Abstract
Purpose
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has revealed the unique genetic characteristics of leptomeningeal metastasis (LM) from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the research in this area is still very limited.
Methods
Patients with LM from NSCLC (n = 80) were retrospectively analyzed. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in CSF was tested by next-generation sequencing (NGS), with paired extracranial tissue or plasma samples included for comparison. An independent non-LM cohort (n = 100) was also analyzed for comparative purposes. Clinical outcomes were compared with Kaplan–Meier log-rank test and Cox proportional hazards methodologies.
Results
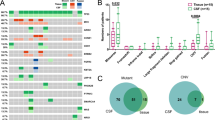
An overwhelming 93.8% of patients carried druggable mutations in NSCLC LM, with EGFR (78.8%) being the most prevalent. Notably, 4 patients who tested negative for driver genes in extracranial samples surprisingly showed EGFR mutations in their CSF and subsequently benefited from targeted therapy. There was a clear difference in genetic profiles between CSF and extracranial samples, with CSF showing more driver gene detections, increased Copy Number Variations (CNVs), and varied resistance mechanisms among individuals. Abnormalities in cell-cycle regulatory molecules were highly enriched in LM (50.9% vs 31.0%, p = 0.017), and CDKN2A/2B deletions were identified as an independent poor prognostic factor for LM patients, with a significant reduction in median OS (p = 0.013), supported by multivariate analysis (HR 2.63, 95% CI 1.32–5.26, p = 0.006).
Conclusions
CSF-based ctDNA analysis is crucial for detecting and characterizing genetic alterations in NSCLC LM. The distinct genetic profiles in CSF and extracranial tissues emphasize the need for personalized treatment approaches.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting this study’s findings are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Remon J, Le Rhun E, Besse B (2017) Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients: A continuing challenge in the personalized treatment era. Cancer Treat Rev 53:128–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.12.006
Li YS, Jiang BY, Yang JJ, Tu HY, Zhou Q, Guo WB, Yan HH, Wu YL (2016) Leptomeningeal Metastases in Patients with NSCLC with EGFR Mutations. J Thorac Oncol 11:1962–1969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.06.029
Zheng MM, Li YS, Jiang BY, Tu HY, Tang WF, Yang JJ, Zhang XC, Ye JY, Yan HH, Su J, Zhou Q, Zhong WZ, Yang XN, Guo WB, Chuai S, Zhang Z, Chen HJ, Wang Z, Liu C, Wu YL (2019) Clinical utility of cerebrospinal fluid cell-free DNA as liquid biopsy for leptomeningeal metastases in ALK-rearranged NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol 14:924–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.01.007
Ahn MJ, Chiu CH, Cheng Y, Han JY, Goldberg SB, Greystoke A, Crawford J, Zhao Y, Huang X, Johnson M, Vishwanathan K, Yates JWT, Brown AP, Mendoza-Naranjo A, Mok T (2020) Osimertinib for patients with leptomeningeal metastases associated with EGFR T790M-positive advanced NSCLC: the aura leptomeningeal metastases analysis. J Thorac Oncol 15:637–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.12.113
Clarke JL, Perez HR, Jacks LM, Panageas KS, Deangelis LM (2010) Leptomeningeal metastases in the MRI era. Neurology 74:1449–1454. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181dc1a69
Le Rhun E, Weller M, Brandsma D, Van den Bent M, de Azambuja E, Henriksson R, Boulanger T, Peters S, Watts C, Wick W, Wesseling P, Rudà R, Preusser M (2017) EANO-ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumours. Ann Oncol 28:iv84–iv99. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx221
Ramkissoon LA, Pegram W, Haberberger J, Danziger N, Lesser G, Strowd R, Dahiya S, Cummings TJ, Bi WL, Abedalthagafi M, Sathyan P, McGregor K, Reddy P, Severson E, Williams E, Lin D, Edgerly C, Huang RSP, Hemmerich A, Creeden J, Brown C, Venstrom J, Hegde P, Ross JS, Alexander BM, Elvin J, Ramkissoon SH (2020) Genomic profiling of circulating tumor DNA from cerebrospinal fluid to guide clinical decision making for patients with primary and metastatic brain tumors. Front Neurol 11:544680. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.544680
Pentsova EI, Shah RH, Tang J, Boire A, You D, Briggs S, Omuro A, Lin X, Fleisher M, Grommes C, Panageas KS, Meng F, Selcuklu SD, Ogilvie S, Distefano N, Shagabayeva L, Rosenblum M, DeAngelis LM, Viale A, Mellinghoff IK, Berger MF (2016) Evaluating cancer of the central nervous system through next-generation sequencing of cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Oncol 34:2404–2415. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2016.66.6487
Li YS, Jiang BY, Yang JJ, Zhang XC, Zhang Z, Ye JY, Zhong WZ, Tu HY, Chen HJ, Wang Z, Xu CR, Wang BC, Du HJ, Chuai S, Han-Zhang H, Su J, Zhou Q, Yang XN, Guo WB, Yan HH, Liu YH, Yan LX, Huang B, Zheng MM, Wu YL (2018) Unique genetic profiles from cerebrospinal fluid cell-free DNA in leptomeningeal metastases of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer: a new medium of liquid biopsy. Ann Oncol 29:945–952. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdy009
Yang H, Wen L, Zhao C, Chen J, Zhou Z, Zhou C, Cai L, Zhou C (2022) Cerebrospinal fluid-derived circulating tumor DNA is more comprehensive than plasma in NSCLC patients with leptomeningeal metastases regardless of extracranial evolution. Heliyon 8:e12374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12374
Ai X, Cui J, Zhang J, Chen R, Lin W, Xie C, Liu A, Zhang J, Yang W, Hu X, Hu X, Zhao Q, Rao C, Zang YS, Ning R, Li P, Chang L, Yi X, Lu S (2021) Clonal architecture of EGFR mutation predicts the efficacy of EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced NSCLC: a prospective multicenter study (NCT03059641). Clin Cancer Res 27:704–712. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-20-3063
