Abstract
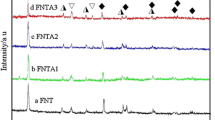
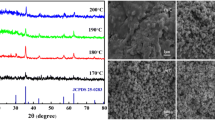
Novel magnetic Au/Fe3O4@TiO2 hollow nanospheres (Au/Fe3O4@hTiO2) have been fabricated via a coating method controlled by versatile kinetics. The details of the structure and morphology, size of the novel catalysts were characterized by TEM, HRTEM, XRD, XPS, VSM and N2 adsorption–desorption. The Au/Fe3O4@hTiO2 nanospheres exhibit favorable catalytic performance in both the photodegradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) under visible light irradiation and the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) to 4-aminophenol (4-AP) by sodium borohydride at room temperature. More importantly, it could be conveniently recycled through an external magnetic field meanwhile without decrement of catalytic activity after running seven times. The unique nanostructure of hollow magnetic nanospheres results in a highly efficient, recoverable, stable, and cost-effective multifunctional system, offering extensive opportunities in the field of versatile catalysts synthesis and application.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Sayed MA (2004) Small is different: shape-, size-, and composition-dependent properties of some colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals. Acc Chem Res 37(5):326–333. doi:10.1021/ar020204f
Yoon K, Yang Y, Lu P, Wan D, Peng HC, Stamm Masias K, Fanson PT, Campbell CT, Xia Y (2012) A highly reactive and sinter-resistant catalytic system based on platinum nanoparticles embedded in the inner surfaces of CeO2 hollow fibers. Angew Chem Int Ed 51(38):9543–9546. doi:10.1002/anie.201203755
Roy S, Palui G, Banerjee A (2012) The as-prepared gold cluster-based fluorescent sensor for the selective detection of As(III) ions in aqueous solution. Nanoscale 4(8):2734–2740. doi:10.1039/c2nr11786j
To WP, Chan KT, Tong GS, Ma C, Kwok WM, Guan X, Low KH, Che CM (2013) Strongly luminescent gold(III) complexes with long-lived excited states: high emission quantum yields, energy up-conversion, and nonlinear optical properties. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(26):6648–6652. doi:10.1002/anie.201301149
Dreaden EC, Alkilany AM, Huang X, Murphy CJ, El-Sayed MA (2012) The golden age: gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem Soc Rev 41(7):2740–2779. doi:10.1039/c1cs15237h
Tian J, Yuan L, Zhang M, Zheng F, Xiong Q, Zhao H (2012) Interface-directed self-assembly of gold nanoparticles and fabrication of hybrid hollow capsules by interfacial cross-linking polymerization. Langmuir 28(25):9365–9371. doi:10.1021/la301453n
Chen Z, Cui ZM, Niu F, Jiang L, Song WG (2010) Pd nanoparticles in silica hollow spheres with mesoporous walls: a nanoreactor with extremely high activity. Chem Commun 46(35):6524–6526. doi:10.1039/c0cc01786h
Zhang N, Xu Y-J (2013) Aggregation- and leaching-resistant, reusable, and multifunctional Pd@CeO2as a robust nanocatalyst achieved by a hollow core-shell strategy. Chem Mater 25(9):1979–1988. doi:10.1021/cm400750c
Kamata K, Lu Y, Xia YN (2003) Synthesis and characterization of monodispersed core-shell spherical colloids with movable cores. J Am Chem Soc 125(9):2384–2385. doi:10.1021/ja0292849
Li Y, Shi J (2014) Hollow-structured mesoporous materials: chemical synthesis. Functionalization and applications. Adv Mater 26(20):3176–3205. doi:10.1002/adma.201305319
Chen M, Wu LM, Zhou SX, You B (2006) A method for the fabrication of monodisperse hollow silica spheres. Adv Mater 18(6):801–806. doi:10.1002/adma.200501528
Du J, Qi J, Wang D, Tang Z (2012) Facile synthesis of Au@TiO2 core–shell hollow spheres for dye-sensitized solar cells with remarkably improved efficiency. Energy Environ Sci 5(5):6914–6918. doi:10.1039/c2ee21264a
