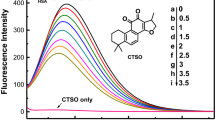
Abstract
Interaction of diclofenac and indomethacin with lysozyme was studied using several spectroscopic and molecular docking methods. Difference UV–visible spectra showed that the absorption profile of lysozyme changed when both diclofenac and indomethacin were mixed with the former. The sequential addition of both drugs to the lysozyme solution caused the decrease of the intrinsic fluorescence of the latter, however, when the data were corrected for inner filter effect, an enhancement in the fluorescence of lysozyme was detected. Accordingly, the fluorescence enhancement data were analyzed using Benesi–Hildebrand equation. Both, diclofenac and indomethacin showed good interaction with lysozyme, although, the association constants of indomethacin were nearly two-fold higher as compared to that of diclofenac. The binding was slightly more spontaneous in case of indomethacin and the major forces involved in the binding of both drugs with lysozyme were hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions. Secondary structural analysis revealed that both drugs partially unfolded lysozyme. Results obtained through molecular docking were also in good agreement with the experimental outcomes. Both, diclofenac and indomethacin, are bounded at the same site inside lysozyme which is located in the big hydrophobic cavity of the protein.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be available on request to the corresponding author.
References
Sharifi-Rad A, Mehrzad J, Darroudi M, Saberi MR, Chamani J (2021) Oil-in-water nanoemulsions comprising Berberine in olive oil: biological activities, binding mechanisms to human serum albumin or holo-transferrin and QMMD simulations. J Biomol Struct Dyn 39:1029–1043
Marjani N, Dareini M, Asadzade-Lotfabad M, Pejhan M, Mokaberi P, Amiri-Tehranizadeh Z, Saberi MR, Chamani J (2022) Evaluation of the binding effect and cytotoxicity assay of 2-ethyl-5-(4-methylphenyl) pyramido pyrazole ophthalazine trione on calf thymus DNA: spectroscopic, calorimetric, and molecular dynamics approaches. Luminescence 37:310–322
Zare-Feizabadi N, Amiri-Tehranizadeh Z, Sharifi-Rad A, Mokaberi P, Nosrati N, Hashemzadeh F, Rahimi HR, Saberi MR, Chamani J (2021) Determining the interaction behavior of calf thymus DNA with anastrozole in the presence of histone H1: Spectroscopies and cell viability of MCF-7 cell line investigations. DNA Cell Biol 40:1039–1051
Taheri R, Hamzkanlu N, Rezvani Y, Niroumand S, Samandar F, Amiri-Tehranizadeh Z, Saberi MR, Chamani J (2022) Exploring the HSA/DNA/lung cancer cells binding behavior of p-Synephrine, a naturally occurring phenyl ethanol amine with anti-adipogenic activity: multi spectroscopic, molecular dynamic and cellular approaches. J Mol Liq 368:120826
Maheri H, Hashemzadeh F, Shakibapour N, Kamelniya E, Malaekeh-Nikouei B, Mokaberi P, Chamani J (2022) Glucokinase activity enhancement by cellulose nanocrystals isolated from jujube seed: A novel perspective for type II diabetes mellitus treatment (In vitro). J Mol Struct 1269:133803
Kalhori F, Yazdyani H, Khademorezaeian F, Hamzkanloo N, Mokaberi P, Hosseini S, Chamani J (2022) Enzyme activity inhibition properties of new cellulose nanocrystals from Citrus medica L. pericarp: A perspective of cholesterol lowering. Luminescence 37:1836–1845
Assaran Darban R, Shareghi B, Asoodeh A, Chamani J (2017) Multi-spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies of interaction between two different angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from gluten hydrolysate and human serum albumin. J Biomol Struct Dyn 35:3648–3662
