Abstract
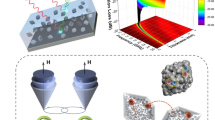
In this study, SiO2 hard template method and phenolic resin carbonization were synthesized to prepare porous hollow carbon microspheres. Porous hollow carbon microspheres with different mesoporous shells and internal cavities were obtained by adjusting the slow addition time of resorcinol-formaldehyde and stirring rate. The samples were characterized by SEM, TEM, nitrogen adsorption and desorption tests, and network vector analyzer. When the slow addition time is 90 min, the stirring rate is 950r/min, and the loading amount is only 6.25%, the optimal performance was observed. The minimum reflection loss rate (RLmin) is − 27.4dB and the maximum effective absorption bandwidth (EABmax) is 6.5 GHz. The reason why the absorbing material has good electromagnetic wave absorption performance is that the material contains internal cavity and mesoporous shell. The interface polarization not only improves the loss capacity, but also the porous structure is more conducive to the impedance matching.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
H. Xu, X. Yin, X. Fan, Z. Tang, Z. Hou, M. Li, X. Li, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Constructing a tunable heterogeneous interface in bimetallic metal–organic frameworks derived porous carbon for excellent microwave absorption performance. Carbon 148, 421–429 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.03.091
H. Xu, X. Yin, M. Li, F. Ye, M. Han, Z. Hou, X. Li, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Mesoporous carbon hollow microspheres with red blood cell like morphology for efficient microwave absorption at elevated temperature. Carbon 132, 343–351 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.02.040
Y. Cheng, J. Cao, Y. Li, Z. Li, H. Zhao, G. Ji, Y. Du, The outside-in approach to construct Fe3O4 nanocrystals/mesoporous carbon hollow spheres core–shell hybrids toward microwave absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6(1), 1427–1435 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03846
M. Kolahdouz, B. Xu, A.F. Nasiri, M. Fathollahzadeh, M. Manian, H. Aghababa, Y. Wu, H.H. Radamson, Carbon-related materials: graphene and carbon nanotubes in semiconductor applications and design. Micromachines (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13081257
L. Kong, X. Yin, M. Han, X. Yuan, Z. Hou, F. Ye, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Z. Xu, J. Huang, Macroscopic bioinspired graphene sponge modified with in situ grown carbon nanowires and its electromagnetic properties. Carbon 9(111), 94–102 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.09.066
H. Sun, R. Che, X. You, Y. Jiang, Z. Yang, J. Deng, L. Qiu, H. Peng, Cross-stacking aligned carbon-nanotube films to tune microwave absorption frequencies and increase absorption Intensities. Adv. Mater. 26(48), 8120–8125 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201403735
L. Kong, C. Wang, X. Yin, X. Fan, W. Wang, J. Huang, Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of a carbon nanotube modified by a tetrapyridinoporphyrazine interface layer. J. Mater. Chem. C 5(30), 7479–7488 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tc02701j
Y. Zhang, Y. Huang, T. Zhang, H. Chang, P. Xiao, H. Chen, Z. Huang, Y. Chen, Broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption of an ultralight and highly compressible graphene foam. Adv. Mater. 27(12), 2049–2053 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201405788
X. Xu, G. Wang, G. Wan, S. Shi, C. Hao, Y. Tang, G. Wang, Magnetic Ni/graphene connected with conductive carbon nano-onions or nanotubes by atomic layer deposition for lightweight and low-frequency microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122980
D. Ding, Y. Wang, X. Li, R. Qiang, P. Xu, W. Chu, X. Han, Y. Du, Rational design of core–shell Co@C microspheres for high-performance microwave absorption. Carbon 111, 722–732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.10.059
C. Zhou, S. Geng, X. Xu, T. Wang, L. Zhang, X. Tian, F. Yang, H. Yang, Y. Li, Lightweight hollow carbon nanospheres with tunable sizes towards enhancement in microwave absorption. Carbon 108, 234–241 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.07.015
H. Xu, X. Yin, M. Zhu, M. Han, Z. Hou, X. Li, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Carbon hollow microspheres with a designable mesoporous shell for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(7), 6332–6341 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b15826
