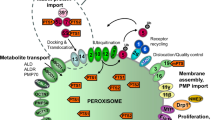
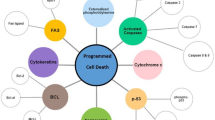
Abstract
Cell death is a fundamental physiological process in all living organisms. Processes such as embryonic development, organ formation, tissue growth, organismal immunity, and drug response are accompanied by cell death. In recent years with the development of electron microscopy as well as biological techniques, especially the discovery of novel death modes such as ferroptosis, cuprotosis, alkaliptosis, oxeiptosis, and disulfidptosis, researchers have been promoted to have a deeper understanding of cell death modes. In this systematic review, we examined the current understanding of modes of cell death, including the recently discovered novel death modes. Our analysis highlights the common and unique pathways of these death modes, as well as their impact on surrounding cells and the organism as a whole. Our aim was to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of research on cell death, with a focus on identifying gaps in our knowledge and opportunities for future investigation. We also presented a new insight for macroscopic intracellular survival patterns, namely that intracellular molecular homeostasis is central to the balance of different cell death modes, and this viewpoint can be well justified by the signaling crosstalk of different death modes. These concepts can facilitate the future research about cell death in clinical diagnosis, drug development, and therapeutic modalities.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bree RT, Stenson-Cox C, Grealy M, Byrnes L, Gorman AM, Samali A (2002) Cellular longevity: role of apoptosis and replicative senescence. Biogerontology 3(4):195–206. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1016299812327
Semont A, Mouiseddine M, Francois A, Demarquay C, Mathieu N, Chapel A et al (2010) Mesenchymal stem cells improve small intestinal integrity through regulation of endogenous epithelial cell homeostasis. Cell Death Differ 17(6):952–961. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.187
Pollina EA, Gilliam DT, Landau AT, Lin C, Pajarillo N, Davis CP et al (2023) A NPAS4-NuA4 complex couples synaptic activity to DNA repair. Nature 614(7949):732–741. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05711-7
Misgeld T, Schwarz TL (2017) Mitostasis in neurons: maintaining mitochondria in an extended cellular architecture. Neuron 96(3):651–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.09.055
Wyllie AH (1987) Cell death. Cytol Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-091882-2.50024-5
Vaux DL, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) Cell death in development. Cell 96(2):245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80564-4
Bertalanffy FD, Lau C (1962) Cell renewal. In: Jeon KW (ed) International review of cytology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 357–366
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Agostinis P et al (2018) Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ 25(3):486–541. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
Evan G, Littlewood T (1998) A matter of life and cell death. Science 281(5381):1317–1322. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.281.5381.1317
D’Arcy MS (2019) Cell death: a review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol Int 43(6):582–592. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11137
Loo DT, Rillema JR (1998) Measurement of cell death. Methods Cell Biol 57:251–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61583-6
Tang D, Kang R, Berghe TV, Vandenabeele P, Kroemer G (2019) The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res 29(5):347–364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-019-0164-5
Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D et al (2015) Essential versus accessory aspects of cell death: recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell Death Differ 22(1):58–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2014.137
Huang Y, Xu W, Zhou R (2021) NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol Immunol 18(9):2114–2127. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-021-00740-6
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26(4):239–257. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1972.33
Jacobson MD, Weil M, Raff MC (1997) Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell 88(3):347–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81873-5
Wyllie AH, Kerr JF, Currie AR (1980) Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol 68:251–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8
Lawen A (2003) Apoptosis-an introduction. BioEssays 25(9):888–896. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.10329
Ndozangue-Touriguine O, Hamelin J, Breard J (2008) Cytoskeleton and apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 76(1):11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2008.03.016
