Abstract
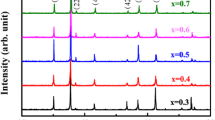
Li0.35+0.5xZn0.3TixFe2..35–1.5xO4 (x = 0–0.4) ferrites waere prepared via a solid-state method. XRD refinement results show that diamagnetic Ti4+ ions enter octahedral lattice and replace Fe3+ at B site, resulting in the redistribution of B sublattice magnetic moment and ultimately reducing saturation magnetization. This mechanism is analyzed from the perspective of ion occupying distribution and substitution law. Globus relation is used to qualitatively analyze the law of initial permeability change with temperature and titanium content, and the main influencing factors are revealed. The variation of initial permeability and permeability loss with frequency and its causes have been explored, which are attributed to domain wall displacement, domain rotation and various resonance effects, especially domain wall resonance. The dominant characteristics and main influencing parameters of the three types of power losses in different frequency bands were studied quantitatively, and the transition law of the main mechanism of power losses with the change of frequency was explored. The variation of dielectric properties with frequency, titanium content and temperature was studied and analyzed utilizing polarization mechanism and Koops model.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Xu, D. Zhang, G. Wang et al., Influence of LZN nanoparticles on microstructure and magnetic properties of Bi-substituted LiZnTi low-sintering temperature ferrites. Ceram. Int. 45, 1946–1949 (2019)
V. Verma, S.P. Gairola, V. Pandey et al., High permeability and low power loss of Ti and Zn substitution lithium ferrite in high frequency range. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3808–3812 (2009)
A.V. Malyshev, E.N. Lysenko, V.A. Vlasov et al., Electromagnetic properties of Li0.4Fe2.4Zn0.2O4 ferrite sintered by continuous electron beam heating. Ceram. Int. 42, 16180–16183 (2016)
E.N. Lysenko, A.L. Astafyev, V.A. Vlasov et al., Analysis of phase composition of LiZn and LiTi ferrites by XRD and thermomagnetometric analysis. Magn. Magn. Mater. 465, 457–4615 (2018)
V.G. Harris, A. Geiler, Y.J. Chen et al., Recent advances in processing and applications of microwave ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2035–2047 (2009)
P. Baba, G. Argentina, W. Courtney et al., Fabrication and properties of microwave lithium ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 8, 83–94 (1972)
D. Ravinder, P.K. Raju, Composition dependence of the elastic moduli of mixed lithium-zinc ferrites. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 136, 351 (1993)
P.V. Reddy, B. Ramesh, G. Reddy, Electrical and dielectric property of zinc substituted lithium ferrite prepared by sol-gel method. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 405, 1852–1856 (2010)
M. Srivastava, A.K. Ojha, S. Chaubey et al., Influence of pH on structural morphology and magnetic properties of ordered phase Co-doped lithium ferrites nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 175, 14–21 (2010)
Z.X. Yue, J. Zhou, X.H. Wang et al., Preparation and magnetic properties of titanium-substituted LiZn ferrites via a sol-gel auto-combustion process. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23, 189–193 (2003)
N. Thomas, T. Shimna, P.V. Jithin et al., Comparative study of the structural and magnetic properties of alpha and beta phases of lithium ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by solution combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 462, 136–143 (2018)
V. Rathod, A.V. Anupama, V.M. Jali et al., Combustion synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of Li-Zn ferrite ceramic powders. Ceram. Int. 43, 14431–14440 (2017)
V. Rathod, A.V. Anupama, R. Vijaya Kumar et al., Correlated vibrations of the tetrahedral and octahedral complexes and splitting of the absorption bands in FTIR spectra of Li-Zn ferrites. Vibrat. Spectrosc. 92, 267–272 (2017)
A.V. Anupama, V. Rathod, V.M. Jali et al., Composition dependent elastic and thermal properties of Li-Zn ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 728, 1091–1100 (2017)
A.V. Anupama, V. Kumaran, B. Sahoo, Magnetorheological fluids containing rod-shaped lithium–zinc ferrite particles: the steady-state shear response. Soft Matter 14, 5407 (2018)
Y. Yang, H. Zhang, J. Li et al., Effects of Bi2O3-Nb2O5 additives on microstructure and magnetic properties of low-temperature-fired NiCuZn ferrite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 44, 10545–10550 (2018)