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, Z. Yang, Z. Jia, H. Wu, L. Yang, H. Li, P. Guo, H. Lv, Design of carbon sphere/magnetic quantum dots with tunable phase compositions and boost dielectric loss behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 333, 519–528 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.174
H. Wu, L. Wang, S. Guo, Z. Shen, Double-layer structural design of dielectric ordered mesoporous carbon/paraffin composites for microwave absorption. Appl. Phys. A 108(2), 439–446 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-6906-6
H. Zhao, Y. Cheng, Z. Zhang, B. Zhang, C. Pei, F. Fan, G. Ji, Biomass-derived graphene-like porous carbon nanosheets towards ultralight microwave absorption and excellent thermal infrared properties. Carbon 173, 501–511 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.11.035
H. Zhao, Y. Cheng, H. Lv, G. Ji, Y. Du, A novel hierarchically porous magnetic carbon derived from biomass for strong lightweight microwave absorption. Carbon 142, 245–253 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.10.027
B. Zhao, X. Guo, W. Zhao, J. Deng, B. Fan, G. Shao, Z. Bai, R. Zhang, Facile synthesis of yolk–shell Ni@void@SnO2(Ni3Sn2) ternary composites via galvanic replacement/Kirkendall effect and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. Nano Res. 10(1), 331–343 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1295-3
H. Lv, G. Ji, X. Liang, H. Zhang, Y. Du, A novel rod-like MnO2@Fe loading on graphene giving excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 3(19), 5056–5064 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5tc00525f
Q. Liu, Q. Cao, H. Bi, C. Liang, K. Yuan, W. She, Y. Yang, R. Che, CoNi@SiO2@TiO2and CoNi@Air@TiO2Microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 28(3), 486–490 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201503149
M.A. Ahsan, O. Fernandez-Delgado, E. Deemer, H. Wang, A.A. El-Gendy, M.L. Curry, J.C. Noveron, Carbonization of Co-BDC MOF results in magnetic C@Co nanoparticles that catalyze the reduction of methyl orange and 4-nitrophenol in water. J. Mol. Liq. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111059
R. Qiang, Y. Du, Y. Wang, N. Wang, C. Tian, J. Ma, P. Xu, X. Han, Rational design of yolk–shell C@C microspheres for the effective enhancement in microwave absorption. Carbon 98, 599–606 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.11.054
H. Lv, Y. Guo, Y. Zhao, H. Zhang, B. Zhang, G. Ji, J. Xu, Achieving tunable electromagnetic absorber via graphene/carbon sphere composites. Carbon 110, 130–137 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.09.009
C. Zhang, Y. Peng, Y. Song, J. Li, F. Yin, Y. Yuan, Periodic three-Dimensional Nitrogen-Doped Mesoporous Carbon Spheres Embedded with Co/Co3O4 nanoparticles toward microwave Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(21), 24102–24111 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c03105
L. Huang, J. Li, Z. Wang, Y. Li, X. He, Y. Yuan, Microwave absorption enhancement of porous C@CoFe2O4 nanocomposites derived from eggshell membrane. Carbon 143, 507–516 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.11.042
X. Zhou, C. Zhang, M. Zhang, A. Feng, S. Qu, Y. Zhang, X. Liu, Z. Jia, G. Wu, Synthesis of Fe3O4/carbon foams composites with broadened bandwidth and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manufac. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105627
Y. Shi. Development status and prospect of aviation materials in China. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 632(5) (2021).https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/632/5/052038
Z. Xiang, Y. Wang, X. Yin, Q. He, Microwave absorption performance of porous heterogeneous SiC/SiO2 microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138742
S. Gao, Q. An, Z. Xiao, S. Zhai, Z. Shi, Significant promotion of porous architecture and magnetic Fe3O4 NPs inside honeycomb-like carbonaceous composites for enhanced microwave absorption. RSC Adv. 8(34), 19011–19023 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra00913a
W. Yang, J. Sun, D. Liu, W. Fu, Y. Dong, Y. Fu, Y. Zhu, Rational design of hierarchical structure of carbon@polyaniline composite with enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 194, 114–126 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2022.03.061
