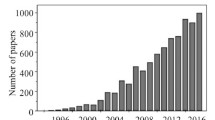
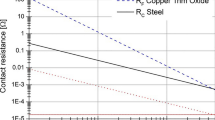
Spark plasma sintering (SPS) is a type of pulsed electric current-assisted sintering technique. This method allows for rapid consolidation of powder materials into dense bulk when simultaneously applying uniaxial pressure and pulsed electrical current in a vacuum or protective atmosphere. Many scholars and researchers have realized the importance of the SPS due to its significant advantages in controlling the powder surface condition, atomic diffusion, phase stability, and crystal growth behavior. All these features inevitably influence the densification behavior and resulting physical and mechanical properties of the sintered materials. This review represents an extensive introduction of recent developments and fundamental principles in SPS techniques after a general description of the method and its outstanding advantages. A possible design for the SPS technique is proposed as well. Subsequently, the effects of each operating parameter, including current, voltage, and uniaxial pressure, on the densification behavior of advanced metals and alloys under various sintering conditions are reviewed. Finally, the successful applications of the SPS in preparing novel metal structural materials, such as high-quality special steels, new lightweight alloy materials with high performance, high entropy alloys, and other metal alloys, are described in detail.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Omori, “Sintering, consolidation, reaction and crystal growth by the spark plasma system (SPS),” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 287, 183–188 (2000).
V. Nečina and W. Pabst, “Influence of the heating rate on grain size of alumina ceramics prepared via spark plasma sintering (SPS),” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 40, 3656–3662 (2020).
D. Paraskevas, S. Dadbakhsh, J. Vleugels, K. Vanmeensel, W. Dewul, and J.R. Duflou, “Solid state recycling of pure Mg and AZ31 Mg machining chips via spark plasma sintering,” Mater. Des., 109, 520–529 (2016).
R.F Liu., W.X. Wang, H.S. Chen, M.B. Tan, and Y.Y. Zhang, “Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of micro-/nano-bimodal size B4C particles reinforced aluminum matrix composites prepared by SPS followed by HER,” Vacuum, 151, 39–50 (2018).
Z.H. Zhang, F.C. Wang, S.K. Lee, Y. Liu, J.W. Cheng, and Y. Liang, “Microstructure characteristic, mechanical properties and sintering mechanism of nanocrystalline copper obtained by SPS process,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 523, 134–138 (2009).
V.N. Chuvildeev, D.V. Panov, M.S. Boldin, A.V. Nokhrin, Yu.V. Blagoveshchensky, N.V. Sakharov, S.V. Shotin, and D.N. Kotkov, “Structure and properties of advanced materials obtained by spark plasma sintering,” Acta Astronaut., 109, 172–176 (2015).
V.N. Chuvildeev, A.V. Nokhrin, and V.I. Kopylov, “Spark plasma sintering for high-speed diffusion bonding of the ultrafine-grained near-αTi–5Al–2V alloy with high strength and corrosion resistance for nuclear engineering,” J. Mater. Sci., 54, 14926–14949 (2019).
E.A. Olevsky, S. Kandukuri, and L. Froyen, “Consolidation enhancement in spark-plasma sintering: Impact of high heating rates,” J. Appl. Phys., 102, 114913 (2007).
S.R. Oke, O.O. Ige, O.E. Falodun, B.A. Obadele, M.B. Shongwe, and P.A. Olubambi, “Optimization of process parameters for spark plasma sintering of nano structured SAF 2205 composite,” J. Mater. Res. Technol., 7, 126–134 (2017).
Z.H. Zhang, Z.F. Liu, J.F. Lu, X.B. Shen, F.C. Wang, “The sintering mechanism in spark plasma sintering-proof of the occurrence of spark discharge,” Scr. Mater., 81, 56–59 (2014).
J.H. Liu, Z.Y. Fu, W.M. Wang, J.Y. Zhang, H. Wang, Y.C. Wang, S. Lee, and K. Niihara, “Ultra-high heating rate densification of nanocrystalline magnesia at high pressure and investigation on densification mechanisms,” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 34, 3095–3102 (2014).