Khashkhashi-Moghadam S, Ezazi-Toroghi S, Kamkar-Vatanparast M, Jouyaeian P, Mokaberi P, Yazdyani H, Amiri-Tehranizadeh Z, Reza Saberi M, Chamani J (2022) Novel perspective into the interaction behavior study of the cyanidin with human serum albumin-holo transferrin complex: Spectroscopic, calorimetric and molecular modeling approaches. J Mol Liq 356:119042
Housaindokht MR, Chamani J, Saboury AA, Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Bahrololoom M (2001) Three binding sets analysis of alpha-Lactalbumin by interaction of tetradecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide. Bull Korean Chem Soc 22:145–148
Lonnerdal B (2003) Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins. Am J Clin Nutr 77:1537s–1543s
Grumezescu V, Holban AM, Barbu I, Popescu RC, Oprea AE, Lazar V, Grumezescu AM, Chifiriuc MC (2016) Chapter 7 - Nanoarchitectonics Used in Antiinfective Therapy. In: Kon K, Rai M (eds) Antibiotic Resistance. Academic Press, pp 145–166
Ali MS, Al-Lohedan HA (2020) Spectroscopic and Molecular Docking Investigation on the Noncovalent Interaction of Lysozyme with Saffron Constituent “Safranal.” ACS Omega 5:9131–9141
Sood D, Kumar N, Singh A, Tomar V, Dass SK, Chandra R (2019) Deciphering the Binding Mechanism of Noscapine with Lysozyme: Biophysical and Chemoinformatic Approaches. ACS Omega 4:16233–16241
Swain BC, Mukherjee SK, Rout J, Sakshi, Mishra PP, Mukherjee M, Tripathy U (2020) A spectroscopic and computational intervention of interaction of lysozyme with 6-mercaptopurine. Anal Bioanal Chem 412:2565–2577
Das S, Santra S, Rohman MA, Ray M, Jana M, Roy AS (2019) An insight into the binding of 6-hydroxyflavone with hen egg white lysozyme: a combined approach of multi-spectroscopic and computational studies. J Biomol Struct Dyn 37:4019–4034
Hosseinzadeh R, Khorsandi K, Sheikh-Hasani V, Khatibi A (2016) Biological interaction of thiamine with lysozyme using binding capacity concept and molecular docking. J Biomol Struct Dyn 34:2146–2154
Mutru O, Penttilä M, Pesonen J, Salmela P, Suhonen O, Sonck T (1978) Diclofenac sodium (Voltaren) and indomethacin in the ambulatory treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a double-blind multicentre study. Scand J Rheumatol 7:51–56
Guan P-P, Yang L-Q, Xu G-B, Wang P (2021) Indomethacin Disrupts the Formation of β-Amyloid Plaques via an α2-Macroglobulin-Activating lrp1-Dependent Mechanism. Int J Mol Sci 22:8185
Hirohata M, Ono K, Naiki H, Yamada M (2005) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have anti-amyloidogenic effects for Alzheimer’s β-amyloid fibrils in vitro. Neuropharmacology 49:1088–1099
Kaur J, Sanyal SN (2011) Diclofenac, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, inhibits DMH-induced colon tumorigenesis through suppression of MCP-1, MIP-1α and VEGF. Mol Carcinog 50:707–718
Choi S, Kim S, Park J, Lee SE, Kim C, Kang D (2022) Diclofenac: A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug inducing cancer cell death by inhibiting microtubule polymerization and autophagy flux. Antioxidants 11:1009
Shaymaa Emam K (2018) Indomethacin from anti-inflammatory to anticancer agent. In: Janka V, Ladislav V (eds) Medicinal chemistry. IntechOpen, Rijeka, pp Ch. 4
Okda TM, Abdelghaffar SK, Katary MA, Abdalhaseeb MM (2021) Chemopreventive and anticancer activities of indomethacin and vitamin D combination on colorectal cancer induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine in rats. Biomed Rep 14:27
Vallecillo-Hernández J, Barrachina MD, Ortiz-Masiá D, Coll S, Esplugues JV, Calatayud S, Hernández C (2018) Indomethacin disrupts autophagic flux by inducing lysosomal dysfunction in gastric cancer cells and increases their sensitivity to cytotoxic drugs. Sci Rep-Uk 8:3593
Chamouard J-M, Barre J, Urien S, Houin G, Tillement J-P (1985) Diclofenac binding to albumin and lipoproteins in human serum. Biochem Pharmacol 34:1695–1700
