Abstract
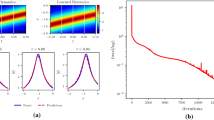
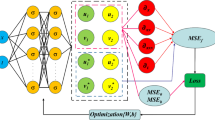
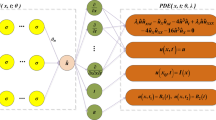
To enhance the precision and efficiency of result prediction, we proposed a parallel hard-constraint physics-informed neural networks (phPINN) by combining the parallel fully-connected neural network structure and the residual-based adaptive refinement method. We discussed the forward and inverse problems of the nonlinear Schrödinger–Maxwell–Bloch equation via the phPINN. In the forward problem, we predict five forms of soliton solutions and rogue wave dynamics under corresponding initial and boundary conditions; In the inverse problem, we predict the equation parameter using the training data with different noise intensities, initial values, and solution forms. The predicted parameters achieve a relative error of less than 1%. These results validate the effectiveness of the phPINN algorithm in solving forward and inverse problems of three-component coupled equations.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Raissi, M., Perdikaris, P., Karniadakis, G.E.: Physics-informed neural networks: a deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 378, 686–707 (2019)
Zhang, E., Dao, M., Karniadakis, G.E., Suresh, S.: Analyses of internal structures and defects in materials using physics-informed neural networks. Sci. Adv. 8, eabk0644 (2022)
Raissi, M., Yazdani, A., Karniadakis, G.E.: Hidden fluid mechanics: learning velocity and pressure fields from flow visualizations. Science 367, 1026–1030 (2020)
Zhang, R.-F., Bilige, S.: Bilinear neural network method to obtain the exact analytical solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations and its application to p-gBKP equation. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 3041–3048 (2019)
Wu, G.Z., Fang, Y., Kudryashov, N.A., Wang, Y.Y., Dai, C.Q.: Prediction of optical solitons using an improved physics-informed neural network method with the conservation law constraint. Chaos Soliton Fract. 159, 112143 (2022)
Zhu, B.W., Fang, Y., Liu, W., Dai, C.Q.: Predicting the dynamic process and model parameters of vector optical solitons under coupled higher-order effects via WL-tsPINN. Chaos Soliton Fract. 162, 112441 (2022)
Bo, W.-B., Wang, R.-R., Fang, Y., Wang, Y.-Y., Dai, C.-Q.: Prediction and dynamical evolution of multipole soliton families in fractional Schrodinger equation with the PT-symmetric potential and saturable nonlinearity. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 1577–1588 (2023)
Pu, J., Li, J., Chen, Y.: Solving localized wave solutions of the derivative nonlinear Schrödinger equation using an improved PINN method. Nonlinear Dyn. 105, 1723–1739 (2021)
Jiang, X., Wang, D., Fan, Q., Zhang, M., Lu, C., Lau, A.P.T.: Physics-informed neural network for nonlinear dynamics in fiber optics. Laser Photon. Rev. 16, 2100483 (2022)
Chen, Y., Lu, L., Karniadakis, G.E., Dal Negro, L.: Physics-informed neural networks for inverse problems in nano-optics and metamaterials. Opt. Express 28, 11618–11633 (2020)
Lin, S., Chen, Y.: A two-stage physics-informed neural network method based on conserved quantities and applications in localized wave solutions. J. Comput. Phys. 457, 111053 (2022)
Fang, Y., Wu, G.Z., Wen, X.K., Wang, Y.Y., Dai, C.Q.: Predicting certain vector optical solitons via the conservation-law deep-learning method. Opt. Laser Technol. 155, 108428 (2022)
Fang, Y., Wu, G.Z., Wang, Y.Y., Dai, C.Q.: Data-driven femtosecond optical soliton excitations and parameters discovery of the high-order NLSE using the PINN. Nonlinear Dyn. 105, 603–616 (2021)
Fang, Y., Han, H.B., Bo, W.B., Liu, W., Wang, B.H., Wang, Y.Y., Dai, C.Q.: Deep neural network for modeling soliton dynamics in the mode-locked laser. Opt Lett. 48, 779–782 (2023)