Álvarez-Fernández M, Malumbres M (2020) Mechanisms of sensitivity and resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition. Cancer Cell 37:514–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2020.03.010
Passaro A, Jänne PA, Mok T, Peters S (2021) Overcoming therapy resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Nat Cancer 2:377–391. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-021-00195-8
Xu H, Chen H, Kong J, Zhang Y, Liu S, Yang G, Yang L, Wang Y (2021) Osimertinib for the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with leptomeningeal metastases and different T790M status. Ann Transl Med 9:937. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-1249
Yang H, Cai L, Zhang Y, Tan H, Deng Q, Zhao M, Xu X (2014) Sensitive detection of EGFR mutations in cerebrospinal fluid from lung adenocarcinoma patients with brain metastases. J Mol Diagn 16:558–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoldx.2014.04.008
Nanjo S, Arai S, Wang W, Takeuchi S, Yamada T, Hata A, Katakami N, Okada Y, Yano S (2017) MET copy number gain is associated with gefitinib resistance in leptomeningeal carcinomatosis of EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 16:506–515. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-16-0522
Escudero L, Martínez-Ricarte F, Seoane J (2021) ctDNA-Based liquid biopsy of cerebrospinal fluid in brain cancer. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13091989
Bronkhorst AJ, Ungerer V, Holdenrieder S (2019) The emerging role of cell-free DNA as a molecular marker for cancer management. Biomol Detect Quantif 17:100087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bdq.2019.100087
Li YS, Zheng MM, Jiang BY, Tu HY, Yang JJ, Zhang XC, Wu YL (2020) Association of cerebrospinal fluid tumor DNA genotyping with survival among patients with lung adenocarcinoma and central nervous system metastases. JAMA Netw Open 3:e209077. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.9077
Song Y, Liu P, Huang Y, Guan Y, Han X, Shi Y (2019) Osimertinib quantitative and gene variation analyses in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of a non-small cell lung cancer patient with leptomeningeal metastases. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 19:666–673. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568009618666181017114111
Shi H, Hugo W, Kong X, Hong A, Koya RC, Moriceau G, Chodon T, Guo R, Johnson DB, Dahlman KB, Kelley MC, Kefford RF, Chmielowski B, Glaspy JA, Sosman JA, van Baren N, Long GV, Ribas A, Lo RS (2014) Acquired resistance and clonal evolution in melanoma during BRAF inhibitor therapy. Cancer Discov 4:80–93. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-13-0642
Testa U, Castelli G, Pelosi E (2018) Lung cancers: molecular characterization, clonal heterogeneity and evolution, and cancer stem cells. Cancers 10:248
Lim Z-F, Ma PC (2019) Emerging insights of tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance mechanisms in lung cancer targeted therapy. J Hematol Oncol 12:134. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0818-2
Zheng MM, Li YS, Tu HY, Jiang BY, Yang JJ, Zhou Q, Xu CR, Yang XR, Wu YL (2021) Genotyping of cerebrospinal fluid associated with osimertinib response and resistance for leptomeningeal metastases in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol 16:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2020.10.008
Ahn ER, Mangat PK, Garrett-Mayer E, Halabi S, Dib EG, Haggstrom DE, Alguire KB, Calfa CJ, Cannon TL, Crilley PA, Gaba AG, Marr AS, Sangal A, Thota R, Antonelli KR, Islam S, Rygiel AL, Bruinooge SS, Schilsky RL (2020) Palbociclib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer with CDKN2A alterations: results from the targeted agent and profiling utilization registry study. JCO Precis Oncol 4:757–766. https://doi.org/10.1200/po.20.00037
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the staff of all centers for their assistance in carrying out this study. Funding agencies had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or manuscript preparation.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province [grant number 2022J01431], National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 82072565], National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 82372954].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QM and XZ Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing– original draft, Project administration. QZ, ZZ, SY and YL Sample collection. XZ, QM, KJ, YX, SW, BW and HW Data curation, Methodology. GL Conceptualization, Resources, Data curation, Formal analysis, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Validation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing– review & editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All the authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Fujian Cancer Hospital (SQ2017-015-01) with an exemption of informed consent.
Consent to participate
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in 2013).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11060_2023_4520_MOESM5_ESM.docx
Supplementary file5 (DOCX 18 KB) Upon careful review, we have noticed an error in the title of this supplementary tables. The correct title should be: “Table S3 Treatment of individual patients from wild-type to EGFR mutation.” Therefore, please change the title from “Table S2” to “Table S3.”
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, Q., Zheng, X., Li, L. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid circulating tumor DNA contributes to the detection and characterization of leptomeningeal metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. J Neurooncol 165, 517–525 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-023-04520-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-023-04520-2