F. Xie, L. Jia, F. Xu et al., Improved sintering characteristics and gyromagnetic properties of low-temperature sintered Li0.42Zn0.27Ti0.11Mn0.1Fe2.1O4 ferrite ceramics modified with Bi2O3-ZnO-B2O3 glass additive. Ceram. Int. 44, 13122–13128 (2018)
T.C. Zhou, H.W. Zhang, L. Jia et al., Enhanced ferromagnetic properties of low temperature sintering LiZnTi Ferrites with Li2O-B2O3-SiO2-CaO-Al2O3 glass addition. J. Alloys Compd. 620, 421–426 (2015)
F. Xue, J. Huang, T. Li et al., Lowering the synthesis temperature of Y3Fe5O12 by surfactant assisted solid state reaction. J. Magn. Magn Mater. 446, 118–124 (2018)
M.A. Gil, D.B. Paul, Study of the physical and magnetic properties of Li0.3Zn0.4−xCaxFe23O4 ferrite. J. Alloys. Compd. 496, 341–344 (2010)
M.S. Ruiz, S.E. Jacobo, Electromagnetic properties of lithium zinc ferrites doped with aluminum. Phys. Rev. B. 407, 3274–3277 (2012)
S. Misra, Modified magnetic and dielectric properties in Gd3+-substituted lithium zinc ferrite nanocrystallites. Mater. Res. Bull. 91, 203–207 (2017)
E.N. Lysenko, S.A. Ghyngazov, The influence of ZrO2 additive on sintering and microstructure of lithium and lithium-titanium-zinc ferrites. Ceram. Int. 45, 2736–2741 (2019)
I. Soibam, Structural and initial permeability studies of Li-Zn-Co Ferrites. Integr. Ferroelectr. 117, 28–33 (2010)
G.O. White, C.E. Patton, ChemInform abstract: magnetic properties of lithium ferrite microwave materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 9, 299–317 (1978)
Z.C. Xu, Magnetic anisotropy and Mssbauer spectra in disordered lithium-zinc ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 4746–4749 (2003)
A. Globus, H. Pascard, V.J. Cagan et al., Improvement of the magnetic properties of Li-Zn ferrite by Bi3+ substitution. J. Phys. 38, 163–168 (1977)
S. Chikazumi, Physics of Magnetism (Wiley, New York, 1964).
A.K. Singh, T.C. Goel, R.G. Mendiratta et al., Magnetic properties of Mn-substituted Ni-Zn ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 3872–3876 (2002)
K. Ishino, Y. Narumiya, Development of magnetic ferrites: control and application of losses. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 66, 1469–1474 (1987)
A.V. Anupama, M. Manjunatha, V. Rathod et al., 57Fe internal field nuclear magnetic resonance and Mössbauer spectroscopy study of Li-Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Reson. 286, 68–77 (2018)
H.K. Choudhary, M. Manjunatha, R. Damle et al., Solvent dependent morphology and 59Co internal field NMR study of Co-aggregates synthesized by a wet chemical method. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 17739 (2018)
A.M. Abdeen, Dielectric behaviour in Ni-Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 192, 121–129 (1999)
S. Madolappa, A.V. Anupama, P.W. Jaschin et al., Magnetic and ferroelectric characteristics of Gd3+ and Ti4+ co-doped BiFeO3 ceramics. Bull. Mater. Sci. 39, 593–601 (2016)
B.R. Thejashwini, V. Khopkar, R. Madhusudhana et al., Crystal growth and effect of defects on the dielectric properties of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP) single crystals. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 10548–10552 (2020)
V. Khopkar, B. Sahoo, Low temperature dielectric properties and NTCR behavior of the BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3 double perovskite ceramic. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22, 2986 (2020)
S. Matteppanavar, I. Shivaraja, S. Rayaprol et al., Evidence for room-temperature weak ferromagnetic and ferroelectric ordering in magnetoelectric Pb(Fe0.634W0.266Nb0.1)O3 ceramic. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 30, 1317–1325 (2017)
S. Matteppanavar, S. Rayaprol, A.V. Anupama et al., On the room temperature ferromagnetic and ferroelectric properties of Pb(Fe1/2Nb1/2)O3. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28, 2465–2472 (2015)
S. Matteppanavar, S. Rayaprol, A.V. Anupama et al., Origin of room temperature weak-ferromagnetism in antiferromagnetic Pb(Fe2/3W1/3)O3 ceramic. Ceram. Int. 41, 11680–11686 (2015)
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant number: No.2018YFF01010701) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Zhu, J. & Li, H. Structure, electromagnetic and dielectric properties of Ti-substituted lithium--zinc ferrite. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 8354–8365 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05419-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05419-2