Guicciardi ME, Leist M, Gores GJ (2004) Lysosomes in cell death. Oncogene 23(16):2881–2890. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207512
Gozuacik D, Kimchi A (2007) Autophagy and cell death. Curr Top Dev Biol 78:217–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0070-2153(06)78006-1
Galluzzi L, Maiuri MC, Vitale I, Zischka H, Castedo M, Zitvogel L et al (2007) Cell death modalities: classification and pathophysiological implications. Cell Death Differ 14(7):1237–1243. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402148
Schweichel JU, Merker HJ (1973) The morphology of various types of cell death in prenatal tissues. Teratology 7(3):253–266. https://doi.org/10.1002/tera.1420070306
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV et al (2012) Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2012. Cell Death Differ 19(1):107–120. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.96
Kroemer G, El-Deiry WS, Golstein P, Peter ME, Vaux D, Vandenabeele P et al (2005) Classification of cell death: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death. Cell Death Differ 12(Suppl 2):1463–1467. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401724
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P, Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH et al (2009) Classification of cell death: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2009. Cell Death Differ 16(1):3–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.150
Lockshin RA, Zakeri Z (2001) Programmed cell death and apoptosis: origins of the theory. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(7):545–550. https://doi.org/10.1038/35080097
Hacker G (2000) The morphology of apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res 301(1):5–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410000193
Cohen GM (1997) Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis. Biochem J 326(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3260001
Martinou JC, Youle RJ (2011) Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell 21(1):92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2011.06.017
Nunez G, Benedict MA, Hu Y, Inohara N (1998) Caspases: the proteases of the apoptotic pathway. Oncogene 17(25):3237–3245. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202581
Nebert DW, Roe AL, Dieter MZ, Solis WA, Yang Y, Dalton TP (2000) Role of the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor and [Ah] gene battery in the oxidative stress response, cell cycle control, and apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 59(1):65–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(99)00310-x
Rossi D, Gaidano G (2003) Messengers of cell death: apoptotic signaling in health and disease. Haematologica 88(2):212–218
Backus KM, Correia BE, Lum KM, Forli S, Horning BD, Gonzalez-Paez GE et al (2016) Proteome-wide covalent ligand discovery in native biological systems. Nature 534(7608):570–574. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18002
Rogers C, Erkes DA, Nardone A, Aplin AE, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES (2019) Gasdermin pores permeabilize mitochondria to augment caspase-3 activation during apoptosis and inflammasome activation. Nat Commun 10(1):1689. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09397-2
Pihan P, Carreras-Sureda A, Hetz C (2017) BCL-2 family: integrating stress responses at the ER to control cell demise. Cell Death Differ 24(9):1478–1487. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.82
Vitale I, Manic G, De Maria R, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L (2017) DNA damage in stem cells. Mol Cell 66(3):306–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.04.006
Allavena G, Cuomo F, Baumgartner G, Bele T, Sellgren AY, Oo KS et al (2018) Suppressed translation as a mechanism of initiation of CASP8 (caspase 8)-dependent apoptosis in autophagy-deficient NSCLC cells under nutrient limitation. Autophagy 14(2):252–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2017.1405192
Liu HR, Gao E, Hu A, Tao L, Qu Y, Most P et al (2005) Role of Omi/HtrA2 in apoptotic cell death after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Circulation 111(1):90–96. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000151613.90994.17
Chipuk JE, Bouchier-Hayes L, Green DR (2006) Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis: the innocent bystander scenario. Cell Death Differ 13(8):1396–1402. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401963
Galluzzi L, Lopez-Soto A, Kumar S, Kroemer G (2016) Caspases connect cell-death signaling to organismal homeostasis. Immunity 44(2):221–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.01.020
Taddei ML, Giannoni E, Fiaschi T, Chiarugi P (2012) Anoikis: an emerging hallmark in health and diseases. J Pathol 226(2):380–393. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.3000
Frisch SM, Francis H (1994) Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 124(4):619–626. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.124.4.619
