Abstract
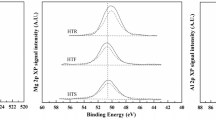
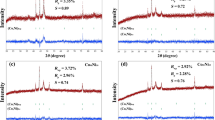
A series of xCoCl2/SiO2 (x = 5, 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 wt%) catalysts were synthesized by two steps impregnation-reduction method. The catalysts were also prepared using other supports (SiO2, Al2O3, and MgO) and Co2B (bulk). The hydrogen generation was monitored using the synthesized catalysts. The prepared catalysts were characterized by using surface area measurement, X-ray diffraction (XRD), SEM images, and Raman spectroscopy analysis. The surface area of the catalyst 50CoCl2/SiO2 gradually increased with increasing calcination temperature. The calcination temperature found to be optimum was 573 K. All the calcined samples were highly amorphous, even after calcining at 773 K. A highly dispersed Co3O4 species formed in all the catalysts during the synthesis. The Co3O4 species did not significantly affect the rate of hydrogen generation. The most active catalyst was the 50CoCl2/SiO2 when the catalyst was prepared by the calcined temperature at 573 K, followed by reduction. The order of catalytic activity for the generation of hydrogen was as follows: 50CoCl2/SiO2 > 50CoCl2/Al2O3 > CoCl2 (Co2B) > 50CoCl2/MgO. The hydrogen generation rate (HGR) was observed with the most active catalyst ~ 4500 ml/min/gcat. Moreover, the TDS (total dissolved solids) of the water used for sodium borohydride solution also affected the hydrogen generation rate. The water possessing the lowest TDS generated the highest amount of hydrogen.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekirogullari M, Kaya M, Saka C (2019) Highly efficient CoB catalysts with Chlorella Vulgaris microalgal strain modified using hydrochloric acid as a new support material for hydrogen production from methanolysis of sodium borohydride. Int J Hydrog Energy 44(14):7262–7275
Shi L, Xie W, Jian Z, Liao X, Wang Y (2019) Graphene modified CoB catalysts for rapid hydrogen production from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 44:17954–17962
Zhao J, Ma H, Chen J (2007) Improved hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution using carbon-supported Co-B as catalysts. Int J Hydrog Energy 32:4711–4716
Mandal TK, Gregory DH (2009) Hydrogen storage materials: present scenarios and future directions. Ann. Rep. Sec. A (Inorg. Chem.) 105:21
Reardon H, Hanlon J, Hughes RW, Godula-Jopek A, Mandal TK, Gregory DH (2012) Emerging concepts in solid-state hydrogen storage: the role of nanomaterials design. Energy Environ Sci 5:5951
Fernandes R, Patel N, Miotello A (2009) Hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of alkaline NaBH4 solution with Cr-promoted Co–B amorphous catalyst. Appl Catal B: Environ 92:68–74
Ding XL, Yuan X, Jia C, Ma ZF (2010) Hydrogen generation from catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride solution using cobalt–copper–boride (Co–Cu–B) catalysts. Int J Hydrog Energy 35:11077–11084
Wang YP, Wang YJ, Ren QL, Li L, Jiao LF, Song DW, Liu G, Han Y, Yuan HT (2010) Ultrafine amorphous Co–Fe–B catalysts for the hydrolysis of NaBH4 solution to generate hydrogen for PEMFC. Fuel Cells 10:132–138
Loghmani MH, Shojaei AF (2014) Hydrogen production through hydrolysis of sodium borohydride: Oleic acid stabilized Co–La–Zr–B nanoparticle as a novel catalyst. Energy 68:152–159
Ferreira MJF, Rangel CM, Pinto AMFR (2012) Water handling challenge on hydrolysis of sodium borohydride in batch reactors. Int J Hydrog Energy 37(8):6985–6994
Beaird AM, Davis TA, Matthews MA (2010) Deliquescence in the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride by water vapor. Ind Eng Chem Res 49(20):9596–9599
Marrero-Alfonso EY, Gray JR, Davis TA, Matthews MA (2007) Minimizing water utilization in hydrolysis of sodium borohydride: the role of sodium metaborate hydrates. Int J Hydrog Energy 32:4723–4730
Demirci UB, Akdim O, Andrieux J, Hannauer J, Chamoun R, Miele P (2010) Sodium borohydride hydrolysis as hydrogen generator: issues, state of the art and applicability upstream from a fuel cell. Fuel Cells 10(3):335–350
Schmid GHS, Bauer J, Eder A, Eisenmenger-Sittner C (2016) A hybrid hydrolytic hydrogen storage system based on catalyst-coated hollow glass microspheres. Int J Energy Res 41(2):297–314
Zhuang DW, Zhang JJ, Dai HB, Wang P (2013) Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of solid sodium borohydride promoted by a cobalt–molybdenum–boron catalyst and aluminum powder. Int J Hydrog Energy 38(25):10845–10850