J.Y. Zhang, F.C. Meng, R.I. Todd, and Z.Y. Fu, “The nature of grain boundaries in alumina fabricated by fast sintering,” Scr. Mater., 62, 658–661 (2010).
D.K. Guan, W.M. Rainforth, J. Sharp, J.H. Gao, and I. Todd, “On the use of cryomilling and spark plasma sintering to achieve high strength in a magnesium alloy,” J. Alloys Compd., 688, 1141–1150 (2016).
S.H. Deng, H.J. Zhao, R.D. Li, T.C. Yuan, L.B. Li, and P. Cao, “The influence of the local effect of electric current on densification of tungsten powder during spark plasma sintering,” Powder Technol., 356, 769–777 (2019).
G. Lee, C. Maniere, J. McKittrick, R. Doerner, D. Nishijima, A. Gattuso, T. Abrams, D. Thomas, C. Back, and E.A. Olevsky, “Consolidation of Molybdenum nanopowders by spark plasma sintering: Densification mechanism and first mirror application,” J. Nucl. Mater., 516, 354–359 (2019).
C.L. Cramer, J.W. McMurray, M.J. Lance, and R.A. Lowden, “Reaction-bond composite synthesis of SiC–TiB2 by spark plasma sintering/field-assisted sintering technology (SPS/FAST),” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 40, 988–995 (2020).
Z.H. Zhang, X.B. Shen, C. Zhang, S. Wei, S.K. Lee, and F.C. Wang, “A new rapid route to in-situ synthesize TiB–Ti system functionally graded materials using spark plasma sintering method,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 565, 326–332 (2013).
Z.H. Zhang, X.B. Shen, F.C. Wang, and S.K. Lee, “A New Rapid Route for In Situ Synthesizing Monolithic TiB Ceramic,“ J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 94, 2754–2756 (2011).
S. Sovizi and M.E. Seraji, “The Densification Behavior of Metals and Alloys During Spark Plasma Sintering: A Mini-Review,” Sci. Sintering, 51, 135–152 (2019).
A.I. Raichenko, G.L. Burenkov, A.F. Khrienko, and V.P. Litvinenko, “Electric discharge sintering of binary powder mixtures,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 15, 602–606 (1976).
O. Ertorer, T. Topping, Y. Li, W. Moss, and E. Lavernia, “Nanostructured Ti consolidated via spark plasma sintering,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 42, 964–973 (2011).
D. Demirskyi and O. Vasylkiv, “Consolidation and grain growth of tantalum diboride during spark plasma sintering,” Ceram. Int., 42, 16396–16400 (2016).
R.Z. Valiev, R.K. Islamgaliev, N.F. Kuzmina, Y. Li, and T.G. Langdon, “Strengthening and grain refinement in an Al-6061 metal matrix composite through intense plastic straining,” Scr. Mater., 40, 117–122 (1998).
Z.H. Zhang, F.C. Wang, L. Wang, and S.K. Li, “Ultrafine-grained copper prepared by spark plasma sintering process,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 476, 201–205 (2008).
R. Sule, P.A. Olubambi, I. Sigalas, J.K.O. Asante, and J.C. Garrett, “Effect of SPS consolidation parameters on submicron Cu and Cu-CNT composites for thermal management,” Powder Technol., 258, 198–205 (2014).
Z.Y. Hu, Z.H. Zhang, X.W. Cheng, F.C. Wang, Y.F. Zhang, and S.L. Li, “A review of multi-physical fields induced phenomena and effects in spark plasma sintering: Fundamentals and applications,” Mater. Des., 191, 108662 (2020).
A.G. Bloxam, GB Patent, No. 9020 (1906).
G.F. Taylor, US Patent No.1, 896, 854 (1933).
I. Sulima, P. Putyra, P. Hyjek, and T. Tokarski, “Effect of SPS parameters on densification and properties of steel matrix composites,” Adv. Powder Technol., 26, 1152–1161 (2015).
E.G. Grigoriev and AV. Rosliakov, “Electro-discharge compaction of WC-Co and W-Ni-Fe-Co composite materials,” J. Mater. Process. Technol., 191, 182–184 (2007).
A. Leich, Röttger, W. Theisen, and M. Krengel, “Densification of nanocrystalline NdFeB magnets processed by electro-discharge sintering-Microstructure, magnetic, and mechanical properties,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 460, 454–460 (2018).
