Abstract
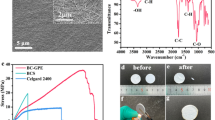
Polymers, such as PVDF and PMMA, have been commonly adopted as host materials for gel polymer electrolytes (GPEs), leading to excessive consumption of fossil fuel as well as severe white pollution. Nanocellulose (NC) is a kind of renewable and biodegradable carbohydrate polymer so that its possible application in gel polymer electrolyte for lithium-ion battery is discussed in this paper. The NC membrane with a porous network is prepared by freeze-drying method. To further extend its application into GPE, glutaraldehyde (GA) is used as cross-link agent to enhance the performance of the membrane. Cross-linked by 6 wt% GA, the skeleton membrane exhibits satisfactory mechanical property and thermal stability. The GPE gives moderate electrochemical performance and reverse capability. The experimental results show that the introduction of nanocellulose provides a direction for the development of carbohydrate polymer applied in GPE.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang F, Yin L, Yu Q, Zhong C, Zhang J (2015) Bacterial cellulose nanofibrous membrane as thermal stable separator for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 279:21–27
Lin C-E, Zhang H, Song Y-Z, Zhang Y, Yuan J-J, Zhu B-K (2018) Carboxylated polyimide separator with excellent lithium ion transport properties for a high-power density lithium-ion battery. J Mater Chem A 6:991–998
Zhang J, Yue L, Kong Q et al (2014) Sustainable, heat-resistant and flame-retardant cellulose-based composite separator for high-performance lithium ion battery. Sci Rep 4(1):3935
Panchal S, Mathew M, Fraser R, Fowler M (2018) Electrochemical thermal modeling and experimental measurements of 18650 cylindrical lithium-ion battery during discharge cycle for an EV. Appl Therm Eng 135:123–132
Panchal S, Dincer I, Agelin-Chaab M, Fraser R, Fowler M (2017) Transient electrochemical heat transfer modeling and experimental validation of a large sized LiFePO4/graphite battery. Int J Heat Mass Transf 109:1239–1251
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414:359–367
Nitta N, Wu F, Lee JT, Yushin G (2015) Li-ion battery materials: present and future. Mater Today 18:252–264
Bruce PG, Scrosati B, Tarascon JM (2008) Nanomaterials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Angew Chem 47:2930–2946
Schadeck U, Kyrgyzbaev K, Gerdes T, Willert-Porada M, Moos R (2018) Porous and non-porous micrometer-sized glass platelets as separators for lithium-ion batteries. J Membr Sci 550:518–525
Zhou Q, Dong S, Lv Z et al (2020) A temperature-responsive electrolyte endowing superior safety characteristic of lithium metal batteries. Adv Energy Mater 10(6):1903441
Wang Z, Xiang H, Wang L et al (2018) A paper-supported inorganic composite separator for high-safety lithium-ion batteries. J Membr Sci 553:10–16
Jiang F, Nie Y, Yin L, Feng Y, Yu Q, Zhong C (2016) Core–shell-structured nanofibrous membrane as advanced separator for lithium-ion batteries. J Membr Sci 510:1–9
Zhang Z, Yuan W, Li L (2018) Enhanced wettability and thermal stability of nano-SiO2/poly(vinyl alcohol)-coated polypropylene composite separators for lithium-ion batteries. Particuology 37:91–98
Chai J, Liu Z, Ma J et al (2017) In situ generation of poly(vinylene carbonate) based solid electrolyte with interfacial stability for LiCoO2 lithium batteries. Adv Sci 4(2):1600377
Zhang Y, Lu W, Cong L et al (2019) Cross-linking network based on poly(ethylene oxide): solid polymer electrolyte for room temperature lithium battery. J Power Sources 420:63–72
Mindemark J, Lacey MJ, Bowden T, Brandell D (2018) Beyond PEO—alternative host materials for Li+-conducting solid polymer electrolytes. Prog Polym Sci 81:114–143
Kim J-K, Manuel J, Lee M-H et al (2012) Towards flexible secondary lithium batteries: polypyrrole-LiFePO4 thin electrodes with polymer electrolytes. J Mater Chem 22:15045–15049
Kang W, Ma X, Zhao H et al (2016) Electrospun cellulose acetate/poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibrous membrane for polymer lithium-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 20:2791–2803
Li G, Li Z, Zhang P, Zhang H, Wu Y (2008) Research on a gel polymer electrolyte for Li-ion batteries. Pure Appl Chem 80:2553–2563
Yue L, Xie Y, Zheng Y et al (2017) Sulfonated bacterial cellulose/polyaniline composite membrane for use as gel polymer electrolyte. Compos Sci Technol 145:122–131
Xiao Q, Deng C, Wang Q, Zhang Q, Yue Y, Ren S (2019) In situ cross-linked gel polymer electrolyte membranes with excellent thermal stability for lithium ion batteries. ACS Omega 4:95–103
Xianhua C, Khanmirzaei MH, Omar FS, Kasi R, Subramaniam RT (2018) The effect of incorporation of multi-walled carbon nanotube into poly(ethylene oxide) gel electrolyte on the photovoltaic performance of dye-sensitized solar cell. Polym Plast Technol Mater 58:97–104