Sharma R, Choudhary S, Kishore N (2012) Insights into the binding of the drugs diclofenac sodium and cefotaxime sodium to serum albumin: Calorimetry and spectroscopy. Eur J Pharm Sci 46:435–445
Zhang Y, Lee P, Liang S, Zhou Z, Wu X, Yang F, Liang H (2015) Structural basis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac binding to human serum albumin. Chem Biol Drug Des 86:1178–1184
Sekula B, Bujacz A (2016) Structural insights into the competitive binding of diclofenac and naproxen by equine serum albumin. J Med Chem 59:82–89
Dohare N, Khan AB, Athar F, Thakur SC, Patel R (2016) Urea-induced binding between diclofenac sodium and bovine serum albumin: a spectroscopic insight. Luminescence 31:945–951
Bou-Abdallah F, Sprague SE, Smith BM, Giffune TR (2016) Binding thermodynamics of Diclofenac and Naproxen with human and bovine serum albumins: A calorimetric and spectroscopic study. J Chem Thermodyn 103:299–309
Ekman B, Sjödin T, Sjöholm I (1980) Binding of drugs to human serum albumin—XV: Characterization and identification of the binding sites of indomethacin. Biochem Pharmacol 29:1759–1765
Zini R, Athis PD, Barre J, Tillement JP (1979) Binding of indomethacin to human serum albumin. Its non displacement by various agents, influence of free fatty acids and the unexpected effect of indomethacin on warfarin binding. Biochem Pharmacol 28:2661–2665
Cots J, Pouplana R, Estelrich J (1987) Conformational changes in the human serum albumin-indomethacin binding. Colloid Polym Sci 265:164–166
Ali MS, Muthukumaran J, Jain M, Al-Sanea ASS, Al-Lohedan HA (2021) Experimental and in silico investigation on the interaction of indomethacin with bovine serum albumin: Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate surfactant monomers on the binding. J Mol Liq 336:116858
Bogdan M, Pirnau A, Floare C, Bugeac C (2008) Binding interaction of indomethacin with human serum albumin. J Pharm Biomed Anal 47:981–984
Zhang J, Sun H-H, Zhang Y-Z, Yang L-Y, Dai J, Liu Y (2012) Interaction of human serum albumin with indomethacin: spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies. J Solution Chem 41:422–435
Khatibi A, Keihan AH, Sheikh Hasani V (2017) Bio thermodynamic studies of diclofenac interaction with lysozyme under various conditions using diclofenac-selective membrane electrode and molecular docking. J Biomol Struct Dyn 35:2789–2793
Basheeruddin M, Khan S, Ahmed N, Jamal S (2022) Effect of pH on diclofenac–lysozyme interaction: structural and functional aspect. Front Mol Biosci 9:872905
Ali MS, Waseem M, Subbarao N, Al-Lohedan HA (2021) Noncovalent molecular interactions between antineoplastic drug gemcitabine and a carrier protein identified through spectroscopic and in silico methods. Int J Biol Macromol 182:993–1002
Ali MS, Al-Lohedan HA (2018) Spectroscopic and computational evaluation on the binding of safranal with human serum albumin: Role of inner filter effect in fluorescence spectral correction. Spectrochim Acta A 203:434–442
Zhao HY, Datta SA, Kim S, Chaturvedi SK, Rein A, Schuck P (2019) Studying multi-protein interactions by fluorescence detected sedimentation velocity combining hydrodynamic separation of complexes with fluorescence quenching analysis. Biophys J 116:194a
Valeur B, Berberan-Santos MN (2012) Molecular fluorescence: principles and applications. Wiley
Rao JH, Dragulescu-Andrasi A, Yao HQ, Yao HQ (2007) Fluorescence imaging in vivo: recent advances. Curr Opin Biotech 18:17–25
Lakowicz JR (2006) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy, 3rd edn. Springer, US
Imoto T, Rupley JA, Tanaka F, Forster LS (1972) Fluorescence of Lysozyme - Emissions from Tryptophan Residues 62 and 108 and Energy Migration. P Natl Acad Sci USA 69:1151–2000