F. Balima, F. Bellin, D. Michau, O. Viraphong, A. Poulon-Quintin, U.C. Chung, A. Dourfaye, and A. Largeteau, “High pressure pulsed electric current activated equipment (HP-SPS) for material processing,” Mater. Des., 139, 541–548 (2018).
F. Balima and A. Largeteau, “Phase transformation of alumina induced by high pressure spark plasma sintering (HP-SPS),” Scr. Mater., 158, 20–23 (2019).
R. Yamanoglu, “A perspective from conventional sintering to accelerated sintering without pressure,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 57, 513–525 (2019).
M.N. Ge, X.F. Wang, G.Y. Li, C. Lu, J.F. Zhang, and R. Tu, “Synthesis of Cr2AlC from elemental powders with modified pressureless spark plasma sintering,” J. Wuhan Univ. Technol., Mater. Sci. Ed., 34, 287–292 (2019).
W.L. Bradbury and E.A. Olevsky, “Production of SiC-C composites by free-pressureless spark plasma sintering (FPSPS),” Scr. Mater., 63, 77–80 (2010).
Y.S. Lin, M.A. Meyers, and E.A. Olevsky, “Microchannelled hydroxyapatite components by sequential freeze drying and free pressureless spark plasma sintering,” Adv. Appl. Ceram., 111, 269–274 (2012).
L. Bertolla, I. Dlouhý, P. Tatarko, A. Viani, A. Mahajan, Z. Chlup, M.J. Reece, and A.R. Boccaccini, “Pressureless spark plasma-sintered Bioglass®; 45S5 with enhanced mechanical properties and stress-induced new phase formation,” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 37, 2727–2736 (2017).
D.V. Dudina, B.B. Bokhonov, and A.K. Mukherjee, “Formation of aluminum particles with shell morphology during pressureless spark plasma sintering of Fe–Al mixtures: Current-related or Kirkendall effect,” Materials, 9, 375 (2016).
R. Yamanoglu, N. Gulsoy, E.A. Olevsky, and H.O. Gulsoy, “Production of porous Ti5Al2.5Fe alloy via pressureless spark plasma sintering,” J. Alloys Compd., 680, 654–658 (2016).
R. Hallett, J.R. Cox, and K. Morsi, “Novel Spark Plasma Extrusion of Titanium Above and Below the β-Transus: Effect on Microstructure and Properties,” Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 51, 1363–1369 (2020).
K. Morsi, A.M.K. Esawi, P. Borah, S. Lanka, A. Sayed, and M. Taher, “Properties of single and dual matrix aluminum-carbon nanotube composites processed via spark plasma extrusion (SPE),” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527, 5686–5690 (2010).
J.H. Yang, J. Trapp, Q.G. Guo, and B. Kieback, “Joining of 316L stainless steel by using spark plasma sintering method,” Mater. Des., 52, 179–189 (2013).
K. Park, D. Kim, K. Kim, and H. Kwon, “Aluminum/Stainless Steel Clad Materials Fabricated via Spark Plasma Sintering,” Materials, 13, 239 (2020).
Z.Y. Fu, W. Ji, and W.M. Wang, “Recent Progress in Flash Sintering Technology of Ceramic Materials,” J. Chin. Ceram. Soc., 45, 1211–1219 (2017).
F. Gucci, T.G. Saunders, B. Srinivasan, F. Cheviré, D.A. Ferluccio, J.W.G. Bos, and M.J. Reece, “Hybrid Flash-SPS of TiNiCu0.05Sn with reduced thermal conductivity,” J. Alloys Compd., 837, 155058 (2020).
C. Manière, U. Kus, G. Chevallier, A. Weibel, L. Durand, J. Huez, D. Delagnes, and C. Estournèss, “How to overcome the main challenges of SPS technology: Reproducibility, multi-samples and elaboration of complex shapes,” Spark Plasma Sintering, 77–108 (2019).
O.E. Falodun, B.A. Obadele, S.R. Oke, A.M. Okoro, and P.A. Olubambi, “Titanium-based matrix composites reinforced with particulate, microstructure, and mechanical properties using spark plasma sintering technique: a review,” Int. J. Adv. Des. Manuf. Technol., 102, 1689–1701 (2019).