Li C, Meng W, Hu G, Wang Y, Cao Z, Zhang K (2018) Preparation and characterization of nanostructured Co Mo B thin film catalysts for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int J Hydrog Energy 43:17664–17672
Mitov M, Rashkov R, Atanassov N, Zielonka A (2007) Effects of nickel foam dimensions on catalytic activity of supported Co–Mn–B nanocomposites for hydrogen generation from stabilized borohydride solutions. J Mater Sci 42(10):3367–3372
Ingersoll JC, Mani N, Thenmozhiyal JC, Muthaiah A (2007) Catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride by a novel nickel–cobalt–boride catalyst. J Power Sources 173(1):450–457
Seven F, Sahiner N (2014) Superporous P(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) cryogel-M (M:Co, Ni, Cu) composites as highly effective catalysts in H2 generation from hydrolysis of NaBH4 and NH3BH3. Int J Hydrog Energy 39(28):15455–15463
Liang Y, Wang P, Dai HB (2010) Hydrogen bubbles dynamic template preparation of a porous Fe–Co–B/Ni foam catalyst for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of alkaline sodium borohydride solution. J Alloys Compd 491(1–2):359–365
Fernandes R, Patel N, Miotello A (2009) Efficient catalytic properties of Co–Ni–P–B catalyst powders for hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of alkaline solution of NaBH4. Int J Hydrog Energy 34(7):2893–2900
Kim DR, Cho KW, Choi YI, Park CJ (2009) Fabrication of porous Co–Ni–P catalysts by electrodeposition and their catalytic characteristics for the generation of hydrogen from an alkaline NaBH4 solution. Int J Hydrog Energy 34(6):2622–2630
Seven F, Sahiner N (2017) Enhanced catalytic performance in hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis by super porous cryogel supported Co and Ni catalysts. J Power Sources 272:128–136
Patel N, Fernandes R, Miotello A (2009) Hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of NaBH4 with efficient Co–P–B catalyst: a kinetic study. J Power Sources 188(2):411–420
Cheng J, Xiang C, Zou Y, Chu H, Qiu S, Zhang H, Xu F (2015) Highly active nanoporous Co–B–TiO2 framework for hydrolysis of NaBH4. Ceram Int 41(1):899–905
Lu YC, Chen MS, Chen YW (2012) Hydrogen generation by sodium borohydride hydrolysis on nanosized CoB catalysts supported on TiO2, Al2O3 and CeO2. Int J Hydrog Energy 37(5):4254–4258
Metin O, Özkar S (2009) Hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia-borane and sodium borohydride using water-soluble polymer-stabilized cobalt(0) nanoclusters catalyst. Energ Fuel 23(7):3517–3526
Umegaki T, Yan JM, Zhang XB, Shioyama H, Kuriyama N, Xu Q (2010) Co–SiO2 nanosphere-catalyzed hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane for chemical hydrogen storage. J Power Sources 195(24):8209–8214
Chen Y, Kim H (2008) Ni/Ag/silica nanocomposite catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of NaBH4 solution. Mater Lett 62(8–9):1451–1454
Wen Y, Qu D, An L, Gao X, Jiang W, Wu D, Yang D, Sun Z (2018) Defective g-C3N4 prepared by the NaBH4 reduction for high-performance H2 production. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:2343–2349
Umegaki T, Yan JM, Zhang XB, Shioyama H, Kuriyam N, Xu Q (2009) Hollow Ni–SiO2 nanosphere-catalyzed hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane for chemical hydrogen storage. J Power Sources 191(2):209–216
Chen Y, Kim H (2008) Use of a nickel-boride–silica nanocomposite catalyst prepared by in-situ reduction for hydrogen production from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Fuel Process Technol 89(10):966–972
Si C, Gao H, Zhou J, Liu G (2010) Catalytic properties of Co/activated carbon catalyst prepared from wheat stalk. React Kinet Mech Catal 101(1):183–193
Rambabu K, Hai A, Bharath G, Banat F, Show PL (2019) Molybdenum disulfide decorated palm oil waste activated carbon as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation by sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 44:14406–14415
Bai Y, Wu C, Wu F, Yi B (2006) Carbon-supported platinum catalysts for on-site hydrogen generation from NaBH4 solution. Mater Lett 60(17–18):2236–2239
Zou YC, Nie M, Huang YM, Wang JQ, Liu HL (2011) Kinetics of NaBH4 hydrolysis on carbon-supported ruthenium catalysts. Int J Hydrog Energy 36(19):12343–12351
