et al (2021) Synthesis and characterization of arginine-doped heliotrope leaves with high clean-up capacity for crystal violet dye from aqueous media. Water Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.446
Dra A, Tanji K, Arrahli A et al (2020) Valorization of oued sebou natural sediments (Fez-Morocco Area) as adsorbent of methylene blue dye: kinetic and thermodynamic study. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2187129
Thiam A, Tanji K, Assila O et al (2020) Valorization of date pits as an effective biosorbent for Remazol brilliant blue adsorption from aqueous solution. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4173152
Dra A, Tanji K, Arrahli A, et al (2020) Erratum: Valorization of oued sebou natural sediments (Fez-Morocco Area) as adsorbent of methylene blue dye: kinetic and thermodynamic study [The Scientific World Journal (2020) 2020 (2187129), https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2187129]. Sci World J 4815767. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4815767
Zouheir M, Assila O, Tanji K et al (2021) Bandgap optimization of sol-gel-derived TiO2 and its effect on the photodegradation of formic acid. Nano Future. https://doi.org/10.1088/2399-1984/abfb7d
Wang NN, Hu Q, Hao LL, Zhao Q (2019) Degradation of acid organic 7 by modified coal fly ash-catalyzed Fenton-like process: kinetics and mechanism study. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1965-7
Saher R, Hanif MA, Mansha A et al (2021) Sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye by Ag/FeWO4/g-C3N4 composites. Int J Environ Sci Technol 18:927–938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02888-6
Hsini A, Benafqir M, Naciri Y et al (2021) Synthesis of an arginine-functionalized polyaniline@FeOOH composite with high removal performance of hexavalent chromium ions from water: adsorption behavior, regeneration and process capability studies. Colloids Surf A 617:126274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126274
Singh R (2021) Different anticipated criteria to achieve novel and efficient photocatalysis via green ZnO: scope and challenges. Springer, Berlin
Padmavathy N, Vijayaraghavan R (2008) Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles—an antimicrobial study. Sci Technol Adv Mater. https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/9/3/035004
Sharma SS, Palaty S, John AK (2021) Band gap modified zinc oxide nanoparticles: an efficient visible light active catalyst for wastewater treatment. Int J Environ Sci Technol 18:2619–2632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02976-7
Zouhier M, Tanji K, Navio JA et al (2020) Preparation of ZnFe2O4/ZnO composite: effect of operational parameters for photocatalytic degradation of dyes under UV and visible illumination. J Photochem Photobiol A 390:112305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112305
Tanji K, Navio JA, Chaqroune A et al (2020) Fast photodegradation of rhodamine B and caffeine using ZnO-hydroxyapatite composites under UV-light illumination. Catal Today. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.07.044
Tanji K, Navio JA, Naja J et al (2019) Extraordinary visible photocatalytic activity of a Co0.2Zn0.8O system studied in the Remazol BB oxidation. J Photochem Photobiol A 382:111877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.111877
Bairy R, Patil PS, Maidur SR et al (2019) The role of cobalt doping in tuning the band gap, surface morphology and third-order optical nonlinearities of ZnO nanostructures for NLO device applications. RSC Adv 9:22302–22312. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra03006a
Rezaei M, Nezamzadeh-Ejhieha A (2020) The ZnO-NiO nano-composite: a brief characterization, kinetic and thermodynamic study and study the Arrhenius model on the sulfasalazine photodegradation. Int J Hydrog Energy 45:24749–24764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.06.258
Chakma S, Moholkar VS (2015) Investigation in mechanistic issues of sonocatalysis and sonophotocatalysis using pure and doped photocatalysts. Ultrason Sonochem 22:287–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.06.008
Lu Y, Lin Y, Wang D et al (2011) A high performance cobalt-doped ZnO visible light photocatalyst and its photogenerated charge transfer properties. Nano Res 4:1144–1152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0163-4
Huynh TP, Pedersen C, Wittig NK, Birkedal H (2018) Precipitation of inorganic phases through a photoinduced pH jump: from vaterite spheroids and shells to ZnO flakes and hexagonal plates. Cryst Growth Des 18:1951–1955. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.8b00093
Vallejo W, Cantillo A, Salazar B et al (2020) Comparative study of ZnO thin films doped with transition metals (Cu and Co) for methylene blue photodegradation under visible irradiation. Catalysts 10:528. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050528
Dhruvashi SPK (2016) Effect of cobalt doping on ZnO thin films deposited by sol-gel method. Thin Solid Films 612:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2016.05.028