Fang, Y., Wu, G.Z., Kudryashov, N.A., Wang, Y.Y., Dai, C.Q.: Data-driven soliton solutions and model parameters of nonlinear wave models via the conservation-law constrained neural network method. Chaos Soliton Fract. 158, 112118 (2022)
Maimistov, A., Manykin, E.: Propagation of ultrashort optical pulses in resonant non-linear light guides. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 85, 1177–1181 (1983)
Yuan, F.: New exact solutions of the (2+1)-dimensional NLS–MB equations. Nonlinear Dyn. 107, 1141–1151 (2021)
Yuan, F.: The dynamics of the smooth positon and b-positon solutions for the NLS–MB equations. Nonlinear Dyn. 102, 1761–1771 (2020)
Marcucci, G., Pierangeli, D., Conti, C.: Theory of neuromorphic computing by waves: machine learning by rogue waves, dispersive shocks, and solitons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 093901 (2020)
Lu, L., Pestourie, R., Yao, W., Wang, Z., Verdugo, F., Johnson, S.G.: Physics-informed neural networks with hard constraints for inverse design. Siam J. Sci. Comput. 43, B1105–B1132 (2021)
Wen, X.K., Wu, G.Z., Liu, W., Dai, C.Q.: Dynamics of diverse data-driven solitons for the three-component coupled nonlinear Schrodinger model by the MPS-PINN method. Nonlinear Dyn. 109, 3041–3050 (2022)
Wu, G.-Z., Fang, Y., Wang, Y.-Y., Wu, G.-C., Dai, C.-Q.: Predicting the dynamic process and model parameters of the vector optical solitons in birefringent fibers via the modified PINN. Chaos Solitons Fractals 152, 111393 (2021)
Zhou, H., Juncai, P., Chen, Y.: Data-driven forward–inverse problems for the variable coefficients Hirota equation using deep learning method. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(16), 14667–14693 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08641-1
Lu, L., Meng, X., Mao, Z., Karniadakis, G.E.: DeepXDE: a deep learning library for solving differential equations. SIAM Rev. 63, 208–228 (2021)
O’neill, M.E.: PCG: a family of simple fast space-efficient statistically good algorithms for random number generation. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. (2014)
He, J.-S., Cheng, Y., Li, Y.-S.: The Darboux transformation for NLS–MB equations. Commun. Theor. Phys. 38, 493–496 (2002)
Guan, Y.-Y., Tian, B., Zhen, H.-L., Wang, Y.-F., Chai, J.: Soliton solutions of a generalised nonlinear Schrödinger–Maxwell–Bloch system in the erbium-doped optical fibre. Z. Naturfor. A 71, 241–247 (2016)
Bai, X.-D., Zhang, D.: Search for rogue waves in Bose–Einstein condensates via a theory-guided neural network. Phys. Rev. E 106, 025305 (2022)
Zhang, R.-F., Li, M.-C., Yin, H.-M.: Rogue wave solutions and the bright and dark solitons of the (3+1)-dimensional Jimbo-Miwa equation. Nonlinear Dyn. 103, 1071–1079 (2021)
He, J.S., Xu, S.W., Porsezian, K.: New types of rogue wave in an erbium-doped fibre system. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 81, 033002 (2012)
Hou, J., Li, Y., Ying, S.: Enhancing PINNs for solving PDEs via adaptive collocation point movement and adaptive loss weighting. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(16), 15233–15261 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08654-w
Zhang, R., Su, J., Feng, J.: Solution of the Hirota equation using a physics-informed neural network method with embedded conservation laws. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 13399–13414 (2023)
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12261131495); the Scientific Research and Developed Fund of Zhejiang A&F University (Grant No. 2021FR0009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, SY., Zhou, Q. & Liu, W. Prediction of soliton evolution and equation parameters for NLS–MB equation based on the phPINN algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 18401–18417 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08824-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08824-w