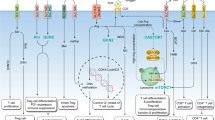
Abstract
Macrophage receptor with collagen structure (MARCO) is a member of scavenger receptor class A (SR-A) and shares structural and functional similarities with SR-A1. In recent years, many studies have shown that MARCO can trigger an immune response and has therapeutic potential as a target for immunotherapy. Studies have shown that alterations in MARCO expression following pathogen infection cause changes in the functions of innate and adaptive immune cells, including macrophages, dendritic cells, B cells, and T cells, affecting the body’s immune response to invading pathogens; thus, MARCO plays a crucial role in triggering the immune response, bridging innate and adaptive immunity, and eliminating pathogens. This paper is a comprehensive summary of the recent research on MARCO. This review focuses on the multiple functions of MARCO, including adhesion, migration, phagocytosis, and cytokine secretion with special emphasis on the complex interactions between MARCO and various types of cells involved in the immune response, as well as possible immune-related mechanisms. In summary, in this review, we discuss the structure and function of MARCO and its role in the immune response and highlight the therapeutic potential of MARCO as a target for immunotherapy. We hope that this review provides a theoretical basis for future research on MARCO.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
Abbreviations
- MARCO:
-
Macrophage Receptor with Collagen Structure
- SR-A:
-
scavenger receptor class A
- PAMPs:
-
pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- PRRs:
-
pattern recognition receptors
- TLRs:
-
Toll-like receptors
- SRs:
-
scavenger receptors
- SRCR:
-
scavenger receptor cysteine rich
- TNFα:
-
tumor necrosis factor alpha
- IFN-γ:
-
interferon-gamma
References
Hirayama D, Iida T, Nakase H (2017) The phagocytic function of macrophage-enforcing Innate immunity and tissue homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci 19:92. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010092
Fearon DT, Locksley RM (1996) The instructive role of Innate Immunity in the Acquired Immune Response. Science 272:50–54. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.272.5258.50
Gareev I, de Jesus Encarnacion Ramirez M, Goncharov E et al (2023) MiRNAs and lncRNAs in the regulation of innate immune signaling. Non-Coding RNA Res 8:534–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.07.002
Ackermann M, Dragon AC, Lachmann N (2020) The Immune-Modulatory properties of iPSC-Derived Antigen-presenting cells. Transfus Med Hemotherapy 47:444–453. https://doi.org/10.1159/000512721
Cheok YY, Tan GMY, Lee CYQ et al (2022) Innate immunity crosstalk with Helicobacter pylori: Pattern Recognition receptors and Cellular responses. Int J Mol Sci 23:7561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147561
Linares-Alcántara E, Mendlovic F (2022) Scavenger receptor A1 Signaling pathways affecting macrophage functions in Innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Invest 51:1725–1755. https://doi.org/10.1080/08820139.2021.2020812
PrabhuDas MR, Baldwin CL, Bollyky PL et al (2017) A Consensus definitive classification of scavenger receptors and their roles in Health and Disease. J Immunol 198:3775–3789. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1700373
Elomaa O, Kangas M, Sahlberg C et al (1995) Cloning of a novel bacteria-binding receptor structurally related to scavenger receptors and expressed in a subset of macrophages. Cell 80:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(95)90514-6
Elomaa O, Sankala M, Pikkarainen T et al (1998) Structure of the human macrophage MARCO receptor and characterization of its Bacteria-binding region. J Biol Chem 273:4530–4538. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.8.4530
Elshourbagy NA, Li X, Terrett J et al (2000) Molecular characterization of a human scavenger receptor, human MARCO. Eur J Biochem 267:919–926. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01077.x
Sankala M, Bra¨nnstro¨m A, Schulthess T et al (2002) Characterization of recombinant soluble macrophage scavenger receptor MARCO. J Biol Chem 277:33378–33385. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M204494200
Bowdish DME, Gordon S (2009) Conserved domains of the class A scavenger receptors: evolution and function. Immunol Rev 227:19–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00728.x
Novakowski KE, Huynh A, Han S et al (2016) A naturally occurring transcript variant of MARCO reveals the SRCR domain is critical for function. Immunol Amp Cell Biol 94:646–655. https://doi.org/10.1038/icb.2016.20
Brännström A, Sankala M, Tryggvason K, Pikkarainen T (2002) Arginine residues in Domain V have a central role for Bacteria-binding activity of macrophage scavenger receptor MARCO. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:1462–1469. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2002.6378