Liu S, Yu J, Jaroniec M (2010) Tunable photocatalytic selectivity of hollow TiO2 microspheres composed of anatase polyhedra with exposed 001 facets. J Am Chem Soc 132(34):11914–11916. doi:10.1021/ja105283s
Chen X, Mao SS (2007) Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem Rev 107(7):2891–2959. doi:10.1021/cr0500535
Sacco O, Vaiano V, Han C, Sannino D, Dionysiou DD (2015) Photocatalytic removal of atrazine using N-doped TiO2 supported on phosphors. Appl Catal B 164:462–474. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.09.062
Dai W-L, Xu H, Yang L-X, Luo X-B, Tu X-M, Luo Y (2015) Ultrasonic-assisted facile synthesis of plasmonic Ag@AgCl cuboids with high visible light photocatalytic performance for Rhodamine B degradation. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 115(2):773–786. doi:10.1007/s11144-015-0870-z
Ye M, Zhang Q, Hu Y, Ge J, Lu Z, He L, Chen Z, Yin Y (2010) Magnetically recoverable core-shell nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chemistry 16(21):6243–6250. doi:10.1002/chem.200903516
Jayaprakash N, Shen J, Moganty SS, Corona A, Archer LA (2011) Porous hollow carbon@sulfur composites for high-power lithium-sulfur batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(26):5904–5908. doi:10.1002/anie.201100637
Lee I, Joo JB, Yin Y, Zaera F (2011) A Yolk@Shell Nanoarchitecture for Au/TiO2 Catalysts. Angew Chem Int Ed 123(43):10390–10393. doi:10.1002/ange.201007660
Caruso F (2001) Nanoengineering of particle surfaces. Adv Mater 13(1):11–22. doi:10.1002/1521-4095(200101)13:1<11:aid-adma11>3.0.co;2-n
Chen JS, Chen C, Liu J, Xu R, Qiao SZ, Lou XW (2011) Ellipsoidal hollow nanostructures assembled from anatase TiO2 nanosheets as a magnetically separable photocatalyst. Chem Commun 47(9):2631–2633. doi:10.1039/c0cc04471g
Choi H, Stathatos E, Dionysiou DD (2006) Sol–gel preparation of mesoporous photocatalytic TiO2 films and TiO2/Al2O3 composite membranes for environmental applications. Appl Catal B 63(1–2):60–67. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2005.09.012
Livage J, Henry M, Sanchez C (1988) SOL–GEL chemistry of transition-metal oxides. Prog Solid State Chem 18(4):259–341. doi:10.1016/0079-6786(88)90005-2
Li W, Yang J, Wu Z, Wang J, Li B, Feng S, Deng Y, Zhang F, Zhao D (2012) A versatile kinetics-controlled coating method to construct uniform porous TiO2 shells for multifunctional core-shell structures. J Am. Chem. doi:10.1021/ja3037146
Chi Y, Yuan Q, Li Y, Zhao L, Li N, Li X, Yan W (2013) Magnetically separable Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2-Ag microspheres with well-designed nanostructure and enhanced photocatalytic activity. J Hazard Mater 262:404–411. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.08.077
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26(1):62–69. doi:10.1016/0021-9797(68)90272-5
Cao C, Wei F, Qu J, Song W (2013) Programmed synthesis of magnetic magnesium silicate nanotubes with high adsorption capacities for lead and cadmium ions. Chem Eur J 19(5):1558–1562. doi:10.1002/chem.201203986
Hui C, Shen C, Tian J, Bao L, Ding H, Li C, Tian Y, Shi X, Gao HJ (2011) Core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles synthesized with well-dispersed hydrophilic Fe3O4 seeds. Nanoscale 3(2):701–705. doi:10.1039/c0nr00497a
Wang M, Han J, Xiong H, Guo R (2015) Yolk@Shell nanoarchitecture of Au@r-GO/TiO(2) hybrids as powerful visible light photocatalysts. Langmuir 31(22):6220–6228. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b01099
Kim J, Lee JE, Lee J, Yu JH, Kim BC, An K, Hwang Y, Shin C-H, Park J-G, Kim J, Hyeon T (2006) Magnetic fluorescent delivery vehicle using uniform mesoporous silica spheres embedded with monodisperse magnetic and semiconductor nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 128:688–689