Liao YH, Li XP, Fu CH et al (2011) Performance improvement of polyethylene-supported poly(methyl methacrylate-vinyl acetate)-co-poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate based gel polymer electrolyte by doping nano-Al2O3. J Power Sources 196:6723–6728
Xie H, Liao Y, Sun P, Chen T, Rao M, Li W (2014) Investigation on polyethylene-supported and nano-SiO2 doped poly(methyl methacrylate-co-butyl acrylate) based gel polymer electrolyte for high voltage lithium ion battery. Electrochim Acta 127:327–333
Ma Y, Ma J, Chai J et al (2017) Two players make a formidable combination: in-situ generated poly(acrylic anhydride-2-methyl-acrylic acid-2-oxirane-ethyl ester-methyl methacrylate) cross-linking gel polymer electrolyte towards 5 V high voltage batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:41462–41472
Terasawa N, Asaka K (2019) High-performance cellulose nanofibers, single-walled carbon nanotubes and ionic liquid actuators with a poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)/ionic liquid gel electrolyte layer. RSC Adv 9:8215–8221
Zhang X, Zhao S, Fan W, Wang J, Li C (2019) Long cycling, thermal stable, dendrites free gel polymer electrolyte for flexible lithium metal batteries. Electrochim Acta 301:304–311
Chotsuwan C, Boonrungsiman S, Asawapirom U et al (2018) Highly viscous composite gel electrolyte based on cellulose acetate and nanoparticles. J Electroanal Chem 828:91–96
Li MX, Wang XW, Yang YQ, Chang Z, Wu YP, Holze R (2015) A dense cellulose-based membrane as a renewable host for gel polymer electrolyte of lithium ion batteries. J Membr Sci 476:112–118
Zhang MY, Li MX, Chang Z et al (2017) A sandwich PVDF/HEC/PVDF gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion battery. Electrochim Acta 245:752–759
Saito T, Kimura S, Nishiyama Y, Isogai A (2007) Cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromol 8:2485–2491
Mahmoud ME, Abdou AEH, Sobhy ME, Fekry NA (2017) Solid-solid crosslinking of carboxymethyl cellulose nanolayer on titanium oxide nanoparticles as a novel biocomposite for efficient removal of toxic heavy metals from water. Int J Biol Macromol 105:1269–1278
Suto S, Ui N (1996) Chemical crosslinking of hydroxypropyl cellulose and chitosan blends. J Appl Polym Sci 61:2273–2278
Du Z, Su Y, Qu Y et al (2019) A mechanically robust, biodegradable and high performance cellulose gel membrane as gel polymer electrolyte of lithium-ion battery. Electrochim Acta 299:19–26
Xiao S, Wang F, Yang Y, Chang Z, Wu Y (2014) An environmentally friendly and economic membrane based on cellulose as a gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv 4:76–81
Wang Z-l, Tang Z-y (2004) A novel polymer electrolyte based on PMAML/PVDF-HFP blend. Electrochim Acta 49:1063–1068
Xu D, Jin J, Chen C, Wen Z (2018) A novel sustainable 3D cross-linked chitosan-PEGGE-based gel polymer electrolyte with excellent lithium-ion transport properties for lithium batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:38526–38537
Zhu Y, Xiao S, Shi Y, Yang Y, Wu Y (2013) A trilayer poly(vinylidene fluoride)/polyborate/poly(vinylidene fluoride) gel polymer electrolyte with good performance for lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 1:7790–7797
Zhu Y, Wang F, Liu L, Xiao S, Chang Z, Wu Y (2013) Composite of a nonwoven fabric with poly(vinylidene fluoride) as a gel membrane of high safety for lithium ion battery. Energy Environ Sci 6:618–624
Chai J, Liu Z, Zhang J et al (2017) A superior polymer electrolyte with rigid cyclic carbonate backbone for rechargeable lithium ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:17897–17905
Fasciani C, Panero S, Hassoun J, Scrosati B (2015) Novel configuration of poly(vinylidenedifluoride)-based gel polymer electrolyte for application in lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 294:180–186
Wang X, Hao X, Xia Y, Liang Y, Xia X, Tu J (2019) A polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-based double-layer multifunctional gel polymer electrolyte for lithium-sulfur batteries. J Membr Sci 582:37–47
Xiao SY, Yang YQ, Li MX et al (2014) A composite membrane based on a biocompatible cellulose as a host of gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 270:53–58
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11972161) and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (No.2016A030311052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gou, J., Liu, W. & Tang, A. A renewable and biodegradable nanocellulose-based gel polymer electrolyte for lithium-ion battery. J Mater Sci 55, 10699–10711 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04667-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04667-7