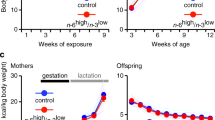
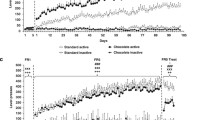
Abstract
Maternal nutritional programming by energy-dense foods leads to the transgenerational heritance of addiction-like behavior. Exposure to energy-dense foods also activates systemic and central inflammation in the offspring. This study aimed to characterize pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine profiles in blood and their correlation to the transgenerational heritance of the addiction-like behavior in rats. F1 offspring of male Wistar diagnosed with addiction-like behavior were mated with virgin females to generate the F2 and the F3 offspring, respectively. Diagnosis of addiction-like behavior was performed by the operant training schedule (FR1, FR5 and PR) and pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine profiles in blood were measured by multiplex platform. Multiple linear models between behavior, fetal programming by diet and pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine profiles were performed. We found that the addiction-like behavior found in the F1 male offspring exposed to energy-dense food (cafeteria, CAF) diet during fetal programing is transgenerational inherited to the F2 and F3 generations. Blood from addiction-like behavior subjects of F2 and F3 generations exposed to CAF diet during maternal programming showed decrease in the anti-inflammatory IL-10 in the plasma. Conversely, decreased levels of the pro-inflammatory MCP-1 was identified in non-addiction-like subjects. No changes were found in plasmatic TNF-α levels in the F2 and F3 offspring of non-addiction-like and addiction-like subjects. Finally, biological modeling between IL-10 or MCP-1 plasma levels and prenatal diet exposure on operant training responses confirmed an association of decreased IL-10 levels on addiction-like behavior in the F2 and F3 generations. Globally, we identified decreased anti-inflammatory IL-10 cytokine in the blood of F2 and F3 offspring subjects diagnosed with addiction-like behavior for food rewards.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trujillo-Villarreal LA, Romero-Díaz VJ, Marino-Martínez IA et al (2021) Maternal cafeteria diet exposure primes depression-like behavior in the offspring evoking lower brain volume related to changes in synaptic terminals and gliosis. Transl Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-020-01157-x
de la Garza AL, Garza-Cuellar MA, Silva-Hernandez IA et al (2019) Maternal flavonoids intake reverts depression-like behaviour in rat female offspring. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030572
Glendining KA, Fisher LC, Jasoni CL (2018) Maternal high fat diet alters offspring epigenetic regulators, amygdala glutamatergic profile and anxiety. Psychoneuroendocrinology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.06.015
Camacho A, Montalvo-Martinez L, Cardenas-Perez RE et al (2017) Obesogenic diet intake during pregnancy programs aberrant synaptic plasticity and addiction-like behavior to a palatable food in offspring. Behav Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.05.014
Peleg-Raibstein D, Sarker G, Litwan K et al (2016) Enhanced sensitivity to drugs of abuse and palatable foods following maternal overnutrition. Transl Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.176
Cruz-Carrillo G, Montalvo-Martínez L, Cárdenas-Tueme M et al (2020) Fetal programming by methyl donors modulates central inflammation and prevents food addiction-like behavior in rats. Front Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00452
Teegarden SL, Scott AN, Bale TL (2009) Early life exposure to a high fat diet promotes long-term changes in dietary preferences and central reward signaling. Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.05.029
Naef L, Moquin L, Dal Bo G et al (2011) Maternal high-fat intake alters presynaptic regulation of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and increases motivation for fat rewards in the offspring. Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.12.037
Koob GF, Volkow ND (2016) Neurobiology of addiction: a neurocircuitry analysis. The Lancet Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(16)00104-8
Sarker G, Berrens R, von Arx J et al (2018) Transgenerational transmission of hedonic behaviors and metabolic phenotypes induced by maternal overnutrition. Transl Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-018-0243-2
Chen Q, Yan M, Cao Z et al (2016) Sperm tsRNAs contribute to intergenerational inheritance of an acquired metabolic disorder. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad7977
Sarker G, Peleg-Raibstein D (2019) Maternal overnutrition induces long-term cognitive deficits across several generations. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010007
Sarker G, Litwan K, Kastli R, Peleg-Raibstein D (2019) Maternal overnutrition during critical developmental periods leads to different health adversities in the offspring: relevance of obesity, addiction and schizophrenia. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53652-x
Sarker G, Sun W, Rosenkranz D et al (2019) Maternal overnutrition programs hedonic and metabolic phenotypes across generations through sperm tsRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820810116
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Shi J et al (2018) Dnmt2 mediates intergenerational transmission of paternally acquired metabolic disorders through sperm small non-coding RNAs. Nat Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0087-2
Tse E, Helbig KJ, Van Der Hoek K et al (2015) Fatty acids induce a pro-inflammatory gene expression profile in Huh-7 cells that attenuates the anti-HCV action of interferon. J Interf Cytokine Res. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2014.0165