Palecanda A, Paulauskis J, Al-Mutairi E et al (1999) Role of the scavenger receptor MARCO in Alveolar Macrophage binding of Unopsonized Environmental particles. J Exp Med 189:1497–1506. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.189.9.1497
Arredouani M, Yang Z, Ning Y et al (2004) The scavenger receptor MARCO is required for Lung Defense against Pneumococcal Pneumonia and Inhaled particles. J Exp Med 200:267–272. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20040731
Arredouani MS, Palecanda A, Koziel H et al (2005) MARCO is the major binding receptor for unopsonized particles and Bacteria on human alveolar macrophages. J Immunol 175:6058–6064. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.175.9.6058
Hamilton RF, Thakur SA, Mayfair JK, Holian A (2006) MARCO mediates silica uptake and toxicity in alveolar macrophages from C57BL/6 mice. J Biol Chem 281:34218–34226. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M605229200
Dahl M, Bauer AK, Arredouani M et al (2007) Protection against inhaled oxidants through scavenging of oxidized lipids by macrophage receptors MARCO and SR-AI/II. J Clin Invest 117:757–764. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI29968
Yang M, Qian X, Wang N et al (2019) Inhibition of MARCO ameliorates silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Toxicol Lett 301:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.10.031
Cai T, Xu L, Xia D et al (2022) Polyguanine alleviated autoimmune hepatitis through regulation of macrophage receptor with collagenous structure and TLR4-TRIF‐NF‐κB signalling. J Cell Mol Med 26:5690–5701. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.17599
Tsay H-J, Huang Y-C, Chen Y-J et al (2016) Identifying N-linked glycan moiety and motifs in the cysteine-rich domain critical for N-glycosylation and intracellular trafficking of SR-AI and MARCO. J Biomed Sci 23:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-016-0244-5
La Fleur L, Boura VF, Alexeyenko A et al (2018) Expression of scavenger receptor MARCO defines a targetable tumor-associated macrophage subset in non‐small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 143:1741–1752. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31545
Grolleau A, Misek DE, Kuick R et al (2003) Inducible expression of macrophage receptor Marco by dendritic cells following phagocytic uptake of dead cells uncovered by Oligonucleotide Arrays. J Immunol 171:2879–2888. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.171.6.2879
Thier K, Möckel M, Palitzsch K et al (2018) Entry of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 into Epidermis and dermal fibroblasts is Independent of the scavenger receptor MARCO. J Virol 92:e00490–e00418. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00490-18
Song Q, Wang X-Q, Holmes TR et al (2021) Epidermal SR-A complexes are lipid raft based and promote nucleic acid nanoparticle uptake. J Invest Dermatol 141:1428–1437e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2020.10.027
Canton J, Neculai D, Grinstein S (2013) Scavenger receptors in homeostasis and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 13:621–634. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3515
Kanno S, Furuyama A, Hirano S (2007) A murine scavenger receptor MARCO recognizes polystyrene nanoparticles. Toxicol Sci 97:398–406. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfm050
Lara S, Perez-Potti A, Herda LM et al (2018) Differential Recognition of Nanoparticle Protein Corona and modified low-density lipoprotein by macrophage receptor with Collagenous Structure. ACS Nano 12:4930–4937. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b02014
Alberts A, Klingberg A, Hoffmeister L et al (2020) Binding of macrophage receptor MARCO, LDL, and LDLR to Disease-Associated Crystalline structures. Front Immunol 11:596103. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.596103
Krieger M (1992) Molecular flypaper and atherosclerosis: structure of the macrophage scavenger receptor. Trends Biochem Sci 17:141–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/0968-0004(92)90322-z
Son K, Miyasaki K, Salter B et al (2023) Autoantibody-mediated macrophage dysfunction in patients with severe asthma with Airway infections. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 207:427–437. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202206-1183OC
Józefowski S, Sulahian TH, Arredouani M, Kobzik L (2006) Role of scavenger receptor MARCO in macrophage responses to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. J Leukoc Biol 80:870–879. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0705357
Kodama T, Doi T, Suzuki H et al (1996) Collagenous macrophage scavenger receptors. Curr Opin Lipidol 7:287–291. https://doi.org/10.1097/00041433-199610000-00005
Suzuki H, Kurihara Y, Takeya M et al (1997) A role for macrophage scavenger receptors in atherosclerosis and susceptibility to infection. Nature 386:292–296. https://doi.org/10.1038/386292a0