S.R. Oke, O.O. Ige, O.E. Falodun, A.M. Okoro, M. R. Mphahlele, and P.A. Olubambi, “Powder metallurgy of stainless steels and composites: a review of mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering,” Int. J. Adv. Des. Manuf. Technol., 102, 3271–3290 (2019).
E. Jajarmi, L. Desogus, R. Orrùa, S.A. Sajjadi, and G. Cao, “On the fabrication of functional graded 3YPSZ/316L materials by SPS: Process optimization and characterization of the obtained products,” Ceram. Int., 42, 8351–8359 (2016).
Z.A. Munir, D.V. Quach, and M. Ohyanagi, “Electric current activation of sintering: A review of the pulsed electric current sintering process,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 94, 1–19 (2011).
O. Guillon, J. Gonzalez-Julian, B. Dargatz, T. Kessel, G. Schierning, J. Räthel, and M. Herrmana, “Field-assisted sintering technology/spark plasma sintering: mechanisms, materials, and technology developments,”.Adv. Eng. Mater., 16, 830-849 (2014).
Z.Q. Fu, W.P. Chen, H.M. Wen, Z. Chen, and E.J. Lavernia, “Effects of Co and sintering method on microstructure and mechanical behavior of a high-entropy Al0.6NiFeCrCo alloy prepared by powder metallurgy,” J. Alloys Compd., 646, 175–182 (2015).
S.X. Song, Z. Wang, and G.P. Shi, “Heating mechanism of spark plasma sintering,” Ceram. Int., 39, 1393–1396 (2013).
N. Chawake, L.D. Pinto, A.K. Srivastav, K. Akkiraju, B.S. Murty, and R.S. Kottada, “On Joule heating during spark plasma sintering of metal powders,” Scr. Mater., 93, 52–55 (2014).
K. Vanmeensel, A. Laptev, J. Hennicke, J. Vleugels, and O.V.D. Biest, “Modelling of the temperature distribution during field assisted sintering,” Acta Mater., 53, 4379–4388 (2005).
S. Ghosh, A.H. Chokshi, P. Lee, and R. Raj, “A huge effect of weak dc electrical fields on grain growth in zirconia,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 92, 1856–1859 (2009).
C. Romaric, L. Sophie, N. Foad, C. Frederic, B. Guillaume, F. Gilbert, C. Jean-Marc, and B. Frederic, “Effect of current on the sintering of pre-oxidized copper powders by SPS,” J. Alloys Compd., 692, 478–484 (2017).
A. Bachmaier, M. Pfaff, M. Stolpe, H. Aboulfadl, and C. Motz, “Phase separation of a supersaturated nanocrystalline Cu-Co alloy and its influence on thermal stability,” Acta Mater., 96, 269–283 (2015).
R. Marder, C. Estournès, G. Chevallier, and R. Chaim, “Plasma in spark plasma sintering of ceramic particle compacts,” Scr. Mater., 82, 57–60 (2014).
M. Tokita, “Development of large-size ceramic/mrtal bulk FGM fabricated by spark plasma sintering,” Mater. Sci. Forum, 308–311, 83–88 (1999).
Z.Q. Fu, A. Hoffman, B.E. MacDonald, Z.F. Jiang, W.P. Chen, M. Arivu, H.M. Wen, and E.J. Laverni, “Atom probe tomography study of an Fe25Ni25Co25Ti15Al10 high-entropy alloy fabricated by powder metallurgy,” Acta Mater., 179, 372–382 (2019).
T. Nagae, M. Yokota, M. Nose, S. Tomida, T. Kamiya, and S. Saji, “Effects of pulse current on an aluminum powder oxide layer during pulse current pressure sintering,” Mater. Trans., 43, 1390–1397 (2005).
M. Omori, T. Hirai, Material and composite formation by spark plasma system (SPS), in: M. Miyake and M. Samandi, Proceedings of the First Symposium on Microwave, Plasma and Thermo-Chemical Processing of Advanced Materials, Osaka University (1997).