Wang Z, Liu D, Wang F et al (2012) Saturated fatty acids activate microglia via Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB signalling. Br J Nutr 107:229–241. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114511002868
Milanski M, Degasperi G, Coope A et al (2009) Saturated fatty acids produce an inflammatory response predominantly through the activation of TLR4 signaling in hypothalamus: Implications for the pathogenesis of obesity. J Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2760-08.2009
Milanski M, Arruda AP, Coope A et al (2012) Inhibition of hypothalamic inflammation reverses diet-induced insulin resistance in the liver. Diabetes 61:1455–1462. https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-0390
Roepke TA, Yasrebi A, Villalobos A et al (2017) Loss of ERα partially reverses the effects of maternal high-fat diet on energy homeostasis in female mice. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06560-x
Matuszewska J, Zalewski T, Klimaszyk A et al (2021) Mothers’ cafeteria diet induced sex-specific changes in fat content, metabolic profiles, and inflammation outcomes in rat offspring. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-97487-x
Bordeleau M, Lacabanne C, Fernández De Cossío L et al (2020) Microglial and peripheral immune priming is partially sexually dimorphic in adolescent mouse offspring exposed to maternal high-fat diet. J Neuroinflammation. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01914-1
Graf AE, Lallier SW, Waidyaratne G et al (2016) Maternal high fat diet exposure is associated with increased hepcidin levels, decreased myelination, and neurobehavioral changes in male offspring. Brain Behav Immun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.08.005
Segovia SA, Vickers MH, Zhang XD et al (2015) Maternal supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid in the setting of diet-induced obesity normalises the inflammatory phenotype in mothers and reverses metabolic dysfunction and impaired insulin sensitivity in offspring. J Nutr Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.07.013
Bilbo SD, Tsang V (2010) Enduring consequences of maternal obesity for brain inflammation and behavior of offspring. FASEB J. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.09-144014
Yuan N, Chen Y, Xia Y et al (2019) Inflammation-related biomarkers in major psychiatric disorders: a cross-disorder assessment of reproducibility and specificity in 43 meta-analyses. Psychiatry Transl. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0570-y
Alfonso-Loeches S, Pascual-Lucas M, Blanco AM et al (2010) Pivotal role of TLR4 receptors in alcohol-induced neuroinflammation and brain damage. J Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0976-10.2010
Hofford RS, Russo SJ, Kiraly DD (2019) Neuroimmune mechanisms of psychostimulant and opioid use disorders. Eur J Neurosci 50(3):2562–2573
Schwarz JM, Smith SH, Bilbo SD (2013) FACS analysis of neuronal-glial interactions in the nucleus accumbens following morphine administration. Psychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3180-z
Lewitus GM, Konefal SC, Greenhalgh AD et al (2016) Microglial TNF-α suppresses cocaine-induced plasticity and behavioral sensitization. Neuron. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.03.030
Snider SE, Hendrick ES, Beardsley PM (2013) Glial cell modulators attenuate methamphetamine self-administration in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 701:124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.01.016
Attarzadeh-Yazdi G, Arezoomandan R, Haghparast A (2014) Minocycline, an antibiotic with inhibitory effect on microglial activation, attenuates the maintenance and reinstatement of methamphetamine-seeking behavior in rat. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.04.008
Tanda G, Mereu M, Hiranita T et al (2016) Lack of specific involvement of (+)-Naloxone and (+)-Naltrexone on the reinforcing and neurochemical effects of cocaine and opioids. Neuropsychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2016.91
Chen J-X, Huang K-M, Liu M et al (2017) Activation of TLR4/STAT3 signaling in VTA contributes to the acquisition and maintenance of morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Behav Brain Res 335:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.08.022
Brown KT, Levis SC, O’Neill CE et al (2018) Innate immune signaling in the ventral tegmental area contributes to drug-primed reinstatement of cocaine seeking. Brain Behav Immun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.08.012
Cardenas-Perez RE, Fuentes-Mera L, De La Garza AL et al (2018) Maternal overnutrition by hypercaloric diets programs hypothalamic mitochondrial fusion and metabolic dysfunction in rat male offspring. Nutr Metab. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-018-0279-6
Maldonado-Ruiz R, Cárdenas-Tueme M, Montalvo-Martínez L et al (2019) Priming of hypothalamic ghrelin signaling and microglia activation exacerbate feeding in rats’ offspring following maternal overnutrition. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061241
Paxinos George WC (2007) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates 6th Edition, 6th Editio. Academic Press, Cambridge
Bale TL (2015) Epigenetic and transgenerational reprogramming of brain development. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(6):332–344
Montalvo-Martínez L, Maldonado-Ruiz R, Cárdenas-Tueme M et al (2018) Maternal overnutrition programs central inflammation and addiction-like behavior in offspring. Int Biomed Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8061389
Maldonado-Ruiz R, Garza-Ocañas L, Camacho A (2019) Inflammatory domains modulate autism spectrum disorder susceptibility during maternal nutritional programming. Neurochem Int 126:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2019.03.009