Alarcón R, Fuenzalida C, Santibáñez M, von Bernhardi R (2005) Expression of scavenger receptors in glial cells. J Biol Chem 280:30406–30415. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M414686200
Chen Y, Pikkarainen T, Elomaa O et al (2005) Defective microarchitecture of the Spleen Marginal Zone and impaired response to a Thymus-independent type 2 Antigen in mice lacking scavenger receptors MARCO and SR-A. J Immunol 175:8173–8180. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.175.12.8173
Matsushita N, Komine H, Grolleau-Julius A et al (2010) Targeting MARCO can lead to enhanced dendritic cell motility and anti-melanoma activity. Cancer Immunol Immunother 59:875–884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-009-0813-5
Komine H, Kuhn L, Matsushita N et al (2013) Examination of MARCO Activity on dendritic cell phenotype and function using a gene knockout mouse. PLoS ONE 8:e67795. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0067795
Li Z, Jiao Y, Fan EK et al (2017) Aging-impaired filamentous actin polymerization signaling reduces alveolar macrophage phagocytosis of Bacteria. J Immunol 199:3176–3186. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1700140
Kanno S, Hirano S, Sakamoto T et al (2020) Scavenger receptor MARCO contributes to cellular internalization of exosomes by dynamin-dependent endocytosis and macropinocytosis. Sci Rep 10:21795. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78464-2
Qianqian Xing Y, Feng H Sun, et al (2021) Scavenger receptor MARCO contributes to macrophage phagocytosis and clearance of tumor cells. Exp Cell Res 408:112862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112862
Rogers NJ, Lees MJ, Gabriel L et al (2009) A defect in Marco expression contributes to systemic Lupus Erythematosus Development via failure to clear apoptotic cells. J Immunol 182:1982–1990. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0801320
Wright AKA, Rao S, Range S et al (2009) Pivotal advance: expansion of small sputum macrophages in CF: failure to express MARCO and mannose receptors. J Leukoc Biol 86:479–489. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.1108699
Sheng X, Zhao J, Li M et al (2021) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes accelerate functional recovery after spinal cord Injury by promoting the phagocytosis of macrophages to clean myelin debris. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:772205. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.772205
Sun Y, Xiao W, Yu Y et al (2023) Colorectal cancer-derived extracellular vesicles containing HSP70 enhance macrophage phagocytosis by up-regulating MARCO expression. Exp Cell Res 426:113565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113565
Carpentier KS, Sheridan RM, Lucas CJ et al (2021) MARCO + lymphatic endothelial cells sequester arthritogenic alphaviruses to limit viremia and viral dissemination. EMBO J 40:e108966. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2021108966
Blanchet C, Jouvion G, Fitting C et al (2014) Protective or deleterious role of Scavenger receptors SR-A and CD36 on Host Resistance to Staphylococcus aureus depends on the site of infection. PLoS ONE 9:e87927. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087927
Maler MD, Nielsen PJ, Stichling N et al (2017) Key role of the scavenger receptor MARCO in Mediating Adenovirus infection and subsequent innate responses of macrophages. mBio 8:e00670–e00617. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00670-17
Thakur SA, Beamer CA, Migliaccio CT, Holian A (2009) Critical role of MARCO in Crystalline silica–Induced Pulmonary inflammation. Toxicol Sci 108:462–471. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfp011
Biswas R, Hamilton RF, Holian A (2014) Role of lysosomes in silica-Induced Inflammasome activation and inflammation in absence of MARCO. J Immunol Res 2014:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/304180
Coats BR, Schoenfelt KQ, Barbosa-Lorenzi VC et al (2017) Metabolically activated adipose tissue macrophages perform detrimental and beneficial functions during Diet-Induced obesity. Cell Rep 20:3149–3161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.096
Wölle S, Via DP, Chan L et al (1995) Hepatic overexpression of bovine scavenger receptor type I in transgenic mice prevents diet-induced hyperbetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest 96:260–272. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI118030
Perez A, Wright MB, Maugeais C et al (2010) MARCO, a macrophage scavenger receptor highly expressed in rodents, mediates dalcetrapib-induced uptake of lipids by rat and mouse macrophages. Toxicol in Vitro 24:745–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2010.01.002
Brunner JS, Vogel A, Lercher A et al (2020) The PI3K pathway preserves metabolic health through MARCO-dependent lipid uptake by adipose tissue macrophages. Nat Metab 2:1427–1442. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-020-00311-5