Zhang D, Zhou X, Zhang K, Yu Y, Cui SW, Nie S (2023) Glucomannan from Aloe vera gel maintains intestinal barrier integrity via mitigating anoikis mediated by Nrf2-mitochondria axis. Int J Biol Macromol 235:123803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123803
Li D, Park Y, Hemati H, Liu X (2023) Cell aggregation prevents anoikis and induces CD44 cleavage by maintaining lipid raft integrity to promote triple negative breast cancer metastasis. Res Sq. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2535728/v1
Zhao Z, Li C, Peng Y, Liu R, Li Q (2022) Construction of an original anoikis-related prognostic model closely related to immune infiltration in gastric cancer. Front Genet 13:1087201. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.1087201
Bose M, Sanders A, De C, Zhou R, Lala P, Shwartz S et al (2023) Targeting tumor-associated MUC1 overcomes anoikis-resistance in pancreatic cancer. Transl Res 253:41–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2022.08.010
Cai C, Peng Y, Shen E, Wan R, Gao L, Gao Y et al (2022) Identification of tumour immune infiltration-associated snoRNAs (TIIsno) for predicting prognosis and immune landscape in patients with colon cancer via a TIIsno score model. EBioMedicine 76:103866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103866
Weems AD, Welf ES, Driscoll MK, Zhou FY, Mazloom-Farsibaf H, Chang BJ et al (2023) Blebs promote cell survival by assembling oncogenic signalling hubs. Nature 615(7952):517–525. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05758-6
Terasima T, Ohara H (1968) Chromosome aberration and mitotic death in x-irradiated HeLa cells. Mutat Res 5(1):195–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/0027-5107(68)90094-8
Vitale I, Galluzzi L, Castedo M, Kroemer G (2011) Mitotic catastrophe: a mechanism for avoiding genomic instability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12(6):385–392. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3115
Huun J, Lonning PE, Knappskog S (2017) Effects of concomitant inactivation of p53 and pRb on response to doxorubicin treatment in breast cancer cell lines. Cell Death Discov 3:17026. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2017.26
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N et al (2005) Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol 1(2):112–119. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio711
Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, Ch’en IL, Korkina O, Teng X et al (2008) Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol 4(5):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.83
Gong Y, Fan Z, Luo G, Yang C, Huang Q, Fan K et al (2019) The role of necroptosis in cancer biology and therapy. Mol Cancer 18(1):100. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1029-8
Moriwaki K, Chan FKM, Miyoshi E (2021) Sweet modification and regulation of death receptor signalling pathway. J Biochem 169(6):643–652. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvab034
Borghi A, Verstrepen L, Beyaert R (2016) TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-kappaB, MAP kinases and cell death. Biochem Pharmacol 116:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.009
Yang J, Hu S, Bian Y, Yao J, Wang D, Liu X et al (2021) Targeting cell death: pyroptosis, ferroptosis, apoptosis and necroptosis in osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:789948. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.789948
Zhang Y, Chen X, Gueydan C, Han J (2018) Plasma membrane changes during programmed cell deaths. Cell Res 28(1):9–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.133
Round-table conference (1969) The surgical therapy of the metastases of the central nervous system. Minerva Neurochir 13(3):265–287
Nadaud B, Depaepe L, Zaharia D, Balme B (2014) Chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis. Ann Dermatol Venereol 141(4):306–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annder.2014.02.001
Vanden Berghe T, Linkermann A, Jouan-Lanhouet S, Walczak H, Vandenabeele P (2014) Regulated necrosis: the expanding network of non-apoptotic cell death pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(2):135–147. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3737
Oberst A, Dillon CP, Weinlich R, McCormick LL, Fitzgerald P, Pop C et al (2011) Catalytic activity of the caspase-8-FLIP(L) complex inhibits RIPK3-dependent necrosis. Nature 471(7338):363–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09852
Jorgensen I, Rayamajhi M, Miao EA (2017) Programmed cell death as a defence against infection. Nat Rev Immunol 17(3):151–164. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.147
Baik JY, Liu Z, Jiao D, Kwon HJ, Yan J, Kadigamuwa C et al (2021) ZBP1 not RIPK1 mediates tumor necroptosis in breast cancer. Nat Commun 12(1):2666. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23004-3