Malek-Esfandiari Z, Rezvani-Noghani A, Sohrabi T, Mokaberi P, Amiri-Tehranizadeh Z, Chamani J (2023) Molecular dynamics and multi-spectroscopic of the interaction behavior between bladder cancer cells and calf thymus DNA with rebeccamycin: apoptosis through the down regulation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Fluoresc 33:1537–1557
Amézqueta S, Beltrán JL, Bolioli AM, Campos-Vicens L, Luque FJ, Ràfols C (2021) Evaluation of the Interactions between Human Serum Albumin (HSA) and Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory (NSAIDs) drugs by multiwavelength molecular fluorescence, structural and computational analysis. Pharmaceuticals 14:214
Ploch-Jankowska A, Pentak D (2020) A comprehensive spectroscopic analysis of the ibuprofen binding with human serum albumin, Part I. Pharmaceuticals 13:205
Ploch-Jankowska A, Pentak D, Nycz JE (2021) A comprehensive spectroscopic analysis of the ibuprofen binding with human serum albumin. Part II. Sci Pharm 89:30
Sudlow G, Birkett DJ, Wade DN (1976) Further characterization of specific drug binding-sites on human-serum albumin. Mol Pharmacol 12:1052–1061
Zhao LZ, Zhao YS, Teng HH, Shi SY, Ren BX (2014) Spectroscopic investigation on the interaction of titanate nanotubes with bovine serum albumin. J Appl Spectrosc 81:719–724
Bhattacharyya J, Bhattacharyya M, Chakrabarty AS, Chaudhuri U, Poddar RK (1994) Interaction of chlorpromazine with myoglobin and hemoglobin - a comparative-study. Biochem Pharmacol 47:2049–2053
Valdebenito S, Zapata-Torres G, Lemp E, Zanocco AL (2015) Experimental and theoretical studies of the photophysics of 7-amino-3-phenyl-2H-benzo[b] [1,4]oxazin-2-one in homogeneous solvents and beta-cyclodextrin aqueous solutions. Afinidad 72:53–59
He WY, Li Y, Si HZ, Dong YM, Sheng FL, Yao XJ, Hu ZD (2006) Molecular modeling and spectroscopic studies on the binding of guaiacol to human serum albumin. J Photoch Photobio A 182:158–167
Chang J-Y, Li L (2002) The unfolding mechanism and the disulfide structures of denatured lysozyme. FEBS Lett 511:73–78
Hosseinzadeh M, Nikjoo S, Zare N, Delavar D, Beigoli S, Chamani J (2019) Characterization of the structural changes of human serum albumin upon interaction with single-walled and multi-walled carbon nanotubes: spectroscopic and molecular modeling approaches. Res Chem Intermed 45:401–423
Chamani J, Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Hakimelahi GH (2005) Structural changes in β-lactoglobulin by conjugation with three different kinds of carboxymethyl cyclodextrins. Thermochim Acta 432:106–111
Atkovska K, Samsonov SA, Paszkowski-Rogacz M, Pisabarro MT (2014) Multipose binding in molecular docking. Int J Mol Sci 15:2622–2645
Lee HS, Jo S, Lim H-S, Im W (2012) Application of binding free energy calculations to prediction of binding modes and affinities of MDM2 and MDMX inhibitors. J Chem Inf Model 52:1821–1832
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support through the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2023R724), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support through the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2023R724), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
“Conceptualization, M.S.A.; methodology, M.S.A., validation, MSA,; formal analysis, MSA; investigation, MSA; resources, HAA.; writing—original draft preparation, MSA, HAA; writing—review and editing, MSA, HAA; visualization, MSA; funding acquisition, MSA".
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, M.S., Al-Lohedan, H.A. Spectroscopic and Molecular Docking Studies of the Interaction of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs with a Carrier Protein: an Interesting Case of Inner Filter Effect and Intensity Enhancement in Protein Fluorescence. J Fluoresc (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03422-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03422-w