Jawad S, Liu B, Li Z et al (2013) The role of Macrophage Class A Scavenger receptors in a Laser-Induced Murine Choroidal Neovascularization Model. Investig Opthalmology Amp Vis Sci 54:5959. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.12-11380
Xu J, Flaczyk A, Neal LM et al (2017) Scavenger receptor MARCO orchestrates early defenses and contributes to Fungal Containment during cryptococcal infection. J Immunol 198:3548–3557. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1700057
Brown JM, Swindle EJ, Kushnir-Sukhov NM et al (2007) Silica-Directed mast cell activation is enhanced by scavenger receptors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 36:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2006-0197OC
Granucci F, Petralia F, Urbano M et al (2003) The scavenger receptor MARCO mediates cytoskeleton rearrangements in dendritic cells and microglia. Blood 102:2940–2947. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-12-3651
Kissick HT, Dunn LK, Ghosh S et al (2014) The scavenger receptor MARCO modulates TLR-Induced responses in dendritic cells. PLoS ONE 9:e104148. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104148
Eisinger S, Sarhan D, Boura VF et al (2020) Targeting a scavenger receptor on tumor-associated macrophages activates tumor cell killing by natural killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 117:32005–32016. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2015343117
La Fleur L, Botling J, He F et al (2021) Targeting MARCO and IL37R on Immunosuppressive macrophages in Lung Cancer Blocks Regulatory T Cells and supports cytotoxic lymphocyte function. Cancer Res 81:956–967. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1885
Sarhan D, Eisinger S, He F et al (2022) Targeting myeloid suppressive cells revives cytotoxic anti-tumor responses in pancreatic cancer. iScience 25:105317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.105317
Chen Y, Wermeling F, Sundqvist J et al (2010) A regulatory role for macrophage class A scavenger receptors in TLR4-mediated LPS responses. Eur J Immunol 40:1451–1460. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200939891
Jordö ED, Wermeling F, Chen Y, Karlsson MCI (2011) Scavenger receptors as regulators of natural antibody responses and B cell activation in autoimmunity. Mol Immunol 48:1307–1318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2011.01.010
Karlsson MCI, Guinamard R, Bolland S et al (2003) Macrophages Control the Retention and trafficking of B lymphocytes in the Splenic Marginal Zone. J Exp Med 198:333–340. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20030684
Kraal G, Mebius R (2006) New insights into the Cell Biology of the marginal zone of the spleen. Int Rev Cytol 250:175–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-7696(06)50005-1
Prokopec KE, Georgoudaki A-M, Sohn S et al (2016) Cutting edge: marginal zone macrophages regulate Antigen Transport by B cells to the follicle in the spleen via CD21. J Immunol 197:2063–2068. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1502282
Xu J, Flaczyk A, Neal LM et al (2017) Exploitation of Scavenger receptor, macrophage receptor with Collagenous structure, by Cryptococcus neoformans promotes alternative activation of Pulmonary Lymph Node CD11b + conventional dendritic cells and non-protective Th2 Bias. Front Immunol 8:1231. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01231
Dong Q, Zhang S, Zhang H et al (2023) MARCO is a potential prognostic and immunotherapy biomarker. Int Immunopharmacol 116:109783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109783
Wu M, Gibbons JG, DeLoid GM et al (2017) Immunomodulators targeting MARCO expression improve resistance to postinfluenza bacterial pneumonia. Am J Physiol-Lung Cell Mol Physiol 313:L138–L153. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00075.2017
Kang M-J, Jang A-R, Park J-Y et al (2020) IL-10 protects mice from the lung infection of Acinetobacter baumannii and contributes to bacterial clearance by regulating STAT3-Mediated MARCO expression in macrophages. Front Immunol 11:270. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00270
Gu C, Wiest M, Zhang W et al (2023) Cancer Cells Promote Immune Regulatory Function of Macrophages by upregulating scavenger receptor MARCO Expression. J Immunol 211:57–70. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.2300029
Bowdish DME, Sakamoto K, Kim M-J et al (2009) MARCO, TLR2, and CD14 are required for macrophage cytokine responses to mycobacterial trehalose dimycolate and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000474. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000474
Doyle SE, O’Connell RM, Miranda GA et al (2004) Toll-like receptors induce a phagocytic gene program through p38. J Exp Med 199:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20031237
Wang L, Yang H-Y, Zang C-X et al (2021) TLR2 potentiates SR-Marco-mediated neuroinflammation by interacting with the SRCR Domain. Mol Neurobiol 58:5743–5755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02463-1