Park HH, Kim HR, Park SY, Hwang SM, Hong SM, Park S et al (2021) RIPK3 activation induces TRIM28 derepression in cancer cells and enhances the anti-tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer 20(1):107. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01399-3
Zhang T, Yin C, Fedorov A, Qiao L, Bao H, Beknazarov N et al (2022) ADAR1 masks the cancer immunotherapeutic promise of ZBP1-driven necroptosis. Nature 606(7914):594–602. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04753-7
Wu NY, Huang HS, Chao TH, Chou HM, Fang C, Qin CZ et al (2017) Progesterone prevents high-grade serous ovarian cancer by inducing necroptosis of p53-defective fallopian tube epithelial cells. Cell Rep 18(11):2557–2565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.049
Chen S, Lv X, Hu B, Shao Z, Wang B, Ma K et al (2017) RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL-mediated necroptosis contributes to compression-induced rat nucleus pulposus cells death. Apoptosis 22(5):626–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1358-2
Deng XX, Li SS, Sun FY (2019) Necrostatin-1 prevents necroptosis in brains after ischemic stroke via inhibition of RIPK1-mediated RIPK3/MLKL signaling. Aging Dis 10(4):807–817. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2018.0728
Kamiya M, Mizoguchi F, Kawahata K, Wang D, Nishibori M, Day J et al (2022) Targeting necroptosis in muscle fibers ameliorates inflammatory myopathies. Nat Commun 13(1):166. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27875-4
Tang R, Xu J, Zhang B, Liu J, Liang C, Hua J et al (2020) Ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in anticancer immunity. J Hematol Oncol 13(1):110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00946-7
Yuan J, Amin P, Ofengeim D (2019) Necroptosis and RIPK1-mediated neuroinflammation in CNS diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 20(1):19–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-018-0093-1
Klempner LB, Preobrazhenskaia TM, Sotnikov VM (1975) Combined lung cancer and systemic scleroderma. Arkh Patol 37(6):55–61
Frank D, Vince JE (2019) Pyroptosis versus necroptosis: similarities, differences, and crosstalk. Cell Death Differ 26(1):99–114. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0212-6
Bousselin M (1786) Observations on necrosis. Lond Med J 7(3):263–279
Espitia O, Agard C (2021) Scalp necrosis in giant cell arteritis. Mayo Clin Proc 96(4):987–988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.11.025
Nicotera P, Leist M, Ferrando-May E (1998) Intracellular ATP, a switch in the decision between apoptosis and necrosis. Toxicol Lett 102–103:139–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4274(98)00298-7
Kroemer G, Dallaporta B, Resche-Rigon M (1998) The mitochondrial death/life regulator in apoptosis and necrosis. Annu Rev Physiol 60:619–642. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.60.1.619
Kayagaki N, Kornfeld OS, Lee BL, Stowe IB, O’Rourke K, Li Q et al (2021) NINJ1 mediates plasma membrane rupture during lytic cell death. Nature 591(7848):131–136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03218-7
Zapletal E, Vasiljevic T, Busson P, Matijevic GT (2023) Dialog beyond the grave: necrosis in the tumor microenvironment and its contribution to tumor growth. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065278
De DC, Berthet J, Berthet L, Appelmans F (1951) Permeability of mitochondria. Nature 167(4245):389–390. https://doi.org/10.1038/167389a0
Lemasters JJ, Qian T, Elmore SP, Trost LC, Nishimura Y, Herman B et al (1998) Confocal microscopy of the mitochondrial permeability transition in necrotic cell killing, apoptosis and autophagy. BioFactors 8(3–4):283–285. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.5520080316
Lemasters JJ, Nieminen AL, Qian T, Trost LC, Elmore SP, Nishimura Y et al (1998) The mitochondrial permeability transition in cell death: a common mechanism in necrosis, apoptosis and autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1366(1–2):177–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0005-2728(98)00112-1
Izzo V, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Sica V, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L (2016) Mitochondrial permeability transition: new findings and persisting uncertainties. Trends Cell Biol 26(9):655–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2016.04.006
Bonora M, Wieckowski MR, Chinopoulos C, Kepp O, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L et al (2015) Molecular mechanisms of cell death: central implication of ATP synthase in mitochondrial permeability transition. Oncogene 34(12):1475–1486. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.96
Whelan RS, Konstantinidis K, Wei AC, Chen Y, Reyna DE, Jha S et al (2012) Bax regulates primary necrosis through mitochondrial dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(17):6566–6571. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1201608109
Xu S, Wang P, Zhang H, Gong G, Gutierrez Cortes N, Zhu W et al (2016) CaMKII induces permeability transition through Drp1 phosphorylation during chronic beta-AR stimulation. Nat Commun 7:13189. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13189