S. Xie, Z. Ji, L. Zhu, J. Zhang, Y. Cao, J. Chen, R. Liu, J. Wang, Recent progress in electromagnetic wave absorption building materials. J. Building Eng. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2019.100963
J. Cheng, H. Zhang, Y. Xiong, L. Gao, B. Wen, H. Raza, H. Wang, G. Zheng, D. Zhang, H. Zhang, Construction of multiple interfaces and dielectric/magnetic heterostructures in electromagnetic wave absorbers with enhanced absorption performance: a review. J. Materiomics 7(6), 1233–1263 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2021.02.017
Y. Cheng, H. Zhao, Y. Zhao, J. Cao, J. Zheng, G. Ji, Structure-switchable mesoporous carbon hollow sphere framework toward sensitive microwave response. Carbon 161, 870–879 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.02.011
J. Xu, Z. Liu, J. Wang, P. Liu, M. Ahmad, Q. Zhang, B. Zhang, Preparation of core–shell C@TiO2 composite microspheres with wrinkled morphology and its microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 607(Pt 2), 1036–1049 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.09.038
Q. Li, J. Zhu, S. Wang, F. Huang, Q. Liu, X. Kong, Microwave absorption on a bare biomass derived holey silica-hybridized carbon absorbent. Carbon 161, 639–646 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.01.087
P. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang, Y. Huang, Y. Wang, J. Luo, Core–Shell CoNi@Graphitic carbon decorated on B,N-codoped hollow carbon polyhedrons toward lightweight and high-efficiency microwave attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(28), 25624–25635 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b08525
B. Li, B. Mao, T. He, H. Huang, X. Wang, Preparation and microwave absorption properties of double-layer hollow reticulated SiC foam. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 1(10), 2140–2149 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.9b00510
W. Gu, X. Cui, J. Zheng, J. Yu, Y. Zhao, G. Ji, Heterostructure design of Fe3N alloy/porous carbon nanosheet composites for efficient microwave attenuation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 67, 265–272 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2020.06.054
C. Grosse, A program for the fitting of Debye, Cole–Cole, Cole–Davidson, and Havriliak–Negami dispersions to dielectric data. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 419, 102–106 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.12.031
X. Wang, T. Zhu, S. Chang, Y. Lu, W. Mi, W. Wang, 3D nest-like architecture of core–shell CoFe2O4@1T/2H-MoS2 composites with tunable microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(9), 11252–11264 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b23489
Y. Huo, K. Zhao, P. Miao, J. Kong, Z. Xu, K. Wang, F. Li, Y. Tang, Microwave absorption performance of SiC/ZrC/SiZrOC hybrid nanofibers with enhanced high-temperature oxidation Resistance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 8(28), 10490–10501 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c02789
F. Wu, P. Liu, J. Wang, T. Shah, M. Ahmad, Q. Zhang, B. Zhang, Fabrication of magnetic tubular fiber with multi-layer heterostructure and its microwave absorbing properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 577, 242–255 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.05.058
Funding
This work was supported by Basic Research Expenses Project for Provincial Colleges and Universities (JYG2021001) and Tangshan Science and Technology Planning Project (21130203 C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XY and YZ contributed toward conceptualization, data curation, and writing—original draft preparation. YC contributed toward visualization, investigation, validation, and writing—reviewing and editing. ZZ contributed toward formal analysis, and reviewing and editing. SZ contributed toward methodology, writing—reviewing and editing, and testing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work. We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, X., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z. et al. Structure construction and wave-absorbing properties of mesoporous hollow carbon microspheres. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2039 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11501-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11501-8