Killpack TL, Ballesteros M, Bunnell SC et al (2017) Phagocytic receptors activate syk and src signaling during Borrelia burgdorferi phagocytosis. Infect Immun 85:e00004–17. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00004-17
Thakur SA, Hamilton R, Pikkarainen T, Holian A (2009) Differential binding of inorganic particles to MARCO. Toxicol Sci 107:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfn210
Toma VAl, Tigu AB, Farcaș AD et al (2019) New aspects towards a molecular understanding of the Allicin Immunostimulatory mechanism via Colec12, MARCO, and SCARB1 receptors. Int J Mol Sci 20:3627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153627
Huang H, Zhang J, Harvey SE et al (2017) RNA G-quadruplex secondary structure promotes alternative splicing via the RNA-binding protein hnRNPF. Genes Amp Dev 31:2296–2309. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.305862.117
Petrovic AG, Polavarapu PL (2008) The quadruplex – duplex structural transition of Polyriboguanylic Acid. J Phys Chem B 112:2245–2254. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0758723
Yang M, Wang N, Li W et al (2019) Therapeutic effects of scavenger receptor MARCO ligand on silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Toxicol Lett 311:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.04.026
Pikkarainen T, Brännström A, Tryggvason K (1999) Expression of macrophage MARCO receptor induces formation of dendritic plasma membrane processes. J Biol Chem 274:10975–10982. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.16.10975
Murthy S, Larson-Casey JL, Ryan AJ et al (2015) Alternative activation of macrophages and pulmonary fibrosis are modulated by scavenger receptor, macrophage receptor with collagenous structure. FASEB J 29:3527–3536. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.15-271304
Yang Y-S, Jin X, Li Q et al (2022) Superenhancer drives a tumor-specific splicing variant of MARCO to promote triple-negative breast cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci 119:e2207201119. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2207201119
Xiao Y, Chen B, Yang K et al (2019) Down-regulation of MARCO associates with tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Cell Res 383:111542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111542
Zhang Q, Wei Y, Li Y, Jiao X (2022) Low MARCO expression is Associated with poor survival in patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma following liver transplantation. Cancer Manag Res Volume 14:1935–1944. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S363219
Lin W-C, Lin F-T (2022) Super-enhanced MARCO variant drives triple-negative breast cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci 119:e2217953119. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2217953119
Chen X, Shen Y, Sun C et al (2011) Anti-class a scavenger receptor autoantibodies from systemic lupus erythematosus patients impair phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells by macrophages in vitro. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R9. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3230
Shi B, Chu J, Huang T et al (2021) The scavenger receptor MARCO expressed by Tumor-Associated macrophages are highly Associated with Poor Pancreatic Cancer Prognosis. Front Oncol 11:771488. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.771488
Lundgren S, Karnevi E, Elebro J et al (2017) The clinical importance of tumour-infiltrating macrophages and dendritic cells in periampullary adenocarcinoma differs by morphological subtype. J Transl Med 15:152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1256-y
Svensson MC, Svensson M, Nodin B et al (2022) High infiltration of CD68+/CD163 – macrophages is an adverse prognostic factor after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Esophageal and gastric adenocarcinoma. J Innate Immun 14:615–628. https://doi.org/10.1159/000524434
Georgoudaki A-M, Prokopec KE, Boura VF et al (2016) Reprogramming Tumor-Associated macrophages by antibody targeting inhibits Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Cell Rep 15:2000–2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.04.084
Sun H, Song J, Weng C et al (2017) Association of decreased expression of the macrophage scavenger receptor MARCO with tumor progression and poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 32:1107–1114. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.13633
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant numbers [2022YFC2704400]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: G.Z. and S.S.; Investigation: G.Z.; Writing - Original Draft: G.Z.; Visualization: G.Z.; Resources: L.Z.; Project administration: L.Z.; Funding acquisition: L.Z.; Writing - Review & Editing: S.S.; Supervision: S.S. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, G., Zhang, L. & Shao, S. The application of MARCO for immune regulation and treatment. Mol Biol Rep 51, 246 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-09201-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-09201-x