Vaseva AV, Marchenko ND, Ji K, Tsirka SE, Holzmann S, Moll UM (2012) p53 opens the mitochondrial permeability transition pore to trigger necrosis. Cell 149(7):1536–1548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.014
Miller DR, Thorburn A (2021) Autophagy and organelle homeostasis in cancer. Dev Cell 56(7):906–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2021.02.010
Buratta S, Tancini B, Sagini K, Delo F, Chiaradia E, Urbanelli L et al (2020) Lysosomal exocytosis, exosome release and secretory autophagy: the autophagic- and endo-lysosomal systems go extracellular. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072576
Liu W, Xu L, Wang X, Zhang D, Sun G, Wang M et al (2021) PRDX1 activates autophagy via the PTEN-AKT signaling pathway to protect against cisplatin-induced spiral ganglion neuron damage. Autophagy 17(12):4159–4181. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2021.1905466
Wang S, Livingston MJ, Su Y, Dong Z (2015) Reciprocal regulation of cilia and autophagy via the MTOR and proteasome pathways. Autophagy 11(4):607–616. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1023983
Yang J, Pi C, Wang G (2018) Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway by apigenin induces apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother 103:699–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.072
Levine B, Kroemer G (2008) Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 132(1):27–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.018
Liu Y, Shoji-Kawata S, Sumpter RM Jr, Wei Y, Ginet V, Zhang L et al (2013) Autosis is a Na+, K+-ATPase-regulated form of cell death triggered by autophagy-inducing peptides, starvation, and hypoxia-ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(51):20364–20371. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1319661110
Nah J, Zablocki D, Sadoshima J (2020) Autosis: a new target to prevent cell death. JACC Basic Transl Sci 5(8):857–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacbts.2020.04.014
Fernandez AF, Liu Y, Ginet V, Shi M, Nah J, Zou Z et al (2020) Interaction between the autophagy protein beclin 1 and Na+, K+-ATPase during starvation, exercise, and ischemia. JCI Insight. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.133282
Friedlander AM (1986) Macrophages are sensitive to anthrax lethal toxin through an acid-dependent process. J Biol Chem 261(16):7123–7126
Zychlinsky A, Prevost MC, Sansonetti PJ (1992) Shigella flexneri induces apoptosis in infected macrophages. Nature 358(6382):167–169. https://doi.org/10.1038/358167a0
D’Souza CA, Heitman J (2001) Dismantling the Cryptococcus coat. Trends Microbiol 9(3):112–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0966-842x(00)01945-4
Bergsbaken T, Fink SL, Cookson BT (2009) Pyroptosis: host cell death and inflammation. Nat Rev Microbiol 7(2):99–109. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2070
Jorgensen I, Miao EA (2015) Pyroptotic cell death defends against intracellular pathogens. Immunol Rev 265(1):130–142. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12287
Chen X, He WT, Hu L, Li J, Fang Y, Wang X et al (2016) Pyroptosis is driven by non-selective gasdermin-D pore and its morphology is different from MLKL channel-mediated necroptosis. Cell Res 26(9):1007–1020. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.100
Tajima T, Yoshifuji A, Matsui A, Itoh T, Uchiyama K, Kanda T et al (2019) beta-hydroxybutyrate attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through its anti-pyroptotic effects. Kidney Int 95(5):1120–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2018.11.034
Xu YJ, Zheng L, Hu YW, Wang Q (2018) Pyroptosis and its relationship to atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta 476:28–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2017.11.005
Wei X, Xie F, Zhou X, Wu Y, Yan H, Liu T et al (2022) Role of pyroptosis in inflammation and cancer. Cell Mol Immunol 19(9):971–992. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-022-00905-x
Yu P, Zhang X, Liu N, Tang L, Peng C, Chen X (2021) Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):128. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00507-5
Yang F, Bettadapura SN, Smeltzer MS, Zhu H, Wang S (2022) Pyroptosis and pyroptosis-inducing cancer drugs. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43(10):2462–2473. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00887-6
Hu JJ, Liu X, Xia S, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Zhao J et al (2020) FDA-approved disulfiram inhibits pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D pore formation. Nat Immunol 21(7):736–745. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-020-0669-6
Yang WS, Stockwell BR (2016) Ferroptosis: death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol 26(3):165–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2015.10.014