Prasad D, Patil KN, Sandhya N, Chaitra CR, Bhanushali JT, Samal AK, Keri RS, Jadhav AH, Nagaraja BM (2019) Highly efficient hydrogen production by hydrolysis of NaBH4 using eminently competent recyclable Fe2O3 decorated oxidized MWCNTs robust catalyst. Appl Surf Sci 489:538–551
Hung A, Tsai S, Hsu Y, Ku J, Chen Y, Yu C (2008) Kinetics of sodium borohydride hydrolysis reaction for hydrogen generation. Int J Hydrog Energy 33(21):6205–6215
Li Z, Li H, Wang L, Liu T, Zhang T, Wang G, Xie G (2014) Hydrogen generation from catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride solution using supported amorphous alloy catalysts (Ni–Co–P/γ-Al2O3). Int J Hydrog Energy 39(27):14935–14941
Kojima Y, Suzuki K, Fukumoto K, Sasaki M, Yamamoto T, Kawai Y, Hayashi H (2002) Hydrogen generation using sodium borohydride solution and metal catalyst coated on metal oxide. Int J Hydrog Energy 27(10):1029–1034
Zou JJ, He H, Cui L, Du HY (2007) Highly efficient Pt/TiO2Pt/TiO2 photocatalyst for hydrogen generation prepared by a cold plasma method. Int J Hydrog Energy 32(12):1762–1770
Liu BH, Li ZP (2009) A review: hydrogen generation from borohydride hydrolysis reaction. J Power Sources 187(2):527–534
Peng S, Fan X, Zhang J, Wang F (2013) A highly efficient heterogeneous catalyst of Ru/MMT: preparation, characterization, and evaluation of catalytic effect. Appl Catal. B: Environ 140–141:115–124
Demirci UB, Garin F (2008) Kinetics of Ru-promoted sulphated zirconia catalysed hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of sodium tetrahydroborate. J Mol Catal A: Chem 279(1):57–62
Wang W, Zhao Y, Chen D, Wang X, Peng X, Tian J (2014) Promoted Mo incorporated Co–Ru–B catalyst for fast hydrolysis of NaBH4 in alkaline solutions. Int J Hydrog Energy 39(28):16202–16211
Ro G, Kim Y (2019) H2 generation using Pt nanoparticles encapsulated in Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 multishell particles. Colloids Surf, A 577:48–52
Wilcox MJ, Groven LJ (2017) Solution combustion synthesized lithium cobalt oxide as a catalytic precursor for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int J Hydrog Energy 42(10):6765–6770
Choi J, Chung J (2016) Preparation and characteristics of novel cobalt oxide catalysts for hydrogen generation from metal borohydride solution. J Energy Eng 142:04015026
Groven LJ, Pfeil TL, Pourpoint TL (2013) Solution combustion synthesized cobalt oxide catalyst precursor for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 38(15):6377–6380
Christie JH, Lockwood DJ (1971) Electronic Raman spectrum of Co2+ in CoCl2. Chem Phys Lett 8(1):120–122
Ma JL, Li N, Zhang Q, Zhang XB, Wang J, Li K, Hao XF, Yan JM (2018) Synthesis of porous and metallic CoB nanosheets towards a highly efficient electrocatalyst for rechargeable Na-O2 batteries. Energy Environ Sci 11:2833–2838
Diallo A, Beye AC, Doyle TB, Park E, Maaza M (2015) Green synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles via Aspalathus linearis: physical properties. Green Chem Lett Rev 8(3–4):30–36
Karuppaiah M, Murugan R, Sakthivel P, Asaithambi S, Yuvakkumar R, Ravi G (2018) Rapid microwave assisted synthesis of Mn2O3 and Co3O4 nanoparticles and their structural, optical and magnetic properties. Int J Adv Eng Res Dev 5(7):1–5
Mcnulty D, Geaney H, Carroll E, Garvey S, Lonergan A, Odwyer C (2017) The effect of particle size, morphology and C-rates on 3D structured Co3O4 inverse opal conversion mode anode materials. Mater Res Express 4:025011
Abu-Zied BM, Alamry KA (2019) Green synthesis of 3D hierarchical nanostructured Co3O4/carbon catalysts for the application in sodium borohydride hydrolysis. J Alloys Compd 798:820–831
Bozkurt G, Özer A, Yurtcan AB (2019) Development of effective catalysts for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride: Ru, Pt, Pd nanoparticles supported on Co3O4. Energy 180:702–713
Shi L, Chen Z, Jian Z, Gu F, Gao C (2019) Carbon nanotubes-promoted Co–B catalysts for rapid hydrogen generation via NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 44:19868–19877
Guo S, Liu Y, Bond AM, Zhang J, Esakki Karthik P, Maheshwaran I, Senthil Kumar SM, Phani KLN (2014) Facile electrochemical co-deposition of a graphene-cobalt nanocomposite for highly efficient water oxidation in alkaline media: direct detection of underlying electron transfer reactions under catalytic turnover conditions. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:19035–19045
