Abstract
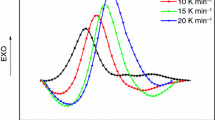
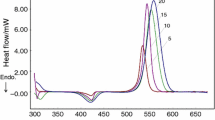
The kinetics of fast thermal curing epoxy resin and the fast-curing ability initiated by 4- hydroxyphenyl dialkyl sulfonium salt cationic curing agent were discussed. The curing reaction is driven by two chain propagation mechanisms. At the initial stage of the polymerization, the propagation is dominated by activated chain end (ACE) mechanism with a faster curing rate. At long time of the polymerization, the propagation is dominated by activated monomer (AM) mechanism with a lower curing rate. With the increase of curing agent content, the activation energy of ACE mechanism reduces, however, the activation energy of AM mechanism decreases first and then increases. In addition, the surface curing test was used to evaluate the fast-curing ability of this epoxy system. By adopting preferred formulation and process, this epoxy system could be cured in several seconds.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi Z. Nanostructured epoxy adhesives: a review. Prog Org Coat. 2019;135:449–53.
Kowalczyk K, Spychaj T. Epoxy coatings with modified montmorillonites. Prog Org Coat. 2008;62(4):425–9.
Liu S, Gu L, Zhao HC, Chen JM, Yu HB. Corrosion resistance of graphene-reinforced waterborne epoxy coatings. J Mater Sci Technol. 2016;32(5):425–31.
Rimdusit S, Ishida H. Development of new class of electronic packaging materials based on ternary systems of benzoxazine, epoxy, and phenolic resins. Polymer. 2000;41(22):7941–9.
Ham YR, Kim SH, Shin YJ, Lee DH, Yang M, Min JH, et al. A comparison of some imidazoles in the curing of epoxy resin. J Ind Eng Chem. 2010;16(4):556–9.
Xu YJ, Wang J, Tan Y, Qi M, Chen L, Wang YZ. A novel and feasible approach for one-pack flame-retardant epoxy resin with long pot life and fast curing. Chem Eng J. 2018;337:30–9.
Zhang BL, Tang GL, Shi KY, You YC, Du ZJ, Yang JF, et al. A study on properties of epoxy resin toughened by functionalized polymer containing rigid, rod-like moiety. Eur Polym J. 2000;36(1):205–13.
Ham YR, Lee DH, Kim SH, Shin YJ, Yang M, Shin JS. Microencapsulation of imidazole curing agent for epoxy resin. J Ind Eng Chem. 2010;16(5):728–33.
Wang YR, Liu WS, Qiu YP, Wei Y. A one-component, fast-cure, and economical epoxy resin system suitable for liquid molding of automotive composite parts. Materials. 2018;11(5):685.
Sangermano M, Malucelli G, Amerio E, Priola A, Billi E, Rizza G. Photopolymerization of epoxy coatings containing silica nanoparticles. Prog Org Coat. 2005;54(2):134–8.
Sangermano M, Roppolo I, Chiappone A. New horizons in cationic photopolymerization. Polymers. 2018;10(2):136.
Penczek S. Cationic ring-opening polymerization (CROP) major mechanistic phenomena. J Polym Sci Pol Chem. 2000;38(11):1919–33.
Penczek S, Kubisa P, Szymański R. Activated monomer propagation in cationic polymerizations. Makromol Chem, Macromol Symp. 1986;3(1):203–20.
Anderson BJ. Cationic cure kinetics of a polyoxometalate loaded epoxy nanocomposite. J Polym Sci Pol Chem. 2012;50(21):4507–15.
Gonzalez L, Ramis X, Salla JM, Mantecon A, Serra A. Kinetic analysis by DSC of the cationic curing of mixtures of DGEBA and 6,6-dimethyl (4,8-dioxaspiro [2.5]octane-5,7-dione). Thermochim Acta. 2007;464(1–2):35–41.