Dolma S, Lessnick SL, Hahn WC, Stockwell BR (2003) Identification of genotype-selective antitumor agents using synthetic lethal chemical screening in engineered human tumor cells. Cancer Cell 3(3):285–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00050-3
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE et al (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149(5):1060–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Tang D, Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G (2021) Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res 31(2):107–125. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-00441-1
Shen Z, Song J, Yung BC, Zhou Z, Wu A, Chen X (2018) Emerging strategies of cancer therapy based on ferroptosis. Adv Mater 30(12):e1704007. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201704007
Chen X, Li J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Tang D (2021) Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Autophagy 17(9):2054–2081. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1810918
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun X et al (2016) Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ 23(3):369–379. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2015.158
Jomova K, Makova M, Alomar SY, Alwasel SH, Nepovimova E, Kuca K et al (2022) Essential metals in health and disease. Chem Biol Interact 367:110173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110173
Zhao L, Zhou X, Xie F, Zhang L, Yan H, Huang J et al (2022) Ferroptosis in cancer and cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Commun (Lond) 42(2):88–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/cac2.12250
Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, Dreishpoon M, Verma A, Abdusamad M et al (2022) Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science 375(6586):1254–1261. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abf0529
Ercal N, Gurer-Orhan H, Aykin-Burns N (2001) Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Curr Top Med Chem 1(6):529–539. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026013394831
Ba LA, Doering M, Burkholz T, Jacob C (2009) Metal trafficking: from maintaining the metal homeostasis to future drug design. Metallomics 1(4):292–311. https://doi.org/10.1039/b904533c
Krzywoszynska K, Witkowska D, Swiatek-Kozlowska J, Szebesczyk A, Kozlowski H (2020) General aspects of metal ions as signaling agents in health and disease. Biomolecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101417
Liu X, Nie L, Zhang Y, Yan Y, Wang C, Colic M et al (2023) Actin cytoskeleton vulnerability to disulfide stress mediates disulfidptosis. Nat Cell Biol 25(3):404–414. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-023-01091-2
Koppula P, Zhuang L, Gan B (2021) Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein Cell 12(8):599–620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-020-00789-5
Rose M, Burgess JT, O’Byrne K, Richard DJ, Bolderson E (2020) PARP inhibitors: clinical relevance, mechanisms of action and tumor resistance. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:564601. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.564601
David KK, Andrabi SA, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2009) Parthanatos, a messenger of death. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 14(3):1116–1128. https://doi.org/10.2741/3297
Andrabi SA, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2008) Mitochondrial and nuclear cross talk in cell death: parthanatos. Ann NY Acad Sci 1147:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1427.014
Wang H, Yu SW, Koh DW, Lew J, Coombs C, Bowers W et al (2004) Apoptosis-inducing factor substitutes for caspase executioners in NMDA-triggered excitotoxic neuronal death. J Neurosci 24(48):10963–10973. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3461-04.2004
Wang Y, Kim NS, Haince JF, Kang HC, David KK, Andrabi SA et al (2011) Poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) binding to apoptosis-inducing factor is critical for PAR polymerase-1-dependent cell death (parthanatos). Sci Signal 4(167):20. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2000902
Wang Y, An R, Umanah GK, Park H, Nambiar K, Eacker SM et al (2016) A nuclease that mediates cell death induced by DNA damage and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad6872
Curtin NJ, Szabo C (2013) Therapeutic applications of PARP inhibitors: anticancer therapy and beyond. Mol Aspects Med 34(6):1217–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2013.01.006
Pilie PG, Gay CM, Byers LA, O’Connor MJ, Yap TA (2019) PARP inhibitors: extending benefit beyond BRCA-mutant cancers. Clin Cancer Res 25(13):3759–3771. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0968
Zeng C, Zeng B, Dong C, Liu J, Xing F (2020) Rho-ROCK signaling mediates entotic cell death in tumor. Cell Death Discov 6:4. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-020-0238-7