R.D.Li, T.C. Yuan, X.J. Liu, J.W. Wang, H. Wu, F.H. Zeng, and X.Z. Hou, “Microstructural evolution and sintering kinetics during spark plasma sintering of Fe and Al blended powder,” Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 27, Issue 7, 1594–1601 (2017).
W.A. Salandro, J.J. Jones, C. Bunget, L. Mears, and J.T. Roth, “The effect of electric current on metals,” Springer International Publishing, 37–54 (2015).
J. Narayan, “A new mechanism for field-assisted processing and flash sintering of materials,” Scr. Mater., 69, 107–111 (2013).
C.M. Tan and A. Roy, “Electromigration in ULSI interconnects,” Mater. Sci. Eng, R, 58, 3-75 (2007).
K. Hu, Q.X. Li, S.G. Qu, and Y.Y. Li, “Spark-Plasma Sintering of W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe Heavy Alloys: Densification and Grain Growth,” Mater. Trans. A, 44, 923-933 (2013).
D. Empl, L. Felberbaum, V. Laporte, D. Chatain, and A. Mortensen, “ Dihedral angles in Cu-1wt.% Pb: Grain boundary energy and grain boundary triple line effects,” Acta Mater., 57, 2527-2537 (2009).
S.Y. Xie, R.D. Li, T.C. Yuana, M. Zhang, M.B. Wang, L. Yin, and P. Cao, “Effect of phase transformation on densification kinetics and properties of spark plasma sintered Al0.7CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy,” Mater. Charact., 160, 11009 (2020).
C.B. Danisman, B. Yavas, O. Yucel, F. Sahin, and G. Goller, “Processing and characterization of spark plasma sintered TZM alloy,” J. Alloys Compd, 685, 860–868 (2016).
D.M. Liu, Y.H. Xiong, T. Troy, Y.Z. Zhou, C. Haines, J. Paras, D. Martin, D. Kapoor, J. Schoenung, and E. Lavernia, “Spark plasma sintering of cryomilled nanocrystalline Al alloy-Part II: influence of processing conditions on densification and properties,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 43, 340–350 (2012).
A. Chua, M. Brochu, and D. Bishop, “Spark plasma sintering of prealloyed aluminium powders,” Powder Metall., 58, 51-60 (2015).
C.K. Kim, S. Lee, S.Y. Shin, and D.H. Kim, “Effects of consolidation temperature and pressure on microstructures and mechanical properties of Cu-based bulk amorphous alloys consolidated by spark plasma sintering,” J. Alloys Compd., 453, 108-114 (2008).
M. Zadra, F. Casari, L. Girardini, A. Molinari, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of cp-titanium produced by spark plasma sintering,” Powder Metall., 51, 59-65 (2008).
I.U.H. Toor, J. Ahmed, M.A. Hussein, and N. Al-Aqeeli, “Optimization of process parameters for spark plasma sintering of nano-structured ferritic Fe–18Cr–2Si alloy,” Powder Technol., 299, 62–70 (2016).
M.I. Makena, M.B. Shongwe, M.M. Ramakokovhu, and P.A. Olubambi, “Effect of sintering parameters on densification, corrosion and wear behaviour of Ni–50Fe alloy prepared by spark plasma sintering,” J. Alloys Compd., 699, 1166–1179 (2017).
G.A. Sweet, M. Brochu, R.L. Hexemer Jr, I.W. Donaldson, and D.P. Bishop, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of air atomized aluminum powder consolidated via spark plasma sintering,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 608, 273–282 (2014).
T.H. De Keijser, J.I. Langford, E.J. Mittemeijer, and A.B.P. Vogels, “Use of the Voigt function in a single-line method for the analysis of X-ray diffraction line broadening,” J. Appl. Crystall., 15, 308–314 (1982).
G. Marnier, C. Keller, J. Noudem, and E. Hug, “Functional properties of a spark plasma sintered ultrafine-grained 316L steel,” Mater. Des., 63, 633–640 (2014).
D. Garbiec and P. Siwak, “Study on microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered Alumix 431 powder,” Powder Metall., 59, 242–248 (2016).
A.H. Barry, G. Dirras, F. Schoenstein, F. Tétard, and N. Jouini, “Noureddine Jouini, Microstructure and mechanical properties of bulk highly faulted fcc/hcp nanostructured cobalt microstructures,” Mater. Charact., 91, 26–33 (2014).