Singh PK, Das T (2017) Generation of hydrogen from NaBH4 solution using metal-boride (CoB, FeB, NiB) catalysts. Int J Hydrog Energy 42(49):29360–29369
Li Y, Qiu W, Qin F, Fang H, Hadjiev VG, Litvinov D, Bao J (2016) Identification of cobalt oxides with Raman scattering and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J Phys Chem C 120:4511–4516
Shi L, Xie W, Jian Z, Liao X, Wang Y (2019) Graphene modified Co–B catalysts for rapid hydrogen production from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 44:17954–17962
Muir SS, Chen Z, Wood BJ, Wang L, Lu GQ, Yao X (2014) New electroless plating method for preparation of highly active Co–B catalysts for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 39(1):414–425
Akdim O, Demirci UB, Muller D, Miele P (2009) Cobalt (II) salts, performing materials for generating hydrogen from sodium borohydride. Int J Hydrog Energy 34(6):2631–2637
Edla R, Gupta S, Patel N, Bazzanella N, Fernandes R, Kothari DC, Miotello A (2016) Enhanced H2 production from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride using Co3O4 nanoparticles assembled coatings prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Appl Catal A: Gen 515:1–9
Pfeil TL, Pourpoint TL, Groven LJ (2014) Effects of crystallinity and morphology of solution combustion synthesized Co3O4 as a catalyst precursor in hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int J Hydrog Energy 39(5):2149–2159
Wu Z, Ge S (2011) Facile synthesis of a Co–B nanoparticle catalyst for efficient hydrogen generation via borohydride hydrolysis. Catal Commun 13(1):40–43
Simagina VI, Komova OV, Ozerova AM, Netskina OV, Odegova GV, Kellerman DG, Bulavchenko OA, Ishchenko AV, Simagina VI, Komova OV, Ozerova AM, Netskina OV, Odegova GV, Kellerman DG, Bulavchenko OA, Ishchenko AV (2011) Cobalt oxide catalyst for hydrolysis of sodium borohydride and ammonia borane. Appl Catal A: Gen 394:86–92
Jeong SU, Cho EA, Nam SW, Oh IH, Jung UH, Kim SH (2007) Effect of preparation method on Co–B catalytic activity for hydrogen generation from alkali NaBH4 solution. Int J Hydrog Energy 32(12):1749–1754
Krishnan P, Advani S, Prasad AK (2008) Cobalt oxides as Co2B catalyst precursors for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride solutions to generate hydrogen for PEM fuel cells. Int J Hydrog Energy 33:7095–7102
Ozerova AM, Simagina VI, Komova OV, Netskina OV, Odegova GV, Bulavchenko OA, Rudina NA (2012) Cobalt borate catalysts for hydrogen production via hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. J Alloys Compd 513:266–272
Krishnan P, Hsueh KL, Yim SD (2007) Catalysts for the hydrolysis of aqueous borohydride solutions to produce hydrogen for PEM fuel cells. Appl Catal B: Environ 77(1–2):206–214
Netskina OV, Komova OV, Mukha SA, Simagina VI (2016) Aqueous-alkaline NaBH4 solutions: the influence of hydride decomposition on catalytic properties of Co3O4. Catal Commun 85:9–12
Izgi MS, Sahin O, Onat E, Saka C (2020) Epoxy-activated acrylic particulate polymer-supported Co-Fe-Ru-B catalyst to produce H2 from hydrolysis of NH3-BH3. Int J Hydrog Energy 45:22638–22648
Kazici HC, Izgi MS, Sahin O (2021) A comprehensive study on the synthesis, characterization and mathematical modelling of nanostructured Co-based catalysts using different support materials for AB hydrolysis. Chem Pap 75:2713–2725
Onat E, Cevik S, Sahin O, Horoz S, Izgi MS (2021) Investigation of high catalytic activity catalyst for high hydrogen production rate: Co-Ru@MOF. J Aust Ceram Soc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-021-00643-9
Sahin O, Izgi MS, Tayboga S, Kazici HC (2021) Effect of plasma pre-treatment of Co-Cu-B catalyst on hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride methanolysis. React Kinet Mech Catal 133:851–861
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P. K. Singh: Investigation, data correction, formal analysis and writing; T. Das: Project administration, resources, supervision, conceptualization, reviewing, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, P.K., Das, T. Hydrogen generation through sodium borohydride hydrolysis over supported cobalt catalysts and the effect of total dissolved solids in water. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 134, 677–696 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-021-02100-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-021-02100-x