Overholtzer M, Mailleux AA, Mouneimne G, Normand G, Schnitt SJ, King RW et al (2007) A nonapoptotic cell death process, entosis, that occurs by cell-in-cell invasion. Cell 131(5):966–979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.040
Fadok VA, Voelker DR, Campbell PA, Cohen JJ, Bratton DL, Henson PM (1992) Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages. J Immunol 148(7):2207–2216
Krajcovic M, Johnson NB, Sun Q, Normand G, Hoover N, Yao E et al (2011) A non-genetic route to aneuploidy in human cancers. Nat Cell Biol 13(3):324–330. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2174
Krajcovic M, Overholtzer M (2012) Mechanisms of ploidy increase in human cancers: a new role for cell cannibalism. Cancer Res 72(7):1596–1601. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3127
Casares N, Pequignot MO, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Roux S, Chaput N et al (2005) Caspase-dependent immunogenicity of doxorubicin-induced tumor cell death. J Exp Med 202(12):1691–1701. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20050915
Ahmed A, Tait SWG (2020) Targeting immunogenic cell death in cancer. Mol Oncol 14(12):2994–3006. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12851
Fucikova J, Kepp O, Kasikova L, Petroni G, Yamazaki T, Liu P et al (2020) Detection of immunogenic cell death and its relevance for cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis 11(11):1013. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03221-2
Radogna F, Diederich M (2018) Stress-induced cellular responses in immunogenic cell death: Implications for cancer immunotherapy. Biochem Pharmacol 153:12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2018.02.006
Franko J, Pomfy M, Prosbova T (2000) Apoptosis and cell death (mechanisms, pharmacology and promise for the future). Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) 43(2):63–68
Wang F, Gomez-Sintes R, Boya P (2018) Lysosomal membrane permeabilization and cell death. Traffic 19(12):918–931. https://doi.org/10.1111/tra.12613
Aits S, Jaattela M (2013) Lysosomal cell death at a glance. J Cell Sci 126(Pt 9):1905–1912. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.091181
Yousefi S, Gold JA, Andina N, Lee JJ, Kelly AM, Kozlowski E et al (2008) Catapult-like release of mitochondrial DNA by eosinophils contributes to antibacterial defense. Nat Med 14(9):949–953. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.1855
Wartha F, Henriques-Normark B (2008) ETosis: a novel cell death pathway. Sci Signal 1(21):pe25. https://doi.org/10.1126/stke.121pe25
Morshed M, Hlushchuk R, Simon D, Walls AF, Obata-Ninomiya K, Karasuyama H et al (2014) NADPH oxidase-independent formation of extracellular DNA traps by basophils. J Immunol 192(11):5314–5323. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1303418
Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS et al (2004) Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 303(5663):1532–1535. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1092385
Song X, Zhu S, Xie Y, Liu J, Sun L, Zeng D et al (2018) JTC801 induces pH-dependent death specifically in cancer cells and slows growth of tumors in mice. Gastroenterology 154(5):1480–1493. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.12.004
Chen F, Zhu S, Kang R, Tang D, Liu J (2023) ATP6V0D1 promotes alkaliptosis by blocking STAT3-mediated lysosomal pH homeostasis. Cell Rep 42(1):111911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111911
Chen Y, Hua Y, Li X, Arslan IM, Zhang W, Meng G (2020) Distinct types of cell death and the implication in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Front Pharmacol 11:42. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00042
Holze C, Michaudel C, Mackowiak C, Haas DA, Benda C, Hubel P et al (2018) Oxeiptosis, a ROS-induced caspase-independent apoptosis-like cell-death pathway. Nat Immunol 19(2):130–140. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-017-0013-y
Kang P, Chen J, Zhang W, Guo N, Yi X, Cui T et al (2022) Oxeiptosis: a novel pathway of melanocytes death in response to oxidative stress in vitiligo. Cell Death Discov 8(1):70. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-022-00863-3
Majno G, Joris I (1995) Apoptosis, oncosis, and necrosis. An overview of cell death. Am J Pathol 146(1):3–15
Van Cruchten S, Van Den Broeck W (2002) Morphological and biochemical aspects of apoptosis, oncosis and necrosis. Anat Histol Embryol 31(4):214–223. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0264.2002.00398.x
Sayk F, Bartels C (2004) Oncosis rather than apoptosis? Ann Thorac Surg 77(1):382. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-4975(02)05014-2
Campisi J (2013) Aging, cellular senescence, and cancer. Annu Rev Physiol 75:685–705. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-030212-183653
Storer M, Mas A, Robert-Moreno A, Pecoraro M, Ortells MC, Di Giacomo V et al (2013) Senescence is a developmental mechanism that contributes to embryonic growth and patterning. Cell 155(5):1119–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.041