M. Pellizzari, A. Fedrizzi, and M. Zadra. “Influence of processing parameters and particle size on the properties of hot work and high speed tool steels by spark plasma sintering,” Mater. Des., 32, 1796–1805 (2011).
O. Ertorer, T. Topping, Y. Li, W. Moss, and E. Lavernia, “Nanostructured Ti consolidated via spark plasma sintering,” Mater. Trans. A, 42, 964–973 (2011).
M.B. Shongwe, M.M. Ramakokovhu, S. Diouf, M.O. Durowoju, B.A. Obadele, R. Sule, M.L. Lethabane, and P.A. Olubambi, “Effect of starting powder particle size and heating rate on spark plasma sintering of FeNi alloys,” J. Alloys Compd., 678, 241–248 (2016).
K. Hu, X.Q. Li, C. Yang, and Y.Y. Li, “Densification and microstructure evolution during SPS consolidation process in W–Ni–Fe system,” Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 21, 493–501 (2011).
R. Yamanoglu, W. Bradbury, E. Karakulak, E.A. Olevsky, and R.M. German, “Characterisation of nickel alloy powders processed by spark plasma sintering,” Powder Metall., 57, 380–386 (2014).
P. Unifantowicz, Z. Oksiuta, P. Olier, Y. de Carlan, and N. Baluc, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of an ODS RAF steel fabricated by hot extrusion or hot isostatic pressing,” Fusion Eng. Des., 86, 2413–2416 (2011).
D. Pazos, M. Suárez, A. Fernández, P. Fernández, I. Iturriza, and N. Ordás, “Microstructural comparison of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Fe-14Cr steels produced by HIP and SPS,” Fusion Eng. Des., 146, 2328–2333 (2019).
A. García-Junceda, E. Macía, D. Garbiec, M. Serrano, J. M. Torralba, and M. Campos, “Effect of Small Variations in Zr Content on the Microstructure and Properties of Ferritic ODS Steels Consolidated by SPS,” Metals, 10, 348 (2020).
M. Pellizzari, A. Fedrizzi, and M. Zadra, “Spark plasma Co-sintering of mechanically milled tool steel and high speed steel powders,” Materials, 9, 482 (2016).
A. Farid, A. Liaqat, P.Z. Feng, and A.S. Jawad, “Enhanced sintering, microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of 316L stainless steel with MoSi2 addition,” J. Alloys Compd., 509, 8794–8797 (2011).
N. Kurgan, “Effects of sintering atmosphere on microstructure and mechanical property of sintered powder metallurgy 316L stainless steel,” Mater. Des., 52, 995–998 (2013).
H. Fallahdoost, H. Khorsand, R. Eslami-Farsani, and E. Ganjeh, “On the tribological behavior of nanoalumina reinforced low alloy sintered steel,” Mater. Des., 57, 60–66 (2014).
D. Chaira, “Development of nano-structured duplex and ferritic stainless steels by pulverisette planetary milling followed by pressureless sintering,” Mater. Charact., 99, 220–229 (2015).
A. Almathami and M. Brochu, “Microstructure and transformation of Al-containing nanostructured 316L stainless steel coatings processed using spark plasma sintering,” J. Mater. Process. Technol., 210, 2119–2124 (2010),
Z.H. Hu, K.J. Ning, and K. Lu, “Study of spark plasma sintered nanostructured ferritic steel alloy with silicon carbide addition,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 670, 75-80 (2016).
S.R. Oke, O.O. Ige, O.E. Falodun, M.R. Mphahlele, and P.A. Olubambi, “Densification behavior of spark plasma sintered duplex stainless steel reinforced with TiN nanoparticles,” IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng., 430, 012034 (2018).
A. Mohammadzadeh, A.S. Namini, M. Azadbeh, and A. Motallebzadeh, “On the physical and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered pure Ti and Ti–TiB composite,” Mater. Res. Express, 5, 126512 (2018).