Li J, C-y Liu, Liu Y (2012) Au/graphene hydrogel: synthesis, characterization and its use for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J Mater Chem 22(17):8426–8430. doi:10.1039/c2jm16386a
Zhang P, Mo Z, Han L, Zhu X, Wang B, Zhang C (2014) Preparation and photocatalytic performance of magnetic TiO2/montmorillonite/Fe3O4nanocomposites. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(19):8057–8061. doi:10.1021/ie5001696
Luo Z, Jiang Y, Myers BD, Isheim D, Wu J, Zimmerman JF, Wang Z, Li Q, Wang Y, Chen X, Dravid VP, Seidman DN, Tian B (2015) Atomic gold-enabled three-dimensional lithography for silicon mesostructures. Science 348(6242):1451–1455. doi:10.1126/science.1257278
Wu S, Dzubiella J, Kaiser J, Drechsler M, Guo X, Ballauff M, Lu Y (2012) Thermosensitive Au-PNIPA yolk-shell nanoparticles with tunable selectivity for catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 51(9):2229–2233. doi:10.1002/anie.201106515
Gao S, Zhang Z, Liu K, Dong B (2016) Direct evidence of plasmonic enhancement on catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol over silver nanoparticles supported on flexible fibrous networks. Appl Catal B 188:245–252. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.01.074
Li X, Zeng C, Jiang J, Ai L (2016) Magnetic cobalt nanoparticles embedded in hierarchically porous nitrogen-doped carbon frameworks for highly efficient and well-recyclable catalysis. J Mater Chem A 4:7476–7482. doi:10.1039/c6ta01054g
Dong F, Guo W, Park SK, Ha CS (2012) Controlled synthesis of novel cyanopropyl polysilsesquioxane hollow spheres loaded with highly dispersed Au nanoparticles for catalytic applications. Chem Commun 48(8):1108–1110. doi:10.1039/c1cc14831a
Fan CM, Zhang LF, Wang SS, Wang DH, Lu LQ, Xu AW (2012) Novel CeO2 yolk-shell structures loaded with tiny Au nanoparticles for superior catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol. Nanoscale 4(21):6835–6840. doi:10.1039/c2nr31713c
Xu D, Diao P, Jin T, Wu Q, Liu X, Guo X, Gong H, Li F, Xiang M, Ronghai Y (2015) Iridium oxide nanoparticles and iridium/iridium oxide nanocomposites: photochemical fabrication and application in catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(30):16738–16749. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b04504
Furube A, Du L, Hara K, Katoh R, Tachiya M (2007) Ultrafast plasmon-induced electron transfer from gold nanodots into TiO2 nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 129(48):14852–14853. doi:10.1021/ja076134v
Lee R, Kumaresan Y, Yoon SY, Um SH, Kwon IK, Jung GY (2017) Design of gold nanoparticles-decorated SiO2@TiO2 core/shell nanostructures for visible light-activated photocatalysis. RSC Advances 7(13):7469–7475. doi:10.1039/C6RA27591E
Chandra R, Mukhopadhyay S, Nath M (2016) TiO2@ZIF-8: a novel approach of modifying micro-environment for enhanced photo-catalytic dye degradation and high usability of TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater Lett 164:571–574. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2015.11.018
Shuang S, Lv R, Xie Z, Zhang Z (2016) Surface Plasmon Enhanced Photocatalysis of Au/Pt-decorated TiO(2) Nanopillar Arrays. Sci Rep 6:26670. doi:10.1038/srep26670
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Science-technology Support Plan Projects (No. 2014BAK16B01) and the Key Laboratory of Catalytic engineering of Gansu Province and Resources Utilization, Gansu Province for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, J., Zhao, S., Gao, W. et al. Au/Fe3O4@TiO2 hollow nanospheres as efficient catalysts for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 121, 797–810 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-017-1185-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-017-1185-z