Zamberletti E, Gabaglio M, Prini P et al (2015) Cortical neuroinflammation contributes to long-term cognitive dysfunctions following adolescent delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol treatment in female rats. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.09.021
Lacagnina MJ, Kopec AM, Cox SS et al (2017) Opioid self-administration is attenuated by early-life experience and gene therapy for anti-inflammatory IL-10 in the nucleus accumbens of male rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.82
Patel RR, Wolfe SA, Bajo M et al (2021) IL-10 normalizes aberrant amygdala GABA transmission and reverses anxiety-like behavior and dependence-induced escalation of alcohol intake. Prog Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101952
Hutchinson MR, Northcutt AL, Hiranita T et al (2012) Opioid activation of toll-like receptor 4 contributes to drug reinforcement. J Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0684-12.2012
Northcutt AL, Hutchinson MR, Wang X et al (2015) DAT isn’t all that: cocaine reward and reinforcement require toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Mol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.177
Frau L, Simola N, Plumitallo A, Morelli M (2013) Microglial and astroglial activation by 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in mice depends on S(+) enantiomer and is associated with an increase in body temperature and motility. J Neurochem. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12060
Pascual M, Montesinos J, Guerri C (2018) Role of the innate immune system in the neuropathological consequences induced by adolescent binge drinking. J Neurosci Res 96(5):765–780
Maldonado-Ruiz R, Trujillo-Villarreal LA, Montalvo-Martínez L et al (2022) MCP-1 signaling disrupts social behavior by modulating brain volumetric changes and microglia morphology. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02649-7
Trettel F, Di Castro MA, Limatola C (2020) Chemokines: key molecules that orchestrate communication among neurons, microglia and astrocytes to preserve brain function. Neuroscience 439:230–240
Tian DS, Peng J, Murugan M et al (2017) Chemokine CCL2-CCR2 signaling induces neuronal cell death via STAT3 activation and IL-1β production after status epilepticus. J Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0315-17.2017
Dong N, Chang L, Wang B, Chu L (2014) Retinal neuronal MCP-1 induced by AGEs stimulates TNF-α expression in rat microglia via p38, ERK, and NF-κB pathways. Mol Vis 20:616
Pierce RC, Fant B, Swinford-Jackson SE et al (2018) Environmental, genetic and epigenetic contributions to cocaine addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 43:1471–1480
Le Q, Yan B, Yu X et al (2017) Drug-seeking motivation level in male rats determines offspring susceptibility or resistance to cocaine-seeking behaviour. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15527
Yamamoto DJ, Nelson AM, Mandt BH et al (2013) Rats classified as low or high cocaine locomotor responders: a unique model involving striatal dopamine transporters that predicts cocaine addiction-like behaviors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:1738–1753
Mathers JC, Strathdee G, Relton CL (2010) Induction of epigenetic alterations by dietary and other environmental factors. Adv Genet 71:3–39
Christ A, Günther P, Lauterbach MAR et al (2018) Western diet triggers NLRP3-dependent innate immune reprogramming. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.013
Arpon A, Riezu-Boj JI, Milagro FI et al (2016) Adherence to Mediterranean diet is associated with methylation changes in inflammation-related genes in peripheral blood cells. J Physiol Biochem 73:445–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0552-6
Nestler EJ (2014) Epigenetic mechanisms of drug addiction. Neuropharmacology 76:259–268
Laplant Q, Vialou V, Covington HE et al (2010) Dnmt3a regulates emotional behavior and spine plasticity in the nucleus accumbens. Nat Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2619
Robison AJ, Nestler EJ (2011) Transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:623–637
Szyf M (2015) Nongenetic inheritance and transgenerational epigenetics. Trends Mol Med 21:134–144
Jasiulionis MG (2018) Abnormal epigenetic regulation of immune system during aging. Front Immunol 9:197
Zhang Q, Cao X (2019) Epigenetic regulation of the innate immune response to infection. Nat Rev Immunol 19:417–432
Li X, Zhang Q, Shi Q et al (2017) Demethylase Kdm6a epigenetically promotes IL-6 and IFN-β production in macrophages. J Autoimmun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2017.02.007
Kleinnijenhuis J, Quintin J, Preijers F et al (2012) Bacille Calmette-Guérin induces NOD2-dependent nonspecific protection from reinfection via epigenetic reprogramming of monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1202870109
Liu GX, Wei JY, Liu M et al (2020) Epigenetic upregulation of hippocampal CXCL12 contributes to context spatial memory-associated morphine conditioning. Brain Behav Immun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.11.009
Lacal I, Ventura R (2018) Epigenetic inheritance: concepts mechanisms and perspectives. Front Mol Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00292
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Council of Science and Technology in Mexico (CONACYT) (Grant number: 255317), 708452 CONACYT for L. J. Montalvo-Martínez, 855559 CONACYT for G. Cruz-Carrillo, 573686 CONACYT for R. Maldonado-Ruiz, 650620 CONACYT for M. Cárdenas-Tueme, 781759 CONACYT for L.A. Trujillo-Villarreal. and IBRO-LARC 2020 for Alberto Camacho-Morales.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montalvo-Martínez, L., Cruz-Carrillo, G., Maldonado-Ruiz, R. et al. Transgenerational Susceptibility to Food Addiction-Like Behavior in Rats Associates to a Decrease of the Anti-Inflammatory IL-10 in Plasma. Neurochem Res 47, 3093–3103 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03660-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03660-7