van Deursen JM (2014) The role of senescent cells in ageing. Nature 509(7501):439–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13193
Baker DJ, Childs BG, Durik M, Wijers ME, Sieben CJ, Zhong J et al (2016) Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)-positive cells shorten healthy lifespan. Nature 530(7589):184–189. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16932
Koenig U, Robenek H, Barresi C, Brandstetter M, Resch GP, Groger M et al (2020) Cell death induced autophagy contributes to terminal differentiation of skin and skin appendages. Autophagy 16(5):932–945. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1646552
Qin X, Zhang J, Wang B, Xu G, Yang X, Zou Z et al (2021) Ferritinophagy is involved in the zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced ferroptosis of vascular endothelial cells. Autophagy 17(12):4266–4285. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2021.1911016
Yu J, Li S, Qi J, Chen Z, Wu Y, Guo J et al (2019) Cleavage of GSDME by caspase-3 determines lobaplatin-induced pyroptosis in colon cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 10(3):193. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1441-4
Kari S, Subramanian K, Altomonte IA, Murugesan A, Yli-Harja O, Kandhavelu M (2022) Programmed cell death detection methods: a systematic review and a categorical comparison. Apoptosis 27(7–8):482–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-022-01735-y
Ketelut-Carneiro N, Fitzgerald KA (2022) Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis-oh my! the many ways a cell can die. J Mol Biol 434(4):167378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167378
He W, Wang Q, Srinivasan B, Xu J, Padilla MT, Li Z et al (2014) A JNK-mediated autophagy pathway that triggers c-IAP degradation and necroptosis for anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 33(23):3004–3013. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.256
Liu J, Liu W, Yang H (2019) Balancing apoptosis and autophagy for Parkinson’s disease therapy: targeting BCL-2. ACS Chem Neurosci 10(2):792–802. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00356
Mei J, Tian H, Huang HS, Hsu CF, Liou Y, Wu N et al (2021) Cellular models of development of ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma: a review of cell of origin and mechanisms of carcinogenesis. Cell Prolif 54(5):e13029. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.13029
Raudenská M, Balvan J, Masařík M (2021) Cell death in head and neck cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Cell Death Dis 12(2):192. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03474-5
Gao W, Wang X, Zhou Y, Wang X, Yu Y (2022) Autophagy, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7(1):196. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01046-3
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D (2021) Ferroptosis in infection, inflammation, and immunity. J Exp Med. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20210518
Hitomi J, Christofferson DE, Ng A, Yao J, Degterev A, Xavier RJ et al (2008) Identification of a molecular signaling network that regulates a cellular necrotic cell death pathway. Cell 135(7):1311–1323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.044
Geng J, Ito Y, Shi L, Amin P, Chu J, Ouchida AT et al (2017) Regulation of RIPK1 activation by TAK1-mediated phosphorylation dictates apoptosis and necroptosis. Nat Commun 8(1):359. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00406-w
Jaco I, Annibaldi A, Lalaoui N, Wilson R, Tenev T, Laurien L et al (2017) MK2 Phosphorylates RIPK1 to Prevent TNF-Induced Cell Death. Mol Cell 66(5):698-710.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.003
Lee S, Karki R, Wang Y, Nguyen LN, Kalathur RC, Kanneganti T-D (2021) AIM2 forms a complex with pyrin and ZBP1 to drive PANoptosis and host defence. Nature 597(7876):415–419. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03875-8
Degen M, Santos JC, Pluhackova K, Cebrero G, Ramos S, Jankevicius G et al (2023) Structural basis of NINJ1-mediated plasma membrane rupture in cell death. Nature 618(7967):1065–1071. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05991-z
Kayagaki N, Stowe IB, Alegre K, Deshpande I, Wu S, Lin Z et al (2023) Inhibiting membrane rupture with NINJ1 antibodies limits tissue injury. Nature 618(7967):1072–1077. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06191-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S-HZ, D-CR and H-XT designed the review and the structure of this manuscript. L-YW and X-JL wrote the manuscript draft. Q-QL, YZ, H-LR, J-NS, JZ and JM helped to search reference of this review and contributed to the writing. S-HZ contributed to the revision and finalization of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LY., Liu, XJ., Li, QQ. et al. The romantic history of signaling pathway discovery in cell death: an updated review. Mol Cell Biochem (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04873-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04873-2