Kayani ZN, Shah I, Zulfiqar B et al (2017) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Co-doped zno thin films grown by sol-gel. Zeitschrift fur Naturforsch A 73:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-2017-0302
Azab AA, Esmail SA, Abdelamksoud MK (2019) Studying the effect of cobalt doping on optical and magnetic properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles. SILICON 11:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9902-4
Ben AS, Belhadjltaief H, Duponchel B et al (2019) Enhanced photocatalytic activity against crystal violet dye of Co and In doped ZnO thin films grown on PEI flexible substrate under UV and sunlight irradiations. Heliyon 5:e01912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01912
Li G, Wang H, Wang Q et al (2015) Structure and properties of Co-doped ZnO films prepared by thermal oxidization under a high magnetic field. Nanoscale Res Lett 10:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-0834-2
Islam MR, Rahman M, Farhad SFU, Podder J (2019) Structural, optical and photocatalysis properties of sol–gel deposited Al-doped ZnO thin films. Surf Interfaces 16:120–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2019.05.007
Abirami N, Arulanantham AMS, Wilson KSJ (2020) Structural and magnetic properties of cobalt doped ZnO thin films deposited by cost effective nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. Mater Res Express 7:026405. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab6e27
Benramache S, Benhaoua B (2012) Influence of substrate temperature and Cobalt concentration on structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by ultrasonic spray technique. Superlattices Microstruct 52:807–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2012.06.005
Vempati S, Shetty A, Dawson P et al (2012) Solution-based synthesis of cobalt-doped ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Films 524:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2012.10.008
Monsalve-Bravo GM, Moscoso-Vasquez HM, Alvarez H (2014) Scaleup of batch reactors using phenomenological-based models. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:9439–9453. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie500587r
Martínez Ruano JA, Taimbu de la Cruz CA, Orrego Alzate CE, Cardona Alzate CA (2019) Techno-economic analysis of chitosan-based hydrogels production. In: Mondal M (ed) Cellulose-based superabsorbent hydrogels. Springer, Cham, pp 1769–1790
Hachhach M, Akram H, Hanafi M et al (2019) Simulation and sensitivity analysis of molybdenum disulfide nanoparticle production using aspen plus. Int J Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3953862
Giannozzi P, Baroni S, Bonini N et al (2009) QUANTUM ESPRESSO: a modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. J Phys Condens Matter 21:395502. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/21/39/395502
Giannozzi P, Andreussi O, Brumme T et al (2017) Advanced capabilities for materials modelling with quantum ESPRESSO. J Phys Condens Matter 29:465901. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-648X/aa8f79
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1997) Generalized gradient approximation made simple (vol 77, pg 3865, 1996). Phys Rev Lett 78:1396–1396
Vanderbilt D (1990) Rapid communications. Phys Rev B 41:7892–7895. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.41.7892
Naciri Y, Hsini A, Ajmal Z et al (2020) Influence of Sr-doping on structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of synthesized Ca3(PO4)2. J Colloid Interface Sci 572:269–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.105
Liu J, Chen J, Wu Z et al (2021) Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performances of ZnO through loading AgI and coupling piezo-photocatalysis. J Alloys Compd 852:156848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156848
Soave G (1972) Equilibrium constants from a modified Redlich-Kwong equation of state. Chem Eng Sci 27:1197–1203. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(72)80096-4
Reyes-Lúa A, Solvik M, Skogestad S (2016) Inclusion of thermodynamic equations for efficient steadystate process optimization. Computer aided chemical engineering. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 613–618
Al-Atta A, Huddle T, Rodríguez YG et al (2018) A techno-economic assessment of the potential for combining supercritical water oxidation with ‘in-situ’ hydrothermal synthesis of nanocatalysts using a counter current mixing reactor. Chem Eng J 344:431–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.058
Chandraseagar S, Abdulrazik AH, Abdulrahman SN, Abdaziz MA (2019) Aspen Plus simulation and optimization of industrial spent caustic wastewater treatment by wet oxidation method. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/702/1/012011
Jellal I, Nouneh K, Jedryka J et al (2020) Non-linear optical study of hierarchical 3D Al doped ZnO nanosheet arrays deposited by successive ionic adsorption and reaction method. Opt Laser Technol 130:106348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106348
