Abstract
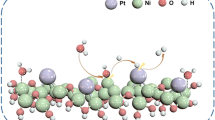
Nanoporous Co100-xNix (x = 1, 5, 10 and 15) solid solutions were synthesized using the chemical coprecipitation followed by hydrogen reduction method and applied as catalysts for the efficient hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis. The obtained catalysts are composed of hcp- and fcc-(Co,Ni) solid solutions phases, and exhibit the special three-dimensional nanoporous structure. With increasing the Ni content, the hydrogen generation rate (HGR) of NaBH4 hydrolysis catalyzed by Co100-xNix solid solutions decreased slightly, whereas the cycling stability of the catalyst can be improved. The HGR remains as much as 73% of the initial value after five times of catalysis for Co85Ni15. This work contributes to the development of advanced non-noble metal-based catalysts for efficient and long-term hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nastasi B, Markovska N, Puksec T et al (2022) Renewable and sustainable energy challenges to face for the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals. Renew Sust Energy Rev 157:112071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2022.112071
Olabi AG (2012) Developments in sustainable energy and environmental protection. Energy 39(1):2–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.12.037
Noorollahi Y, Pourarshad M, Veisi A (2021) The synergy of renewable energies for sustainable energy systems development in oil-rich nations; case of Iran. Renew Energy 173:561–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.04.016
Sharma S, Basu S, Shetti NP et al (2020) Waste-to-energy nexus for circular economy and environmental protection: Recent trends in hydrogen energy. Sci Total Environ 713:136633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136633
Dawood F, Anda M, Shafiullah GM (2020) Hydrogen production for energy: an overview. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45(7):3847–3869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.12.059
Qusay H, Aws ZS, Olushola O et al (2023) Hydrogen fuel as an important element of the energy storage needs for future smart cities. Int J Hydrogen Energy 48(78):30247–30242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.03.413
Zhang L, Jia C, Bai F et al (2024) A comprehensive review of the promising clean energy carrier: Hydrogen production, transportation, storage, and utilization (HPTSU) technologies. Fuel 355:129455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2023.129455
Singh R (2021) Reversible chemical hydrogen storage in borohydrides via thermolysis and hydrolysis: recent advances, challenges, and perspectives. Int J Hydrogen Energy 47(62):26549–26573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.10.022
Santos DMF, Sequeira CAC (2011) Sodium borohydride as a fuel for the future. Renew Sust Energy Rev 15(8):3980–4001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.07.018
Liu Y, Paskevicius M, Humphries TD et al (2022) Simultaneous preparation of sodium borohydride and ammonia gas by ball milling. Int J Hydrogen Energy 47(60):25347–25356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.05.262
Zhu Y, Ouyang L, Zhong H et al (2020) Closing the loop for hydrogen storage: Facile regeneration of NaBH4 from its hydrolytic product. Angew Chem Int Ed 59(22):8623–8629. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201915988
Zhong H, Ouyang L, Liu J et al (2018) Sodium borohydride regeneration via direct hydrogen transformation of sodium metaborate tetrahydrate. J Power Sources 390:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.04.037
Coşkuner B, Kantürk Figen A, Pişkin S (2013) Solid state preparation and reaction kinetics for Co/B as a catalytic/acidic accelerator for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 109(2):375–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-013-0569-y
Kojima Y, Kawai Y, Nakanishi H et al (2004) Compressed hydrogen generation using chemical hydride. J Power Sources 135(1–2):36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.03.079
Abdelhamid HN (2021) A review on hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46(1):726–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.09.186
Sermiagin A, Meyerstein D, Rolly GS et al (2021) Mechanistic implications of the solvent kinetic isotope effect in the hydrolysis of NaBH4. Int J Hydrogen Energy 47(6):3972–3979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.11.040
Dragan M (2022) Hydrogen storage in complex metal hydrides NaBH4: Hydrolysis reaction and experimental strategies. Catalysts 12(4):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040356
Metin Ö, Koçak E, Özkar S (2011) Effect of stabilizer type on the activity and stability of water-dispersible cobalt(0) nanocluster catalysts in hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 103(2):325–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-011-0306-3
Zhang H, Zhang L, Rodríguez-Pérez IA et al (2021) Carbon nanospheres supported bimetallic Pt-Co as an efficient catalyst for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Appl Surf Sci 540:148296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148296
Wang Y, Liu X (2021) Catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride for hydrogen production using magnetic recyclable CoFe2O4-modified transition-metal nanoparticles. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4(10):11312–11320. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c03067
Avci Hansu T, Sahin O, Caglar A et al (2020) A remarkable Mo doped Ru catalyst for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride: the effect of Mo addition and estimation of kinetic parameters. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 131(2):661–676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-020-01884-8
Zhang H, Feng X, Cheng L et al (2019) Non-noble Co anchored on nanoporous graphene oxide, as an efficient and long-life catalyst for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride. Colloid Surf A 563:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.12.002
Paladini M, Arzac GM, Godinho V et al (2014) Supported Co catalysts prepared as thin films by magnetron sputtering for sodium borohydride and ammonia borane hydrolysis. Appl Catal B 158–159:400409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.047
Ekinci A, Cengiz E, Kuncan M et al (2020) Hydrolysis of sodium borohydride solutions both in the presence of Ni-B catalyst and in the case of microwave application. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45(60):34749–34760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.08.264
Lim D, Özkan G, Özkan G (2021) Ni-B and Zr-Ni-B in-situ catalytic performance for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride, ammonia borane and their mixtures. Int J Hydrogen Energy 47(5):3396–3408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.03.039
Kılınç D, Şahin Ö (2019) Effective TiO2 supported Cu-Complex catalyst in NaBH4 hydrolysis reaction to hydrogen generation. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44(34):18858–18865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.225
Nabid MR, Bide Y, Kamali B (2019) Hydrogen release from sodium borohydride by Fe2O3@nitrogen-doped carbon core-shell nanosheets as reasonable heterogeneous catalyst. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44(47):25662–25670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.08.038
Coşkuner FB, Kantürk FA (2019) Insight into the role of solvents in enhancing hydrogen production: Ru-Co nanoparticles catalyzed sodium borohydride dehydrogenation. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44(53):28471–28482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.01.038
Nie M, Zou YC, Huang YM et al (2012) Ni-Fe-B catalysts for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int J Hydrogen Energy 37(2):1568–1576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.10.006
Nunes HX, Ferreira MJ, Rangel CM et al (2016) Hydrogen generation and storage by aqueous sodium borohydride (NaBH4) hydrolysis for small portable fuel cells (H2-PEMFC). Int J Hydrogen Energy 41(34):15426–15432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.06.173
Eugénio S, Demirci UB, Silva TM et al (2016) Copper-cobalt foams as active and stable catalysts for hydrogen release by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41(20):8438–8448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.03.122
Li Z, Liu R, Liu D et al (2021) Three-dimensional porous cobalt as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen production by NaBH4 hydrolysis. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 134(2):665–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-021-02099-1
Izumi F, Ikeda T (2000) A Rietveld-analysis program RIETAN-98 and its applications to zeolites. Mater Sci Forum 321–323:198–203. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.321-324.198
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52071001), Key Research and Development Program of Anhui Province of China (No. 2022l07020011), Scientific Research Foundation of Education Department of Anhui Province of China (No. 2022AH010025 and 2022AH050341).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China,52071001,Dongming Liu
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, A., Zhuang, X., Li, Z. et al. Hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis catalyzed by nanoporous Co100−xNix (x = 1, 5, 10 and 15) solid solutions. Reac Kinet Mech Cat (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-024-02643-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-024-02643-9