Crivello JV. Cationic polymerization-Iodonium and sulfonium salt photoinitiators. Adv Polym Sci. 1984;62:1–48.
Wang Y, Wei RB, He YN, Wang XG. Synthesis of hyperbranched azo-polymer-grafted graphene oxide hybrid. Chem Lett. 2012;41(4):430–1.
Chen Y, Jia XQ, Wang MQ, Wang T. A synergistic effect of a ferrocenium salt on the diaryliodonium salt-induced visible-light curing of bisphenol-a epoxy resin. RSC Adv. 2015;5(42):33171–6.
Ahn YS, Chen Y, Hahn HT. A resist for electric imprint lithography. Microelectron Eng. 2009;86(3):392–6.
Crivello JV, Lam JHW. Photoinitiated cationic polymerization with triarylsulfonium salts. J Polym Sci Pol Chem. 1996;34(16):3231–53.
Crivello JV, Lam JHW. Photoinitiated cationic polymerization by dialkylphenacylsulfonium salts. J Polym Sci Pol Chem Ed. 1979;17(9):2877–92.
Crivello JV, Lam JHW. Photoinitiated cationic polymerization by dialkyl-4-hydroxyphenylsulfonium salts. J Polym Sci Pol Chem Ed. 1980;18(3):1021–34.
Boey F, Rath SK, Ng AK, Abadie MJM. Cationic UV cure kinetics for multifunctional epoxies. J Appl Polym Sci. 2002;86(2):518–25.
Canavate J, Colom X, Pages P, Carrasco F. Study of the curing process of an epoxy resin by FTIR spectroscopy. Polym-Plast Technol. 2000;39(5):937–43.
Barkoula NM, Karabela M, Zafeiropoulos NE, Tsotra P. Fast curing versus conventional resins–degradation due to hygrothermal and UV exposure. Express Polym Lett. 2020;14(5):401–15.
Xiao GZ, Delamar M, Shanahan MER. Irreversible interactions between water and DGEBA/DDA epoxy resin during hygrothermal aging. J Appl Polym Sci. 1997;65(3):449–58.
Olmos D, Aznar AJ, Gonzalez-Benito J. Kinetic study of the epoxy curing at the silica particles/epoxy interface using the fluorescence of pyrene label. Polym Test. 2005;24(3):275–83.
Kissinger HE. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1957;29(11):1702–6.
Crane LW, Dynes PJ, Kaelble DH. Analysis of curing kinetics in polymer composites. J Polym Sci Pol Lett Ed. 1973;11(8):533–40.
Salla JM, Fernandez-Francos X, Ramis X, Mas C, Mantecon A, Serra A. Influence of the proportion of ytterbium triflate as initiator on the mechanism of copolymerization of DGEBA epoxy resin and gamma-butyrolactone. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;91(2):385–93.
Perrin FX, Nguyen TMH, Vernet JL. Modeling the cure of an epoxy-amine resin with bisphenol a as an external catalyst. Macromol Chem Phys. 2007;208(1):55–67.
Akahira T, Sunose T. Method of determining activation deterioration constant of electrical insulating materials. Res Rep Chiba Inst Technol (Sci Technol). 1971;16:22–31.
Kowalczyk K, Kowalczyk A. Influence of cationic photoinitiator type on properties of coating materials based on cycloaliphatic and glycidyl epoxy resins. Prog Org Coat. 2017;112:1–8.
Rodriguez-Uicab O, Abot JL, Aviles F. electrical resistance sensing of epoxy curing using an embedded carbon nanotube yarn. Sensors. 2020;20(11):3230.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the Ji’an Double Hundred Plan Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Investigation, Writing–original draft. JC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources. HW: Investigation, Writing–review & editing. HL: Supervision, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–review & editing.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Chen, J., Wang, H. et al. Kinetics of fast-curing epoxy resin cationic thermopolymerization: Propagated by ACE and AM mechanism. J Therm Anal Calorim 147, 11899–11907 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11381-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11381-w