Tarwal NL, Gurav KV, Mujawar SH et al (2014) Photoluminescence and photoelectrochemical properties of the spray deposited copper doped zinc oxide thin films. Ceram Int 40:7669–7677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.12.108
Jellal I, Ahmoum H, Khaaissa Y et al (2019) Experimental and ab-initio investigation of the microstructure and optoelectronic properties of FCM–CVD-prepared Al-doped ZnO thin films. Appl Phys A 125:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2947-4
López R, Gómez R (2012) Band-gap energy estimation from diffuse reflectance measurements on sol-gel and commercial TiO2: a comparative study. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 61:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-011-2582-9
Abu Amr SS, Aziz HA, Bashir MJK (2014) Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for optimization of semi-aerobic landfill leachate treatment using ozone. Appl Water Sci 4:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0156-z
Nam S-N, Cho H, Han J et al (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of acesulfame K: optimization using the Box-Behnken design (BBD). Process Saf Environ Prot 113:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PSEP.2017.09.002
Ghafari S, Abdul H, Hasnain M, Akbar A (2009) Application of response surface methodology (RSM) to optimize coagulation–flocculation treatment of leachate using poly-aluminum chloride (PAC) and alum. J Hazard Mater J 163:650–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.090
Sohrabi S, Akhlaghian F (2015) Modeling and optimization of phenol degradation over copper-doped titanium dioxide photocatalyst using response surface methodology. Process Saf Environ Prot 99:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2015.10.016
Loqman A, El Bali B, Lützenkirchen J et al (2017) Adsorptive removal of crystal violet dye by a local clay and process optimization by response surface methodology. Appl Water Sci 7:3649–3660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0509-x
Kiwaan HA, Atwee TM, Azab EA, El-Bindary AA (2019) Efficient photocatalytic degradation of acid red 57 using synthesized ZnO nanowires. J Chin Chem Soc 66:89–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.201800092
Sheik Mydeen S, Raj Kumar R, Kottaisamy M, Vasantha VS (2020) Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles through extract from Prosopis juliflora plant leaf: Antibacterial activities and a new approach by rust-induced photocatalysis. J Saudi Chem Soc 24:393–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2020.03.003
Samet B, Mnif T, Chaabouni M (2007) Use of a kaolinitic clay as a pozzolanic material for cements: formulation of blended cement. Cem Concr Compos 29:741–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2007.04.012
Boughelout A, Macaluso R, Kechouane M, Trari M (2020) Photocatalysis of rhodamine B and methyl orange degradation under solar light on ZnO and Cu2O thin films. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 129:1115–1130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-020-01741-8
Huang Q, Zhao Q, Yang C, Jiang T (2020) Facile synthesis of mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride/SnO2 nanocomposite photocatalysts for the enhanced photodegradation of Rhodamine B. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 129:535–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-019-01712-8
Dai WL, Xu H, Yang LX et al (2015) Ultrasonic-assisted facile synthesis of plasmonic ag@agcl cuboids with high visible light photocatalytic performance for rhodamine b degradation. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 115:773–786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-015-0870-z
Cheng J, Zhao S, Gao W et al (2017) Au/Fe3O4@TiO2 hollow nanospheres as efficient catalysts for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 121:797–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-017-1185-z
Shen K, Gondal MA, Li Z et al (2013) 450 nm visible light-induced photosensitized degradation of Rhodamine B molecules over BiOBr in aqueous solution. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 109:247–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-013-0540-y
Liu Y, Zhang Q, Yuan H et al (2021) Comparative study of photocatalysis and gas sensing of ZnO/Ag nanocomposites synthesized by one- and two-step polymer-network gel processes. J Alloys Compd 868:158723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158723
Acknowledgements
In the present work, the authors are grateful for the Innovation Center (University Sidi Mohammed Ben Abdellah of Fez, Morocco for performing the XRD analysis and for the general research services (SEM and DRS) at the CNRST (Morocco).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanji, K., Zouheir, M., Hachhach, M. et al. Design and simulation of a photocatalysis reactor for rhodamine B degradation using cobalt-doped ZnO film. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 134, 1017–1038 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-021-02116-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-021-02116-3