Z.G. Li, A.P. Dong, H. Xing, H. Xu, D.F. Du, T. Zhang, H. She, D.H. Wang, G.L. Zhu, and B.D. Sun, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of bimodal Ti–Bi alloys fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering for biomedical applications,” Mater. Charact., 161, 110134 (2020).
O.J. Akinribide, G.N. Mekgwe, B.A. Obadele, O.O. Ajibola, S.O. Akinwamide, and P.A. Olubambi, “Microstructural and phase evolution of spark plasma sintering of graphitized Ti(C0.9N0.1) composites,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 78, 164–169 (2019).
B.A. Obadele, O.E. Falodun, S.R. Oke, and P.A. Olubambi. “Spark plasma sintering behaviour of commercially pure titanium micro-alloyed with Ta–Ru,” Particul. Sci. Technol., 37, 890–896 (2019).
R. Dong, W.W. Zhu, C.C. Zhao, Y.W. Zhang, and F.Z. Ren, “Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Sliding Wear Behavior of Spark Plasma Sintered Ti–Cu Alloys,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 49, 6147 (2018).
Z.F. Liu, Z.H. Zhang, J.F. Lu, A.V. Korznikov, E. Korznikova, and F.C. Wang, “Effect of sintering temperature on microstructures and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered nanocrystalline aluminum,” Mater. Des., 64, 625–630 (2014).
C.O. Ujah, A.P.I. Popoola, O.M. Popoola, V.S. Aigbodion, “Influence of CNTs addition on the mechanical, microstructural, and corrosion properties of Al alloy using spark plasma sintering technique,” Int. J. Adv. Des. Manuf. Technol., 106, 2961–2969 (2020).
W.N.A.W. Muhammad, Z. Sajuri, Y. Mutoh, Y. Miyashita, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of magnesium composites prepared by spark plasma sintering technology,” J. Alloy. Comp., 509, 6021–6029 (2011).
C.S. Lee, H.C. Lee, G.H. Kimb, J.H. Hanc, and W.J. Kimd, “Design of Mg–6 wt.% Al alloy with high toughness and corrosion resistance prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering,” Mater. Charact, 158, 109995 (2019).
Y. Liu, Y.Z. Ma, W.S. Liu, Y.F. Huang, L. Wu, T. Wang, C. Liu, and L. Yang, “The mechanical properties and formation mechanism of Al/Mg composite interface prepared by spark plasma sintering under different sintering pressures,” Vacuum, 176, 109300 (2020).
C. Sun, X. Zhang, N.Q. Zhao, and C.N. He, “Influence of spark plasma sintering temperature on the microstructure and strengthening mechanisms of discontinuous three-dimensional graphene-like network reinforced Cu matrix composites,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 756, 82–91 (2019).
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Sun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang, “Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes,” Adv. Eng. Mater., 6, 299–303 (2004).
L. Liu, L.J. He, J.G. Qi, B. Wang, Z.F. Zhao, J. Shang, and Y. Zhang, “Effects of Sn element on microstructure and properties of SnxAl2.5FeCoNiCu multi-component alloys,” J. Alloy Compd., 654, 327– 332 (2016).
P.F. Zhou, D.H. Xiao, Z. Wu, and M. Song, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys produced by spark plasma sintering,” Mater. Res. Express, 6, 0865e7 (2019).
Y.C. Sun, B. Ke, Y.L. Li, K. Yang, M.Q. Yang, W. Ji, and Z.Y. Fu, “Phases, microstructures and mechanical properties of CoCrNiCuZn high-entropy alloy prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering,” Entropy, 21, 122 (2019).
Acknowledgements
The National Science Foundation of China supported this work (Grant No. 51374039), the Chinese Defense Advance Research Program of Science and Technology (Grant No. 41422010905), and the National Defense Foundation of China (Grant No. 6142902010603). The authors acknowledge Dr. Zhengyang Hu and Dr. Weiguo Wang for their help with discussions and suggestions during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Poroshkova Metallurgiya, Vol. 60, Nos. 7–8 (540), pp. 32–66, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X.Y., Zhang, Z.H., Cheng, X.W. et al. The Development and Application of Spark Plasma Sintering Technique in Advanced Metal Structure Materials: A Review. Powder Metall Met Ceram 60, 410–438 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-021-00254-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-021-00254-w